Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02692415 2010-02-10
Vehicle Vision System
Description
Background of the Invention
This invention is a system for generating and distributing real time vehicle
accident data
and provides an accident scene record which is automatically recorded and
quickly
accessible by authorized parties. This invention also provides real time video
and audio
monitoring of the inside of a said vehicle which is automatically recorded and
accessible
by authorized parties.
The formatted video/audio data is transmitted wirelessly from Unit A, received
and saved
into the portable memory storage in Unit B. Non authorized parties will not
have access
to the portable memory storage.
Summary of the Invention
This invention uses three cameras mounted on the vehicle, one camera provides
a visual
record in the region in front of the vehicle, a second camera provides a
visual record in
the region behind the vehicle and a third camera provides a visual and audio
record of the
inside of the vehicle. For a specified time interval covering current, recent
past and post-
accident, camera images are digitally recorded into a compressed format and
stored into
portable memory wirelessly. The contents of portable memory will be over-
written with
new video/audio data at programmable intervals.
An accelerometer onboard the vehicle generates a trigger in response to an
accident, such
as the vehicle hitting something or being struck by another vehicle. When the
system
receives this trigger data is no longer wirelessly stored into portable
memory.
The data can then be accessed by an authorized party (e.g. insurance company,
fleet
facility or private user) by directly or wirelessly (Bluetooth or WI-FI)
accessing the
portable memory storage (USB, SD memory card) and providing a password to open
the
contents of the portable memory.
Description of the Drawings
FIG. 1 is a pictorial diagram of one instance of the CCD locations in a
vehicle vision
system in accordance to the description of the invention.
FIG. 2 is a functional block diagram of one instance of a vehicle vision
system in
accordance to the description of the invention.
FIG. 3 is a data flow diagram of the steps used to capture and make available
vehicle and
monitoring data in accordance to the description of the invention.
CA 02692415 2010-02-10
FIG. 4 is a pictorial drawing of one instance of Unit A in a vehicle vision
system in
accordance to the description of the invention.,
FIG. 5 is a pictorial drawing of one instance of Unit B in a vehicle vision
system in
accordance to the description of the invention.
Detailed Description of the Invention
As shown in FIG.1 the front camera (2) is oriented so that its field of view
is forward of
the vehicle, the inside camera (3) is oriented so that its field of view is
that of the inside
of the vehicle. A third stand-alone camera (4) is located so that its field of
view is behind
the vehicle.
Referring to FIG. 4 the Unit A housing (8) which contains the video cameras
(1) front &
(2) inside is mounted at the front of a vehicle. Unit A housing (8) also
contains the data
input connector (3) from the stand-alone rear view camera and a power input
connector
(5). System programming is accomplished by accessing the switches (6) located
on Unit
A. Referring to FIG. 1 the Unit B housing (1) is located at a concealed
location within the
vehicle and contains the portable memory storage.
As further explained in FIG. 4, the housing (8) contains system hardware and
software
necessary to detect when an accident has occurred and to record video and
audio data
related to the accident scene to portable memory. Additional data including
the vehicles
operation prior to the accident, during the accident and immediately after the
accident is
also recorded.
The system automatically stores all encrypted image and audio data and
includes an
interface (e.g. USB, SD card, Bluetooth, WI-FI) that allows the contents of
the portable
memory to be read by a personal computer.
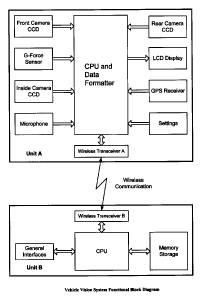
Referring to FIG. 2 the vehicle vision system is comprised of hardware and
software
components included in both Unit A and Unit B.
The functions of each block in the camera unit (Unit A) are explained as
follows:
Front Camera CCD: This block contains the camera CCD sensor that is installed
facing
towards the front of the vehicle.
G-Force Sensor: This is a G-Force sensor to detect the G-Force of the vehicle
as a trigger
input to the CPU and Data Formatter block.
Inside Camera CCD: This block contains the camera CCD sensor that is installed
facing
towards the inside of the vehicle.
CA 02692415 2010-02-10
Microphone: This microphone is installed inside the vehicle to monitor and
record audio
sound.
Rear Camera CCD: This block contains the camera CCD sensor that is installed
facing
towards the rear of the vehicle. This camera CCD sensor is a wired connection
to Unit A.
LCD Display: This is a device which can display live or playback video. The
system
setting/status can also be displayed on this device.
GPS Receiver: This GPS receiver can receive GPS location data and have the
data stored
into system memory. The GPS data can be displayed on the LCD screen and used
as a
vehicle GPS device.
Settings: This block contains the control and setting selection buttons.
CPU and Data Formatter: CPU and Data Formatter block receives the data from
the
CCD cameras and microphone, formats it into video/audio files and then sends
it to the
storage unit (Unit B) via wireless communication. This block also receives
data from
Wireless Transceiver A.
Wireless Transceiver A: This is a wireless transceiver used to transmit and
receive
video/audio data with storage unit (Unit B).
The functions of each block in the storage unit (Unit B) are explained as
follows:
Wireless Transceiver B: This is a wireless transceiver used to transmit and
receive
video/audio data with camera unit (Unit A).
General Interfaces: This block may contain some general interfaces (for
example USB,
SD card) to communicate with PCs.
CPU.- The CPU in Unit B takes the video/audio data from the Wireless
Transceiver B and
saves it into the portable memory storage. This block also sends data to
Wireless
Transceiver B.
Memory Storage: This is the portable memory space used to store the
video/audio data.
This physical interface can be USB stick or a SD memory card.
Software components include the processor's operating system, a real time
video
compression application program (e.g. AVI, MPEG II) and an encryption
application
program.
Referring to FIG.2 and FIG. 3, the three CCD video cameras produce digital
data of their
viewing area, for example, the front of the vehicle, the inside of the vehicle
and the rear
of the vehicle. CCD camera data outputs go to the processor where the data is
compressed, processed and then stored into portable memory. Digital data is
stored into
CA 02692415 2010-02-10
portable memory in a programmable time interval (for example 1- 5 minutes) and
overwrites its memory contents when full.
The vehicle vision system detector is a two axis accelerometer which generates
a trigger
signal when an accident occurs. The output of the accelerometer is constantly
being
monitored and compared by the system CPU for a valid trigger signal. When the
CPU
receives the accelerometer trigger input it will stop recording from the
front, inside and
rear cameras after a programmable predetermined interval.
The contents of the portable memory can be read by an authorized user by
removing from
Unit B, uploading to a personal computer, executing the file (AVI, MPEG) and
providing
the necessary password. The contents of the portable memory storage can also
be read
wirelessly by an authorised user from a personal computer.
The vehicle vision system contains a LCD screen FIG.4 (7) to display real time
video,
help align camera angles and to display system setting and status. The LCD can
also be
used to playback data from Unit B portable memory storage wirelessly upon
request.
The vehicle vision system can contain a GPS receiver to receive GPS data. In
combination with the other functional blocks in the system it can then be used
as a GPS
device.
Although the vehicle vision system contains three video cameras, the system
may contain
just one or all of the cameras depending on the requirements. For example, for
the usage
of vehicle accident evidence, the system may just contain the front and rear
cameras,
while for the usage of vehicle surveillance the system may just contain the
inside camera.