Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~82~2
BUILDING VENTILATION SYSTEM WITH AIR INLET FLAP CONTROL
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
This invention relates to a building ventilation
systertl and p~rticularly to an inlet flap arrangement which
automatically controls air movement through an inlet opening in
dependence upon a reduction in pressure within the interior of
the building.
In various buildings with particular attention
to animal husbandry barns, it is important to maintain air
quality at required levels to ensure proper health and survival
of the animals contained.
For maximum efficiency it is often required to
provide maximum density of animals within the barn and hence
the enkry of fresh air into the building is essential to
maintain the atmosphere within the building at proper levels so
as to reduce the concentrations particularly o~ water vapour
and ammonia. By proper introduction of fresh air, the health
of the livestock and the operator is protected.
In many cases air control is provided by air
extraction fans which pull contaminated air from the interior
of the building for direct extraction to the exterior. It is
then necessary to replace the extracted air with incoming air.
This can of course be achieved merely by providing suitable
~;~8;~ 2
-- 2
openings which allow air to flow directly into the interior of
the building. However such openings have a number of
disadvantages. Firstly the openings cannot be closed and hence
air flow cannot be controlled even though the fans may be
rendered inoperative. Air movement may continue by way of
external air pressure on the building and by way of convection
currents. Secondly the air entering into the interior of the
building is not controlled in its direction. In this regard it
is important in many cases to control the air direction either
to ensure that it is properly presented as fresh cooling air
directly on to animals that require cooling or in other cases
to avoid air being directed s-traight to animals in such cases
where the animals are small and can be killed by excess
cooling.
Various designs of inlet duct have been made
available and in particular there are provided various
arrangements which can be mounted to provide a housing which
pro~ects through the wall of the building with the housing
possibily including in some cases directional control louvres
or plates which direct the air in the particularly required
direction either onto or away from the animals as required.
Housings of this type in some cases can also include within the
housing a flap valve which can open and close au~ornically in
~829~:
-- 3
dependence upon air pressure across the valve so as to prevent
any unwanted backflow of air and also to effectively totally
halt the flow of air when no air is required.
However devices of this type have the
disadvantage that they are very expensive in comparison with
the provision of a simple opening and in large barns of course
many quch inlet control devices are necessary. Part of this
cost penalty is due to the fact that it is necessary to provide
a moveable flap valve and in addition to seperately provide
control surfaces for guiding the air in the required
directions.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is one ob~ect of the present invention,
therefore, to provide an improved inlet arrangement for use in
building ventilation system.
According to the first aspect of the invention,
therefore, there is provided in a building having walls and a
substantially horizontal ceiling defining a substantially
closed interior area of the building, an air ventilation system
comprising air extraction means for withdrawing air frorn the
area, and an air inlet means seperate from the air extraction
means for allowing air into the area to replace air withdrawn
therefrom, the air inlet means comprising an opening formed in
~2~9Z
the ceiling through which air can pass, a flap member, hinge
means of said flap member being mounted directly on the ceiling
for pivotal movement of the flap member about an axis along one
side of the opening such that the flap member can move from a
closed position covering the opening and preventing air
movement therethrough to an open position in which the flap
member extends from the axis downwardly to allow air to pass
through the oper.ing, and spring means biasing the flap member
to a closed position.
According to a second aspect of the invention,
there is provided for use in a building having walls and a
substantially horizontal ceiling defining a substantially
closed interior area of the building and an air ventilation
system comprising air extraction means for withdrawing air from
the area, a kit of parts for forming an air inlet means for
allowing air into the area to replace air withdrawn therefrom
comprising a flap member, formed of a foamed plastics material
panel, hinge means for mounting said flap member for pivotal
movement of the flap member about an axis along one side of an
opening such that the flap member can move from a closed
position covering the opening ~nd preventing air movement
therethrough to an open position in which the flap member
extends from the axis downwardly to allow air to pass through
~2~9;~
the opening, and tension spring means for attachment to said
flap member for biasing the flap member to a closed position
covering said opening said hinge means being adapted for direct
attachment to a surface surrounding the opening.
With the foregoing in view, and other advantages
as will become apparent to those skilled in the art to which
this invention relates as this specification proceeds, the
invention is herein described by reference to the accompanying
drawings forming a part hereof, which includes a description of
the best mode known to the applicant and of the preferred
typical embodiment of the principles of the present invention,
in which:
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 is an isometric view showing a part of
a building including an air inlet provided in the ceiling of
the building and a flap member for controlling movement of air
therethrough.
Figure 2 is a cross sectional view along the
lines 2-2 of Figure 1.
Figure 3 is an exploded isometric view showing
an opening similar to the opening of Figure 1 controlled by an
alternative form of flap member.
Figure 4 i9 a transverse cross sectional view
~8~9~Z
through the arrangement of Figure 3 showing the flap member in
a closed position.
Figure 5 is a cross sectional view similar to
Figure 4 showing the flap member in the opened position.
Figure 6 is a cross sectional view similar to
Figure 2 of an alternative mounting arrangement for the flap
member.
Figure 7 is an underside view of the arrangement
of Figure 6.
In the drawings like characters of reference
indicate corresponding parts in the different figures.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
In Figures 1 and 2 is shown a first arrangement
of the building ventilation system in which the building is
illustrated with a ceiling indicated at 10 and one wall
indicated at 11 defining what is generally a closed interior
area of the building including further walls, doors as
necessary to complete the structure as will be well known to
one skilled in the art.
In the wall 11 is provided a fan schematically
indicated at 12 which may be one of a number of such fans which
act to extract air under automatic or manual control from the
interior of the building as that air becomes contaminated with
-- 7
moisture, ammonia or excess heat.
A plurality OL air inlets are provided to allow
air to enter the interior of the building to replace the air
extracted by the panel of fans 12. One of the inlets is shown
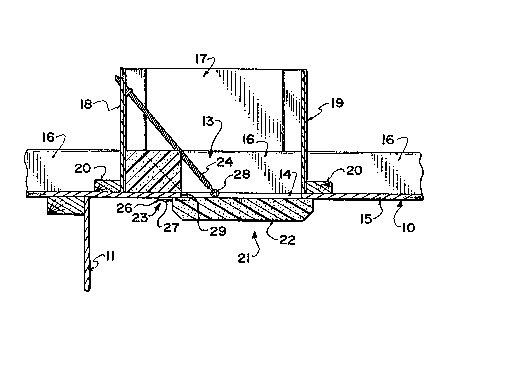
in Figures 1 and 2 and is indicated generally at 13.
Specifically the inlet 13 comprises an opening 14 defined in
the ceiling 10 and formed simply by cutting a rectangular hole
in the sheathing material of the ceiling. The sheathing
material is indicated at 15 and is carried upon ceiling joists
16 of conventional construction. The size of the opening is
preferably chosen so that it extends between two such joists 16
which may in one example be on 24 inch spacing.
Above the ceiling sheathing 15 and between the
joists 16 is provided a rectangular box construction 17 which
acts as a retaining barrier for insulation material sitting on
the sheathing 15, if such is provided. Walls of the box
structure are shown at 1~ and 19 which extend across between
the joists 16 and supported in place by transverse batons 20.
The inlet opening thus formed allows air to
enter in an uncontrolled manner from the roof space or area
above the ceiling into the interior of the building to replace
the air withdrawn by the fan 12. Control of the a.ir movement
is provided by an inlet control device generally indicated at
~32~312
21 which includes a flap member 22, a hinge mounting mechanism
23 and a control spring 24.
The flap member 22 is formed from a sheet of
foamed material having a thickness which may in one example be
of the order two inches and which defines a flat upper surface
and a flat lower surface with the side edges chamfered to
provide a pleasing appearance. The panel of the foamed
material is rectangular in shape having a length of
approximately 24 inches and a width of the order of 12 inches
enabling it to span and fully cover the opening 14.
The hinge mechanism 23 comprises a pair of
flexible hinge members each arranged at an end of the panel and
bridging one side edge of the panel. One portion Gf the
flexible hinge member is firmly attached into a recess 25
shaped to receive the hinge member and of a depth sufficient
just to receive the hinge member so that the outer surface of
the hinge member is flush with the upper surface of the panel.
A trailing part of the hinge member indicated at 26 extends
beyond the edge of the panel so that it can be attached to the
ceiling by a screw indicated in Figure 2 at 27 which passes
through a washer (not shown), through the flap of the hinge
member and into the joist 16 to provide a firm attachment of
the flap member to the ceiling.
The sharp edge of the panel at the hinges
provides a hinge line around which the flap member can pivot as
controlled by the hinge members 23.
The spring 24 comprises a tension spring
preferably of the coil spring type which is attached to a hook
28 on the upper surface of the panel at a position thereon
halfway along the length of the panel but spaced from the
longitudinal centre line toward the hinge members 23 thus
ensuring that the spring acts to push the flap member toward
the hinge members to reduce forces thereon. The spring is
inclined upwardly from the upper surface of the panel and in a
direction toward the axis defined by the edge of the panel
about which pivotal movement takes place. The upper end of the
spring is attached to the wall 18 at a position adjacent its
upper edge.
As the panel 22 is formed of a foa~ed material
for example, polystyrene foam, it has an insulating effect when
closed so as to at least partly replace the insulation in the
ceiling removed by the presence of the opening. However such
foamed material has a significant mass.
The flat foamed plastic panel 22 thus pivots
around the hinges 23 in dependence upon differences in air
pressure on the upper surface and on the lower surface caused
i
~L~28;29~92
-- 10 --
by a reduction in pressure within the building. The panel
member has its cen~re of gravity at or near the same elevation
as the pivot axis and i9 held forcibly against the ceiling by
the spring 24 which is attached to the hook or rotating pivot
28 at the lower end and to an adjustable connection at the
upper end attached to the wall 18. The upper connection it
will be noted from Figure 2 is on an opposite side of the pivot
axis to the coupling 28 so that as the flap member moves
through an arc in its opening direction, there is generated a
progressively reducing effective force arm of the spring on the
flap member so that the increasing tension of the spring is
partly offset by the reducing force arm. In other words, the
resultant increase in torque on the flap member around the
hinge axis is relatively small.
At the same time the torque applied by the
weight of the flap member around the hinge axis gradually
reduces as the flap member is opened since the centre of
gravity moves closer to a vertical plane containing the hinge
axis.
The tension in the spring i~ controlled so that
the flap member can rotate to its open position at an angle of
the order of 60 from the horizontal. This amount of rotation
results in such a significant reduction of the effective force
~2~ 2
arm of the spring that the torque exerted by the spring, after
a point, actually declines. This decline is halted by the
provision of a stop member indicated at 29 which is engaged by
the spring 24 after opening of the flap member to an angle
approaching the required angle of 60. Without preventing such
decline, the inlet would hang in the wide open position even
when some of the exhaust fans are shut down so that large
volumes of air would continue to enter the interior when
reduced volumes are required.
The stop member 29 can be adjustable or fixed
and in the arrangernent illustrated is provided simply by an
edge of the opening which is arranged to be a requ~red distance
from the hinge line by adjusting the position of the hinges on
the ceiling accordingly. Because the spring is held against
the edge of the opening, the tendency is for the lower end of
the spring to do the majority of any further stretching thus
providing a greater increase in tension of the spring for
further movement of the flap member than would be the case if
the entire spring was being stretched uniformly.
The above arrangement of inlet control has the
advantages that when reduced amounts of air are required for
example during the cooler periods, the flap member only opens
over a small extent thus acting to retain air movement in a
- 12 -
direction parallel to the upper surface of the flap member so
that it runs basically along the underside of the ceiling for
mixing with warm air before moving to the animals.
When however more air is required for example
during warm weather, the inlet opens wide to an angle of
approxirnately 60 and permits the roof space air to drop down
directly to floor level so a~ to apply the benefit frorn the
cooling air directly onto the livestock beneath the ceiling.
The flap member thus acts to directly control
the movement of air through the opening and in addition to
control the direction of the air so that its effect is properly
managed in dependence upon the circumstances.
A stop member 45 can be provided mounted upon
the ceiling and extending over a short length of the ceiling so
as to hold the edge of the flap member away from sealing
contact with the ceiling to allow a continual slight flow of
air past the flap member even in the fully closed position.
This can be used to avoid freezing of relatively stationary
moist air around the flap member which can in some severe cases
cause the flap member to adhere to the underside of the ceiling
and prevent its opening when required.
In a further arrangement (not shown) the flap
member can be arranged to cooperate with an opening in an
12~
- 13 -
inclined surface for example a surface inclined between the
wall and ceiling of the barn. In this case, an additional
counterbalance mass is applied to the flap member extending
upwardly therefrom 90 as to raise the centre of gravity of the
flap member as a whole to approximately the height of the hinge
line. In this way, the weight of the flap member continues to
generate a torque in an opening direction as the flap member
moves toward the open position.
Turning now to Figures 3, 4 and 5 , there is
shown an opening 14 in the ceiling substantially as previously
described including a box construction 17 mounted above the
opening. A ceiling trim 30 is provided for attachment to the
undersurface of the ceiling. This trim is omitted from the
illustration of Figures 4 and 5 for convenience. ~he trim 30
is formed from a strip of polystyrene foam. In severe climates
this trim prevents condensation at the ceiling which otherwise
could collect in the inlet and act as an additional weight
interfering with the spring controlled operation. In addition,
for use with poultry or other high insulation requirement, a
rubber gasket (not shown) can be attached between the trim and
the flap member, the gasket being attached at an inner edge and
hanging downwardly to act as a seal with the flap member. The
gasket is not essential and is provided only in cases whera
~L7~
- 14 -
improved sealing of the air flow in the closed position is
necessary.
A modified flap member is shown in Figures 3, 4
and 5 and is indicated generally at 31. The flap member is
L-shaped in cross section defining a first plate portion 32 and
a second plate portion 33 arranged at right angles thereto and
of reduced length as best shown in Figure 4. At the ends of
the flap member is provided a pair of triangular end members 34
and 35 which are shaped so that two sides coincide with the
outer edges of the plate portions 32 and 33 and the third side
of the triangular member follows a line joining the upper edges
of the plate member 32 and 33. In this way as best shown in
Figure 4, the upper edges of the plate members 32 and 33 can
lie in contact with the ceiling on either side of the opening
14 with the end members 34 and 35 at the ends of the opening
14. In this way the flap member defines a rectangular upper
face as best ~hown in Figure 3 which engages the ceiling around
the opening 14 to hold the opening closed in the position shown
in Figure 4.
The flap member is hinged to the ceiling in a
manner similar to that previously described employing flexible
hinge strips 36 and 37 which can be formed of neoprene which
are attached to the end members 3~ and 35 at the apex thereof
~L2~
- 15 -
adjacent the upper edge of the plate member 33 and are attached
by screws passing through the trim.
As best shown in Figure 3, the triangular member
is shaped to form an apex 37 defining a pivot axis. The
apex 37 coincides with a flat portion 38 of the upper edge of
the plate member 33 with a further portion of the upper edge
inclined relative thereto and indicated at 39 with the angle
between the flat portion 38 and the incline portion 39 being of
the order of 30 (in the example shown) to enable the device to
open through an angle of the order of 30 at which time the
surface 39 engages the under surface of the ceiling in the
position shown in Figure 5. Similarly to the previous
embodiment, the flap member is controlled by a spring 40 which
extends upwardly from a hook member 41 on an upper surface of
the flap member. In this case the angle of the spring 40 from
vertical is very much reduced relative to the angle of the
spring 24. An additional mass 42 is mounted on the flap member
at a position slightly raised from the upper surface of the
plate member 32 with both the mass 42 and the hook member 41
being carried on a plate 43 which provides sufficient strength
to accomodate the forces involved and to transmit those forces
to the relatively weaker plastics foam material from which the
flap member is formed.
~z~
- 16 -
The edge of the plate member 32 at its point of
contact with the underside of the ceiling is chamfered as
indicated at 44 so as to provide a line of contact with the
ceiling.
The type of flap member shown in Figures 3, 4
and 5 defines a scoop-type air inlet which is shaped 90 as to
direct fresh air entering through the opening 14 onto the
ceiling even in its wide open position. In this way, young
livestock such as chicks and caged livestock such as dry sows
are not subjected to cold blasts of air which could result in
sickness and even death.
Because the flap member is scoop-shaped, there
is sufficient material in it to obtain a weight of
approximately two pounds. As well its shape results in a
centre of gravity that is significantly below the line around
which it is pivoted defined by the apex 37. As the inlet opens
this centre of gravity describes an arc around the hinge line
progressively reducing its rotational force (torque) against
which the spring tension is adjusted for proper closure of the
ceiling opening. This reduction of opening torque resulting
from the shift of the flap member's centre of gravity causes
the Elap member to require much greater pressure difference
across it in order to continue opening. In fact at
~2~Z~%
- 17 -
approximately 40 per cent of its travel toward the open
position, very little further opening occurs until the pressure
difference has risen to almost the full operating pressure
considered acceptable. At this point the inlet suddenly swings
to its wide open position. This is due to the fact that the
arc described by the lower rotating spring pivot as the inlet
opens results in a substantial reduction of the spring's
effective force arm. As well, the pressure difference across
the inlet was extra-ordinary before the shift to the wide open
position because of the loss of opening torque described above.
This excess pressure and the reduction of the spring's
effective force arm are responsible for the sudden swing to the
wide open position. As a typical installation includes many
inlets in one area, this non-linearity in its operation results
in some units swinging into the wide open position ahead of
others because of slight differences in adjustment.
By installing the weight 4~, the centre of
gravity of the flap member as a whole is shifted so that it is
further away from and slightly below the hinge line. With this
arrangement the opening torque caused by the weight of the
assembly is not reduced as significantly and the non-linearity
described above is largely eliminated.
Relatively uniform operation of the inlet is
~zg~
- 18 -
obtained by proper adjustment of the spring tension. The
spring tension is adjusted by movement of the upper end of the
spring in its attachment to a mounting block 46 carried in on
an inner face of the box 17 as shown in Figure 3.
The upper end of the spring pivot is located so
that the upper end of the spring leans slightly toward the
hinge line as best shown in Figure 4. In addition the lower
connection of the spring at the hook member 41 is well below
the hinge line so that as the inlst opens the arc described by
this pivot significantly reduces the effective force arm of the
spring. This arrangement allows the inlet to open much further
against the increasing spring tension which is partly offset by
the progressive reduction of the effective force arm.
It should be notd that a stop is not required
for the spring in this arrangement as is required for the
device relatively illustrated in Figures 1 and 2. This is due
to the fact that the flap member in this case only rotates
through an angle of the order of 30 so that the reduction of
the effective force arm is not as great.
In broiler barns which start up with young
chicks requiring high temperatures and very little ventilation,
the sealing trim 30 including the gasket (not shown) can be
used. The sealing trim 30 consists of a one half inch strip of
~q~
-- 19 --
styrofoam fitted with the flexible gasket which lays against
the flap member. To the upper surface of the trim 30, two
beads of caulk can be applied to attach the trim to the
ceiling. The trim and the flap member are located at the
ceiling with the spring hooked onto its upper and lower
connections forcing the flap rnember against the trim~
In the arrangement of Figures 6 and 7, a device
is shown which is substantially of the same construction as
that shown in Figures 1 and 2 except that in this case a
surrounding insulating trim 50 is provided which is rectangular
in shape so as to define a strip extending a short distance
outwardly from the opening 14. In this case the trim 50 is
raised along the hinge line and two sides to define a recess 51
into which the flat-type flap member 52 can be received.
In place of the flexible strip type hinge
members of Figures 1 and 2, in this case the hinging action is
provided between an apex 53 of the flap member 52 which engages
into a right angled receiving area 54 of the trim 50. The
right angled receiving area can be reinforced by a right angle
strip 55 formed of a rigid plastics material. Side to side
movement of the flap member 52 is prevented by spring loops 56
formed of plastic strip which act to centre the flap mernber
within the recess 51 to allow it to freely pivot within the
9~:
- 20 -
area 54. AS shown best in Figure 6, in the closed position the
upper surface of the flap member engages one side of the strip
55. In the open position (not shown) a side surface 57 of the
flap member is arranged at an angle of the order of 60 to the
upper surface so as to engage the other side of the strip 55
and tend to restrain the flap member to the opening angle of
60.
The two raised sides and the raised edge of the
trim act to confine the air to escape over the fourth edge
remote from the hinge line so as to assist in controlling air
movement and improving air mixing.
Since various modifications can be made in my
invention as hereinabove described, and many apparently widely
different embodiments of same made within the spirit and scope
of the claims without departing fcom such spirit and scope, it
is intended that all matter contained in the accompanying
specification shall be interpreted as illustrative only and not
in a limiting sense.