Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02552083 2003-02-03
74935-39D
MESSAGE PROPAGATION METHOD AND MESSAGE PROPAGATION
SYSTEM
This is a divisional application of Canadian Patent Application No. 2,418,423
filed an February 3, 2003.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention:
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for
transmitting information to a limited range but wider than the range of a
radio communication means which is a short-range radio communication
means while using a portable information terminal including the
l0 short-range radio communication means.
Description of the Related Art:
If a request of "please contact me if you find a missing pet" is to be
transmitted by an individual person or "special price information" is to be
transmitted by a small-scale shop, it is a classical method to put up a poster
in front of the person's house or shop.
Meanwhile, following the recent spread of the Internet, information
can be delivered more widely by constructing an information server by an
individual person, using a bulletin board system (BBS) available to every
one or transmitting e-mails to many people.
2 o However, if the former method is used, only the persons who chance
to pass the poster can know the information. Since the pet actually moves
around, the person who looks fox the pet must want to let the poster known
more widely On the other hand, if the latter method is used, the range of
spreading the information is so wide that the information is spread to many
2 5 people who do not actually want and trouble actually occurs.
1
., r,...4 ~ ,..~.m~im ~n..,.11..,q.l..n.ln~,nn,r~...1 ..,
CA 02552083 2003-02-03
74935-39D
SUlYXMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method and an
apparatus for delivering information to a certain limited range which a
sender considers appropriate if the information to be transmitted is
effective.
According to the first aspect of the present invention, there is
provided a message propagation method comprising the steps of:
transmitting a message from a message transmission source apparatus to a
first portable terminate and repeating transferring the message from an
(i-1)~ portable terminal to i~ terminal encountering the (i-1)th portable
~ terminal in ascending order, for every i which is not greater than an
integer
n exceeding 1.
According to the second aspect of the present invention, there is
provided a message propagation method, comprising the steps of:
transmitting a message from a message transmission source apparatus to a
first portable terminate and repeating transferring the message from an
(i-1)~ portable terminal to ith terminal encountering the (i-1)~ portable
terminal in ascending order, for an integer i exceeding 1 until a
predetermined time elapses since the message is transmitted from the
message transmission source apparatus to the first portable terminal.
According to the third aspect of the present invention, there is
provided a message propagation system comprising a message transmission
source apparatus and a plurality of portable terminals, wherein one of the
portable terminals receives a message from the message transmission
source apparatus, and transfer of the message is repeated between the
portable terminals encountering each other until a transfer frequency
reaches a .predetermined frequency.
According to the fourth aspect of the present invention, there is
2
~, ~ "".."i~,~n~".. ,"".,~.m.,a..,d., .."" i...~
CA 02552083 2003-02-03
74935-39D
provided a message propagation system comprising a message
transmission source apparatus and a plurality of portable
terminals, wherein one of the portable terminals receives a
message from the message transmission source apparatus, and
transfer of the message is repeated between the portable
terminals encountering each other until the predetermined
time elapses.
According to the fifth aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a portable terminal comprising:
means for receiving a message from a first other portable
terminal encountering the portable terminal; means for
determining a life of the message; and means for
transmitting the received message to a second other portable
terminal encountering the portable terminal if the life of
the message is left.
In the portable terminal according to the fifth
aspect of the present invention, the life may be a transfer
frequency for transferring the message between the portable
terminals, and the portable terminal further comprises means
for decreasing the transfer frequency.
In the portable terminal according to the fifth
aspect of the invention, the life may be a period since
transfer of the message between the portable terminals
starts.
In accordance with a sixth aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a message propagation method
comprising the steps of: transmitting a message from a
message transmission source apparatus to a first portable
terminal; and repeating transferring the message from an
(i-1)th portable terminal to ith terminal encountering the
3
CA 02552083 2003-02-03
74935-39D
(i-1)th portable terminal in ascending order, for an integer
i exceeding 1 until a predetermined time elapses since the
message is transmitted from the message transmission source
apparatus to the first portable terminal.
In accordance with a seventh aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a message propagation system
comprising a message transmission source apparatus and a
plurality of portable terminals, wherein one of the portable
terminals receives a message from the message transmission
source apparatus, and transfer of the message is repeated
between the portable terminals encountering each other until
a predetermined time elapses.
BRIEF DISCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 is an explanatory view showing the outline
of the operation of a system according to the present
invention;
Fig. 2 is a block diagram showing the
configuration of the first embodiment according to the
present invention;
Fig. 3 is a flow chart showing the operation of a
transmit message processing section in the first embodiment;
3a
CA 02552083 2003-02-03
Fig. 4 is a flow chart showing the operation of a received message
processing section in the first embodiment
Fig. 5 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the second
embodiment according to the present invention and
Fig. 6 is a flow chart showing the operation of the transmit message
processing section in the second embodiment.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
[FIRST EMBODIMENT]
The first embodiment according to the present invention is
characterized by limiting an information distribution range to a certain
range by relaying to-be-transmitted information among portable
information terminals by a preset frequency.
First, the outline of the overall operation of a system will be
described with reference to Fig. 1. It is to be noted that the basic concept
for the outline of the operation applies to the following other embodiment in
common.
A person, who is to transmit information, registers to-be-transmitted
information and the frequency for transmitting the information in a fixed
station 80 provided at each location or a portable information terminal 81
which the person owns. It is assumed hereafter that the person registers
that "information can be transmitted up to three times" including the
transmission of the information from the fixed station 80 or portable
information terminal 81 which is an information transmission source.
Further, to help understand the system, a remaining transmission
frequency is shown in each balloon. The method for registering the
information and the transmission frequency is not limited to a specific one
4
CA 02552083 2003-02-03
but various methods may be considered such as a method, for example, by
uploading the information and the transmission frequency over a network or
directly using input means provided at the fixed station if the information
and the transmission frequency are to be transmitted to the fixed station or
by using input means provided at the portable information terminal if they
axe to be transmitted to the portable information terminal. Furthermore, it
is unnecessary to link a transmission frequency for transmitting
information from the fixed station 80 or the portable information terminal
81 which serves as the transmission source with the registered transmission
frequency. The former transmission frequency may be unlimited until data
is deleted or may be determined according to the other rule.
Portable information terminals (three portable information
terminals in Fig. 1) which chance to pass the fixed station 80 or the portable
information terminal 81, receive the registered information and
transmittable frequency Among them, the portable information terminal
82 is assumed to encounter a portable information terminal 83, a portable
information terminal 84 and a portable information terminal 85 at points A,
B and C, respectively while moving. The portable information terminal 82
can transmit information up to twice since the registered transmission
frequency is decreased by one (first transmission from the information
source). Therefore, the portable information terminal 82 transmits the
received information as well as a remaining transmittable frequency at the
time of transmission to each of the portable information terminals 83 and 84
but does not transmit any information and transmission frequency to the
portable information terminal 85. Here, as explained as "the remaining
transmittable frequency at the time of transmission", the transmittable
frequency is naturally decreased by one whenever the information is
5
CA 02552083 2003-02-03
transmitted.
Likewise, the portable information terminal 83, which receives the
information from the portable information terminal 82 at the point A,
transmits the information as well as the remaining transmittable frequency
at the time of transmission to a portable information terminal 86 which the
portable information terminal 83 encounters while moving but transmits
nothing to the other terminals which the terminal 83 encounters later on.
This is because the remaining transmittable frequency at the time of
transmission which the portable information terminal 83 receives is one.
It is noted that if a short-range communication system such as
Bluetooth is used for the communication between portable information
terminals or between the portable information terminal and the fixed
station so as to appropriately set the information transmittable frequency, it
is possible to transmit information only to a certain limited range.
An example of the configuration of the portable information terminal
to realize the above-stated operation will next be described with reference to
the block diagram of Fig. 2. Information which the above-stated sender is
to distribute will be referred to as a " message" and a message transmittable
frequency will be referred to as a " message life" hereinafter.
As shown in Fig. 2, the portable information terminal according to
the present invention consists of a data processor 1 which operates under
the control of a program, a storage device 2 which stores data, a radio
communication section 3 which includes the other portable information
terminal or a fixed station and a short-range radio communication means,
an input section 4 realized by a touch panel, a button or the like, and an
output section 5 realized by a liquid crystal display or the like.
The storage device 2 includes a message and message life storage
6
" ,. w.*~"~un , an,".~~n,~"H ,p..
CA 02552083 2003-02-03
section 21 which store received information (hereinafter referred to as a
" message") and a transmittable frequency for transmitting the information
(hereinafter referred to as a "message life").
In addition, the data processor 1 includes a received data analysis
section 11 which analyzes data received by the radio communication section
3, notifies the content of the data to an appropriate constituent element,
and,
if correct information is received, transmits a message receipt
acknowledgement notification through the radio communication section 3, a
transmit message control section 12 which transmits or controls the
l0 message and the message life if the message receipt acknowledgment for
terminal detection or message transmission is notified by the received data
analysis section 11, a received message processing section 13 which stores a
message and a message life in the message life storage section 21 if the
received data analysis section 11 notifies the reception of the message and
the message life from the other portable terminal or the fixed station, and a
main control section 14 which is responsible for ordinary functions as the
portable information terminal (such as a user interface and the
management of the received message) irrelevant to the present invention.
The operation of the transmit message control section 12 and that of
the received message processing section 13 which are characteristics of the
present invention will next be described with reference to Figs. 3 and 4.
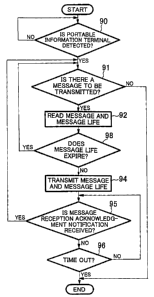
Fig. 3 is a flow chart for explaining the operation of the transmit
message processing section 12. Normally, the transmit message processing
section 12 continues to await a notification, which indicates the detection of
the other portable information terminal, from the received data analysis
section 11 (in step S90). When receiving the notification, the transmit
message processing section 12 determines whether or not there is a message
7
, a."il~i i...,n,u~i, .i..,..y.Nn"..Inr,m.r "b r,
CA 02552083 2003-02-03
to be transmitted (in step S91).
If there is no message to be transmitted, the transmit message
processing section 12 finishes its processing. If there is a message to be
transmitted, the transmit message processing section 12 reads the first
message from the message and message life storage section 21 (in step 92)
and determines whether or not the life of the message is zero (in step 93).
If the message life does not expire yet, the transmit message processing
section 12 transmits the message and the message life through the radio
communication section 3 (in step 94) and awaits a message receipt
acknowledgement notification from a transmission destination (in step 95).
If the message receipt acknowledgment notification arrives within a preset
period, the transmit message processing section 12 subtracts the message
life by one (in step 97) and moves to a processing for the next message.
Conversely, if the message life read in the step 92 is zero, the transmit
message processing section 12 does not transmit the message and the
message life but moves to the processing for the next message.
Further, if the message receipt acknowledgement notification does
not arrive within the preset period despite of the reception of the message
and the message life ("NO" in step 96), the transmit message processing
section 12 considers that the terminal which serves as the transmission
destination is out of a communication range and finishes the processing.
Fig. 4 is a flow chart for explaining the operation of the received
message processing section 13. Normally, the received message processing
section 13 continues to await a notification which indicates the reception of
the message and the message life from the received data analysis section 11
(in step 100). When receiving the notification, the received message
processing section 13 determines whether or not the message has been
8
.. ,..,b..,."id", ,.J.».",.a".~~..".,.p "
CA 02552083 2003-02-03
received before so as to prevent the same message from being accumulated
in the storage section (in step 101). The determination method is not
limited to a specific one but various methods may be considered including a
global-consistency based method, a method by embedding ID's into
messages in advance or the like.
If determining that there is no same message, the received message
processing section 13 updates the message life (in step 102) and stores the
message and the message life in the storage section 21 (in step 103).
[SECOND EMBODIMENT]
l0 The second embodiment according to the present invention is
characterized not by utilizing a message transmittable frequency as a
message life but by limiting an information distribution range to a certain
range while using a time.
Fig. 5 is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of
a system to realize the second embodiment. The second embodiment
differs from the first embodiment in that a count section 6 is added as a
constituent element for the system.
Fig. 6 is a flow chart showing the operation of the transmit message
control section 12. The transmit message control section 12 in the second
embodiment differs from that of the first embodiment in the following
respects. In step 98 which corresponds to step 93 shown in Fig. 3, the
transmit message control section 12 determines whether or not the hour or
date and hour set for a message life passes using the hour or date and hour
counted by the count section 6. Even if receiving a message receipt
acknowledgment notification from a transmission destination, the transmit
message processing section 12 does not need to update the message life.
Likewise, in the operation of the received message processing section
9
* . ,a "..,.",~ ", , ., ~ ",.,,,y.,..",.* , n ,,
CA 02552083 2003-02-03
13, the section 13 does not need to update the message life (step 102 shown
in Fig. 4) (although the processing flow of the received message processing
section 13 is not shown particularly). Needless to say, it is necessary to
update the message life, depending on the description format of the message
life, which is within the scope of the present invention.
The two embodiments according to the present invention have been
described so far. However, the present invention is not limited to these
embodiments. In the embodiments, the portable information terminal
which a person carries with him or her has been used. However, the
present invention is applicable to every method and apparatus for
transferring information by relay using portable terminals each having a
short-range radio communication function while conditions are satisfied.
As described so far, the portable information~terminal which
includes communication means having a narrow communication range (e.g.,
about two to three meters) transmits a message by relay and the relay
frequency and relay time are limited. Therefore, it is possible to provide
information to only a certain limited range.