Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
12~80~g
APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR STRIPPING
MOLDED U-SHAPED ARTICLE FROM MO~D
The present invention relates to molds and
more particularly to an improved apparatus and
method for stripping a molded U-shaped article
from the mold.
Generally, molded U-shaped articles are
formed by using an injection molding machine
which comprises a molding unit and an injection
unit. The molding unit has a frame on which
a mold is mounted and a hydraulic apparatus for
opening and closing the mold. The injection
unit fluidizes plastic material and injects the
fluidized plastic material into the mold.
The mold typically comprises two mold plates.
One mold plate houses a plurality of cup molds
while the other mold plate has an equal plurality
of mandrels which are registered for a respective
cup mold. When the mold is closed, one mandrel
fits inside one cup mold and a closed cavity
is formed. The closed cavity defines the shape
of the molded U-shaped article.
Conventionally, a molded U-shaped article
is formed by injecting plastic material into
the closed cavity of the mold and allowing the
12~8049
plastic material to solidify. The hardened molded
article is then removed from the mold by opening
the mold.
Typically, the molded U-shaped article is
intended to stick on the mandrel when the mold
is opened and an ejector is used to push the
molded article off of the mandrel once the molded
article clears the cup mold. The molded article
falls away from the mold due to gravity.
A problem associated with this type of injection
molding machine is that the molded article often
sticks in the cup mold. When the molded article
sticks in the cup mold, either the machine is
stopped and an operator physically removes the
article or the supply of fluidized plastic material
is cut off from that cavity and eventually, when
enough cavities become blocked, the machine is
shut down and an operator physically removes
the stuck articles.
A solution to the sticking problem has been
to coat the cup mold with a chemical compound
such as a conventional mold release agent. Although
this release agent does help, it eventually wears
off and the molded articles stick.
i298049
--3--
Applicant has discovered an apparatus and
method to prevent molded U-shaped articles from
sticking in injection molding machines of the
type having a mandrel and a cup mold. Specifically,
-5 applicant has discovered an apparatus and method
for stripping the molded U-shaped articles from
the cup mold which virtually eliminate the sticking
of molded articles in the cup mold.
The present invention has been proven to
provide especially good results in the manufacture
of golf ball cover halves.
These and other aspects of the present invention
may be more fully understood with reference to
the drawings wherein:
Fig. 1 illustrates an injection molding
machine in a closed position employing the present
invention;
Fig. 2 is a cross-sectional view through
a closed mold employing the present invention;
Fig. 3 is a cross-sectional view through
the mold of Fig. 2 wherein the mold is partially
open;
Fig. 4 is a cross-sectional view through
the mold of Fig. 3 wherein the mold is in an
open position; and
--3--
~2~80~g
--4--
Fig. 5 is an alternative mandrel configuration.
Referring to Fig. 1, an injection molding
machine 10 is shown employing the improved mold
of the present invention. Mold machine 10 employs
injection unit 12 and molding unit 14. Injection
unit 12 feeds fluidized plastic material to nozzle
16 which injects the plastic material into mold 18.
Molding unit 14 comprises mold 18, fixed
platen 20 and movable platen 22. Hydraulic cylinder
24 moves platen 22 thereby opening and closing
mold 18. Tie rods 26 are used to guide movable
platen 22. Both injection unit 12 and molding
unit 14 are mounted on base 28.
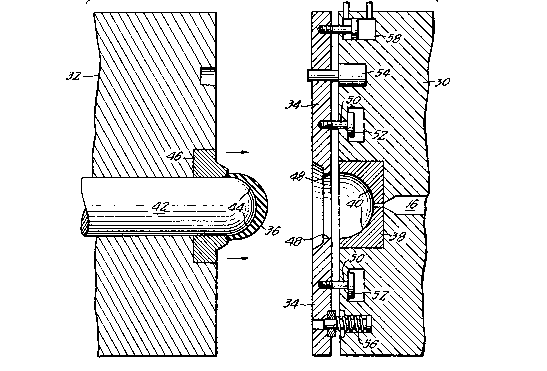
Mold 18 comprises fixed mold plate 30 which
is fixed to platen 20 and movable mold plate
32 which is fixed to movable platen 22. Positioned
between fixed mold plate 30 and movable mold
plate 32 is cavity stripper plate 34. Cavity
stripper plate 34 is movably fixed to fixed mold
plate 30. Although not shown, it is to be understood
that fixed mold plate 30 houses a plurality of
cup molds and that movable mold plate 32 houses
a plurality of mandrels which are registered
with the cup molds.
--4--
lZ~8Q4~
Fig. 2 is a cross-sectional view of mold
18 through a single closed cavity. Nozzle 16
extends into fixed mold plate 30 such that it
can inject the closed cavity with fluidized plastic
5 . material. The closed cavity is shown with molded
U-shaped article 36 therein.
Cup mold 38 is fixed inside mold plate 30.
Effective cup mold inner surface 40 defines a
portion of the boundary of the closed cavity
in which molded U-shaped article 36 is formed.
Mandrel 42 is fixed on movable mold plate 32
and effective mandrel outer surface 44 defines
another portion of the boundary of the closed
cavity in which molded U-shaped article 36 is
formed. Ejector 46 is movably fixed in movable
mold plate 32. Ejector 46 operates in a conventional
manner to push molded U-shaped article 36 off
of mandrel 42 when mold 18 is opened and once
molded U-shaped article 36 is clear of cup mold
38 and cavity stripper plate 34. A bore through
cavity stripper plate 34 is in registration with
cup mold 38 and mandrel 42 such that bore wall
48 also defines a portion of the boundary of
the closed cavity in which molded U-shaped article
36 is formed.
~298049
Cavity stripper plate 34 is movably attached
to fixed mold plate 30 by means of bolts 50.
Heads 52 of bolts 50 ensure that cavity stripper
plate 34 moves a set distance from fixed mold
plate 30. Good results are obtained when the
distance that cavity stripper plate 34 moves
from fixed mold plate 30 is about 0.5 cm. Guide
pin 54 is used to aid in aligning cavity stripper
plate 34 during its movements.
To urge cavity stripper plate 34 away from
fixed mold plate 30, compression spring means
56 is positioned in fixed mold plate 30 and applies
a force against cavity stripper plate 34 such
that when mold 18 is opened, cavity stripper
plate 34 is forced to move away from fixed mold
plate 30 until the movement of cavity stripper
plate 34 is halted by bolts 50. Any compression
spring means can be used, such as a compression-
type helical spring or a hydraulic means, which
is coordinated to push cavity stripper plate
34 away from fixed mold plate 30 for a fixed
distance at the same time as mold 18 is opened
and movable mold plate 32 moves away from fixed
mold plate 30. Good results are obtained with
~2~804g
--7--
a Bellville spring that provides about 1900 pounds
of pressure to cavity stripper plate 34. Thus,
cavity stripper plate 34 follows movable mold
plate 32 a short distance upon initial opening
of the mold and is then halted by bolts 50.
When closing mold 18, good results are obtained
by first joining cavity stripper plate 34 to
fixed mold plate 30 and then moving movable mold
plate 32 to fully close mold 18 and form a closed
cavity.
In order to join cavity stripper plate 34
to fixed mold plate 30, conventional mechanical
means 58 is employed. Mechanical means 58 is
a conventional hydraulic cylinder arrangement.
The surface area of bore wall 48 is less
than the surface area of effective mandrel outer
surface 44 and preferably the surface area of
bore wall 48 is about one half the size of the
surface area of effective mandrel outer surface
44. Good results are obtained with bore wall
48 having a surface area about one fourth that
of the surface area of effective mandrel outer
surface 44.
lZ~8049
--8--
The method of operation of the present invention
will now be described with reference to Figs.
3 and 4. Fig. 3 illustrates a portion of mold
18 just as it starts to open. Compression spring
means 56 urges cavity stripper plate 34 to follow
movable mold plate 32 as it moves away from fixed
mold plate 30. At this point in time, cavity
stripper plate ~34 abuts movable mold plate 32
and has moved away from fixed mold plate 30.
Due to the mechanical interference exerted
by bore wall 48 on molded U-shaped article 36
during opening of mold 18, molded U-shaped article
36 sticks to mandrel 42 and not to cup mold 38.
The distance which cavity stripper plate 34 moves
in abutment with movable mold plate 32 is such
that molded U-shaped article 36 is broken loose
from cup mold 38.
Fig. 4 illustrates the portion of mold 18
shown in Fig. 3 at a point in time subsequent
to that shown in Fig. 3. Movable mold plate
32 is still moving away from fixed mold plate
30. In Fig. 4 cavity stripper plate 34 is not
moving. In order to remove molded U-shaped article
~2~80~9
g
36 from mandrel 42, ejector 46 pushes molded
U-shaped article off of mandrel 42 and, due to
the force of gravity, molded U-shaped article
36 falls free of mold 18. Once mandrel 42 is
clear, mold 18 is closed and fluidized pl~stic
material is injected into the closed cavity formed
by mandrel 42, cavity stripper plate 34 and cup
mold 38.
To assist cavity stripper plate 34 to strip
molded U-shaped article 36 from cup mold 38,
mandrel 42 can be tapered at the base where the
ejector 46 meets mandrel 42. This tapering aspect
of mandrel 42 is conventional. Alternatively
or additionally, the base of mandrel 42 is groove
60 to assist in stripping molded U-shaped article 36
from cup mold 38. Fig. 5 illustrates mandrel
42 with groove 60. Preferably, mandrel 42 has
groove 60.
Cavity stripper plate 34 is illustrated
as a plate having a bore therethrough that is
in registration with mandrel 42 and cup mold
38. Cavity stripper plate 34 can also be an
individual ring which is in registration with
cup mold 38 and mandrel 42. In the employment
_g_
` 12g8049
--10--
of such cavity stripping rings, the number of
rings equals the number of mandrels and cup molds.
Alternatively, cavity stripper plate 34 can comprise
diametrically opposed hands that partially encircle
.the base of molded ~-shaped article 36. Thus,
instead of a closed ring, these hands merely
apply a mechanical interference to a portion
of the base of the molded article.
The present invention discloses cup mold
38 affixed to and cavity stripper plate 34 movably
affixed to fixed mold plate 30 and mandrel 42
affixed to movable mold plate 32. Obviously,
mandrel 42 could be fixed to fixed mold plate
30 and cup mold 38 and cavity stripper plate
34 could be part of movable mold plate 32. In
such a case, the present invention would function
in the same manner except the direction of movement
would change with respect to the plates 30, 32
and 34.
It will be understood that the claims are
intended to cover all changes and modifications
of the preferred embodiments of the invention,
herein chosen for the purpose of illustration,
which do not constitute a departure from the
spirit and scope of the invention.
--10--