Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
- 8 -
THE EMBODIMENTS OF THE INVENTION IN WHICH AN EXCLUSIVE
PROPERTY OR PRIVILEGE IS CLAIMED ARE DEFINED AS FOLLOWS:
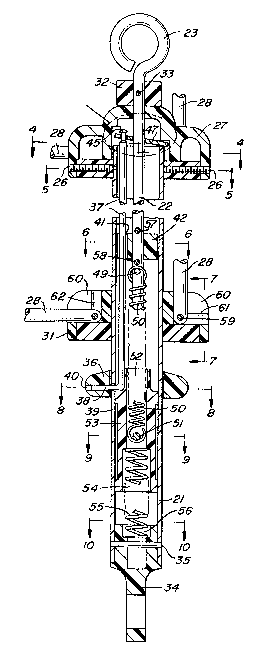
1. An elongated telescopic carrier device for suspend-
ing intravenous fluid containers or the like, comprising
in combination,
a) an elongated hollow tubular shell having upper
and lower ends,
b) an extension rod slidably disposed within said
tubular shell with one end of said rod extending
out of said upper end of said tubular shell and
the other end of said rod being disposed within
said tubular shell,
c) retaining means preventing said extension rod
from being completely withdrawn from said tubular
shell,
d) locking actuator means operatively coupled to
said extension rod effective when actuated in a
first way to release said extension rod for move-
ment of the latter out of and into said tubular
shell, and effective when actuated in a second
way to lock said extension rod at least against
movement out of said tubular shell,
e) biasing means coupled to said extension rod
effective to constantly bias said rod for movement
into said tubular shell, and
f) support means carried by said tubular shell for
suspending fluid containers therefrom.
2. A carrier device as described in claim 1 wherein
said biasing means comprises a spring coupled at one
place to said extension rod and coupled at another
place to said locking actuator means.
3. A carrier device as described in claim 1 wherein
a part of said locking actuator means is intercoupled
with said tubular shell.
4. A carrier device as described in claim 1 further
including anti-rotation means coupled to said exten-
sion rod effective to prevent more than a predeter-
mined amount of relative rotation between said ex-
tension rod and said tubular shell.
5. A carrier device as described in claim 1 further
including anti-rotation means coupled to said exten-
sion rod effective to prevent more than a predetermined
amount of relative rotation between said extension rod
and said tubular shell, said anti-rotation means when
operative engaging a part of said locking actuator
means.
6. A carrier device as described in claim 1 wherein
said locking actuator means comprises an actuator
ring extending around the periphery of said tubular
shell with the plane of said ring substantially ortho-
gonal to the longitudinal tubular axis, whereby said
locking actuator means is readily actuatable from any
peripheral position.
7. A carrier device as described in claim 1 wherein
said locking actuator means comprises, a manually
operable actuator at least a part of which is external
to said tubular shell, an actuating rod at least a
part of which is disposed within said tubular shell
and which is coupled to said manually operable actu-
ator, and a lock plate coupled to said actuating rod
and releasably lockingly engaged with said extension
rod, said lock plate being released from locking en-
gagement with said extension rod by said actuating
rod when said manually operable actuator is actuated
in a first way.
8. A carrier device as described in claim 1 wherein
said locking actuator means comprises, a manually
operable actuator at least a part of which is external
to said tubular shell, an actuating rod at least a
part of which is disposed within said tubular shell
and which is coupled to said manually operable actu-
ator, and a lock plate coupled to said actuating rod
and releasably lockingly engaged with said extension
rod, said lock plate being released from locking en-
gagement with said extension rod by said actuating
rod when said manually operable actuator is actuated
in a first way, said manually operable actuator com-
prising an actuator ring extending around the periphery
of said tubular shell with the plane of said ring sub-
stantially orthogonal to the longitudinal tubular axis,
whereby said locking actuator means is readily actu-
atable from any peripheral position.
9. A carrier device as described in claim 1 wherein a
part of said locking actuator means is intercoupled
with said tubular shell, and wherein said biasing means
comprises a spring coupled at one place to said exten-
sion rod and coupled at another place to said locking
actuator means.
10. A carrier device as described in claim 1 wherein a
part of said locking actuator means is intercoupled
with said tubular shell, and wherein said biasing means
comprises a spring coupled at one place to said exten-
sion rod and coupled at another place to said locking
actuator means, and further including anti-rotation
means coupled to said extension rod effective to prevent
more than a predetermined amount of relative rotation
between said extension rod and said tubular shell.
11. A carrier device as described in claim 1
a) wherein a part of said locking actuator means
is intercoupled with said tubular shell,
b) wherein said biasing means comprises a spring
coupled at one place to said extension rod and
11
coupled at another place to said locking actu-
ator means,
c) wherein said locking actuator means comprises
a manually operable actuator at least a part of
which is external to said tubular shell, an actu-
ating rod at least a part of which is disposed
within said tubular shell and which is coupled
to said manually operable actuator, and a lock
plate coupled to said actuating rod and releas-
ably lockingly engaged with said extension rod,
said lock plate being released from locking en-
gagement with said extension rod by said actua-
ting rod when said manually operable actuator is
actuated in a first way, and
d) further including anti-rotation means coupled
to said extension rod effective to prevent more
than a predetermined amount of relative rotation
between said extension rod and said tubular shell.
12. A carrier device as described in claim 1
a) wherein a part of said locking actuator means
is intercoupled with said tubular shell,
b) wherein said biasing means comprises a spring
coupled at one place to said extension rod and
coupled at another place to said locking actu-
ator means,
c) wherein said locking actuator means comprises,
a manually operable actuator at least a part of
which is external to said tubular shell, an
actuating rod at least a part of which is disposed
within said tubular shell and which is coupled to
said manually operable actuator, and a lock plate
coupled to said actuating rod and releasably lock-
ingly engaged with said extension rod, said lock
plate being released from locking engagement with
12
said extension rod by said actuating rod when
said manually operable actuator is actuated in
a first way, said manually operable actuator
comprising an actuator ring extending around the
periphery of said tubular shell with the plane
of said ring substantially orthogonal to the
longitudinal tubular axis, whereby said locking
actuator means is readily actuatable from any
peripheral position, and
d) further including anti-rotation means coupled
to said extension rod effective to prevent more
than a predetermined amount of relative rotation
between said extension rod and said tubular shell,
said anti-rotation means when operative engaging
a part of said locking actuator means.
13. A carrier device as described in claim 1 wherein
said support means carried by said tubular shell for
suspending fluid containers therefrom comprises a
plurality of support arms swingably coupled to said
tubular shell for movement between a use position in
which said arms extend outward away from said tubular
shell and a storage position in which said arms lie
substantially parallel to and closely alongside of
said tubular shell.
14. A carrier device as described in claim 1 wherein
said support means carried by said tubular shell for
suspending fluid containers therefrom comprises,
a) a plurality of support arms swingably coupled
to said tubular shell for movement between a use
position in which said arms extend outward away
from said tubular shell and a storage position
in which said arms lie substantially parallel
to and closely alongside of said tubular shell, and
b) detent means effective to releasably latch said
13
support arms in said use position.
15. A carrier device as described in claim 1 wherein
said support means carried by said tubular shell for
suspending fluid containers therefrom comprises,
a) a plurality of support arms swingably coupled
to said tubular shell for movement between a
use position in which said arms extend outward
away from said tubular shell and a storage posi-
tion in which said arms lie substantially paral-
lel to and closely alongside of said tubular
shell, and
b) detent means effective to releasably latch
said support arms in said storage position.
16. A carrier device as described in claim 1 wherein
said support means carried by said tubular shell for
suspending fluid containers therefrom comprises,
a) a plurality of support arms swingably coupled
to said tubular shell for movement between a
use position in which said arms extend outward
away from said tubular shell and a storage
position in which said arms lie substantially
parallel to and closely alongside of said
tubular shell,
b) detent means effective to releasably latch
said support arms in said use position, and
c) detent means effective to releasably latch
said support arms in said storage position.
17. A carrier device as described in claim 12 wherein
said support means carried by said tubular shell for
suspending fluid containers therefrom comprises,
a) a plurality of support arms swingably coupled
to said tubular shell for movement between a use
position in which said arms extend outward away
from said tubular shell and a storage position
14
in which said arms lie substantially parallel
to and closely alongside of said tubular shell,
b) detent means effective to releasably latch
said support arms in said use position, and
c) detent means effective to releasably latch
said support arms in said storage position.
18. A carrier device as described in claim 16 wherein
said detent means are formed from resilient material
which at least partially surrounds a region of each
said support arm proximate to the region where each
said arm is swingably coupled to said tubular shell.