Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
62~46
NITRODIARYL SUL~'OXIDE DERIVATIVES, PROC~SS ~OR THEIR
PREPARATION AND PHARMACEUTICAL AND PESTICIDAL
COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING THEM AS ACTIVE IMGREDIENT
The invention relatea to new nitrodiar.yl
10 sulfo2ide derivative~, to a procea~ for their prepara- -
tion and pharmaceutical and peaticidal composition
containing them a~ active ingredient. More particu-lar~y,
the invention concerns new nitrodisr.yl aulfoxide
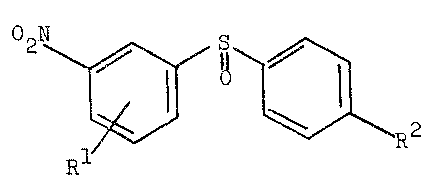
derivative~ of tne formula (I)
02N ~ ~ ~ R2 (I)
wherein
Rl i9 halogen or alXoxy having from 1 to 6 carbon
atom~,
R2 i9 hydrogen, h~logen, al~yl having from 1 to 6
carbon atom~, alko~y ha~ing from 1 to 6 carbon
A 3431-67 MR
~ ~ 2~
atom~ or phe~yl or phe~ylt~io optionalLy
sub~tituted b.y one or more identical or different
halogen(9) and/or nitro group(s).
According -to another aspect of the invention
there i~ provided a process for the preparation of the
new compound~ of the formula (I~, wherein Rl and R2 have
the same meanings as defined above~ by reducing ~n ar~yl-
sulfonyl halide of the formula (II)
02N ~ S02Xl (II)
Rl
wherein Rl i~ a~ defined above, and
Xl is halogen,
with an alXali metal sulfite, treating the aryl~ulfinate
of the formula ~III)
2N~S 02M
l~ ~ (III)
Rl /~'
obtained~ in which
R i~ as defined above, and
M is an ~lkali metal~
with an acid, re~ctin~ the aryl9ulfinic acid of the
formul~ (IV)
, .
~26~ 6
-- 3 ~
02N S02H
~ ~ ~IV)
Rl
obtained 9 in which Rl iY as defined above 9
or the ar.Ylsulfinate of formula (III), in ~which Rl
and M are as defined ~bove~ with a halogenating agent,
and reacting the new ar.yl~ulfi~yl halide of the formula
10 (V)
: 02N ~ sox2
~ (V)
: :~ : R
; ~15
obtained, in which Rl i~ a~ defined above and ~2 i9
~: ~ halogen, with û benzene derivative of the formula (VI),
; 20 ~ (VI~
R2
wherein R i3 as defined in co~nection with the formula
(I), in the pre~e~ce of a metal halide cata~yst of the
~ewis acid t,ype~
The ~ew compound3 of the formula (I~ are pharma-
~,
:
,
~L~6~
ceutical~y active, and can in particular be used in
the veterinary therap.y, e.g. a_ nem~tocidesttaenicide3,
etc., and preferabLy as anthelmintics, and show
pe~qticidal~ e.g. acaricidal, fungicidal, antimicrobial
and herbicidal, preferabLy inqecticidal activit.y.
The compounds of the formula ~I~ are further
valuable intermediates in the preparation of other new
and known, biologicalLy active aromatic ~qulfoxide
derivative~, such as benzimidazole ~nd sub~tituted
diamino qulfoxide derivatives having anthelmintic and
fungicidal activit.y, e.g~ Oxfendazole. The.~ can be
prepared from t~he compoundq according to the invention
b.y reaction with an amine derivati~e~ ~ub~equent reduction
and coupling with a carbamic acid derivative.
CompoundY of the formula (I) ~re new. In the
hitherto known nitro-2ub~tituted diar.yl qulfoxides the
nitro ~roup wa~ attached to one of the phe~yl ri~gs in
ortho- or para-position related to the sulfoxide group~
~nd the other sub~tituents were different from thoYe
in the compoundq ~ccordlng to the invention a~ to their
qualit~, number and position related to the ~ulfoxide
group; while the onLy known compound containing an o-nitro
group w~ unsubstituted The structurall.y related, known
diaryl sulfo~ides were generalLy prepared by a different
procedure, i.e. o~idation of the corre~ponding diaryl
~ulfides ~ Ber. 41~ 2836 ~1908), J. Am. Chem, Soc. 1381
(194~7,
,
~fi2
-- 5 --
In the for~ulfl ~I) Rl and R2 a~ halogen repre~ent
fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine, preferabl.y
chlorine; while a3 alkoxy having from 1 to 6 carbon atoms
the.y 3tand for any straight-chained or branched alko~y
group, e.g. metho~y, ethox.y, n-propo~y, i~opropo~y,
n-buto~y, sec.~butox.y, i~obuto~y, n-pento~y, i~opentoxy,
_-he~yloxy, i~ohe~ylo~y, etc.~ preferably metho~y. In
the definition of R2 the term "al~yl having from 1 to 6
carbon atom.a" ia used to refer to straight-chained or
branched alk.yl group3, e.g. met~yl, ethyl, n-propyl,
isoprop.yl, n-but.yl, ~ec.-butyl, isobut.yl, tert~-but.yl,
n-pent.yl, iYopent.yl, n-he~Y19 i~ohe~yl, etc.
In the compounda of' formula (III) M a3 an alkali
metal preferably atanda for potaa~ium or ~odium.
In -the compound3 of formulae (II) ard (V) Xl and
X aa halogen repreaent fluorine, chlorine, bromine or
iodine, preferabLy chlorine.
~ he intermediatea o~ tt~e ~or~ula ~V) are n2w
compound~, and their preparation is also within -the
qcope of the'pre~ent invention.
The reduction of the ar.ylYulfonyl halides of the
formula ~II) with alkali metal sulfites is preferably
carried out in an aqueous medium, b.y using the alkali
metal sulfite in a 91ight exee99, preferably in an amount
o~ 1.1 to 4 moles related to 1 mole of ar.yl3ulfo~yl~halide.
The reduction is performed ~t a tempera-ture of 20 to 35C,
iZ~416
-- 6
preferabLy 22 to 28 C. The reduction ic~ preferabl.y
accompli~hed under m:ildly alkaline condition~, between
pH 7 and 9, preferabl.y 7.5 and 8.5, for example b.y adding
to the reaction mixture an alkali metal bicarbonate,
alkali metal carbonate or alkali metal ~ydroxide
~imultaneouql.~. Alternativel.y, the above agentq ma.y be
added to the reaction mixture prior to the addition of
the reducing agent. The alkali metal component~ of the
above reactants are preferabLy identical with the alkali
metal of the alkali metal ~ulfite uc~ed a~ a reducing
~gent, The above alkaline agent~ C~erve alqo for acid
binding. The slkali metal bicarbonatec~, carbonateq or
hydroxic3e9 can be uqed either in a qolid form or in the
form of their ~aturated aqueous solutionq or qir.~ultaneously
in both formq.
The acid treatment of the compoundc~ of t~e formula
(II~) iq preferabLy carried out with ~ ~trong mineral
acid, preferabLy concentrated aqueous ~ydrochloric acid,
~ulfuric acid, etc. The mineral ~cid i9 preferab~y
used in an exces~ amount. The aryl~ulfinic acid obt~ined
after ~ydrolysis 19 very pure (has a purit.y of ~t least
98 %3 and stable, ln contrary to the ~rylsulfinic acids
prepared earlier by different proceC~ses. Compounds of
for~ulfl (IV) are obtained in a very high .yield, which
con9iderabLy exceed9 the yield of the hitherto known
processes L Houben~Weyl, ~, 317.
Both t~e ~r.yl~ulfinates of for~ulq ~III) and
-the arylaulfinic acid~ of formula (IV) can be reacted
with a halogenating agent, to .yie~d the correaponding
aryl~ulfi~yl halide of the formula (V). As a halogenating
agent an inorganic ox organic halogenating agent can
be u~aed. Inorganic halogenating agents include for
example the compoundq o~ qulfur and pho~phorus wi-th
halogen or with halogen and o~y~en. T.ypical representatives
of these compounds are thionyl chloride, pho~phoruY tri
chloride, phoagene, phoaphorus pentachloride, pho~phorua
o~ychloridet and a combination of phosphorus o~ychloride
and chlorine. Organic halogenating agenta include orgflnic
acid halides, ~uch as oxal.yl chloride. The ar.yl~ulfi~yl
halide~ of the formula ~V) are new compounds, which are
con~iderab~y more ~table -than the differentLy substituted
ar.yl~ulfinyl halidea known in the art.
~ ing the reaction of the compounda of formula (V~
with the compound~ of formula (VI) as a metal h~lide
cataLy~t of the Lewi~ acid type a~y cataLyst conventionall.y
u9ed in Friedel-Crafts acylation9, e.g. preferably
aluminium trichloride, can be used. According to a
preferred embodiment of the reaction compounds of the
formula (V) are reacted with the compound~ of the
formula ~VI) without iYolation, directl.y after elimination
of the halogenating agent. The metal halide catalyst
of the Lewis acid t.ype i9 preferabLy u~ed in an amount
~ ,2~E;2~ 6
of 1~1 to 1.8 moles related to 1 mole of the ar~l~ulfi~yl
halide o~ ~ormula (V). The reac-tion i~ performed between
0 C and 80 C, preferabLy 25 C and 42 C.
The proces~ according to the invention yield~
the new nitrodiaryl sul~o~ides in a high purit.y (at
least 98 %) with excellent .yield (90 to 96 % related to
the correqponding ar~lsul~inic acid, and sbout 85 %
related -to the corresponding ar.ylsul~o~yl halide). The
process according to the invention ca~ ea~ily be carried
out even on industrial scale
The reaction mixtures can be proce~sed b.y
conventional techniques, for e~ample extraction9 filtra-
tion, evaporation, precipitation with ~ater, elimination
of the solvent or the excess of reactants, decantation,
etc.
The compound~ o~ the formula (I) can be ~ubjected,
if desired, to further purification, e.g. recr.ystallization.
The solvent~ used for recr.ystallization are selected
depending on the solubilit.y ~nd cry~talli~stion properties
of the compound to be c ~ stallized.
The active compounds of the ~ormula (I) mfl.y be
formulated for therapeutic purpose~. The i~vention
therefore relate~also to pharmaceutical compositions
comprising a~ active ingredient at least o~e compound of
form~lla (I), in as90ciation with pharmaceutical carriers
and/or exciPients, Carriers conventional for this purrose
and 9uitable for parenteral or enteral admi~i9tration
~ Z6 ~ 6
aq well as other additives may be used. As carriers
solid or liquid compounds, for example water, gelatine,
lactose, starch, pectin, magneslum stearate, stearic acid,
talc, vegetable oils, such ag peanut oil~ olive oil, etc,
can be used. The compounds can be formulated as conventional
pharmaceutical formulations, for example in a solid
~globular and angular pills, dragées, e.g. hard gelatine
capsules) or liquid (injectable oiLy or aqueous 901u-
tions or cucpensions) form. The quantit.y of the solid
carrier can be v3ried within wide ranges~ but preferabLy
it is between ~5 mg. and 1 g. The compositions optionall.y
contain also conventional p~arrnaceutical ~dditives,
~uch as preserving agents, wetting agents, qalts for
adjusting the o~motic pressure, buffers, flavouring and
odouring substances.
The compositions according to the invention
optionall.y contain the compound~ of formul~ (I) in
a~qociation with other known acti~e ingredients. T~e
unit do~e~ are selected dependin~ on the route o*
admini~tr~tion. The pharmaceutical compositions are
prepared by conven-tional techniques includin~ sieving,
mi~ing, granulation, pressing or dissolution of the
active ingredients. The formulations obtained are then
subJected to additional conventional treatments, such
a~ qterilization.
~or u~e as pesticides~ the compound2 of the
;2~
-- 10 --
formula (IJ flre f`ormulated a~ conventional ~ormulation~,
e.g. qolutions, e~ulsion~, soluble powders, suspension~ 9
powder compositions, aerosol compositiona, qu~penaion
and emulsion concentrate~ 9 powders for aeed dre~ing.
The compounds can be u~ed for impre~nating natural and
synthetic materials, may be formulated as microcapaulea,
using poLymeric ~ubstances and materials ~uitable for
coating ~eed~, or can be converted into ~ormulation~
~upplied with burnable Iilling, auch as amoke patron~
boxe~, spiral~, and warm or cold fog compositionai which
ma.y be applied by ULV (ultra-low-volume) technique.
The pecticidal compo~itiona can be prepared in a
manner known per ae, ~or example by admixing the active
ingredientq ~rith carriera, i.e. liquid aolventa,
liquified gaaes under preaaure and/or solid carriers.
If de ired, alao aurfactanta 9 emulcif.~ing and/or diapercing
and/or ~oaming agents can be added to -the a.ystem. If water
is u~ed as a carrier, a~a a co-~aol~ent or~anic aolventa
ma.y alYo be emplo.yed. The liquid ~olvents essentiall.y
include aroma~ic compound~ such a~ x.ylene, toluene or
alkylnaphthalenea; chlorinated aromatic or chlorinated
aliphatic hydrocarbon~ ~uch as chlorobenzene, chloro-
ethylene or methylene chloride; aliphatic hydrocarbons,
~uch as c.yclohexane or paraffines ~uch as mineral oil
fractions, aa well as alcohola ~uch a9 butanol or gLycol
and the ether~ and ester9 thereo~; ketones 9uch as
46
11 -
acetone, methyl et~yl ketone, methyl i~obut.yl ketone
or c.yclohexanone; strong~y polar ~olven-ts ~uch a~
dimet~yl ~ormamide, dimethyl qulfoxide and water. Under
liquidified ga~eou9 carriers for example aerosol
propellant~ ~uch as halogenated hYdrocarbon~, butane,
propane, nitrogen and carbon dioxide are mean-t. As solid
carriers for example natural fo~ail meala, e.g. caoline,
clay esrth, t~lc, chalkctone, quartz1 attapulgite1
montmorillonite or diatomaceous earth, and ~.ynthetic
foq~qil meals quch as highLy di~per~ed ~ilicic acid,
alu~ina and silicatea are emplo.yed~ As carriers for
granulates for example broken and fractionated natural
rock3, e.g. calcite, marbel, pumice, ~epiolite, dolomite,
and granulate~ of inorganic and organic mealq, a~ well
as granulates prepared from orgsnic material~ ~uch as
sawdust~ coconut~ ~helll corn hu~k and tobacco stem~
can be u~ed. As emul~if.ying agents and/or foami.ng agent~
non-ioni.c and anionic amulsifier~ ~uch aq pol.yoxyeth.ylene
fatty acid ether~, polyo~yet~ylene fatt.y ~lcohol ether~,
e.g. al~ylar.ylpolyg~ycol ether, alkylsulfonates, alkyl-
aulfates, ar.yl~ulfonate~ and protein hydrol.y~a-te~, while
as diqpersing agents e.g. lignine, ~ulfite waste liquors
and methyl cellulose ma.y be emplo.yed~
The pe~ticidal composition~C according to the
invention ma.y contain al~o adhesives ~uch a~ carbox.y-
meth~yl cellulose, natural and qynthetic, powder.~,
~L:2Ç;21.~4~
,,
granular or latex-like pol.ymers, e~g. acacia gum,
pol.yvi~yl slcohol, poLyvinYl acetate, etc
The peqticidal compoqitions according to the
invention ma.y ~urther contain various pigment~ quch
aq inorganic pigment~, e.g. iron oxide, titanium dioxide,
ferroc.yane blue and organic pigmentq, e.g. alizarine,
azometal phthaloc.yanine pigment~, as well a~ micro-
nutrients, e.g. iron, mangane~e, boron, copper, cobalt9
moLybdenum and zinc salts.
The pe~ticidal compo~ition~ generalLy contain
0.1 to 95 ~ b.y weight, preferably 0.5 to 90 % by weig~t
of active ingredient.
The active ingredients ma.~ be applled in the form
of commercial formulation3 and/or read.y-to-use formulation~
prepared therefrom~
The active ingredient concentration of the ready-
to-use formulation~ prepared from the co~ercisl
pe~ticidal compositions ma.y var.y ~Iqithin ~de limit~, and
generalLy iq between 0.000 000 1 and 95 ~ b.y weight,
preferabLy 0.01 and 10 % by .weight,
~ he route o~ application alwa.ys depends on the
specific formulation uqed.
The invention is elucidated in det~il b.y the aid
of the ~ollowing non-limiting Examples.
: :
~ 2
- 13 -
Ex~mple 1
Sodium 4-chloro-3-nitro-benzeneculfinate
To a ~olu-tion of 24 g. of ~odium bicarbonate in
30 ml. of water 71.8 g. (0.57 moles) of qolid 9 anhydrou~
~odium sulfite are added~ To the homogenous solution
a mi~ture of 58.4 g. (0.228 moles) of 4-chloro-3-nitro-
benzenesulfo~yl chloride and 2~ g. of sodium bicarbon~te
i~ uniformly sdded in 2 hours, at 23 to 25 C. When the
addition i~ complete, the su~pen~ion i~ ~tirred at
23 to 25 C for 4 hours and sub~equently, after addition
o~ 20Q ml. of toluene, at 35 C for 15 minutes. It i~
then cooled to 23 to 25 C ~nd ~tirred. T~e product iq
filtered off and air dried.
56 g. of ~odium 4-chloro-3-nitro-benzenesulfinate
are obtained. Accordin~ to the pota~ium permangan~te
analytical method the product contains 85 ~0 of active
sub~tance and 15 % of water.
Yield: 90 % o~ theoretical
4-Chloro-3-nitro-benzene~ulfinic acid
The sodium ~alt prep~red according to Example 1
i~ dis~olved in 300 ml, of water at 40 C and filtered
at the ~ame temperature. The filtrate i~ cooled to
10 to 15 C, acidified with 100 'nl. of concentr~ted
aqueou~ hydrochloric acid 901ution under thorou~h
stirring~ cooled to 5 C, filtered and the product
1
~ 6
- 14 -
obtained i~ dried at a temperature not exceedlng
4o C
43 g. of white, cr.y2talline 4-chloro-3-nitro-
benzenesulfinic acid are obtained.
Purit.y: 99 ~0
~elting point: lO to 103 C.
Yield related to the ~ulfonyl chloride: 85 % of theoretical
Example 3
Phe~yl-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl) ~ulfoxide
a) 36 g. (0.1625 moles) of 4-chloro-3-nitro-
benzene2ulfinic acid prepared accordi.ng to Example 2,
75 ml. of benzene and 15.1 ml. of t~ionyl chloride are
ad~ixed. T'ne reaction mixture ic boiled for one hour
and di2tilled in vacuo at a temperature below 60 C.
To the re2idue two further 25-ml-portion2 of benzene are
added and the ~olvent i eli~in~ted e~ch time. To the
re~idue weighing about 40 g. ~n24 = 1.6240), which i~
crude 4-chloro-3-nitro-benzene~ulfin.~l chloride, 20 ml.
of dichloroethane are added, ~ollowed b.y t~e addition
of 28.2 g. (0.21 mole~) aluminium chloride under cooling,
at a temperature below 40 C. Thereafter 35 ml. of benzene
are added to the mixture at 40 C within half an hour~
The reaction mixture is 2tirred at 4~ C for two hour9,
diluted with 50 ml. of benzene, poured onto a mixture of
lO0 g. of ice and 50 ml. of water, the org~nic phase i9
extracted with 50 ml. of benzene. The combined ben~ene
-- 15 --
phaseq are decoloured wit~ 5 g. of charcoal~ filtered
ancl the ~olvent i~7 elirninated from the filtra te in vacuo .
45 g. of white pher~yl-( 4-c~loro-3-nitro-pher~yl)
qulfoxide are obtained.
5 Melting point: 86 to 87 C
Purity: 9~ -~ (according to high-presqure liquid chromato-
graphy )
Yield: 96 ~ of theoretical
b) There are admixed 36 ~;. (0.1625 moleq) of 4~
10 chloro-3-nitro-benzene~ulfinic acid prepared accordin~3
to Example 2, 20 ml. of dichloroethane~ 13.5 ml. (22 g.,
0~185 mole~) of thiorLyl chloride and 0.1 ~l. of tri-
et'n.yl amine. The qulfinic acid iq gradualLy diYsolved
;~rhile gas evolution i~ obc~erved. The reaction. mixture i9
15 he3ted at 50 C for one hour, cooled to 5 to lO C,
and 28.2 g. (0.21 mole~ of alurr~iniurn chlo-ide ~re added
to the Yolution, taking care that the temperature of`
the reaction mixture ~hould not exceed 40 C. Thereafter
35 ml. of benzene are added to the mixture at 40 C,
20 in half an hour. The reaction mixture i~ ~tirred at 40 C
for two hour~, diluted with 50 ml. of benzene, end
poured onto a mixture of lO0 g. of ice and 50 mlO OI
weter. The organic pha~e i9 separated, and the aqueou~
pha~e i~ extracted sNith 50 ml. of benzene. The combined
25 benzene pha~e~ are decoloured with 5 g. of activated
carboIl, filtered and from the filtrate he overwhelming
_ 16 -
part of benzene is eliminated b.y distillation in vacuo,
when a solid qub~tance is precipitated. Therea~ter, the
remaining psrt of benzene i~ eliminated with methanol,
under atmo~pheric pre~sure, 90 that the reaction mixture
~hould contain about 60 to 70 ml. of methanol. The ~olution
i~ then allowed to cool alowl.y. At 40 to 50 C
cr.ystallization qtarts. When the product form~ a thick
cr~3tal pulp, 100 ml. of water having a temperature of
40 to 50 C are added to the reaction mixture at 40
to 50 C, initiall.y at a low rate. The loo~e, finel.y
diaper~ed auapenqion i9 cooled to 15 to 20 C under
~igoroua stirrin~ filtere~ and dried.
45 g. of the deaired compound are obtained. The
p~ysical properties of the product are identical with
15~ those of the product prepared according to variant aJ.
Examp_e 4
Phe~yl-(4-chloro-3-nitrophe~yl) aulfo~ide
; 23 g. (0.08 moles) o~ 84.7 % ~odium 4-chloro-
3-nitro-benzene~ulfinate prepared according to 3xample 1
are diasolved in 50 ml. of benzene~ To the solution 9.2
ml. (0~112 molea) o~ phosphorus trichloride and 10 ml.
o~ benzene are added at a temperature below 30 C, under
vigorous stirring, in about 1.5 hours. The mixture is
stirred for turther 2.5 hour9 at 22 to 25 C, the
benzene ~olution of the sulfi~yl chloride deriva-tiYe
~, i9 decanted or filtered off b.y suction~ ~rom the solution
~ I
~262
-- 17 --
obtained the ~olvent i~ eliminated in vacuo and
distillation i9 repeated wit~ two 20-ml portions of
benzene. The pale-yellow oil.y ~ul$i~yl chloride derivative
(nD4 - 1.6250~ iq diluted with 18 ml. of benzene, and
is then added to the ~u~pen~ion of 11.34 g. (0O085
moles) of aluminium chloride in 18 ml~ of benzene at a
temperature below 15 C. When the addition is complete,
the reaction mixture i~ allowed to warm up to 40 C,
and it i~ stirred at this temperature for two hours.
The reaction mi~ture is then poured on-to 100 ml. of ic.y
water. The ~eparated aqueous phase is extracted with
25 ml. of benzene. The combined benzene phase~ are
decoloured with activated carbon, filtered and the
~iltrate is evaporated in ~acuo.
21 g, of the deaired compound are obtained.
Melting point: 86 to 87 C
Yield: 95 % of theoretical
Example ~
(4-Chloro-3-nitrophenyl)-4-methylphe~yl ~ulfoxide
To about 4~ g. of benzene- and thienyl chloride-
free 4-chloro-3-nitrobenzene sulfinyl chloride prepared
according to Example 3 100 ml. of toluene ~nd subsequently
28,2 g, (0~21 moles) of aluminium chloride are added at
20 Cs under cooling. The reaction mixture is stirred
at 35 C for 2.5 hours, and is further treated a9
described in Example 3.
~2~ a6
42 g. of the desired compound are obtained.
Melting point: 82 to 84 C
Yield: 87 rO of theoretical
Exflmple 6
(4-Chloro-3-nitrophe~yl)-4-chlorophenyl sulfoxide
T~e procedure described in Example 5 is followed,
except that instesd of toluene chlorobenzene is used,
and the reaction mixture is stixred at 50 C for 4 hours.
The title compound iq obtained with ~ .yield of 89 ~.
~elting point: 110 to 112 C.
Phe~yl-(4-metho~y-3-nitrophen~ylJ ~ulfoxide
4-Metho~y-~-nitrobenzene qul~onyl chloride
~meltin~ point: 66 C) is reduced with sodium ~ulfite as
described in Example 1, and the ~odium 4-methox~-3-nitro-
benzene ~ulfinate is further trea-ted as described in
~ample 4.
The tiile compound i9 obtained with a ~ield o~
88 ~. Melting point: 135 to 137 C.
~xamPle 8
2-Chloro-5-nitrobenzene sul~'inic acid
321 ml. (4.7 moles) of chlorosul~onic acid and
79 ~. (0.5 moles) of 4-chloro-nitrobenzene are stirred
at 130 C for 6 hour9~ The reaction mixture is then
cooled to a temperature below 10 C ~nd is poured onto
750 ml. of i~.y water. The mixture is filtered at room
~ ~ 2
- 19 -
temperature ancl t~e sub~tance collected on the filter
i9 washed acid-Yree with about 2 litre~ of water. The
crude 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzene ~ulfo~yl chlorlde obtained
i9 su~jected to the subsequent reaction ateps without
purification. 118 g. (0.~35 mole~) of anh~drous qodium
sulfite and 20 g, of qodium bicarbonate are di~solved
in 250 ml. of water, and to the solution obtained a
mixture of the crude 2-chloro-5-nitrobenæene culfo~yl
chloride and 20 g. of ~odium bicarbonate is added at a
temperature of 23 to 25 C, in one hour. The reaction
n~xture i9 3tirred for t~o hours at a temperature of
23 to 25 C, and, after the addition of 200 ml~ of
toluene, for further 15 minutes. The mi~ture iq stirred
at 25 C and the cubctance filtered o~f ic wa~hed with
100 ml. of toluene. The ~odium 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzene
qulfinate obtained i9 discolved in 400 ml. of water at
40 C, and the colution iq admixed with 200 ~1. of
toluene. The insoluble part i9 -~`iltered off and the
toluene pha~e is ~eparated from the filtrate. Ihe
~queous phase is cooled to 10 C, acidified with 100 ml.
of concentrated aqueous hydrochloric acid solution and
the precipitated cr.y~tals are ~tirred, filtered off at
C and dried. 61 g. of 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzene sul~inic
acid are obtained, Yield: 55 ~ of theoretical related
to 4-chloro-nitrobenzene.
Melting point: 128 to 130 C
~ 2
_ 20 -
Purit,y: 98 ,~ (according to potasqium permanganate anal.ytical
method)
Example 9
Phe~yl-(2-chloro-5-nitrophe~yl) ~ulfoxide
26 ~. (0,1625 mole~) oY 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzene
sulfinic acid a~e admixed with 60 ml~ of benzene and
36 ml. of thion,yl chloride. The reaction ~ixture is
boiled for one hour. ~urtheron the procedure de~cribed
in Example 3 is follo~Yed, except that instead o~` benzene
dichloroethane is uqed for dilution and extraction.
40 g. o~ phenyl-(2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl) sulfoxide
are obtained as a white microcr.ystalline ~ubstance.
Melting point: 150 to 152 ~
Purit,y: 97 % (according to high-preq3ure liquid chromato-
graphy)
Yield: 85 % of theoretical
Example 10
4-(4-Chloro-3-nitrobenzene~ulfi~yl)-biphenyl
The procedure deqc~ibed in Example 5 is ~ollowed
except that inqtead of toluene biphe~yl is employed. ~he
desired compound i,~ obtained with a .yield of 90 %,
Melting point: 98 ~to 99 C.
~xample 11
4-(4-Chloro-3-nitrophenylthio~-phenyl-(4-chloro-3-nitro-
phe~yl) sulfoxide '
36 ~. (0~1625 ~ole~) of 4-chloro-3-nitrobenzene
~ 2
- 21 -
sulfinic acid prepared accordi~ to Example 2, 35 ml, o~
ben2ene, 10.5 ~1, (0~143 mole~) of thio~yl chloride and
0.1 g. of anhydrou~ ferric chloride are boiled for
one hour. q`o t~e ~olution 28.2 g. (0.21 moles) of
aluminiumchloride are added at a temperature below 40 C.
The reaction mixture is ~tirred ~t 40 C for 2 hours,
whereupon the procedure de~cribed in Example 3 i~ followed.
The oiLy product obtained i~ di~olved in hot ~ce-tone,
to the solution a ~mall amount of aqueous methanol i9
added, whereupon the separated oil is dis~olved in hot
acetone and treated again with aqueous meth~nol. The
oil.y portion i9 qeparated, ~pon addition of acetone
the desired compound i~ obtained in a crystalline formO
11.4 g~ of the title compound are obtained,
~5 Yield: 30 ~0 of theoretical
Melting point: 144 to 146 ~C
Example 12
(4-Chloro-3-nitrophe~yl)-4 methox~phe~yl ~ulfoxide
The reaction mixture containing 4-chloro-3
nitrobenæene ~ulfi~yl chloride prepared as described
in Ex~mple 3, variant bJ is released from thionyl
chloride b.y distill~tion in vacuo, To the residue 50 ml,
o~ dichloroethane and 21,6 g. of anisole are added, the
mixture i9 cooled to -5 C and 33.4 g~ of aluminium
chloride are portionwlse added, taking care that the
temperat~re of the mixture should not e~ceed 20 C. The
reaction mi~ture i9 then kept at 20 C for 4 hours? poured
~L2~Z~6
-- 22 --
onto 300 ml~ o~ ic.y water, extracted with dichloro-
ethane and the solvent i2 eliminated ~`rom the organic
~olvent pha~e in vacuo.
46.5 g. o~ (4-chloro-3 nitrophenyl) 4-methox,y-
phenyl qul~oxide are obtained.
Yield: 92 ~ o~ theoretical
Melting point: 1~4 to 126 C
~L~
(4-Chloro-3-nitrophenyl)-4-fluorophen,yl ~ulfoxide
To about 40 g. of crude, benzene- and thionyl
chlorid~-Yree 4-chloro-3-nitrobenzene ~ul~inyl chloride
prepared according to a~y v~riant o~ Example 3 90 ml. of
luorobenzene are added~ followed by the addition of
~3.6 g. o~ alumirium chloride under cooling. The reaction
mixture l~ then 9 tirred st 55 C for 5 hours and i9
further Ireated a9 deqcribed in ~xample 3, except that
the reaction mixture i~ not diluted with benzene.
42 g. of the de~ired compound are obtained~
Yield: 86 ,~o of theoretical
Meltin~ point: 84 to 85 C
Example 14
?( 4-Bromophenyl)-(4-chloro-4-nitrophenylJ ~ulfoxide
To about 40 g. of crude 4-chloro-3-nitrobenzene
~ulfinyl c~loride prepared according to any variant of
25 Example 3 100 ml. o~ bromobenzene are ~dded, Under
cooling 33~6 g~ of alumi~m chloride are added to the
.
~ Z6 2~6
- 23 -
mixture~ which iY -then stirred at 50 C for 3 hours
and i~ ~urther treated a~ de~cribed in ~xample 3,
except that benzene i9 added to the reaction mixture
after pouring onto water, and the e~ce~s of bromobenzene
i9 eliminated from the reaction mixture by distillation
at 6G to 70 C, under a pressure of 30 to 40 mmHg.
54.5 g~ o~ the deaired compound are obtained.
Yield: ~3 % of theoretical
Melting point: 138 to 140 C
10 ~
4-Chlorophenyl~ chloro~5-nitrophenyl) aulfoxide
36 g. (0.1625 moles) of 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzene
sulfinic acid prepflred according to ~xample 8 are converted
into 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzene ~ulfinyl chloride as
described in Example 3. It i9 then releaaed from benzene
and thionyl chloride, diluted with 100 ml. o~ chloro-
benzene, and to the mixtuxe 28 2 g. o~ alumimlm chloride
are added under ~tirring. The reaction mixture i9 then
~tirred at 55 C for 5 hour~ and i~ further t~eqted ~g
described i~ Example 3, exeept that the dilution with
benzene i9 carried out on~y after pouring onto waterO
44 g. of the de3ired compound are obtained.
~ield: 86 % of theoretical
Melting point: 142 to 144 C
_ 24 -
(4-E-tho~y-3-nitrophe~yl~-phe~yl ~ulfoxide
The procedure de~cribed in Ex~mple 7 i9 followed,
except that 4-etho~y-3-nitrobenzene ~ulfo~yl chloride
iq u~ed as a qtarting material and from this sodium
4-etho~y-3-nitro`oenzene ~ulfinate i9 prepared a~ deqcribed
in Example 1, with a yield of 70 ~,~ which ~9 then
treated further a3 deqcribed in Example 4,
The desired compound i9 obtained with a .yield of
86 %.
Melting ~oint: 119 to 121 C.
~:Z
1-(4-~romophe~yl)-4-(4-chloro-3-nitrophe~ylqulfinyl)-
benzene
The procedure described i~ Example 5 is followed,
except that in~tead of toluene 4-bromo-biphe~yl i~ used.
The de~ired compound i9 obtained with a yield of 80 %.
Melting poi~t: 1~3 to 175 C.
(4-Chloro-3-nitrophe~yl)-4-methylthiophenyl ~ulfoxide
The procedure described in E~ample 5 is followed~
e~cept that instead o~ toluene thioanisole is used.
1-(4-Nitrophe~yl) 4 (4-chloro-3-nitrophe~ylsulfi~yl)
benzene
The procedure described in Example 5 i9 followed~
~,2~ 6
25 --
except th~t toluene is replaced by 4-nitro-bipherLyl.
~he title compound i~ obtai.~ed wi-th a .yield of 50 %.
Melting point: 220 to 222 C.