Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
1~4345
Thi~ application relates to an "add-on" suspension ~y~tem
for supporting a cab on a vehicle, and more particularly to an
"add-on" air su~pen~ion system for supporting ~uch cab.
Yieldably mounting a body with respect to a vehicle frame
whereby latitude for relative movement therebetween has previous-
ly been provided. For example, Canadian Patent Number 250,562
patented June 9, 1925 by A.F. Masury provided a wholly non-
metallic connection and support interpo~ed between the frame and
body of a motor vehicle. The support comprised a housing carried
with one of such parts and having an opening in one side thereof.
A resilient arm was carried with the other of the parts and
entered the opening. Yielding non-metallic material wa~ carried
within the housing and engaged the end of the arm.
Canadian Patent Number 911,491 patented October 3, 1972 by
N.G. Pierce provided a cab suspension arrangement involving
hinging the cab at the rear, near the pitch nodal axis, rather
than at the front as in conventional practice with cab-over-
engine tractors. Isolation from chassis pitch was provided by
mounting the front of the cab on the frame with pneumatic,
hydraulic, or mechanical spring cushions having much lower spring
rates than conventional mounts. The design of the front cushions
provided a spring rate which resulted in a cab natural frequency
substantially lower than the natural chassis pitch frequency.
Furthermore, the cab pitch was said to be alleviated without
exceeding acceptable static deflection of the cab. The rear
mounts were constructed not only to act as pivots in fore-and-aft
1~6434S
pitch, but also to remain comparatively rigid in other direc-
tions, in order to provide cab stability. ~owever, the rear
mount~ were ~aid to have ~pring rates which furnished i~olation
from high frequency chassis vibration~, e.g., as noise, harsh-
ness, engine and drive line vibration~.
Canadian Patent Number 990,324 patented June 1, 1976 by W.
Zajichek provided a mean~ of resiliently mounting a platform
assembly on a tractor having cross-bars resiliently supported on
cross beams by detachable resilient mounting mean~. The cross
beams were fastened to the top portion of the transmission
housings and extended transversely to support the platform
assembly. The cross beams defined an inverted hat-shaped cross-
section to provide ~tiffness to the beams and a similar pair of
bars on the platform assembly were nestled in the beams providing
the platform support. The platform assembly included a subas-
sembly which included cross-bars which were fabricated to lon-
gitudinal connecting means to provide a rigid structure for
supporting the platform. The platform was formed with a plural-
ity of plates mounted on the platform subassembly and defined aplatform surface at the operator's ~tation. Resilient i~olators
were carried on the platform subassembly and resiliently sup-
ported the subas~embly by resilient surfaces bearing on the upper
and lower portion of the cross-bars of the subassembly. The
resilient isolators rested on the cross beam~ of the platform
support and threadedly-engaged a nut which was fabricated to the
~2643~S
cro~s beams, thereby providing a mean~ for quickly as~embling and
disa~Qembling the platform suba~sembly from the platform support.
The platform ~upport wa~ astened to the chas~is by means of a
plurality of bolt~ which were readily di~assembled from the
chaQsis.
Canadian Patent Number 1,060,925 patented August 21, 1979 by
A.R. Smith et al provided a system for the mounting of a cab
forming the personnel compartment of a tractor on a safety frame
of the vehicle. The safety frame served the function to protect
the occupants of the cab in the event the vehicle was over-
turned. The safety frame included a pair of front and rear,
upstanding leg members ~paced longitudinally, fore and aft, on
each side of the vehicle body. The passenger compartment was
enclosed by a cab which was supported within the safety frame on
the leg members thereof. The cab was secured to the leg members
by resilient support means located generally within a common
plane containing the centre of gravity of the cab and its operat-
or each of which included at least one layer of elastomeric
material secured between each of the leg members and the cab for
resiliently supporting the cab. The layer of elastomeric materi-
al was loaded only in shear by the cab. The elastomeric member
was interconnected with the attachment members in ~uch a manner
that the elastomeric member was loaded both in compression and
shear in supporting the cab while one of the attachment members
was supported from a given leg of the safety frame in a can-
tilevered manner.
~26434~;
Canadian Patent Number 1,148,582 patented June 21, 1983 by
J.K. Ochsner provided a tractor cab which was vibration i~olated
from the tractor cha~ by means of an adju~table mount sy~tem
S for eliminating low frequency vibrations introduced into the cab
by tire lug~. The adju~table mount system included an additional
mount having an adjustable capscrew which was accessiblè to the
operator. Loo~ening or tightening the ~crew changed the ~pring
rate and therefore the resonant frequency of the cab on its
mounts. The system allowed the cab resonant frequency to be
adjusted so that it differed from the frequency of the vibration
induced into the tractor chassi~ by the tire lug~ at the field-
working ~peed. The isolation effectivenes~ of the mount system
at higher frequencies was ~aid to remain relatively unchanged.
Canadian Patent Number 1,215,413 patented December 16, 1986
by R.G. Frey et al provided an operator's compartment that was
~upportèd for independent up and down movement independe~tly of
the up and down movement of the vehicle. A connecting assembly
supported the operator's compartment for independent upward and
downward movement of the operator'~ compartment of the vehicle
body portion so that the operator's compartment was free to move
independently of the mobile body a~ the mobile body moved.
Canadian Patent Number 1,219,017 patented March 10, 1987 by
R.C. Loy et al provided a ~tabilizing and isolation syYtem for
mounting an operator cab on a vehicle frame. Such system per-
mitted controlled vertical motion of the cab relative to the
frame
~26~345
s
while restraining relative rolling and pitching motion of the
cab. The system had mean~ di~posed between the underside of the
cab and the frame or re~iliently ~upporting the cab on the
frame. A stabilizer linkage assembly was connected to the frame
and the cab for re~training rolling and pitching motion of the
cab relative to the frame. The as~embly included resilient means
to permit relative vertical motion between the cab and the frame.
The stabilizer linkage assembly included an essentially trian-
gularly-shaped plate extending in a horizontal plane between the
cab and the frame. The apex of the plate was secured to the side
of the cab and the base of the plate was secured to the frame.
Motion limiting means was connected to the frame and the cab for
restraining vertical displacement of the cab relative to the
frame in the event the re~ilient support means and the stabilizer
linkage assembly should fail during a catastrophic event.
~ nited States Patent Number 3,415,535 patented December 10,
1968 by R. Gamard provided a suspension system for a vehicle
having a sprung portion and an unsprung portion, a ~uspension
sy~tem, and a control member responsive to variations in the
su~pension system. Elastic means, separate from the suspension
sy~tem proper, extended from the sprung portion to the unsprung
portion of the vehicle. A control linkage was connected at one
end to an intermediate point on the elastic means and at the
other end to the control member. The control member was adjusted
by movement of the control linkage. The elastic means thereby
~Z~ 4~i
damped vibration~ in the ~uspen~ion syRtem before transmittal to
the control member via the control linkage.
United State~ Patent Number 3,667,565 patented June 6, 1972
by A. Steiner et al provided a driver cab for commercial-type
vehicle~ which wa~ ~pring-supported with respect to the vehicle
superstructure. Such cab was spring-supported in its forward
area by an approximately hairpin-shaped bending ~pring. Adai-
tionally, two longitudinal guide members were provided on each
side for the guidance of the driver cab which were connected with
each other at one end thereof and whose other end was pivotably-
connected at the driver cab and at the vehicle frame, respective-
ly, whereby the torsion rod was rigidly clamped between two lower
or upper longitudinal guide memberR.
United States Patent Number 3,883,153 patented May 13, 1975
by B. Singh et al provided a suspension system between the wheel
mounts and chassis of a vehicle. The suspension system included
a strut bar between each wheel mount and the cha~sis of the
vehicle and means on the chassis which embraced each such strut
bar for grippingly-engaging the ~trut bar to prevent its motion
relative to the chassis whereby the wheel mounts became affixed
relative to the frame and chassis of the vehicle. The means for
grippingly-engaging each strut bar included a calliper-type
braking clamp for each of such b~rs and a hydraulic brake actuat-
ing system for operating such braking clamps.
~z643a~5
~ nited State~ Patent Number 3,953,040 patented April 27,1976 by D.H. Unrah provided a suspension system for a vehicle
which had a vehicle frame and an axle. The axle was su~pended
from the vehicle frame and wa~ capable of moving toward and away
from the vehicle frame. Further, the axle wa~ capable of rotat-
ing about an axis disposed generally-longitudinally of the
vehicle. Means were incorporated to sense the relative position
of the axle toward and away from the frame. In response to this
sensed relative position, the system included means to maintain
the axle and vehicle frame generally within a desired range of
relative positions. A cushioning, levelling and lockup sy~tem
for a suspended axle vehicle which had a levelling control
subsystem was provided which automatically corrected any changes
in the distance between a vehicle frame and axle by communicating
pressurized fluid from a pressure source to reposition fluid
suspension cylinder struts. A lockup subsystem was provided
which had a lockup valve which isolated spring cushioning devices
from the su~pen~ion struts, to reduce suspension cushioning. The
lockup subsy~tem permitted rotation about the longitudinal axis
of the vehicle or roll oscillation during lockup by interconnect-
ing the cylinders through a flow path across the lockup valve.
Ride cushioning could be selectively activated and deactivated.
~Z64345
United State~ Patent Number 4,079,986 patented March 21,
197~ by J. Redford provided a tie-down device for mating vehicle
part~ and in particular, to a mounting arrangement for non-
rigidly-connecting a cab enclo~ure and vehicle body. It included
a rigid, elongate plate fixedly-attached to the ba~e of the
enclosure, which extended around a marginal ~urface of the
vehicle body. A plurality of pins were attached to, and depended
perpendicularly from, the plate in a spaced-apart and generally-
aligned relationship, and were telescopically-inserted into
mating apertures positioned in the vehicle body for sliding
cooperation therewith. A flexible and resilient gasket was
positioned between the plate and the vehicle body marginal
8urface and received the pins through as~ociated apertures
positioned therein whereby the gasket resisted the transmission
of vibratory motion between the vehicle enclosure and the body.
A plurality of longitudinally-resilient fasteners were spaced-
apart along the body marginal surface and had one end thereof
connected with a sidewall portion of the vehicle enclosure and
the other end connected with the vehicle body. A resilient
member urged the ends of the fastener convergingly-together,
thereby pulling the plate toward the vehicle body marginal
surface and securely, yet yieldingly- connecting the cab enclo-
~ure with the vehicle body.
1~6434~;
United State~ Patent Number 4,23~,470 patented Nove~ber 25,
1980 by W. Krau~ provided a driver compartment with spring and
damping elements by which the driver compartment wa~ elastically-
supported on the rest of the vehicle ma~s. Located centrallybetween the driver compartment and the rest of the vehicle wa~ a
guide arrangement which guided the driver compartment in all its
motions relative to the rest of the vehicle and which consisted
of a vertical guide as well as two rotating guide~ couple wi~h
it. The pivot axes of the guide were in the longitudinal direct-
ion of the vehicle, but were transverse to it.
United States Patent Number 4,278,918 patented June 30, 1981
by B. Franco provided a tracked agricultural tractor in which the
frame of the driver's cab was mounted on the tractor body by a
suspension which included respective front and rear transverse
suspension structures. Each of such structure~ comprised two
struts formed by respective leaf springs upstanding from the
vehicle body disposed ~ubstantially in longitudinal planes when
relaxed, and interconnected by a cross member formed by a leaf
spring lying, when relaxed, in a plane which was perpendicular to
the planes of the two struts and parallel to the longitudinal
axis of the vehicle. Shock absorber means were provided to damp
rolling and pitching oscillations of the cab, relative to the
vehicle body, due to the flexural resilience of the suspension
structures.
126~345
United States Patent Number 4,390,187 patented June 28, 1983
by K. Maeda provided a vehicle levelling ~y~tem compri~ing a
compression mean~ for producing pres~urized air, mean~ for
accumulating the pre~urized air produced by the compres~ion
means, pneumatic ~pring means dispo~ed between a chas~is and a
vehicle axle for ~etting the di~tance ~etween the cha~sis and the
vehicle axle by the pressurized air supplied thereto, and means
for controlling the ~upply of the pres~urized air ~o that the
pre~surized air was supplied from the compres~ion means only to
the pneumatic spring means after a predetermined period of time
had elapsed from the start of the air ~upply from the accumulat-
ing means the pressurized air to the pneumatic spring means until
the predetermined distance wa~ set between the chassis and the
vehicle axis.
United States Patent Number 4,418,985 patented December 6,
1983 by L. Muncke et al provided a support unit for the cab of a
utilitarian vehicle having a separate cab and cha~sis. The
support unit included a hydraulic piston and cylinder, including
a compression spring, connected between the cab and the chassis.
Fixed to the hydraulic support cylinder unit was a directional
control valve which selectively directed and drained pres~urized
hydraulic fluid to or from the hydraulic support cylinder unit.
The directional control valve wa~ journalled to a lever pivoted
to the cab. Also journalled to the lever was an elastically-
centred rod and an ab~orber element having an inela~tically-
adjustàble length. Dynamic fluctuations of the distance between
~2~;~345
the chassis and cab were oppo~ed by the hydraulic ~upport cylind-
er unit a~ actuated by the directional control valve. Static
fluctuation~ in the distance between the chassis and the cab were
accommodated by the hydraulic ~upport cylinder unit together with
the absorber element.
~ nited States Patent Number 4,638,878 patented January 27,
1987 by ~.J. Komp provided a device for cu hioned support of a
driver~ 8 cab on the chassis of a tractor. The device included a
transversal swinging arm mounted on the cha~sis in the rear area
of the cab, the transversal arm being pivoted around a lateral
axis and, at its front end, acting through a ball joint on the
cab at or near its centre of gravity. The device al~o included
mounting points in the form of damping ~pring elements. With
such a device, the cab was secured against rotation about the
vertical axis and was also buffered again~t exce~sive pitching
motion.
While all of the above patents are directed, in one way or
another, to mounting a cab on a vehicle, none are directed to the
essence of the pre~ent invention, namely the provi~ion of an
"add-on" su~pension unit for the mounting of a cab on a truck.
Thus, as noted above, structure has previously been provided
for:
~ a) overcoming for-and-aft pilot of highway tractor~;
126434~i
12
tb) providing for a convenient mean~ of a~sembling a
platform support on the vehicle chassis and a con-
venient mean~ of mounting a platform a~embly through
re~ilient means on the platform support;
(c) overcoming vibration of the cab and other part~ of the
vehicle body, and the attendant resulting high noi~e
level;
(d) providing an adjustable mount system for a tractor cab
which reduces or eliminated cab resonance~ at the
operating speed without noticeable reduction in noi~e
and vibration isolation effectiveness at higher fre-
quencies;
(e) increasing the degree of isolation of the cab from the
frame 80 that vibration~ and impacts caused by vibrat-
ing bodies used on the vehicle or transmitted from the
exterior of the vehicle, are not applied to the oper-
ator's cab thereby lowering the noise level in the cab
and concomitantly increa ing the comfort level of the
operator;
(f) providing a relatively soft, yet stable, suspension
system 80 that the need to isolate the engine from the
vehicle frame is either reduced or eliminated;
(g) minimizing the vibration inherent to the unsprung
portion which may be transmitted to the apparatus;
~2~;43~
13
(h) providing a driver cab of commercial-type~ of motor
vehicle~ which i~ relatively ~table in curve drive~
notwithstanding a relatively soft ~pring-~upport of the
driver cab, and which avoid~ exce~ive cro~-titling
during curve drive~ without large expenditure~;
(i) providing a ~pring ~uppressor for preventing dipping of
the front end of a vehicle during braking action
thereof;
~j) providing a cushioning, levelling lockup ~ystem in a
~uspenaed axle vehicle which provides for continuous
load levelling and selective cushioning of road shocks,
and which permit~ dampened roll oscillation while the
cushioning capability i~ deactivated;
~k) providing a mounting arrangement for securely and
yieldingly-connecting a vehicle cab enclo~ure with a
vehicle body;
(l) providing a utility vehicle having a driver compartment
which exhibits a more suitable and controlled vibration
and ~hock behaviour;
~m) providing a re~ilient ~uspension for the cab of a
vehicle which en~ures sufficient driver comfort, when
the tractor is used on rough ground, to permit the
forward speed of the tractor to be increased beyond
that tolerated with previous cab Quspen~ion~;
~n) providing a ~upport unit for a cab of a vehicle in
which the relative motions between cha~ and cab,
~2643AS
14
i.e., the vibrations and rocking motions, are largely
preVentea 80 that the cab i9 thereby kept essentially
free of motion;
and ~o) providing a device for a tractor cab which allows
sufficient freedom of movement of the entire cab,
particularly in the vertical direction, and, at the
same time, in the pitching and rolling direction to
reduce vibratory stresses for the driver under all
operational conditions.
On the other hand, the present invention has for its main
object the provision of an "add-on" suspension unit for ~ecuring
to the frame of the truck to provide for an air ~uspension of a
cab to such truck.
lS It is an object of another aspect of this invention to
provide such an "add-on" suspension unit which al~o may provide a
resiliently-mounted assembly to a cab on a truck.
It is an object of yet another aspect of this invention to
provide such an "add-on" suspension unit which may al~o provide
means for controlling the amplitude of vertical movement and the
resiliency of the cab assembly support.
It is an object of still another aspect of this invention to
provide such an "add-on" suspension unit which also may provide a
cross-beam mounted on the vehicle chassis for supporting a cab
assembly with means for supporting such assembly on the cross-
beams.
12643~S
It is an object of a general a~pect of this invention to
provide ~uch an "add-on" suspen~ion unit which i5 economical to
manufacture, efficient in u~e, capable of long operating life,
S and particularly adaptea for the proposed use.
By one broad a~pect of this invention a support for a cab
for a truck i8 provided comprising: a plurality of cross-beams
supported between the longitudinal frame members of the truck;
means connected between each lateral frame member of the truck
and each respective lateral edge of a transverse platform sup-
porting the cab, such means including damping means; pneumatic
means dispo~ed between the cross-beamæ and the transverse plat-
form inboard of the frame members; stabili2er valve means for
supplying air to, and withdrawing air from, the pneumatic means;
and control means sensing the vertical position of the platform
to maintain the elevation of the platform within preset upper and
lower limit positions.
By another a~pect of this invention a su~pension is provided
for a cab of a vehicle, the cab being springingly-supported by
shock absorbing means, the suspension comprising a longitudinal-
ly-extending sub-frame disposed between the cab and a main frame
of the vehicle, the sub-frame including: transverse means con-
necting two longitudinally-extending lateral sub-frame members;
fluid-actuated levelling means disposed between the transverse
means and the support for such cab; means for controlling the
ingress and the egress of fluid to the fluid-actuated levelling
lZ`6434~i
16
means; and means interposed between the lateral mean~ and the cab
support mean~ for actuating the controlling means.
In such suspension, the cab is preferably supported on a
platform, the platform extending longitudinally between at least
two longitudinally-spaced-apart, transversely-extending frame
members, the frame members supporting an hydraulic shock absorber
laterally-disposed between the transver~e frame members and the
main longitudinally-extending frame members of the vehicle.
The hydraulic shock ab~orber preferably is mounted with its rod
end connected to a downwardly-depending ear of the tran~versely-
extending frame member and with its rod end connected to a
laterally-extending ear of the longitudinally-extending main
frame member of the vehicle.
The fluid-actuated levelling means preferably comprises a
pneumatic balloon, with the control means preferably being a
pneumatic stabilizer valve, and with the interposed means prefer-
ably being a vertically-movable rod, whose lower end is opera-
tively-connected to a three-way pneumatic valve.
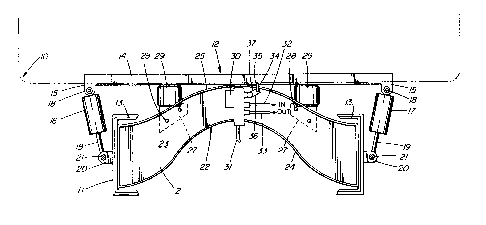
In the accompanying drawing,
the single Figure shows a transverse cross-section through a
vehicle fitted with the "add-on~ cab suspension device of one
embodiment of this invention.
As seen in the drawing, a conventional cab 10 shown in
dotted lines, was previously mounted, in a manner known to those
skilled in the art, to the frame 11 of a truck. The "add-on~ air
~264345
17
~uspension unit 12 interpo~ea between cab 10 and frame 11 will
now be de~cribed.
The "add-on" air su~pension unit 12 includes a longitudi-
nally-extending channel-shaped sub-frame 13 adapted to be dis-
posed within, and secured to, longitudinally-extending main rame
11 of the truck. The cab 10 is secured to at least two tran~-
verse, channel-shaped members, only one of which, 14, is shown.
The channel-shaped transverse member 14 are each provided with
depending lateral ears 15 to which a hydraulic choke 16, of
conventional design is mounted. The cylinder end 17 of hydraulic
choke 16 is secured to ear 15 at pivot pin 18, while rod end 19
of hydraulic choke 16 is secured to laterally-outwardly-extending
ear 20, which is secured to main longitudinally-extending frame
11, at pivot pin 21.
Situated transverse~y between channel-shaped longitudinally-
extending sub-frame members 14 are cros~-member a~emblies, only
one of which, 22, being shown. Cross-member assembly 22 includes
a pair of transversely-spaced-apart, longitudinally-extending
plates, indicated generally as 23, the bottom face of which are
connected by a lower curved cros~-panel 24, the top faces of
which are connected by an upper curved panel 25. Upper curved
panel 25 and lower curved panel 24 are interconnected by a
transverse plate 26. Secured to Yymmetrically-situated areas of
the transverse plate on either side of the central longitudinal
axis is a pair of mounting plates 27, secured to transver~e plate
12643~5
18
26 by bolt~ 28. Mounting plate~ 27 each ~upport a pneumatic bal-
loon 29, secured between mounting plate 27 and the channel-shap~d
cross-member 14. Pneumatic balloons 29 are supplied with air
under pre~sure by mean~ of stabilizer valve 30. Stabilizer valve
30 includes a main line 31, and inlet line 32 and outlet line 33
to and from pneumatic balloon 29. The operation of the ~tabiliz-
er valve 30 is controlled by means of a sensitive control rod 34,
whose upper end 35 contacts the bottom ~urface of cross-member 14
and whose bottom end 36 is connected to a control valve lever 37.
In operation, the cab 10 is suspended by means of hydraulic
chokes 16 and pneumatic balloons 29. If the cab 10 should move
horizontally either upwardly or downwardly, the movement is
sensed by sensitive control rod 34. This then controls stabili-
zer valve 30, either to cause air under pressure to escape fromhydraulic balloons 29 ~thereby to lower cab 10), or to cause air
~ t~
under pressure to be forced op~r~the hydraulic balloon~ 29
(thereby to raise cab 10).
In this way, the cab 10 is maintained at a constant vertical
level regardless of the vertical vibrations to which the cab 10
may be subjected.