Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O96/11195 PCT~EP9~/03884
INDOLE DERIYATIVES AS 5HTl-LIKE AGONISTS
The present invention relates to indole derivatives
which act on 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptors.
More particularly the present invention relates to
3,5-disubstituted indoles which are selective agonists at
the "5-HTl-like" subtype of the 5-hydroxytryptamine
receptor. Such "5-HT1-like" receptors are present in the
carotid vascular bed and their activation causes
vasoconstriction with a consequent reduction in carotid
blood flow. Compounds which have "5-HT-like" agonist
activity are therefore useful in the treatment of medical
conditions which are thought to result from excessive
dilation of the carotid bed, such as migraine, cluster
headache, chronic paroxysmal hemicrania and headache
associated with vascular disorders. Certain compounds of
the present invention are also agonists at central 5-HT
receptors and are therefore useful for the treatment of
depression, anxiety, eating disorders, obesity, drug
abuse and emesis.
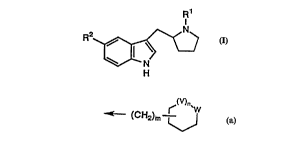
The present invention provides compounds of formula:
R2~ ( I )
N
and ph~rm~ceutically acceptable salts thereof, and
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O96111195 PCT/EP9~/03884
ph~rm~ceutically acceptable solvates (including
hydrates) of either entityr
wherein Rl is
~(V)n~
~ (CH2)m
R2 is R3R4C(oH)A;
V is C=O or CH2;
W is O or NR5;
R3 and R4 are each independently selected
from H and Cl-C4 alkyl; or, together with the
carbon atom to which they are attached, form
a 4- or 5-membered carbocyclic ring;
R5 is H, benzyl, Cl-C5 alkanoyl or SO2(Cl-
C4) alkyl;
A is C2-C3 alkylene;
m is O or l;
and n is O or l;
with the provisos that when n is 1 and V is C=O then W
is NH, and when n is 1 and V is CH2 then W is 0.
In the above definition, unless otherwise
indicated, alkyl groups having three or more carbon
atoms and alkanoyl groups having four or more carbon
atoms may be straight chain or branched chain.
The compounds of formula (I) may contain one or
more asymmetric centres and thus can exist as
stereoisomers, i.e. as enantiomers or as
diastereoisomers, and the invention includes both the
separated individual stereoisomers as well as mixtures
thereof.
The preferred stereoisomers are those compounds of
formula (IA) which possess the R-configuration at the
2-position of the pyrrolidine ring, as represented by
formnl~ (IA):
CA 02202348 1997-04-lo
W 096/11195 PCT~P95/03884
R1
R2~"*.~ ( IA )
N
Also included in the invention are radiolabelled
derivatives of compounds of form~ (I) which are
suitable for biological studies.
The ph~rm~ceutically acceptable salts of compounds
of formula (I) are, for example, non-toxic acid
addition salts formed with inorganic acids such as
hydrochloric, hydrobromic, sulphuric and phosphoric
acid, with organo-carboxylic acids, or with organo-
sulphonic acids. For a review of suitable
ph~rm~ceutical salts, see J. Pharm. Sci., 1977, 66, 1-
19 .
A preferred group of compounds of formula (I) is
that wherein W is NR5; R3 and R4 are both methyl; R5 is
H, benzyl, COCH3 or SO2CH3; A is ethylene; m is O or l;
and n is O.
A more preferred group of compounds of formula (I)
is that wherein W is NR5; R3 and R4 are both methyl;
R5 is benzyl or SO2CH3; A is ethylene; m is l; and n is
o.
Particularly preferred individual compounds of the
invention include:
3-[N-(N-benzyl-3(R,S)-pyrrol;~;nylmethyl)-2(R)-
pyrrolidinylmethyl3-5-(3-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-butyl)-lH-
indole
and 5-(3-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-butyl)-3-[N-(N-
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W 096/11195 PCT~P95/0388
methanesulphonyl-2(R)-pyrrolidinylmethyl)-2(R)-
pyrrolidinylmethyl]-lH-indole;
and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and
pharmaceutically acceptable solvates (including hydrates)
of either entity.
In another aspect, the present invention provides
processes for the preparation of compounds of formula (I),
their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, and
ph~rm~ceutically acceptable solvates (including hydrates)
of either entity, as illustrated below. It will be
appreciated by persons skilled in the art that, within the
various processes described, the order of the synthetic
steps employed may be varied and will depend inter Glia on
factors such as the nature of other functional groups
present in a particular substrate, the availability o~f key
intermediates, and the protecting group strategy (if any)
to be adopted. Clearly, such factors will also influence
the choice of reagent for use in the said synthetic steps.
It will also be appreciated that various standard
transformations within certain compounds of formula (I)
will provide other compounds of formula (I); examples are
debenzylation of N-benzylpyrrolidine groups, and N-
acylation and N-sulphonylation of the N-unsubstituted
pyrrolidines thus formed.
A compound of formula (I) may be obtained by selective
N-alkylation of the saturated heterocyclic ring of a
compound of formula (II):
,
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O96/11195 PCTAEP95/03884
~2 ~ ( rI)
wherein R2 is as previously defined for formula (Il,
using one or more of the following methods.
1. By reaction of a compound of formula (II) with a
compound of formula RlX, wherein Rl is as defined for
form~ (I) or is a conventionally protected precurs~r
thereof (e.g. con~;n;ng -7.~H protected as the benzyl,
Boc or Z derivative), and X is a suitable leaving
group, e.g. halo (preferably chloro, bromo or iodo),
Cl-C4 alkanesulphonyloxy, trifluoromethanesulphonyloxy
or arylsulphonyloxy (preferably benzenesulphonyloxy or
p-toluenesulphonyloxy), in the presence of an
appropriate base, e.g. sodium or potassium carbonate or
bicarbonate, or triethylamine, in a suitable solvent
such as Cl-C4 alkanol, 1,2-dimethoxyethane,
acetonitrile, dimethylfor~mide or N,N-
dimethylacetamide, and optionally in the presence of
sodium or potassium iodide, and/or 4-dimethylamino-
pyridine. The reaction can be conducted at from about
0C to about 150C, preferably at from about room
temperature to about 100C, and, where appropriate, is
; followed by a st~n~rd deprotection step.
2. By reductive alkylation of a compound of forml71
(II) using the appropriate aldehyde-, ketone- or
CA 02202348 1997-04-lo
W O96/11195 PCT~EP95/03884
carboxylic acid-contA;n;ng Rl precursor. In the case
of an aldehyde or ketone precursor, the substrate (II)
and carbonyl reagent may be reacted together under
conventional catalytic hydrogenation conditions or in
the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride, in a suitable
solvent such as methanol or ethanol, at about room
temperature. Alternatively, the reductive alkylation
may be achieved by a two-step procedure in which the
intPr~-~;Ate enAm;ne is formed initially, under
conventional conditions, and subsequently reduced to
the required amine, e.g. using sodium cyanoborohydride
in tetrahydrofuran-methanol at about room temperature.
In the case of a carboxylic acid precursor, the
substrate (II) and the said acid reagent may be reacted
together in the presence of excess sodium borohydride
in a suitable solvent; preferably the carboxylic acid
itself is used as solvent whenever possible. Since
this reductive alkylation proceeds via in situ
formation of the corresponding sodium
triacyloxyborohydride, obvious variations are to employ
preformed reagent when commercially available or to
preform it in a separate in situ step using the
stoichiometric amount of carboxylic acid in a suitable
solvent. An example of the latter procedure involves
the treatment of six equivalents of the carboxylic acid
with two equivalents of sodium borohydride in dry
tetrahydrofuran at about room temperature. When
formation of the required sodium triacyloxyborohydride
is complete, the reaction mixture is treated with a
solution of one equivalent of the substrate (II) in the
same solvent and the subsequent reaction step is
conducted at from about room temperature to about 70C,
preferably at about 50-55C.
3. When Rl contains an electron withdrawing group
such as -CONH- in the ~-position with respect to the
point of attachment of Rl to the pyrrolidine nitrogen
atom, by conjugate addition (Michael-type reaction) of
CA 02202348 1997-04-lo
W O96111195 PCT~EP95/03884
..
a compound of formlllA (II) to the corresponding a,~-
unsaturated amide-contA;n;ng Rl precursor, optionally
in the presence of a tertiary amine base such as
triethylamine. The reaction may optionally be
conducted in a suitable solvent, e.g. 1,2-
dimethoxyethane or N,N-dimethylacet~m;~e, at from about
0C to about 100C, preferably at about 85C or about
100C respectively. Alternatively, the reaction may be
effected in pyridine, which serves both as tertiary
amine base and as solvent, preferably at about 115C.
Certain compounds of formula (I) can be prepared
from other compounds of f ormll1 A (I) by, for example,
the following stAn~Ard transformations within the
substituent:-
(a) a compound of formula (I) wherein Rs is H isobtA;nAhle from the corresponding compound of formula
(I) wherein Rs is benzyl by conventional debenzylation
procedures, e.g. catalytic hydrogenation. Preferably
the reaction is effected using nAllA~;um as catalyst
and conducted in a suitable solvent such as ethanol at
about room temperature and atmospheric pressure.
(b) a compound of formlllA (I) wherein Rs is Cl-Cs
AlkAnoyl or SO2(Cl-C4 alkyl) is obt~;nAhle from the
corresponding compound of fo~mlllA (I) wherein Rs is ~I
by conventional acylation or sulphonylation procedures,
respectively, e.g. by using the appropriate acyl or
sulphonyl hAl;~e or anhydride in a suitable solvent,
optionally in the presence of a base, at from about 0C
to about 85C. Preferably the solvent is
dichloromethane, the base is a tertiary amine such as
triethylAm;ne, and the reaction temperature is from
about 0C to about 40C.
,.
A compound of formula (II) may be obtained from a
compound of formula (III):
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O 96/11195 PCT/EP9~/03884
Co2Rl3
R2
H
wherein R2 is as previously defined for formula (II)
and Rl3 forms part of a conventional amino acid N-
protecting group, i.e. a carbamate, wherein Rl3 is
preferably benzyl or t-butyl. N-Deprotection of a
compound of formula (III) can be achieved using
st~nr1Ard methodology; for example, when Rl3 is benzyl,
by palladium-catalysed hydrogenolysis and, when Rl3 is
t-butyl, by protonolysis using trifluoroacetic acid or
hydrogen chloride.
Alternatively, when Rl3 is benzyl, N-deprotection
can be effected by modification of the procedure
reported in Tetrahedron Letters, 1988, 29, 2983, in
which (III) is treated with an excess of a tri(lower
alkyl)silane in the presence of a palladium(II) salt
and an excess of a tri(lower alkyl)amine in a suitable
solvent such as a Cl-C4 alkanol. Preferably the
reaction is conducted using triethylsilane,
palladium(II) acetate and triethylamine in ethanol at
about room temperature.
A compound of formlll A (III) may be obtained from a
compound of formula (IV):
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O 96/11195 PCTAEP95/03884
~ 9
CO2R
- R14~ (IV)
N
wherein Rl4 is R3R4C ( OH ) or R3R4C ( OH )CH2, and Rl3 is as
previously defined for formula (III). This may be
achieved by conventional catalytic or catalytic
transfer hydrogenation, preferably using p~ ;um as
catalyst and, in the latter process, ammonium formate
as the hydrogen source. Alternatively, the
trialkylsilane/p~ ;um(II) salt procedure described
above may be employed.
Clearly, when Rl3 is benzyl, a compound of formula
(IV) may be converted directly to a compound of formula
(II) wherein R2 is CH2CH2Rl4 under these conditions.
A compound of form~ (IV) may be obtained from a
compound of form~ (V):
Ct:)2R13
wherein Y is chloro, bromo or iodo (preferably bromo),
CA 02202348 1997-04-lO
W 096/11195 PCT~P9~/03884
' 10
and Rl3 is as previously defined for formula (IV), with
an alkene of formula CH2=C~Rl4, wherein Rl4 is as
previously defined for formula (IV), using the Heck
reaction. Thus the desired coupling is achieved using,
for example, an excess of the required alkene, in the
presence of p~ ;um(II) acetate, tri-o-tolylphosphine
and triethylamine, in a suitable solvent such as
acetonitrile or dimethylform~m;~e, at from about 80C
to about 160C.
A compound of form~ (V) may be obtained as
described in WO-A-93/21177.
An alternative approach to a compound of formula
(I) involves the reaction of a compound of formula
(VI):
~S`~ ( VI )
wherein Rl is as previously defined for formula (I) and
Y is as previously defined for formula (V), with an
alkene of formula CH2=C~Rl4 wherein Rl4 is as previously
defined for formula (IV), under the ~eck reaction
conditions previously described for the conversion of
(V) to (IV), followed by reduction of the resulting
alkene as already described for the reduction of (IV)
to (III) or directly to (II).
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O 96111195 PCTAEP9~/03884
A compound of formula (VI) may be obtained by
selective N-alkylation of a compound of formula (VII):
~b ( VII )
wherein Y is as previously defined for formula (VI), by
analogy with the procedures described earlier for the
conversion of (II) to (I).
A compound of formula (VII) may be obtained from a
compound of formula (V) wherein Rl3 and Y are as
previously defined for formula (V) by the st~n~rd N-
deprotection methodology already described. Preferably
however, when Rl3 is benzyl, deprotection is effected
by a non-hydrogenolytic procedure such as protonolysis
in a suitable solvent using, for example, hydrogen
bromide in glacial acetic acid or hydrogen chloride in
methanol, at about room temperature, a Lewis acid-
catalysed nucleophilic deprotection using, for example,
boron trifluoride etherate and excess ethanethiol in a
suitable solvent such as dichloromethane at about room
temperature, or an ~lk~l;ne deprotection using, for
example, potassium hydroxide in a suitable solvent such
as a Cl-C4 alkanol, preferably n-butanol.
Compounds of formula CH2=CHR14 wherein Rl4 is as
previously defined for form~ (IV), and the various
reagents required for the processes hereinbefore
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
WO96/11195 PCT~P95/03884
disclosed, when neither commercially available nor
subsequently described, can be ob~; n~ either by
analogy with the reactions described in the Examples
and Preparations sections or by conventional synthetic
procedures, in accordance with st~n~rd textbooks on
organic chemistry or literature precedent, from readily
accessible starting materials using appropriate
reagents and reaction conditions. Clearly, when the
preferred stereoisomers of formula (IA) are required,
the compounds of formula (V) will possess the 2R-
configuration.
Persons skilled in the art will recognise that the
alkenes depicted hereinbefore may be obtained in cis-
or trans-stereoisomeric forms, or as mixtures of cis-
and trans-stereoisomers, and are represented in one
such form only in the interests of clarity and
convenience. Such persons will also be aware of
variations of, and alternatives to, those reactions~
described hereinafter for the preparation of compounds
of formula (I).
The ph~rm~ceutically acceptable acid addition
salts of compounds of formula (I) may also be prepared
in a conventional manner. For example a solution of
the free base is treated with the appropriate acid,
either neat or in an appropriate solvent, and the
resulting salt isolated either by filtration or by
evaporation under vacuum of the reaction solvent.
Certain such salts may be formed or interconverted
using ion-exchange resin techni~ues.
The compounds of the invention are selective
agonists at the "5-HT1-like" subtype of the 5-HT
(serotonin) receptor and are therefore useful in the
curative or prophylactic treatment of migraine and
associated conditions such as cluster headache, chronic
paroxysmal hemicrania and h~ che associated with
vascular disorders. Certain of these compounds are
CA 02202348 1997-04-lO
W 096tlll95 PCT~P95/03884
13
also agonists at central 5-HTl receptors and are
therefore useful for the treatment of depression,
anxiety, eating disorders, obesity, drug abuse and
emesis .
The in vitro evaluation of the "5-HTl-like"
receptor agonist activity of the compounds of the
invention is carried out by testing the extent to which
they mimic sumatriptan in contracting the isolated dog
saphenous vein strip (P.P.A. Humphrey et al., Brit. J.
ph~rm~ol., 1988, 94, 1123). This effect can be
blocked by methiothepin, a known 5-HT antagonist.
Sumatriptan is known to be useful in the treatment of
migraine and produces a selective increase in carotid
vascular resistance in the anaesthetized dog and a
consequent decrease in carotid arterial blood flow. It
has been suggested (W. Feniuk et al., Brit. J.
ph~rr-col.~ 1989, 96, 83) that this is the basis of its
efficacy.
The 5-HTl agonist activity of the compounds of the
invention can be measured in in vitro receptor binding
assays as described for the 5-HT~ receptor, using rat
cortex as the receptor source and [3H]8-OH-DPAT as the
radioligand (D. Hoyer et al., Europ. J. Ph~rm~col.,
1985, 118, 13), and as described for the 5-HTlD
receptor, using bovine caudate as the receptor source
and [3H]5-HT as the radioligand (R.E. Heuring and S. J.
Peroutka, J. Neuroscience, 1987, 7, 894).
In therapy, the compounds of formula (I), their
ph~rm~ceutically acceptable salts, and ph~rm~ceutically
acceptable solvates of either entity, can be
~m;n;stered alone, but will generally be ~m;n;stered
in admixture with a ph~rr~çeutical carrier selected
with regard to the intended route of ~m;n;stration and
st~n~rd ph~rm~ceutical practice. For example, they
can be ~m;n;stered orally in the form of tablets
cont~;n;ng such excipients as starch or lactose, or in
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O96/11195 PCTAEP95/0388
14
capsules or ovules either alone or in admixture with
excipients, or in the form of ~ ; rS~ solutions or
suspensions cont~;n;ng flavouring or colouring agents.
They can also be injected parenterally, for example,
intravenously, intramuscularly or subcutaneously. For
parenteral A~m;n;~tration, they are best used in the
form of a sterile aqueous solution which may contain
other substances, for example, enough salts or glucose
to make the solution isotonic with blood. For buccal
or sublingual a~m;n;~tration they may be A~m;n;stered
in the form of tablets or lozenges which can be
form~ ted in a conventional manner.
For oral, parenteral, buccal and sublingual
~m;n;stration to patients, the daily dosage level of
the compounds of formula (I), their pharmaceutically
acceptable salts, and phArm~ceutically acceptable
solvates of either entity, will be from 0.1 ng to 20
mg/Kg (in single or divided doses). Thus tablets or
capsules will contain from 5 ng to 0.5g of active
compound for A~m; n;stration singly, or two or more at a
time, as appropriate. The physician in any event will
determine the actual dosage which will be most suitable
for an individual patient and it will vary with the
age, weight and response of the particular patient.
The above dosages are exemplary of the ave~age case;
there can, of course, be individual instances where
higher or lower dosage ranges are merited, and such are
within the scope of this invention.
Alternatively, the compounds of formula (I), their
- phArm~ceutically acceptable salts, and ph~rm~ceutically
acceptable solvates of either entity, can be
A~m;n;~tered in the form of a suppository or pessary,
or they may be applied topically in the form of a
lotion, solution, cream, ointment or dusting powder.
For example, they can be incorporated into a cream
consisting of an aqueous emulsion or polyethylene
glycols or liquid paraffin; or they can be
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O 96/11195 PCT~EP95103884
incorporated, at a concentration of from 1 to 10%, into
an ointment consisting of a white wax or white soft
paraffin base together with such stabilisers and
preservatives as may be required.
The compounds of formlllA (I), their
phArm-ceutically acceptable salts, and phArm~ceutically
acceptable solvates of either entity, can also be
~m; n;stered intranasally or by inhalation and are
conveniently delivered in the form of a solution or
suspension from a pump spray container, which is
squeezed or pumped by the patient, or as an aerosol
spray presentation from a pressurised container or a
nebuliser with the use of a suitable propellant, e.g.
dichlorodifluoromethane, trichlorofluoromethane,
dichlorotetrafluoroethane, carbon dioxide or other
suitable gas. In the case of a pressurised aerosol,
the dosage unit may be determined by providing a valve
to deliver a metered amount. The pressurised container
or nebuliser may contain a solution or suspension of
the active compound. Capsules and cartridges (made,
for example, from gelatin) for use in an inhaler or
insufflator may be formulated contA;n;ng a powder mix
of a compound of the invention and a suitable powder
base such as lactose or starch.
Aerosol formulations are preferably arranged so
that each metered dose or "puff" of aerosol contains
from 1 ng to 1000 yg of a compound of formula (I), or a
ph~rm~ceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a
phArm~ceutically acceptable solvate of either entity,
for delivery to the patient. The overall daily dose
with an aerosol will be within the range of from 5 ng
to 10 mg which may be ~m; n;stered in a single dose or,
more usually, in divided doses throughout the day.
- Thus the invention provides phArm~ceutical
compositions comprising a compound of f orml11 A (I), or a
phArmAceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a
phAr~-ceutically acceptable solvate (including hydrate)
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O 96/11195 PCT~P95/0388
of either entity, together with a ph~rr ceutically
acceptable diluent or carrier.
The invention also provides a compound of formula
(I), or a ph~rm~ceutically acceptable salt thereof, or
a ph~rm~ceutically acceptable solvate (including
hydrate) of either entity, or a ~hArm~ceutical
composition cont~;n;ng any of the foregoing, for use
as a medicament.
The invention further includes the use of a
compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically
acceptable salt thereof, or a ph~rm~ceutically
acceptable solvate (including hydrate) of either
entity, or a pharmaceutical composition containing any
of the foregoing, both for the manufacture of a
medicament for the curative or prophylactic treatment
of migraine or an associated condition such as cluster
headache, chronic paroxysmal hemicrania or headache
associated with a vascular disorder, or of depression,
anxiety, an eating disorder, obesity, drug abuse or
emesis, and also for the manufacture of a medicament
for the curative or prophylactic treatment of a medical
condition for which a selective agonist of 5-HTI-like
receptors is ;n~;c~ted.
In a further aspect, the invention provides both a
method of treating a human being to cure or prevent
migraine or an associated condition such as cluster
headache, chronic paroxysmal hemicrania or headache
associated with a vascular disorder, or depression,
anxiety, an eating disorder, obesity, drug abuse or
emesis, and also a method of treating a human being to
cure or prevent a medical condition for which a
selective agonist of 5-HTl-like receptors is indicated,
which comprises treating said human being with an
effective amount of a compound of f orm~ ( I), or a
ph~rm~ceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a
ph~rr-ceutically acceptable solvate (including hydrate)
of either entity, or a phAr~~ceutical composition
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O96/11195 PCT~EP95/03884
17
contA;n;ng any of the foregoing.
The syntheses of the compounds of the invention
and of the interr^~;Ates for use therein are
illustrated by the following Examples and Preparations.
The purity of the compounds was routinely monitored by
thin layer chromatography (Rf) using Merck Rieselgel
60 F254 plates and the following solvent systems (SS):
1. dichloromethane:methanol:0.880 aqueous ammonia,
90:10:1;
2. hexane:ethyl acetate, 3:1;
3. hexane:ethyl acetate, 1:1.
lH Nuclear magnetic reasonance (NMR) spectra were
recorded using either a Nicolet QE-300 or a Bruker AC-
300 spectrometer and were in all cases consistent with
the proposed structures.
LRMS ~AnS low resolution mass spectrum.
Room temperature means 20-25C.
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
WO96/11195 PCT~EP95/0388
EXAMP~E 1
3-rN-(N-BenzYl-3(Rrs)-pyrrolidinylmethyl)-2(R)
PvrrolidinYlmethY11-5-(3-hYdroxy-3-methyl-l-butyl)
indole
A stirred mixture of 5-(3-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-
butyl-3(2(R)-pyrroldinylmethyl)-l~-indole (Preparation
3; 400 mg, 1.35 mmol), N-benzyl-3(R,S)-p-toluene-
sulphonyloxymethylpyrrolidine (Preparation 7; 465 mg,
1.35 mmol), anhydrous sodium carbonate (130 mg, 1.23
mmol), sodium iodide (203 mg, 1.35 mmol) and 1,2-
dimethoxyethane (12 ml), under nitrogen, was heated
under reflux for 52 hours. The cool reaction mixture
was partitioned between ethyl acetate (100 ml) and 2M
agueous sodium carbonate solution (100 ml), then the
organic phase separated, washed with 2M aqueous sodium
carbonate solution, dried (Na2SO4) and filtered.
Evaporation of the filtrate under reduced pressure gave
the crude product which was purified by column --
chromatography on silica gel, eluting with
dichloromethane:methanol:0.880 aqueous ammonia
(90:10:0.2), to afford the title compound (439 mg) as
an off-white foam. Rf 0.60 (SS 1).
[a]25 +16 (c = 0.1, CH30H). Found: C,73.85; H,8.63;
D
N~8-45- C30~4lN3O; 0-42 C~2C12 requires C,73.79;
H,8.52; N,8.49%.
EXAMP~E 2
5-(3-~ydroxy-3-methYl-l-butYl)-3- r N-(3(R,S)-
PvrrolidinYlmethyl)-2(R)-PYrrolidinYlmethyll-lH-indole
A stirred solution of the title compound of
ple 1 (530 mg, 1.07 mmol) in ethanol (100 ml) was
hydrogenated over 10% palladium on charcoal (250 mg) at
15 p.s.i. (1.04 bar) and room temperature ~or 18 hours,
then filtered. Evaporation of the filtrate under
reduced pressure provided the crude product which was
purified by column chromatography on silica gel,
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O 96/11195 PCT~EP95/03884
19
eluting with dichloromethane:methanol:0.880 aqueous
ammonia (90:10:1), to furnish the title compound (291
mg) as a white foam. Rf 0.06 (SS 1). [a~25 ~50 (c =
D
0.1, CH30H). Found: C,68.77; H,9.19; N,10.22.
C23H35N30; 0.45 CH2Cl2 requires C,69.07; H,8.87;
N,10.30%.
EXAMoe~E 3
5-(3-HYdroxy-3-methvl-l-butYl)-3-rN-(N-methane-
sulphonyl-3(R,S)-PyrrolidinYlmethYl)-2(R)-pyrrolidin
methyll-lH-indole
Methanesulphonyl chloride (34.1 mg, 23 ~1, 0.30
mmol) was added dropwise to a stirred, ice-cooled
solution o~ the title compound of Example 2 (110 mg,
0.27 mmol) and triethylamine (42 ~1, 0.30 mmol) in
dichloromethane (10 ml) under nitrogen. The reaction
mixture was heated under reflux for 24 hours, allowed
to cool to room temperature, diluted with
dichloromethane (40 ml), washed with 2M aqueous sodium
carbonate solution (50 ml), dried (Na2S04) and
filtered. Evaporation of the filtrate under reduced
pressure gave the crude product which was purified by
column chromatography on silica gel, eluting with
dichloromethane:methanol:0.880 aqueous ammonia
(90:10:0.1) to aford the title compound (71 mg) as a
white foam. Rf 0.40 (SS 1). [a]25 +38 (c = 0.1,
CH30H). Found: C,62.g2; H,8.33; N,8.92. C24H37N303S;
0.17 CH2Cl2 requires C,62.86; H,8.15; N,9.10~.
EXAMP~E 4
3-rN-(N-Acetyl-3(R,S)-pvrrolidinYlmethvl)-2(R)-
Pyrrolidinylmeth~yll-5-(3-hYdroxv-3-methyl-1-~utYl)-lH-
indole
Acetic anhydride (30.6 mg, 28 ~1, 0.30 mmol) was
added dropwise to a stirred, ice-cooled solution of the
title compound of Example 2 (110 mg, 0.27 mmol) in
CA 02202348 l997-04-lO
W O 96/11195 PCT~P95/03884
dichloromethane (10 ml) under nitrogen. The reaction
mixture was heated under reflux for 4 hours, allowed to
cool to room temperature and evaporated under reduced
pressure. Residual acetic acid was removed
azeotropically using dichloromethane and the crude
product purified by column chromatography on silica
gel, eluting with dichloromethane:methanol: 0.880
aqueous ammonia (90:10:0.1) to yield the title compound
(96 mg) as a white foam. Rf 0.33 (SS 1). ta]25 +37
(c = 0.1, CH30H). Found: C,69.60; H,8.97; N,9.40.
C25H37N302; 0.30 CH2C12 requires C,69.53; H,8.67; N,9.6196.
EXAMP~E 5
5-(3-HydroxY-3-methyl-1-butYl)-3- r N-(N-methane-
sulphonyl-2(R)-pyrrolidinYlmethYl)-2(R)-Pyrrolidin
methyll-lH-indole
A stirred mixture of the title compound of
Preparation 3 (250 mg, 0.87 mmol), N-methanesulphonyl-
2(R)-methanesulphonyloxymethylpyrrolidine (Preparation
5; 247 mg, 0.96 mmol), triethyl~ine (0.25 ml, 1.75
mmol), 4-dimethylaminopyridine (5.5 mg, 0.04 mmol) and
1,2-dimethoxyethane (5.0 ml), under nitrogen, was
heated under reflux for 28 hours and then evaporated
under reduced pressure. The residue was dissolved in
ethyl acetate (200 ml) and the resulting solution
successively washed with 2M aqueous sodium carbonate
solution (200 ml) and water (200 ml), dried (Na2SO4)
and evaporated under reduced pressure. The resulting
crude product was purified by column chromatography on
silica gel, eluting with dichloromethane:methanol
(96:4), to furnish the title compound (194 mg) as a
foam. Rf 0.41 (SS 1). [c~]25 +46 (c = 0.1, CH30H).
Found: C,63.14; H,8.22; N,8.74. C24H37N303S; 0.10 CH2Cl2;
0.20 H2O requires C,62.96; H,8.24; N,9.14%
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O96/11195 PCT/EP9~/03884
21
EXAMPLE 6
5-(3-Hydroxv-3-methyl-l-butvl~-3-rN-(N-
methanesulphonvl-2(S)-PyrrolidinvlmethYl)-2(R~-
pyrrolidinvlmethyll-lH-indole
The title compound (23% yield) was obtained from
the title compound of Preparation 3 by a procedure
similar to that described in Example 5, but using N-
methanesulphonyl-2(S)-methanesulphonyloxymethyl-
pyrrolidine (Preparation 6) as the alkylating agent, as
a foam. Rf 0.42 (SS 1). Found: C,62.61; H,8.12;
N,8.82. C24H37N3O3S; 0.20 CH2Cl2 requires C,62.56;
H,8.11; N,9.04%. LRMS: m/z 448.7 (M+l)+.
EXAMPLE 7
5-(3-Hydroxy-3-methvl-1-butyl)-3-rN-(N-methane-
sulphonyl-3(R,S)-Pyrrolidinvl)-2(R)-pyrrolidinyl-
methvll-lH-indole
The title compound (32% yield) was obtained from
the title compound of Preparation 3 by a procedure
similar to that described in Example 5, but using N-
methanesulphonyl-3(R,S)-methanesulphonylo~y~lrolidine
(Preparation 4) as the alkylating agent and
dichloromethane:methanol:0.880 aqueous ammonia
(95:5:0.1) as the column chromatography eluent, as a
foam. ~f 0.40 (SS 1). Found: C,62.99; ~,8.12; ~,9.36.
C23H35N3O3S; 0-40 H2O requires C,62.67; H,8.19; N,9.5396.
LRMS: m/z 434.0 ( M+l)~.
EXAMPLE 8
5-(3-Hydroxv-3-methvl-1-butvl~-3- r N-(2(R~-tetrahvdro-
furanylmethyl~-2(R)-pyrrolidinylmethvll-lH-indole
and
5-(3-Hvdroxv-3-methvl-1-butvl)-3- r N-(2(S)-tetrahvdro-
furanylmethyl)-2( R)-pvrrolidinvlmethyll-lH-indole
The title compounds were obtA; ne~ from the title
compound of Preparation 3 by a procedure s;m;lAr to
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O96/lll9S PCTAEP95/0388
that described in Example l, but using 2(R,S)-
tetrahydrofuranylmethyl bromide as the alkylating agent
and dichloromethane:methanol: 0.880 aqueous ammonia
(gO:lO:l~ as the eluent to effect separation of the
diastereoisomers by column chromatography on silica
gel, as foams.
Diastereoisomer A (22% yield):
Rf 0.80 (SS l). [a]25 -3 (c = 0.1, CH30H).
Found: C,67.39; H,8.53; N,6.83. C23H34N2O2; 0.58 CH2C12
requires C,67.43; H,8.44; N,6.67%.
Diastereoisomer B (30% yield):
Rf 0.72 (SS l). [a]25 +14 (c = 0.1,CH30H).
Found: C,69.65; H,9.04; N,7.05. C23H34N202; 0.375 CH2C12
requires C,69.77; H,8.70; N,6.96~6
The stereochemical identity of each
diastereoisomer was not determined and thus it is not
known which diastereoisomer corresponds with which
title compound.
EXAMP~E 9
5-(3-Hydroxy-3-methyl-l-butY1~-3-rN-(2-oxo-3(R)-
piperidylmethyl~-2(R)-PYrroiidinYlmethyl1-lE~-indole
and
5-(3-Hydroxv-3-methyl-l-butyl)-3-rN-(2-oxo-3(S)-
piDeridylmethyl)-2(R)-pyrrolidinylmethyll-lH-indole
A stirred mixture of the title compound of
Preparation 3 (400 mg, 1.40 mmol), 3-methylidene-2-oxo-
piperidine (Preparation 10; 172.5 mg, 1.55 mmol) and
pyridine (2 ml), under nitrogen, w25 heated under
reflux for 8 days. The cool reaction mixture was
diluted with ethyl acetate (250 ml) and washed with 2M
aqueous sodium carbonate solution. The combined
aqueous washings were extracted with ethyl acetate,
then the combined organic solutions dried (Na~SO4)
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O 96/11195 PCT~EP95/03884
and evaporated under reduced pressure to yield the
crude mixture of diastereoisomers which were separated
by column chromatography on silica gel, using an
elution gradient of dichloromethane:methanol:0.880
aqueous ammonia (95:5:0.1 to 95 5 0.5), and obtained as
foams.
Diastereoisomer A (120 mg):
Rf 0.42 (SS 1). [a]25 ~55 (c = 0.1, CH30H).
Found: C,70.23; H,8.83; N,10.02. C24H3sN3O2; 0.20 C~2Cl2
requires C,70.11; H,8.61; N,10.14~. LRMS: m/z 398.6
(M+l)i.
Diastereoisomer B~52 mq):
R 0.31 (SS 1). ~ 25 t 11 (c = 0.1, C~3OE~).
Found: C,69.56; H,8.42; N,9.88. C24H35N3O2; 0.25 CH2Cl2
requires C,69.55; H,8.54; N,10.03%. ~RMS: m/z 398.1
(M~l)+.
The stereochemical identity of each
diastereoisomer was not determined and thus it is not
known which diastereoisomer corresponds with which
title compound.
EXAMPLE 10
5-(3-HYdroxv-3-methYl-l-butYl)-3-rN-(4-tetrahydr
pYranylmethYl)-2(R)-pYrrolidinYlmethyll-lH-indole
The title compound (61~ yield) was obtained from
the title compound of Preparation 13 by a procedure
similar to that described in Example 2 as a foam. Rf
0.48 (SS 1). [c~]25 ~34 (c = 0.1, C~30H). Found:
C,72.99; H,9.52; N,6.95. C24H36N202; 0.50 H2O requires
C,73.24; H,9.48; N,7.12~.
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O 96/11195 ~ PCT~EP95/03884
24
PREPARATION 1
3-(N-BenzvloxYcarbonvl-2(R)-~YrrolidinYlmethyl)-5-
bromo-lH-indole
3-(N-Benzyloxycarbonyl-2(R)-pyrrolidinylcarbonyl)-
5-bromo-lH-indole (WO-A-92/06973; 0.67 g, 1.57 mmol)
was dissolved in dry tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) and, at
room temperature under nitrogen, lithium borohydride
(2M solution in tetrahydrofuran; 1.2 ml, 2.4 mmol) was
added. The reaction mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 3 hours, heated under reflux for 16
hours, then allowed to cool to room temperature. 2M
Hydrochloric acid (10 ml) was added dropwise and the
reaction mixture then partitioned between ethyl acetate
and water. The separated organic phase was washed with
saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution (x2) and
brine (xl), dried (Na2SO4), and evaporated under
reduced pressure to give a colourless oil.
Purification by column chromatography on silica gel,~
eluting with dichloromethane, gave the title compound
as an oil (0.32 g). Rf 0.20 (SS 16). Found: C,59.94;
~,5.07; N,6.58. C2lHzlBrN2O2; 0.10 CH2Cl2 requires
C,60.08; H,5.07; N,6.64%.
PREPARATION 2
3-(N-Benzvloxycarbonyl-2(R)-PyrrolidinYlmethyl)-5-(3-
hvdroxy-3-methvl-1-but-1-enyl)-lH-indole
A stirred solution of the title compound of
Preparation 1 (1.0 mol equiv), 2-methylbut-3-en-2-ol
(1.3 mol equiv), tri-o-tolylphosphine (0.3 mol equiv),
palladium(II) acetate (0.067 mol equiv) and
triethylamine (2.0 mol equiv) in acetonitrile, under
nitrogen, was heated under reflux for 24 hours, allowed
to cool, then partitioned between ethyl acetate and 2M
aqueous sodium carbonate solution. The organic phase
was separated, washed sequentially with 2M aqueous
sodium carbonate solution (x2) and brine (xl), dried
(NazSO4) and evaporated under reduced pressure. The
-
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
96/11195 PCT~P9~/03884
crude product was purified by column chromatography on
silica gel, eluting with a solvent gradient of
dichloromethane:methanol:0.880 aqueous ammonia (95:5:0
to 95:5:0.5), to afford the title compound as a foam.
Rf 0.40 (SS 2). [c~]25 -10 (c = 0.l, CH301I). Found:
D
C,73.72; H,6.92; N,6.18. C~6~30N2O3; 0.l0 CH2Cl2 requires
C,73.41; H,7.13; N,6.56%.
PREPA~ATION 3
5-(3-Hydroxy-3-methyl-l-butYl)-3(2(R)-
pyrrolidinylmeth~l)-lH-indole
A solution of the title compound of Preparation 2
in ethanol was hydrogenated over l0~ palladium on
charcoal at 15 p.s.i. (l.04 bar) and room temperature
for 18 hours, then filtered. Evaporation of the
filtrate under reduced pressure yielded an oil, which
was azeotroped with dichloromethane (x2) to give a
foam. Purification of the foam by column
chromatography on silica gel, eluting with a solvent
gradient of dichloromethane:methanol:0.880 aqueous
ammonia (l00:0:0 to 95:5:0 to 96:3.5:0.5), provided the
title compound as a ~oam. Rf 0.l0 (SS l). [a]25 -8
(c = 0.l, CH30~). Found: C,70.77; H,8.96; N,9.09.
C~8H26N2O; H2O requires C,71.02; H,9.27; N,9.20%.
PREPARATION 4
N-Methanesulphonvl-3(R S)-methanesulPhonYloxy-
~vrrolidine
Methanesulphonyl chloride (l.95 ml, 25.3 mmol) wasadded dropwise to an ice-cooled, stirred solution of
3(R,S)-pyrrolidinol (l.0 g, 11.5 mmol), triethylamine
(3.5 ml, 25.3 mmol) and 4-dimethylaminopyridine (70 mg,
0.575 mmol) in dichloromethane (l0 ml) under nitrogen.
The resulting slurry was stirred at room temperature
for 24 hours, then diluted with dichloromethane (50
ml), washed successively with saturated aqueous sodium
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O96/11195 PCT~EP9S/03884
26
bicarbonate solution (50 ml) and water 50 ml), dried
(Na2SO4) and filtered. Dilution of the filtrate with
ethyl acetate provided the title compound (1.67 g) as a
white cryst~ll;ne solid. Rf 0.84 (SS 1). Found:
C,29.89; H,5.12; N,5.74. C6Hl3NO5S2 requires C,29.62;
H,5.39; N,5.76%.
PREPARATION 5
N-Methanesulphonyl-2(R)-methanesulphonyloxymethyl-
pyrrolidine
The title compound (66% yield) was obtained from
2(R)-pyrrol;~;nemethanol by a procedure s;m; l~r to that
described in Preparation 4, but using dilution of an
ethyl acetate solution of the product with hexane,
followed by ch;ll;ng~ to effect crystallisation. Rf
0.81 (SS 1). Found: C,32.82; H,5.62; N,5-30- C7Hl5NO5S2
requires C,32.67; H,5.88; N,5.44%.
PREPARATION 6
N-Methanesul~honyl-2(S)-methanesulPhonyloxymethyl-
Pvrrolidine
The title compound (64~ yield) was obtained as forPreparation 5, using 2(S)-pyrrolidinemethanol. Rf 0.81
(SS 1). Found: C,32.76; H,5.87; N,5.55. C7Hl5NO5S2
requires C,32.67; H,5.88; N,5.44s.
PREPARATION 7
N-Benzyl-3(R,S)-p-toluenesulPhonYloxymethylpyrrolidine
The title compound (69%) was obtained from N-
benzyl-3(R,S)-pyrrolidinemethanol (WO-A-91/10650) by a
procedure s; m; 1 ~r to that described in Preparation 4,
but using only 1.1 mol. equiv. of p-toluenesulphonyl
chloride and triethylamine. The crude product was
purified by column chromatography on silica gel,
eluting with hexane:ethyl acetate (1:1), to provide a
viscous oil. Rf 0.24 (SS 3). Found: C,62.07; H,6.42;
CA 02202348 1997-04-1o
W O96/11195 PCTAEP95/03884
27
N,3.81. ClgH23NO3S; 0.33 CH2C12 requires C,62.13;
H,6.38; N,3.75%.
PREPARATION 8
Ethyl N- ! 4-methoxybenzyl)-3-Piperidinecarboxylate
hydrochloride
A solution of trichloroacetyl chloride (11.1 ml,
99 mmol) in toluene (30 ml) was added dropwise over 45
minutes to a stirred, ice-cooled solution of 4-
methoxybenzyl alcohol (12.4 ml, 99 mmol) and N,N-
dimethyl~n;l;ne (12.6 ml, 99 mmol) in toluene (100 ml).
The cooling bath was removed and stirring continued at
room temperature for 1.5 hours, then the reaction
mixture was filtered to remove the N,N-dimethyl ~n; line
hydrochloride which was washed with toluene (30 ml). A
stirred mixture of the combined filtrate and washings,
ethyl 3-piperidinecarboxylate (14.0 ml, 90 mmol) and
anhydrous potassium carbonate (13.7 g, 99 mmol), under
nitrogen, was heated under reflux for 110 hours,
allowed to cool and filtered. Evaporation of the
filtrate under reduced pressure gave a brown oil which
was dissolved in dichloromethane (100 ml) and the
resulting solution washed successively with 2M aqueous
sodium carbonate solution (100 ml) and ca. 5M
hydrochloric acid (200 ml), dried (Na2SO4) and
evaporated under reduced pressure to provide a viscous
oil. This oil was stirred at room temperature with a
1:1 mixture of ethyl acetate:hexane (100 ml) to produce
a solid which was purified by successive trituration
with the same solvent mixture (4 x 50 ml) to afford the
title compound (6.11 g). Rf 0.85 (SS 1). Found:
C,59.41; H,7.50; N,4.15. Cl6H23NO3; HCl; 0.50 H2O
re~uires C,59.52; H,7.80; N,4.34%
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O96/11195 PCT~EP95/03884
PREPARATION 9
N-(4-Methoxybenzvl)-3-methylidene-2-oxo~iperidine
A solution of the title compound of Preparation 8
(4.0 g, 12.75 mmol) and potassium hydroxide (1.43 g,
25.5 mmol) in a 20:1 mixture of methanol:water (126 ml)
was stirred for 24 hours and then evaporated under
reduced pressure. Residual water was removed
azeotropically and then acetic anhydride (120 ml) and
~triethylamine (18 ml) added to the residue. The
resulting mixture was stirred and heated under reflux
for 6 hours, then evaporated under reduced pressure.
The residue was dissolved in dichloromethane (100 ml)
and the solution washed with water (2 x 100 ml), dried
(MgSO4) and evaporated under reduced pressure. The
resulting oil was purified by column chromatography on
silica gel, eluting with hexane:ethyl acetate (1:1), to
furnish the title compound (956 mg). Rf 0.19 (SS 3).
Found: C,70.39; H,7.45; N,6.04. Cl4H,7NO2; 0.40 H2O
requires C,70.50; H,7.50; N,5.87~.
PREPARATION 10
3-Methylidene-2-oxopiperidine
A stirred mixture of the title compound of
Preparation 9 (917 mg, 3.96 mmol), anisole (726 mg,
7.14 mmol) and trifluoroacetic acid (10 ml) was heated
under reflux for 18 hours and allowed to cool.
Evaporation under reduced pressure yielded a dark
orange oil which was dissolved in ether (25 ml). The
solution was extracted with water (3 x 25 ml) and the
combined aqueous extracts saturated with solid
potassium carbonate and then extracted with
dichloromethane (4 x 35 ml). Evaporation under reduced
pressure of the combined and dried (Na2SO4) organic
extracts provided the title compound (406 mg) as a pale
yellow oil. Found: C,64.61; H,8.07; N,12.14. C6H9NO;
0.01 CH2C12 requires C,64.45; H,8.12; N,12.51%
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O96111195 PCT~EP95/03884
PREPA~TION 11
5-Bromo-3-(2( R)-p~rroldinvlmethYl)-lH-indole
The title compound was prepared by any of the
following methods.
(A)
A mixture of the title compound of Preparation 1
(10.0 g, 24.2 mmol) and a solution of hydrogen bromide
in glacial acetic acid (36% w/w; 17 ml) was stirred at
about 0C for 1 hour, then the solvent removed under
reduced pressure and the residue azeotroped with
toluene. The resulting oil was partitioned between
dichloromethane and 2M aqueous sodium carbonate
solution, then the organic phase separated, combined
with a further dichloromethane extract of the aqueous
phase, dried (Na2SO4) and evaporated under reduced
pressure. Purification o the crude product by column
chromatography on silica gel, eluting with a solvent
gradient of dichloromethane:methanol:0.880 aqueous
ammonia (95:5:0 to 95:5:2), gave the title compound as
an oil (2.01 g). Rf 0.10 (SS 1). ~]25 -9 (C = 0.1,
CH30H). Found: C,54.75; H,5.41; N,9.63. Cl3Hl5BrNz;
0.20 CH2Cl2 requires C,54.84; H,5.37; N,9.67~.
(B)
A solution of the title compound of Preparation 1
(5.0 g, 12.1 mmol) in dichloromethane was added
dropwise to a stirred mixture of boron trifluoride
etherate (17.15 g, 14.9 ml, 12.1 mmol) and ethanethiol
(21.4 g, 25.5 ml, 344 mmol) at room temperature under
nitrogen. After 68 hours the reaction mixture was
poured into 10% a~ueous sodium carbonate solution, then
extraction with ethyl acetate (3 x 400 ml~ effected.
Evaporation under reduced pressure of the dried
(Na2SO4), combined extracts, followed by column
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O 96/11195 PCT~EP9~/03884
chromatography on silica gel of the crude product,
eluting with dichloromethane:methanol:0.880 aqueous
ammonia (90:10:1), provided the title compound as a
foam (2.10 g). Rf 0.10 (SS 1). [C~]Z5 -12 (c =
0.1, CH30H). Found: C,55.04; H,5.29; N,9.83.
Cl3HlsBrN2; 0.06 CH2Cl2 requires C,55.10; H,5.35;
N,9.83%.
(C)
A saturated solution of hydrogen chloride in
methanol (20 ml) was added to a stirred, ice-cooled
solution of the title compound of Preparation 1 (10.0
g, 24.2 mmol) in dichloromethane (20 ml) under
nitrogen. After 1 hour the ice bath was removed and
the reaction mixture stirred at room temperature for 48
hours and then evaporated under reduced pressure. The
residual oil was triturated with ether (2 x 20 ml3,
then partitioned between ether (50 ml) and water (50
ml). The aqueous phase was washed with ether (2 x 75
ml), basified with solid sodium carbonate and extracted
with ethyl acetate (2 x 75 ml), then the combined
extracts washed with saturated brine, dried (Na2S04)
and evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was
purified by column chromatography on silica gel,
eluting with a solvent gradient of dichloromethane:
methanol:0.880 aqueous ammonia (100:0:0 to 90:10:0 to
90:10:1), to afford the title compound as a solid, m.p.
120-123.5C. Rf 0.15 (SS 1). Found: C,55.06; H,5.33;
N,9.59. C~3Hl5BrN2; 0.25 H20 requires C,55.04; H,5.51;
N,9.88%.
(D)
A stirred solution of the title compound of
Preparation 1 (360 mg, 0.87 mmol) and potassium
hydroxide (1.0 g, 17.8 mmol) in ethanol (20 ml) was
heated under reflux for 72 hours. The ethanol was
-
CA 02202348 1997-04-10
W O 96/11195 PCTAEP95/03884
31
removed by evaporation under reduced pressure and
replaced with n-butanol (20 ml), then the resulting
mixture stirred under reflux for a further 48 hours and
evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was
purified as in (C) above to provide the title compound
'~ (73 mg). Rf 0.10 (SS 1).
PREPARATION 12
5-Bromo-3-rN-(4-tetrahydroPyran~rlmethyl~-2(R)-
pyrrolidinylmethyll-lH-indole
The title compound (54% yield) was obtained from
the title compound of Preparation 11 and 4-p-
toluenesulphonyloxymethyltetrahydropyran (J. Amer.
Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 8401) by a procedure similar to
that described in Example 1, but using an elution
gradient of dichloromethane:methanol:0.880 aqueous
ammonia (95:5:0.0 to 95:5:1) for column chromatographic
purification, as a sticky solid. Rf 0.83 (SS 1).- --
[a~25 +35 (c = 0.1, CH30H). Found: C,58.79; H,6.52;
D
N,6.77. ClgH25N2OBr; 0.20 CH2Cl2 requires C,58.45;
H,6.49; N,7.10%
PREPAR~TION 13
5-(3-Hvdroxy-3-methYl-l-but-l-enYl)-3-rN-(4-
tetrahydropyranvlmethYl)-2(R)-DyrrolidinYlmethyll-lH
indole
The title compound (40% yield) was obtained from
the title compound of Preparation 12 and 2-methylbut-3-
en-2-ol by a procedure similar to that described in
Preparation 2 but using an elution gradient of
dichloromethane:methanol:0.880 aqueous ammonia
(92:8:0.25 to 92:8:1) for column chromatographic
puri~ication, as a foam. Rf 0.48 (SS 1). Ic~]25 ~42
(c = 0.1, CH30H). Found: C,74.31; H,8.93; N,6.88.
C24H34N2O2; 0.33 H2O requires C,74.23; H,8.99; N,7.21%.
CA 02202348 1997-04-lo
W O96/11195 PCT~EP95/03884
Biological activity
The following Table illustrates the in vitro
activities for a range of the compounds of the invention on
dog isolated saphenous vein strip. EC50 represents the
concentration of compound which causes 50~ of the m~i mllm
contraction effected by it.
TABLE
RELATIVE POTENCY
EX~MPLE EC50 (M) EC50 (compound)/
EC50 (5-HT)
1 6.2 x 10-7 11 . 0
1.8 x 10-7 2.4
9A 3.0 x 10-6 71
9B 1.8 x 10-6 78
Safety profile
One of the compounds of the invention has been tested
in conscious dog and showed no overt signs of adverse acute
toxicity at doses of up to 0.5 mg/Kg i.v. and 1 mg/Kg p.o.