Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~ 7 ~
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a rotary threaded fastener of
the self-drilling and threading type, and more particularly to a
fastener of that type which is manufactured by a pair of forging
dies.
Various threaded fasteners of the self-drilling and thread
forming type are known in the art, some of which are particularly
adopted for manufacture by a milling process, while others are
manufactured by a forging process which employs a pair of matched
dies. A typical example of the type oF drilling and thread forming
Fastener which is preferably formed by the forging process is shown
in U.S. Patent No. 3395603, issued August 6, 1968 to E.J. Skierski
and assigned to khe assi~nee of the present invention. Fasteners
manufactured in accorclance with the teachings of this patent have
met with wide acceptance as they provide a fastener which is simple
to use, requiring no pre-drilling of the structure to which it is
assembled, and fasteners of this type have proven to be easy to
manufacture by mass production methods.
Recently, however, there has been a demand for self-drilling
fasteners to be manufactured from high carbon steel, stainless
steel, or metallic alloys which are of a hardness exceeding those of
normal requirements. In some instances, it has been found that the
~2~8~
forging dies employed to manufacture a drill point on these
fasteners is susceptible to premature breakage, when these harder
materials are employed. It is considered that the stresses inherent
in present point forging die configurations trap the harder material
of the headed blank being worked on during the point forging
operation, and that the entrapment of the blank material and its
subsequent cold flow generates excessive stresses in the point
forging die, causing in some instances, a premature point forging
die breakage.
With the wide use of the self-drilllng and thread forming
fasteners there has also been a requirement for the reduction in
drilling time of the fastener. While existing point configurations
which contain two flutes provide a satisfactory drill time in most
applications, it is considered tilat they do not have sufficient
clearance for chip flow to remove drilled material from the
resultant hole, and thus to reduce drilling time. This occurs
particularly when multi-layered assemblies of similar and dissimilar
materials are operated upon . Such failure to remove drilled
material can result in binding between the point and drilled hole
surface causing excessive heat generation and resultant slower drill
times.
The present invention therefore has as an object to provide a
drilling and thread forming fastener of the type manufactured by a
die forging process, which is effective to facilitate an increase in
point forging die life.
Another object of the present invention is to provide a
drilling and thread for~ling fastener wherein a greater clearance for
escape of drilling chips is provided in the resultant drilled hole,
during the dril1ing process.
Another object of the present invention is to provide a
drilling and thread forming fastener which is susceptible to a
reduction in drilling time over those drilling and thread fornning
fasteners of the prior art.
~27~8~
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The aforementioned objects and other objectives which will
become apparent as the description proceeds are accomplished by
providing a drilling and thread forming fastener having a threaded
shank and a pilot end wherein the pilot end has a transverse major
axis and a transverse minor axis intersecting at the center line of
the fastener. A pair of flutes extending longitudinally over the
pilot end serve to form a pair of cutting surfaces, in cross-section
defining the major axis. A pair of lands concentric with the center
line of the shank are each formecl of an arcuate surface extending
outwardly to define the minor axis at its radial extent on any cross
section of the pilot end. A substantially wedged shaped cuttiny tip
is formed at the ternlinal portion of the pilot end. The minor axis
increases in a linear progression from adjacent the cutting tip to a
point remote from the cutting tip to thereby form an angular portion
of said pilot end which longitudinal outer surface defines an angle
with the fastener center line.
In a more detailed sense, the cutting surfaces are formed
substantially parallel to one another over a greater portion of the
pilot end angular portion.
h pair of mating dies are also provided for forming the above
described structure in a forged pointing process, the inner surface
~;~75~
of the dies substantially conforming to the confi~uration set forth
above.
~275~
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Reference is made to the accompanying drawing in which there is
shown an illustrative embodiment of the invention from which its
novel features and advantages will be apparent wherein
FIG. 1 is a fragmentary elevational view showing a portion of a
drilling and thread forming fastener constructed in accordance with
the teachings of the subject invention;
FIG. 2 is an elevational view showing the fastener portion of
FIG. 1 rotated through 90;
FIG. 3 is an encl view showing further details of the fastener
of FTGS. 1 and 2;
FlG. 4 is a sectional view taken along the lines IV-IV of FIG.
3 showing details of the outer peripheral configuration of the
fastener of FIGS. 1 though 3 at that section;
FIG. 5 is a sectional view taken along the lines V-V of FIG. 3
showing details of the outer peripheral configuration at that
section;
FIG. 6 is a sectional view taken along the lines IV-IV of FIG.
3 shohing details of the outer peripheral configuration of the
fastener of FIGS. 1 through 3 at that section,
~2~751 341)
FIG. 7 is an elevational view similar to FIG. 2 showing the
entire fastener of FIGS. 1 through 3 during the drilling operation;
FIG. 8 is a fragmentary elevational view similar to FIG. 1
showing the fastener of FIG. 7 rotated through 90 during the
drilling operation;
FIG. 9 is a fragmentary elevational view showing an alternate
embodiment of the structure of FIGS. 7 and 8; and
FIG. 10 is a perspective view showing one of a pair of dies
which comprise the d;e set for manufacture of the fastener shown in
FIGS. 1 through 9.
~275~
DESCRIPTION OF A PREFERRED EMBODlMENT
Referring now to the drawings, and in particular to Figures I
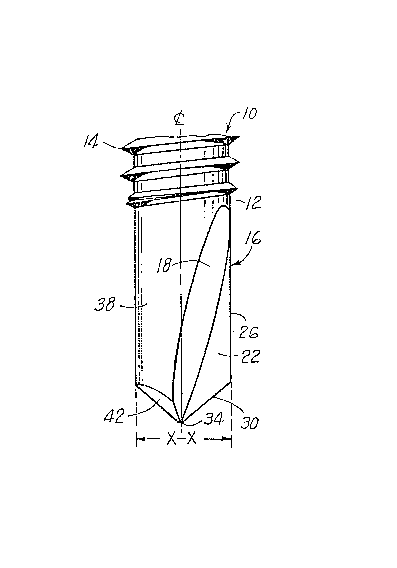
through 3, there is shown a dril1ing and threaded forming fastener
10 having a shank 12 bearing the continuous thread 14 and a pilot
end 16. The fastener 10 is substantially symmetrical about the
center line oF the shank 12 and has a transverse major axis XX and a
transverse minor axis YY intersecting at the center line. A pair of
flutes 18 and 20 are formed in the pilot end 16 and extend
longitudinally over the length of the pilot end to form a pa-,r of
cutting surfaces 22, 24 extending along the major ax;s and in
general defining the extent of the major axis of the fastener at any
section thereof.
Each of the cutting surfaces 22 and 24 defines a cutting edge
26, 28 running substantially parallel to the center line of the
fastener and terminating in an angular portion 30, 32. Each oF the
angular portions 30 and 32 of the cutting edge terminates at a wedge
shaped cutting tip 34. The cutting tip is disposed for preliminary
entry into the metal surface to provide a lead for the cutting edges
30, 32, 26 and 28.
A pair of arcuate surfaces 36 and 38 extend along the length of
the pilot end and terminate at an angular surface 40 and 42,
~L~7 5 ~34L~9
respectively, which extend toward the center line of the fastener to
join the cutting tip 34.
Referring now to Figures 4 through 6 it will be noted that as
the cross section of the pilot end 16 progresses from the cutting
tip 34 to the threaded shank 12, the major axis remains
substantially constant while the minor axis increases, approaching
the length of the major axis but remaining less throughout the
length of the pilot end.
The taper of the pilot end 16 is considered to extend from the
minimum dinlension M as shown in Figures 2 and 3, to a maximum
dimension W which is slightly less than the dimension of the X-X
axis at that point. The minimum dimension M is in the range of 20%
to 50, of the dimension W, and the taper generally extends over a
length L which is in the range between 75% to 95% oF the pilot end
16.
In each of the sections shown in Figures 4 through 6, it can be
seen that each of the arcuate surfaces 36, 38 is connected to a
cutting surface 26 or 28 by a concave surface 44, 46 the concave
surface forming the base of the flute 18 or 20 over the length of
the pilot end 16.
Referring to Figures 7 and 8, a fastener 10 of the type
described with reference to Figures 1 through 6 is shown having a
hex head ~0 for driving the fastener. The fastener 10 is shown in
~L2~5~
its drilling position having progressed through the workpiece W
forming an opening H therein by rotation during the yet incomplete
drilling operation. As will be noted, when the fastener 10 rotates
to its position shown in Figure 7 there is a substantial space
formed between the fastener and the opening H providing for material
to be moved into the flutes 18 and 20 and subsequently removed from
the opening during the operation. The drilling itself takes place
by the action of the cutting edges 26, 28 and 30, 32 of the fastener
10 as shown positioned in Figllre 8.
Referring to Figure 9, there is a alternate embodiment of the
invention similar to that shown in Figures 1 through 8. The
Fastener 10a shown in Figure 9 is provided with threads 14a which
extend down onto the pilot end 16a which is otherwise constructed in
accordance with ~he description of Figures 1 through 8, above.
In Figure 10, there is shown a die which is constructed to form
the fastener o~ Figures 1 through 9 by a Forging process. The die
48 is one of a pair of dies, or a die set, similarly constructed,
which when forced together under high pressure are capable of
forming the pilot end 16 of the fastener 10.
With the above described fastener, the objective of the
invention have been achieved since the resultant shape of the point
forging dies which are employed to form the elliptical cross section
forces the excess headed blank material to flow more naturally and
~ 7 ~i~3~
easily from the point forging die contour, thereby reducing the
resultant bursting stresses that accompany the compaction of
material during the forging operation. Also, by forming the cutting
surfaces 22 and 24 such that they meet the arcuate surfaces 36 and
38 of the lands at the concave surfaces 44 and 46, there are no
sharp edges provided in the die structure to cause die failure. The
elliptical reduction in cross sectional area also allows for a
greater thickness of material in the forging dies at the point of
greatest pressure, which strengthens the forging die and thus
reduces breakaye. As also is evident from Figures 7 and 8 of the
drawing, the new configuration achieves nearly 360 of clearance for
chip and material renloval, that is, since the end points of the
major axis of the elliptical cross section and the cutting edge of
the point are the only points in contact with the material being
drilled there is a reduced possibility of drilled material binding
the drill point with the resultant slow down of drilling.
The fastener 10 has therefore provided an improvement over
drilling and thread forming fasteners of the forged type which are
known in the prior art and the configuration has proven to be
advantageous in those applications where high carbon steels and
stainless steel are employed in the manufacture of this type of
fastener.