Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02578982 2007-03-01
Disc brake, especially for a utility vehicle
The present invention relates to a disk brake, in
particular for a utility vehicle, as per the preamble
of claim 1.
In disk brakes of said type, the brake caliper, also
referred to as a sliding caliper, is connected by means
of fastening elements to the brake carrier which is
attached to the vehicle. Here, guide bars engage into
the brake carrier, which guide bars are guided at the
other side in sliding bearings of the brake caliper in
such a way as to permit an axial displacement of the
brake caliper relative to the positionally fixed brake
carrier. Of the sliding bearings, one is embodied as a
fixed bearing with little sliding play, while the other
functions as a floating bearing, as a result of which
in particular production tolerances are compensated.
It is known from DE 102 48 948 Al to arrange a spring
between the brake caliper, or a component which is
fixed therein, and the sliding ring of the floating
bearing, which spring serves to improve the wear
resistance and rattle-resistance of the floating
bearing. The spring in particular provides damping in
the case of vibrations as they usually occur during
driving operation. Here, the sliding ring and, with the
latter, the guide bar are held under load in a
specified position, so that disturbing rattling noises
are avoided.
In the known disk brake, the spring is preferably of a
meandering design and engages fully in terms of its
width around the sliding ring, with the individual
spring limbs also bearing against the sliding ring in
CA 02578982 2007-03-01
- 2 -
regions in which axial compensation takes place, such
as is necessary for compensating production tolerances
or else for compensating changes in position of the
guide bar relative to the guide sleeve transversely
with respect to the axial movement direction of the
guide bar. The axial compensating travel is however
restricted to a certain extent as a result of the
adjoining resilient limbs.
The present invention is therefore based on the object
of further developing a disk brake of the generic type
in such a way that the functioning of the floating
bearing is improved.
Said object is achieved by means of a disk brake which
has the features of claim 1.
As a result of said design embodiment, the travel of
the required axial compensation is practically
unhindered, since it is now possible to permit damping,
that is to say .to position the lugs which assume the
spring action, only at the point where no axial
compensation takes place, that is to say
perpendicularly with respect to the direction of the
axial compensation.
The lugs are advantageously shaped such that the spring
action is also incorporated in the axial compensation.
Here, the corresponding travel movement is damped by
limbs of the lugs which are preferably of trapezoidal
cross-sectional contour, with the result that the
rattling mentioned in the introductory part of the
description is effectively prevented.
According to an advantageous refinement of the
CA 02578982 2007-03-01
- 3 -
invention, the lugs are fixedly arranged on opposite
sides of the sliding ring or of the component which is
fixedly connected to the brake caliper and is
expediently in the form of a retaining ring.
Here, the spring can be composed of two approximately
identical parts, each of which has a strap and two lugs
which are attached at the end sides and, in the
assembled state, bear against one another, that is to
say overlap.
This permits a small initial thickness of the two
spring parts which are produced from a spring steel
sheet, preferably as punched parts.
Said production of the spring offers the advantage of
extremely cost-effective production, it being possible
in principle for the spring to initially be produced in
one piece and then divided in a further production step
in such a way as to produce two substantially identical
half-parts.
In order to fix the spring, in particular to
rotationally lock and axially secure the latter, the
receptacle of the brake caliper or of the component
which is fastened therein can be provided with a
corresponding locking means. The latter is composed,
according to a preferred refinement of the invention,
of a plastic cage which is vulcanized into the
component and has cut-outs for receiving the resilient
lugs. The receptacles correspond in shape and
dimensions to the associated lugs.
In addition to said axial compensation which is
unimpeded in this respect on account of the new
configuration of the spring, it is also possible in
CA 02578982 2007-03-01
- 4 -
this context to provide inclination compensation
without any problem when the longitudinal axis of the
receptacle in the brake caliper deviates from the
functional profile of the longitudinal axis of the
guide bar or of the sliding ring, with both axes then
being aligned at a certain angle to one another.
The spring therefore serves to provide a so-called
floating bearing which, in addition to the stated
damping, also permits precise, misalignment-free
guidance of the guide bar in the sliding ring.
Further advantageous embodiments of the invention are
characterized in the subclaims.
One exemplary embodiment of the invention is described
in the following on the basis of the appended drawings,
in which:
Figure 1 shows a partial longitudinal section through
a disk brake according to the invention,
Figure 2 shows a detail of the disk brake in a
longitudinal section,
Figure 3 shows a further detail of the disk brake in a
plan view,
Figure 4 shows a part of the detail according to
figure 3 in a perspective view,
Figure 5 shows a detail according to figure 2 in a
perspective view, and
Figure 6 shows an exemplary embodiment of a spring of
the disk brake in an exploded illustration.
CA 02578982 2007-03-01
- 5 -
Figure 1 illustrates a disk brake, in particular for a
utility vehicle, which in terms of its basic
construction has a brake caliper 2 which surrounds an
internally-ventilated brake disk 1 which is fastened to
an axle (not illustrated) of the utility vehicle.
The brake caliper 2 is connected to a brake carrier 7
of the utility vehicle so as to be axially displaceable
relative to the brake disk 1.
For this purpose, two fastening elements 5, 6 are
provided, of which the fastening element 5 is embodied
as a floating bearing and the fastening element 6 is
embodied as a fixed bearing.
The two fastening elements 5, 6 have in each case one
guide sleeve 8, 9 and a guide bar 10 guided therein,
with the guide sleeves 8, 9 being fixed in bores 3 of
the brake caliper 2.
The guide bars 10 are screwed into the brake carrier 7
and are therefore positionally fixed relative the brake
caliper 2, while the guide sleeves 8, 9 are fixedly
connected to the brake caliper 2 and are therefore
mounted so as to be axially displaceable on the guide
bar 10 together with the brake caliper 2.
Figure 2 illustrates the guide sleeve 8 of the floating
bearing 5, with the guide sleeve 8 having a sliding
ring 11 which surrounds the guide bar 10.
At one end, the sliding ring 11 is surrounded by a
shank guide 14 which is of sleeve-shaped form and is
supported laterally against a shank 16 of the guide bar
CA 02578982 2007-03-01
- 6 -
10. Arranged at the end region situated opposite the
shank guide 14 is a support ring 17 which encloses the
sliding ring 11 in said end region and at the other
side bears with a lip against the guide bar 10.
The floating bearing permits, for example for tolerance
compensation, an axial displacement of the guide bar 10
transversely with respect to the axial displacement
direction corresponding to the arrow.
In order to provide the greatest possible degree of
damping of transverse movements for example in the case
of vibrations, a spring 12 is provided which bears in
regions against the outer face of the sliding ring 11
and, at the opposite side, against the inner wall of a
retaining ring 13 which concentrically surrounds the
sliding ring 11 and is placed in the bore 3 of the
brake caliper 2.
According to the invention, the spring is composed of a
strap which at least partially surrounds the sliding
ring 11 and lugs 19 which are attached to said strap,
extend in the longitudinal direction of the sliding
ring 11 and bear in regions against the sliding ring 11
and against a retaining ring 13 which constitutes a
component of the brake caliper 2.
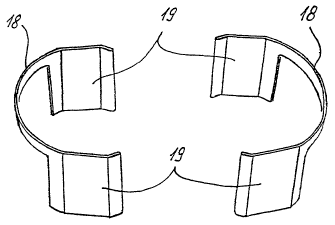
Figure 3 shows the contoured spring 12 in a plan view.
It can also be seen in said figure that the spring is
composed of two half-parts as illustrated individually
in figure 6.
Here, each half-part has a circular-segment-shaped
strap 18 whose respective ends are each adjoined by a
CA 02578982 2007-03-01
- 7 -
lug 19, with the associated strap 18 forming an upper
delimitation of the lugs 19.
The half-parts are dimensioned such that, in the
assembled state, two lugs 19 always bear against one
another, with said lugs 19 being trapezoidal in cross
section, so that two edges of the outer lugs bear
against the inner wall of the retaining ring 13, while
the inner lugs 19 are tangent to the sliding ring 11.
The damping travel in said region is smaller than the
axial compensation which takes place in one direction
which is 90 offset in relation to the lugs 19.
Nevertheless, as a result of the shaping of the lugs
19, damping is also provided by the resilient lugs 19
during axial compensation.
Figure 5 illustrates an axial compensation caused by an
angular misalignment, with the shank 16 deviating from
an axially parallel arrangement with the retaining ring
13 which is fixed in the brake caliper 2. It can be
very clearly seen here that even relatively large
angular misalignments can be compensated by the spring
12 embodied according to the invention.
In order to lock the spring 12, a cage 20 which is
preferably composed of plastic is provided in the
retaining ring 13, which cage 20 is fixedly connected
to the retaining ring 13 and has two opposing
receptacles 21 in which in each case the lugs 19 of the
spring 12 rest so as to be rotationally locked. Said
cage 20 is preferably vulcanized in.
CA 02578982 2007-03-01
- 8 -
List of reference symbols
1 Brake disk
2 Brake caliper
3 Bore
4
Fastening element
6 Fastening element
7 Brake carrier
8 Guide sleeve
9 Guide sleeve
Guide bar
11 Sliding ring
12 Spring
13 Retaining ring
14 Shank guide
16 Shank
17 Support ring
18 Strap
19 Lug
Cage
21 Receptacle