Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~2~7S86~
The present invention relates to a bogie for rail~ay
vehicles of the tilting body type.
It is known that the railroads, in curve, show a cer-
tain degree of superelevation of the track, ~or reducing the
effect of the centrifugal acceleration to which the vehicles are
subject. Such a superelevation allows the curves to be faced at
higher speeds. E'or stability reasons, the superelevation values
are limited by international regulations.
For ~urther increasing the speed of the vehicles in the
curves, without submitting the passengers to unacceptable values
of the centrifugal acceleration, the principle is known of ren-
dering variable the position of the body of the railway vehicle,
by suitably tilting the same relatively to the bogles towards the
inside of the curve, by means of suitable mechanical devices. In
this way, to the track superelevatlon angle, the angle is added
of body tilting, compensating in the curve totally or partly on
the passengers the greater accelerations produced by the higher
speed. The systems known suffer however from the drawback that
they do not allow bodies to be used of traditional structure for
tilting body vehicles, and hence require special bogies and bod-
ies to be built.
The present invention provides a railway bogie, either
a driving or idler bogie, for use in passenger cars and also in
locomotives, adapted to suitably tilt the body of the vehicle in
relation to the curvature radius of the track, at the highest
reachable speed, as well as to ths general conditions of track
equipment, said bogies being capable of using, without structural
changes, the existing vehicle bodies, or new bodies of tradi-
tional design, by replacing the existing bogies.
According to the present invention there is provided a
bogie for railway vehicles of the tilting body type comprising a
tlltable transverse beam interposed between the bogie frame and
-- 1 --
, ~1 ~
~ " .
~ ~ 7 ~
the body, and a footstep bearing coupling the tiltable beam with
the bogie frame or the body, the footstep bearing including con-
necting means in the form of a pivot pin extending substantially
vertically through the components of the footstep bearing, cou-
pling them together and allowing relative rotation of the partscoupled by the footstep bearing about the pivot axis and the
footstep bearing also being constructed to allow relatlve rocklng
movement of the parts coupled by the bearing about a horizontal
longitudinal axis.
A bogie according to the invention offers therefore,
compared to conventional bogies, many advantages, such as e.g.
the structural simpleness, the quickness of existing vehicles
transformation, in that it does not require long times and great
investments for new vehicles, and consequently strong reduction
of the starting investment, and of the avallability delays of the
tilting body vehicles to be put into service.
In one embodiment of the present invention the footstep
bearing includes a part-spherical hollow part which is movable
between mating parts which are fastened to one another by the
pivot pin, and the part-spherical part has a central opening
around the pivot pin which permits said rocklng movement.
In another embodiment of the present invention the
footstep bearing includes two sets of bearing parts held together
by the pivot pin, each set having mating cylindrical surfaces
which are relatively rotatable about the respective common axes
of the cylindrical surfaces, one of the common axes coinciding
with that of the pivot pin, the other being orthogonal to it.
Sultably the bogle has hydraulic cylinders mounted between the
tiltable beam and the bogi~ frame or the body fsr effecting the
sa1d relative rocking movement. Desirably the pistons of the
hydraulic cylinders engage the part to be moved through thrust
bearings which reduce horizontal stresses during the rotation of
the bogie relative to the body.
~Z75~60
The bogie of the present invention, can have e.g. its
frame of the welded type, consisting of two side members, and of
one or more transverse beams, they too being welded. That
notwithstanding, such elements of the structure of the frame
could be cast as well, instead of being welded.
The bogie can be provided with primary and seconda-
- 7.a -
.., "_ . .
ry suspen3ions, which may be of any presently u3ed
types, and are not bound to the specific struct~Are wnich
rea~izes the variable position of tilting body relativ~
ly to the bogies according to the present inventlon.
The bo~ie can be provided with a tilting tranaJerse
beam positioned on the upper side, or on the lo~er side
relatively to the springs of the secondary suspension.
The bogie may be integrated by side suspension3 of
the pneumatic cylinder type, or of the pneumatic-h~dr-
aulic cylinder type, whose function is of keeping the
centre of the footstep bearing at the centre of the
frame of the bogie during the running in the curve, e-
quilibrating the centrifugal force. ~he tilting of the
body takes place around an axis lyin~ on the longitudin
al sy~etry plane. In this way, the tilting of the body
is obtained, which produced the partial or total compen
sation of the centrifugal acceleration in curve.
Further details of the invention will be clearer
from the following disclosure, which relates to some
exemplifying ernbodimen~s of tne lnvention, shown in the
drawings, in which:
Fig. 1 is a transversal view, partly in sectiont of
a bo~ie according to the invention;
Fig 2 ls a view si~llar to that of fig. 1~ but with
~5 a different suspension system;
Figs 3 and 4 are transveraal views, partly in sec
tion, of another prac-tlcal embodiment of the invention,
wi-th t-~o different suspension systems;
Fi~. 5 is a -top view of a bogie accordin~ to the
invention;
Fig. 6 ~hows a fur-ther prac-tical ernboditt~ell-t of a
5~6~
boDie, in a partly in section tran3versal vi w.
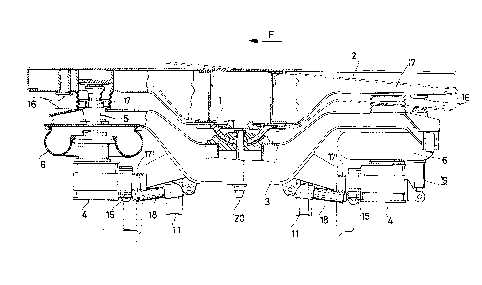
The spherical footstep bearir.g 1 allo~s the rota-
tion of the tilting beam 3 and of the frame of the bogiP
4 in ~ll directions reiatively to the body 2, i.e., both
around a vertical axis and around a horizontal axi~.
The spherical footstep bearing 1 is provided with the
vertical safety pivot 20 and with two pairs of facir~g
supports 21 and 22 (fig. 5). ~he elements 21 are solid
with the upper co~ponent of the footstep bearing, the
elements 22 with the lower component of the footstep
bearing. ~he purpose of said support~ is of suitably
limiting -the tilting angle of the footstep bearing 1 in
the longitudinal vertical plane.
The present invention has all the notable advan-
tages described above, consequent to the simpleness of-the system, owlng to the fact that the characteristic
described above of the spherical footstep bearing is
also used -to the purpose of obtaining the angular move
ment of the body, by varying its position relatively to
the tilting beam 3 and to -the fra~e of the bogie 4 in
-the tran~versal vertical plane, as shown by dotted lines.
As it can be seen in figs. 1 and 2, the footstep
bearing comprises a substantially seT~is~herical hollow
part, rnovable between two conjugated parts held together
and respec-tively fastened to the oscillating transverse
beam 3 and to the body 2. The hollow semispherical part
has such an opening, as to allow it to ro-tate relatively
to the conjugated parts ~lso around a horizontal axis.
The drive of the tllting o~ the body 2 rela-tively
to the osoi]la-ting -transverse beam 3 in function of the
centrifugal force F is carried out by Illean~ of hydralll
~LZ75~36~1
5.
ic cylinders 5 of simple type, or of telescopic type.
The cylinders 5 are protected by suitable protecting
covers 17.
The basis of each cylinder 5 i3 fastened inside
suitable cavity provided in the oscillating beam 3,
whilst the upper end of the relevant piston i3 hovsed
and leant, with the interposition of a thrust bearing
of the ball bearing type or o~ another type, inside a
co.rresponding cavity provided in the body-, 30 as to re-
duce the space occupied by them.
Cylinders 15 of pneumatic type or of pneurn~tic-
hydraulic type are additionally foreseen1 for the drive
of the ].ateral active suspension; -they are installed
between the oscillating transverse beam 3 and the side
members 4 of the frame of the bogie and their pistons
are protected by protecting covers 17'.
Stop pads 16 po~itioned between the oscillating
transverse beam 3 snd the body 2 have the ~unction of
mechanically li~i-ting the rotation of the body 2 rela-
tively to the oscil].ating transverse beam 3 to the maximum allo~able limitt at -the same time avoiding possible
dangerous irnpact stresses on -the cylinders 5.
Said stop pads 16 are provided with anti~rictlon
contact surfaces for a rigid or elasti2ized contact,
as well as with a device for the adjustment, a~ter the
assemblin~, in a preci.se way, of the maxiT~.um value of
the rotation angle of -the body in its tilting condition.
The stop pads 16 can be o~ fixed type~ or of ~lovable
type. The stop pads of the movable type are in -their
~0 resting condition during the normal operating of the
tilt~.ng systeTn, thus ac-ting, in -that sense~ oniy as
~Z758~0
6.
stroke end pads. Under their operating conditi~n, they
extend out of their seat, beina hydraulically and/or
mechanically actuated, going along a same stroke, to the
purpose of acting as a safety device, which brings back
the body 2 to itsver-tic~l position, and blocks it in said
position, should the tilting system be excluded. The
movable pads 16 can also be used as emergency device,
totally replacing the drive cylinders 5, for actuating
the tilting positioning.
Figs. 1 and 2 differ to each other only in that in
fig. 1 the secondary suspension of the bogie is realiz-
ed by means of pneumatic springs 6, whilst in fig. 2
it is realized by means of traditional steel helical
springs 6!. In both cases, the secondary suspension is
integrated by lateral 18 and ve~al 19 side hydraulic
dampeners, positioned between the transverse beam 3 and
the side members 4 of the frame of the bogie.
In practical embodiment shown in Figs. 3 and 4, the
function of rotating the bogie relatively to the body
in the horizontal plane is effected by the lower cylin
drical footstep bearing 7, whilst the function of rotat
ing the body ~ in the transversal ~ertical plane is ef
fected only by the upper footstep bearing 8 of cylindric
al sector shape~ The front and rear ends, in longitudinal
sense3of -the intermediate element 9 of the footstep
bearing are formed by vertical walls suitable to bear
the lGngitudinal pushes which are shown between the bod
y 2 and the bo~ie ~ 4.
Basically, the foo-tstep bearing comprises in this
case an intermediate part 9 linked with a cylindrical
~Z75~36~
geometrical coupling to the footstep bearing parts re~
pec-tively fixed to the body and to the frarrle, the axes
of the cylindrical parts being orthogonal to each other.
Ihe parts are assembled together by the vertical pivot
In fig. 5 8 type of bogie is shown, for exemplify-
ing purposes~ in its basic components, having æ struc-
ture according to the invention.
~he bogie is formed by the axles 10, by the disc
brakes 11, by the brake cylinders 12, while the frame
of the bogie is formed by: end transverse beams 13, in
termediate transverse beams 14, side members 4, as well
as by the oscillating transverse beam 3, drive hydraul-
ic cylinders 5 and spherical footstep bearing , e.g.
of the type shown in figs. 1 and 2
In fig. 6 -the transversal section is sho-~nt for ex
emplifying purposes, of another possible type of bogie
according to the invention. This allows the advantageous
characteristics according to the invention to be evidenc
ed, which, always thanks to i-ts characteristics of struc
tural simpleness9 can be used in a simple way on any
types of bogie provided wi-th the tilting transverse
beam 3, transforming the bogie from a normal type bogie
to a bogie of the type for tilting body systems.
~he bogie shown in fig. 6 differs ~rom that sho~
in figs~ 1 - 5, in tnat the -tilting tran~verse beam~is
Tnounted beneath the s-prings 6 of the pneumatic type
shovjn in the figure, or of the cylindrical helical
sL!ring type.
In this ~igurel the body 2 i3 supported by the tilt
ing trarlsverse beam 3 by the interposi-tion of the 3pr;ng3
~LZ758~;~
8.
6, ~nd the same transverse beam 3 leans on the fr~e
o-f the bogie 4 with the interposition of the footstep
bearing of compound type 7, 8, 9 as shown in fig. 3 or
4, or with the interposition of the footstep bearin~
of type 1 shown in figs. l or 2.
The tilting of the frame 4 of the bogie in curve,
in the horizontal plane, takes place relatively to the
tilting transverse beam 3 and hence relatively to ~he
body 2, as these latter do not rotate relatlvely to
each other in curve in this plane.
The tilting of the body 2 and of the tilting tr~ns
verse 3 in the transvers~l vertical plane ~akes place
alwzys by means of the footstep bearing of compound type
7, 8, 9 or by Tneans of the footstep bearing of simple
type 1, rel2tively to the frame of the bogie 4.
The drive hydraulic cylinders 5 confer to the tilt
ing tr~nsverse beam 3 and hence to the body 2 the an-
gular transversal tilting positioning motion.
The basis of the cylinders 5 is fastened e.g. inside
the side mernbers 4, while the upper end of relevant pis
tons i9 leant inside a cavity provided inside the trans
verse beam 3 with the interposition of a thrust bear
ing of the ball bearing type~ or of another type. The
bearing is used to the purpose of making slide freely
the upper end of the relevant piston relatively to the
-traII~verse beam 3 during the sliding movement which
takes place when -the frame 4 of -the bogie rotates when
entering a cl~rve.
The bogie sho~Yn in fig. 6 is elluipped wi-th ~ll the
fundarr;ental elernents typical for a railway bogie, al~
ready sho~in in fig. 5.
P~9S~6~
~ s it can be easily seen from wnat disclosed, a
railway bogie of the tilting type, provided with the
system according to the inYention 7 i3 suitable to allo~
during the running in a curve, with co~plete 3afety,
higher speeds than those which can be obtained -~ith th~
traditional bogies, partly or totally compensating the
effect of the centrifugal acceleration on the passer.-
gers.
Moreover, with a bogie according to the inventi3n,
the structure of the body may remain the traditional
structure, so that a bogie according to the invention
is also suitable to be applied to already existing rail
way vehicles~ as a replacement for the traditional bo-
gies, with notable econornic advantages.
~he bogie disclosed, in addition to performing all
the existing functions between the body and the bogie,
i.e. 9 of rotation in all planes and in all directions,
included the rotation of the body in the vertical trans
versal plane for obtaining the tilting positioning ac-
tion, performs also the function of transmitting all
dyr.amic and static forces produced by the weights, and
all the horizontal dynamic7 longitudinal and transvers
al forces produced by the traction, by the braking and
by the centrifugal force