Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
1~859~1)
-1- 03 GP 6073
CLOSED SLOT ROTOR CONSTRUCTION
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
FI LD OF THE INVENTION --
- The present invention relates generally to closed
~lot rotor lamlnations or punchings for use in dynamo-
electric machines, and more particularly to a laminati
~ J- ~h~,~e ~
in which the ~lots are rormed with generally~L-~ep ends.
DESCRIPTION OF THE R~OWN ART
Rotors rormed of a ~tack Or laminatlons having
closed slots equally spaced ~rom one another about the
periphery of each laminatlon are known rrom, ~or example,
` U.S. Patents 2,794,138 (May 28, 1957) and No. 3,401,280
(September 10, 1968), both having been assigned to the
assignee of the present lnvention.
; ;Such rotors are ordlnarily used in inductive AC
otors, wherein conducting members which extend axially
along the rotor through aligned slots o~ the stacked
laminatlons lnter-ct w~th a rotatlng magnetlc field
; oreated ~n an air gap between the outer circumrerence o~
the rotor and the inner circum~erence o~ the machine
tator. ~indlrgs embedded in lot~ between radially
128s98~)
-2- 03 GP 6073
inwardly proJectlng teeth Or the ~tator, ad~acent the a$r
~ap, are connected to the AC mains, and the ~tator winding
conductors pass through a certain order of the qtator
slots so as to cause magnetlc rlux in the air gap to
rotate in synchronism with the fre~uency Or the AC mains.
To obtain high efriciency during normal rotational
speed conditions for the rotor, the conducti~e members or
bar~ in the rotor slots should have minimal resistance.
Low rotor resiQtance, however, results in low starting
torque with a high starting current and a low Rtarting
power ~actor. One way to achie~e an erfectively high
rotor resistance at motor ~tart-up, is to employ a so-
called double -Qquirrel cage rotor bar arrangement in which
two parallel conductive bars pass through each rotor ~lot
with top bars (i.e., the bars closer to the rotor
circumrerence) ha~ing smaller cross-sectional area and,
hence, higher reslstance, than bottom bars set deeper in
the slots, i.o. clo~er to the axis Or the rotor.
The top bars and the bottom bars are all shorted together
; at the axial ends Or the rotor.
~ By oonstricting the rotor slotg between the top and
: the bottom barq in the radial direction to rorm a ~o-
called neck portion Or the slot, the bottom bars will have
, ~: .: . ....... . ,- -
. . . . .
.~ , ~ - ,:
~ . . . , .. - . - , . .
128~9~
-3- 03 GP 6073
a much 8reater inductance in relation to the top barQ and,
thus, relati~ely llttle current ls lnduced in the bottom
bars at motor start-up when the alr gap ~lux rotates at
greatest speed relative to the rotor bars. The efrecti~e
rotor reslstance at start-up $Q then about eQual to that
of the top barQ and, thus, sufficlent start-up torque may
be obtained. ~hen the rotor approaches normal running
~peed, however, the air gap field interacts with the rotor
bars at a much lower frequency 80 that the inductance Or
the bottom bars becomes lesQ signiricant. The lower
re~istance of the bottom bars then provides greater
operat~ng e~ficiency, the actual rotor re~iQtarce
approximating that of both the bottom and top bars in
parallel.
Closed ~lot rotor~ Or the double cage ~ariety
con~entionally ha~e the slots in the rotor laminations
formed with a generally V -Qhaped edge at the top of the
~lot w~th the center Or the V creating a narrow bridge
part between the top of the slot and the outer
clrcumference of the lam$natlon. ~urther, the angle
def~ned between each leg Or the V and a l~ne drawn
perpendicular to the radial center line o~ the qlot
con~entionally haQ been between about 40 to 45 degree~.
.,.. ~..: .... .. .. . .
::' , : .......................................... . .
~ . . .
1~598~
-4- 03 GP 6073
Such angles aQ 40 degrees and 45 degrees ror the V shaped
edge and would requlre a narrower br$dge ln order t~
dell~er the same performance, and would thererore present
diff~culties ln machinlng Or the closed slots at the
peripheries Or the rotor laminatlons.
, ~ , . . . . .
12~3598-)
-5- 03 GP 6073
SUMMARY _ THE INVENTION
An object of the invention is to provide a closed slot
rotor lamination which can be manufactured without imposing
costly production procedures.
Another object of the invention is to provide a closed
',~l'
slot rotor lamination having V-shaped top wherein the angle of
the V allows for optimum electromagnetic performance.
A further object of the invention is to provide a
closed slot rotor lamination in which neck portions of the
slots are located to optimize machine performance.
According to the invention, a lamination used to form a
rotor in a dynamo-electric machine, includes a flat circular
plate of ferromagnetic material having a number of equally
circumferentially spaced closed slots extending radially near
the outer periphery of the plate. As will be understood by
persons skilled in the art, the 810ts are formed to contain
conducting members which extend along the rotor when a number
of the plates (also called punchings or laminations) are
stacked together and corresponding 610ts are placed in com-
munication with one another. Each slot is substantially
V-shaped at an upper slot region and symmetrical about a ra-
dial center line. The legs of the V diverge from one another
towards the center of the plate, and each leg of the V forms an
.. ,.~ ., , , ~ , .
~''," ~ '. . .
8 59~
-6- 03 GP 6073
angle of about 30 degrees with respect to a line drawn
perpendicular to the radial center line Or the slot.
The various features of novelty which characterize
the invention are pointed out with particularity in the
claims annexed to and forming a part Or the present
disclosure. For a better understanding of the invention,
lts operating advantages and speciric ob~ects attalned by
its use, reference should be had to the accompanying
drawing and descriptive matter in which there are
illu~trated and described prererred embod~ments Or the
invention.
.
.
.-
~8598-)
-7- 03 GP 6073
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
In the drawlng:
Fig. 1 is a side view, partly in ~ection, o~ a
dynamo-electric machine in which the present in~entlon may
be embodied;
Fig. 2 lq a front end view of the machine ln Fig. 1;
Fig. 3 is a plan view Or a rotor lamination
according to one embodlment of the present ln~ention;
Flg. 4 ls an enlarged ~iew Or a closed slot in the
lamination Or Fig. 3;
Fig. 5 is an enlarged view Or an upper slot region
Or the slot in Fig. 4;
Fig. 6 i~ a plan view a rotor lamination according
to a second embodiment Or the in~ention; and
Fig. 7 is an enlarged view o~ a ~lot in the
lamination of Fig. 6.
. .
, ~
lZ8~981~
-8- 03 GP 6073
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE Il~VENTION
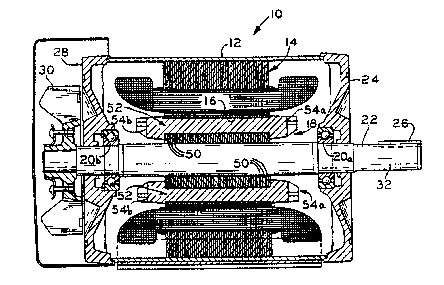
Fig. 1 ~hows a ~lde vlew, ln ~ectlon, of a dynamo
electrlc machlne 10, in which the present inventlon may be
embodled. A rront vlew Or the machlne 10 is shown in Fig.
2.
Basically, the machlne 10 lncludes a generally
cylindrical outer casing 12, and a generally cyllndrlcal
stator 14 fixed coaxlally withln the outer casing 12 and
having a coaxial stator bore 16. A rotor 18 18 ~upported
by suitable bearings 20a, 20b at the rront and back Or
caslng 12, to extend axially within the rotor bore t6 and
~r rotational movement about the bore axis. In the
partlcular example ~hown a Qhaft part 22 Or the rotor 18
extends axially rrOm a front end shield 24 Or the machine
10, and has a key 26 pro~ecting radially outward from a
rece~s cut axlally a certaln di~tance from the rront of
the Qhart part 22. ~ey 26 serves to lock the sha~t part
22 into a corresponding key way cut in a load member (not
~hown) e.g. a ran, to which rotational motive power 18 to
be supplied by the machlne 10.
A back end shield 28 (Fig. 1) together wlth the
caslng 12 and the rront end ~hield 24 serve to contaln and
protect the stator 14, rotor 18 and a~sociated conductive
wlndings. In the example ~hown a machine cooling ~an 30 ls
mounted on a rotor ~tub part 32 which extends outside the
:: .. . ' ~, . . .
:-` lX8598-t
~9~ 03 GP 6073
back end ~hleld 28, and dlrects an a~r current M ow o~er
the casing.
~ s shown ln Flg. 1, the ~hart part 22 Or the rotor
18 extends axlally through the mac~lne ca~ing 12 and haQ a
stac~ Or rotor lamlnations 50 rlxed coaxlally on the Jhart
22 lntermedlate the rront and back bearings20a, 20b. Sets
of conducti~e bars 52 pass through axlally extending slots
rormed ln the rotor 18 near the outer per~phery Or each Or
the laminations 50. The bar~ 52 are ~horted to one
another at the axlal ends or the stack o~ lamlnations 50
by a set Or end rlngs 54a, 54b.
Fig. 3 ls a plan ~lew Or one Or the rotor
laminations 50. The lamination ls rormed Or a flat
clrcular plate Or ferromagnetic material. The plate
lamination 50 has a number (e.g., 28) Or unif~rmly
clrcumrerentially spaced closed slots 56 extendlng
symmetrically about radial center llne~ ln a region near
the outer perlphery Or the laminat$on 50. Slots 56 are
ormed to contain conductl~e bar~ 52 (Flg. 1) whlch extend
~ubstantially parallel to the aXlQ Or the rotor lô when the
laminations 50 are stacked face-to-face with the corresponding
slots 56 aligned (i.e., in communication with one another.)Each of
, . . .. .. . .
, ~ - ~ , . . . .
12~3598~
-10- 03 GP 6073
the ~lotq 56 is substantlally V-shaped at an upper ~lot
region 58 as ~hown in Figs.4 and ~. A Y-shaped edge 60
torming the upper ~lot region 58 ls symmetrical about the
radlal center line, with the legs Or the V diverging rrom
one another in the directlon toward the center Or the
lamination 50.
In one preferred form, as specifically shown in Fig. 5, each
leg o~ the ~ derining the edge 60, rorms an angle o~ about
30 tegrees with respect to a line drawn perpendicular to
the radial center llne Or the slot 56. Further, the
center of the V Qhaped cdge 60 is curved at a rirst radiu~
Rt between the ~traight legs Or the edge 60. A bridge
area 62 is thus rormed between the upper slot region 58
and the outer circumference Or the lamination 50.
~referably, the radial dimen-~lon Or a narrowest part Or
the ~ridge area 62 at the center Or the V-shaped edge 60
1~ at lea t .25 mm., and may be ln the range rrom about
.25 mm. to about .4 mm.
As ~een more clearly in Fig. 4, the edges Or each
~lot 56 conQtrict toward the rad~al center line Or the
nlot wlth opposing edges curvcd cont$nuously at a Jecond
radlu~ R2 between d~tal ends 64a, 64b Or the ~tralBht
legs Or the Y-shaped edge 60 to a rlr~t set Or polnt~ 66a,
--10--
- , . . . -, .
128598-)
~ 03 GP 6073
66b, where the slot edges have a common tangent T which is
perpendicular to the radial center line.
From the tangent line T, the opposite edges of the slots
are curved continuously at a third radius R3 to constrict
toward the center line over an arc of 90 degrees to a second set
of points 68a, 68b defining tops of nec~ portions 70 of the
slots 56. The tops of the neck portions 70 of the slots 56 are
located at points radially of the laminations 50 such as to
optimize electromagnetic performance when the conductive bars 52
are inserted in upper and lower regions of the slot 56 of a
lamination stack to form a double cage rotor as in Fig. 1. In
some specific cases, the segments of the slot contour that joins
or blends the radii R2, R3 may be extremely small, or
approach a limit such that such segments are essentially
non-measurable in terms of length.
Table 1, below shows preferred values for the first,
second, and third radii Rl, R2, R3 with the V-shaped edge
60 forming the 30 degree angle represented in Fig. 5.
TABLE 1
LAMINATION 50
PUNCHED DIAMETER R R R
2 3
95 mm. .932 mm..813 mm. .7 mm.
122 mm. .892 mm..919 mm. .76 mm.
122 mm. .933 mm..715 mm. .76 mm.
150 mm. .934 mm.1.105 mm. .762 mm.
: - : . . .
1 2~598~)
-12- 0~ GP 6073
Table 2, below, Qhows preferred locations o~ the
topQ Or neck portions 70, l.e., the radial di-Qtance ~rom
the center of the la~ination 50 (Point C in Fig. 3 or
Fig. 6) to a line mer~endicular to the radial center line
of the slot 56 which line intersects the second set of points
68a, 6~b in Fig. 4. AS shown, the locations of the to~s of
the neck Portions 70 ~referablv vary according to the
diameter of the lamination 50.
TABLE 2
" .
LAMINATION 50 RADIAL DISTANCE
DIAMETER _ NECK PORTION 70 TOP_ _
95 mm. 43.462 mm
122 mm. 56.9 mm.
150 mm. 70. mm.
Figs. 6 and 7 shows a closed slot rotor lamination
according to a ~econd embodlment o~ the ~nventlon. Parts
corresponding to those shown in the embodiment Or Fig. 3-
5, ha~e corresponding reference character~. AQ shown in
Fig. 7, however, the edge Or the slot 56' in the upper
. - .
~28598-)
- 13 - 03 GP 6073
regions 58' which leads away from the distal ends of
the straight legs of the V-shaped edge 60', is only
partially curved at a second radius R2, until such
edge is parallel to the slot center line and then
extends parallel to the center line a certain distance
L before curving towards the slot center line at the
second radius R2, until becoming tangent to the line
T'. For a diameter of 115 mm. for the lamination 50',
the distance L is preferably about .531 mm. with a
first radius Rl, of .932 mm., and second and third
radii R2, R3, all of .76 mm. The top of the neck
portion 70' is preferably at 52.5 mm. from the center
of the circular lamination 50'.
Machines constructed with double cage rotors
comprised of laminations according to the present
invention exhibited superior performance over rotors
having slots with V-shaped edges defining angles of about
45 degrees with respect to breakdown torque, locked rotor
torque, full load speed and full load efficiency.
Providing the 30 degree angle according to the invention
allows sufficient material at the bridge area 62 (or 62')
to avoid costly machining or casting procedures to
fabricate the laminations 50 (or 50'), and enables th~ top
conductive bars in the upper slot regions 58 to present a
lower bar resistance at normal running speed. Moreover,
,,
i~85~
-14- 03 GP 6073
undesirable reactance effects for the conductive bars 52 have
been found to be diminished in accordance with the slot con-
struction of the present invention.
Reference is made herein to "punched diameter", and
"diameter" in the context of the outer diameter of a lamina-
tion. In this context, "punched diameter" means "as punched"
by a punch press and does not contemplate finishing operations
for establishing air gap defining finished surfaces. Thus, it
should be understood that reference to, for example, a "plate
diameter of about 150 mm." would be inclusive of an as punched
lamination having a nominal as punched diameter of lS0 mm.,
but also a lamination within a finished rotor having a nominal
finished outer diameter somewhat less than 150 mm. (so that an
appropriate air gap will be maintained between rotor and
stator).
While the foregoing description represents preferred
embodiments of the present invention, it will be obvious to
those skilled in the art that various changes and modifica-
tions may be made, without departing from the true spirit and
scope of the present invention.
,
~28S98~
- 15 - 03 GP 6073
RE:LATIONSHIP TO OTHBR APPLICATIONS
This application has been filed on March 10,
1988 as well as commonly assigned Canadian Application
Serial No. 561,117 - BASE ASSEMBLY FOR DYNAMOELECTRIC
5 MACHINE,in the name of Robert L. Sieber, filed March
10, 1988; Canadian Application Serial No. 561,730 -
DYNAMOELECTRIC MACHINE LAMINATION CONSTRUCTION in the
name of Thomas W. Neumann, filed March 17, 1988; and
Canadian Application Serial No. 561,110 - LIP
10 STRUCTURE FOR A STATOR IN A DYNAMOELECTRIC MACHINE in
the names of Deepakkumar J, Gandhi et al, filed March
10, 1988.
- ,: