Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
13~120~
FL U I D OPERATE D CLAMP I NG DEV I CE
INCLUDING FLUID PRESSURE
LOCK I NG MEANS
F I ELD OF THE I NVENT I ON
The invention relates to pneumatically
operated clamping and gripping devices for engaging a
workpiece and more particularly to such apparatus
including means for selectively locking the air in a
pneumatic cylinder of a clamping or gripping device.
BACKG_OUND TO PRIOR ART
U.S. patent 4,576,367, issued March 18,
1986, to Horn et al. and assigned to the assignee of
the present invention illustrates a pneumatically
operated clamp of the type for use in industrial
applications and for use, for example, in securing a
workpiece in place during a machining, grinding,
fabrication, assembly or welding operation. Such
clamps generally include a clamp member autornatically
moveable between a workpiece clamping position and a
release position. They also include a pneumatic
cylinder for causing such movement of the clamp
member and eor maintaining a clamping force on the
clamp member when the clamp member is in a clamping
~301Z04
position. Similar apparatus are used in conveying
assemblies as gates for selectively stopping movement
of conveyed articles. Attention is also directed to
prior art apparatus for selectively locking or
controlling fluid flow in a hydraulic or pneumatic
circuit. Such apparatus is illustrated in the U.S.
Kepner Patent No. 2,959,188, issued November 8, 1960;
the U.S. Kepner Patent 3,335,750, issued August 15,
1967; U.S. Kaetterhenry Patent 4,018,136, issued
April 19, 1977; and the U.S. Panis Patent 3,975,987,
issued August 24, 1976. Attention is also directed
to the U.S. Gerulis Patent 4,192,338, issued March
11, 1980; the U.S. Bobnar Patent 4,172,582, issued
October 30, 1979; the U.S. Bitonti Patent 3,980,336,
issued September 14, 1976; the U.S. Martin Patent
3,817,154, issued June 1~, 1974; the U.S. Parrett et
al Patent 3,792,715, issued February 19, 1974; the
U.S. Reith Patent 4,531,449, issued July 30, 1985;
and the U.S. Bingel Patent 3,229,721, issued January
18, 1966.
Prioe art locking valve cartridges for
use in connection with a fluid cylinder and for
preventing discharge of fluid pressure from the
cylinder are illustrated in a catalog titled
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Check and Relief Check
Valves, issued by Kepner Products Company, Villa
Park, Illinois.
Z04
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an
improved apparatus for engaging a workpiece or
article, the apparatus having a pneumatic cylinder
assembly with an improved means for selectively
locking air in the pneumatic cylinder to thereby
maintain the apparatus in engagement with the
workpiece. More particularly, the invention includes
an improved apparatus for engaging a workpiece or
article and including a pneumatic cylinder assembly
having a valve assembly for selectively permitting
exhaust of air ~rom the pneumatic cylinder and for
locking the air in the pneumatic cylinder in the
event of loss of air pressure in the supply conduit
supplying air pressure to the cylinder.
The apparatus embodying the invention
includes a base, a workpiece or article engaging
member supported by the base for shiftable movement
between a workpiece engaging position and a workpiece
release position, and means for causing selective
movement of the workpiece engaging member between the
workpiece engaging position and the workpiece release
position, the means for causing selective movement
including a pneumatic cylinder and a piston housed in
the cylinder, the piston being connected to the
workpiece engaging member such that movement of the
piston in a first direction causes movement of the
workpiece engaging member to the workpiece engaging
~L~OlZO~
--4--
position and movement of the piston in an opposite
direction causes movement of the workpiece engaging
member to a release position. The apparatus also
includes means for supplying air pressure to the
cylinder including means for selectively locking air
in the cylinder in the event the supply of air
pressure to the cylinder is interrupted.
In one embodiment of the invention the
means for selectively locking air in the cylinder
includes a valve bore, the first portion of the valve
bore being in communication with the source of air
pressure, and a second portion of the valve b~re
being in communication with end valve bore
communicating with one end of the cylinder whereby
air can be supplied to the cylinder to cause movement
of the piston in the first direction, a valve seat
between the first portion of the valve bore and the
second portion of the valve bore, a valve member
selectively engageable with the valve seat, and means
for resiliently biasing the valve member against the
valve seat to releasably prevent air flow from the
air pressure source to the first end of the cylinder.
In one embodiment of the invention the
valve bore is formed in the cylinder base.
In one embodiment of the invention
means are provided for forcing the valve member away
from the valve seat and including a valve cylinder
and a plunger housed in the cylinder, one end of the
130~ZO~L
s--
plunger being adapted to selectively engage the valve
member to force the valve member away from the valve
seat and an opposite end of the plunger piston, and
means for providing fluid communication between the
opposite end of the clamp cylinder and the valve
cylinder to provide for air pressure on the plunger
to force the plunger into engagement with the valve
member.
In one embodiment of the invention the
valve bore has a longitudinal axis colinear with the
valve cylinder longitudinal axis.
In one embodiment of the invention
means are also provided for manually forcing the
valve member away from the valve seat and including a
pin having opposite ends, one end of the pin being
adapted to engage the plunger to force the plunger
against the valve member to move the valve member
away from the valve seat, the pin including an
opposite end positioned so as to be adapted to be
manually engaged whereby the pin can be ~orced
against the plunger to cause the plunger to move the
valve member away from the valve seat.
Various features and advantages of the
invention will be apparent by reference to the
following description of a preferred embodiment, from
the drawings and from the claims.
~;~012~4
--6--
BRIEF DESCRIPTIO~S OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure l is an elevation view of a
fluid pressure operated clamp apparatus embodying the
invention.
Figure 2 is an enlarged partial view of
apparatus shown in Figure l and with portions broken
away.
Figure 3 is a cross section view taken
along line 3-3 in Figure 2.
Figure 4 is a view taken along line 4-4
in Figure 2.
Figure 5 is a reduced schematic view
illustrating fluid pressure control apparatus for
controlling operation of the fluid cylinder shown in
Figs. 1-4.
Figure 6 is a view similar to Figure 3
and showing an alternative embodiment of the
invention.
Figure 7 is a view similar to Figure 2
and showing another alternative embodiment of the
invention in cross section.
Before describing a preferred
embodiment of the invention in detail, it is to be
understood that the invention is not limited to the
details of construction and to the arrangement of the
components set forth in the following description or
illustrated in the drawings. The invention is
capable of other embodiments and of being practiced
1301~4
--7--
and carried out in various ways. Also, it is to be
understood that the phraseology and terminology
employed herein is for the purpose of description and
should not be regarded as limiting.
DESCRIPTION OF A PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
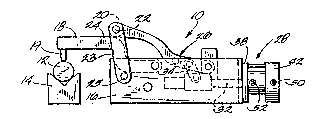
Illustrated in Figure 1 is a clamp
assembly 10 ~or use in selectively securing a
workpiece 12 in place in a fixture 14. The clamp
assembly includes a frame 16 and a pivotably moveable
clamp member 18 supported for pivotal movement
between a clamping position, shown in Fig. 1, wherein
an end 19 of the clamp member 18 clampingly engages
the workpiece 12, and a second position (not shown)
wherein the workpiece 12 is released. While in the
illustrated arrangement, the apparatus embodying the
invention includes a single moveable clamp member 18
for securing a workpiece to the fixture 14, in other
arrangements, the apparatus could have one or more
moveable workpiece engaging members and could
comprise an apparatus for clamping a workpiece
against a fixed workpiece support or an apparatus for
gripping and moving a workpiece from one work station
to another.
In the construction shown in Figure 1,
means are also provided for causing movement of the
clamp member 18 between the clamping position and the
release or retracted position. This means includes a
~30~204
--8--
roller 20 supported on a shaft 22 and adapted to engage
in upper surface 24 of the clamp member 18. The shaft
22 is supported by the upper ends of a pair of
pivotable links 23, the lower ends of the links 23
being pivotally joined to the frame 16 by pins 25. A
toggle linkage 26 having an end connected to the roller
20 is provided for causing movement of the roller 20
into engagement with the upper surface 24 of the clamp
member. The construction and operation of the toggle
assembly 26 and the clamp member 18 are illustrated and
described in greater detail in applicant's U.S. Patent
~,576,367.
The means for causing clamping movement of
the clamp member 18 also includes a pneumatic cylinder
assembly 28 fixed to the frame 16 and including a
reciprocating piston 30 (Fig. 2) having an end 32
connected by means of a link 34 to the toggle assembly
26. In operation of the pneumatic cylinder assembly,
when the piston 30 is extended, the toggle mecharli3m 26
will force the clamp member 1~ lnto a clamping
position. When the piston 30 is retracted, the toggle
mechanism 26 will move the clamp member 18 to the
retracted or workpiece release position.
In the specific construction shown in the
drawings, the pneumatic cylinder assembly 28
sd/~,~
1~01204
g
includes a cylinder head 38 adapted to be secured to
the frame 16 of the clamp device, a cylinder 40 and a
cylinder base 42. The piston 30 is housed in the
cylinder 40, and the piston rod 32 projects through
the cylinder head 38 and includes an end connected to
the link 34 of the toggle mechanism 26 in such a
manner that extension of the piston 30 in the
cylinder 40 to the position shown in Figure 2 will
cause clamping movement of the clamp member 18, and
retraction of the piston 30 will cause movement of
the clamp member 18 to a release position.
Means are also provided for selectively
supplying fluid pressure to the opposite ends of the
fluid cylinder 28 to selectively cause extension and
retraction of the piston 30. This means for
supplying fluid pressure is best illustrated in Figs.
2-5 and includes a fluid supply line 46 operably
connected through a 4-way valve 48 to an advance port
50 and to a return port 52. As will be described in
greater detail hereina~ter, the advance port 50
supplies fluid to the cylinder 40 to cause advance of
the piston 30, and the return port 52 will
alternatively provide fluid under pressure to the
opposite end of the cylinder 40 to effect return of
the piston.
As illustrated in Fig. 3, the cylinder
base includes a valve bore 56 including a valve seat
58. Fluid entering the advance port 50 will flow
1301204
-lQ-
through a passage 54 into the valve bore 56, past the
valve seat 58 and through a passage 60 to the advance
end of the cylinder~ Means are also provided for
permitting flow of fluid from the advance port 50
into the advance end of the cylinder 40 but
selectively locking the fluid in the advance end of
the cylinder. In the illustrated arrangement the
means for selectively locking the fluid in the
advance end of th,e cylinder 40 includes a ball valve
62 housed in the valve bore 56 for movement toward
and away from a position wherein the ball 62 engages
the valve seat 58. The locking means also includes a
compression spring 66 housed in the valve bore 56 and
engaging the ball 62 to bias the ball into engagement
with the valve seat 58. An opposite end of the
compression spring is supported by a plug 68 fixed in
place in the end of the bore 56.
In operation of the valve assembly,
when the air or Eluid pressure in the passage 54 is
greater than the air pressure in the advance side of
the cylinder 40, the pressure in the passage 54 may
force the ball 62 away from the valve seat 58 against
the force of the spring 66 to permit fluid flow into
the advance end Oe the cylinder 40. If, on the other
hand, the fluid pressure in the advance end of the
cylinder 40 is greater than that in the advance port
50, the ball 62 will be forced against the valve seat
58 by the fluid pressure in the advance end of the
1301204
cylinder and by the pressure of the spring 66 on the
ball.
This construction provides a positive
means for locking the piston 30 in position despite
any sudden loss of fluid pressure in the supply line
46. One of the principal features of the invention
is that in the event of a loss of fluid pressure in
the supply line 46, there is no significant loss of
fluid pressure in the advance end of the cylinder 40
and the locking force of the cylinder assembly 28 on
the clamp arm 18 remains sufficiently high that the
workpiece 12 is firmly held in position. For
example, if there is air pressure in the advance end
of the cylinder 40 applying a clamping force on the
clamp member 18, in the event of a rupture of the air
line 46 connected to the cylinder or some other
failure causing an immediate loss of air pressure in
the air pressure source, the air pressure in the
fluid cylinder 40 will be locked in the cylinder and
the clamping force on the workpiece 12 will be
maintained.
Means are also provided eor selectively
forcing the ball 62 away from the valve seat 58 to
permit discharge of air from the advance side of the
cylinder 40 and movement of the piston to the return
position. In the arrangement shown in Figs. 2-4, a
plunger 70 is housed in an end portion 72 of the
valve bore 56 in the cylinder base 42 and includes an
1~0120~
end engageable with the ball 62 to force the ball
away from the valve seat 58 against the force of the
compression spring 66. A portion 74 of the valve
bore 56 defines a cylinder, and the plunger includes
an end portion 76 defining a piston. A fluid
pressure port 78 and an air line 80 provide fluid
communication between the return side of the cylinder
42 and the cylinder 74. In operation of the clamp
10, when the valve 48 is actuated to cause the
advance side of the cylinder 40 to be exhausted, air
pressure is supplied to the return side of the
cylinder. This air pressure is also supplied by air
line 80 to the port 78. The plunger 70 i5 then
forced against the ball 62 to force the ball away
from the valve seat 58 and to permit air to be vented
from the advance side of the cylinder past the valve
seat 58 through passage 54 and valve 48 to
atmosphere.
In the illustrated arrangement means
are also provided for permitting manual movement of
the ball 62 away from the valve seat 58 and release
of fluid pressure from the advance side of the
cylinder. In the illustrated construction this means
includes a manually operable release pin or second
plunger 82 housed in the plunger cylinder 74 and
including an end engageable with the piston head 76
of the plunger 70. The opposite end of the manually
moveable pin 82 comprises a piston head 84 sealing
~0120~
-13-
the end of the cylinder 74, and a plug 86 is fixed in
the end of the cylinder 74 to restrain the piston 84
against movement out of the cylinder 74. The piston
84 is located adjacent the periphery o~ the cylinder
base 42 and an operator can insert a tool through a
central aperture 85 in the plug 86 to apply pressure
on the manually moveable pin 82 to thereby force the
plunger 70 against the ball 62 and move the ball away
from the valve seat 58 to thereby release the fluid
pressure from the advance side of the cylinder and
permit release of the clamp member 18.
In a preferred eorm of the invention
illustrated in Figs. 1-4, the valve bore 56 and the
bore 72 and 74 housing the plunger 70 and the
manually moveable pin 82, respectively, have a common
longitudinal axis defining a chord extending through
the cylinder base 42. This arrangement provides a
construction which is conveniently machined and
facilitates assembly of the various valve components.
In operation o the clamp arrangement,
in the event of an air line failure, the locking
valve assembly will lock air in the advance end of
the pneumatic cylinder 40 and maintain the clamp
member 18 in a clamped position. In the event of
such a failure, it is often desirable to provide for
release of the workpiece to permit removal of the
workpiece and thereby facilitate commencement of a
new machining operation once the air line is
14-
repaired. The construction of the lockiny valve
assembly as illustrated in Figs. 1-4 facilitates
inclusion of the manually operable release plunger
82, and the provision of the manually operable
plunger 82, in turn, permits convenient release of
the clamp 18 and removal of the workpiece 12.
Illustrated in Fig. 6 is an alternative
embodiment of the apparatus described above in
connection with Figs. 2-4. In the illustration shown
in Fig. 6, the advance port 150 includes a check
valve lSl comprised of a valve seat 153, a ball 155
engageable with the valve seat 153 and a compression
spring 157 positioned so as to bias the ball 155
toward the valve seat 153. The advance port 150 is
connected by a passage 160 to the advance side of the
cylinder 140. Exhaust of fluid from the advance side
of the cy:Linder 140 is through a second check valve
161 and an exhaust passage 163. The second check
valve includes a valve seat 158, a ball L62
engageable with the valve sea~ 158 and a compression
spring 166 biasing the ball 16Z into engage~ent with
the valve seat 158.
Means are also provided for selectively
opening the exhaust valve 161 when fluid pressure is
supplied to the return side of the cylinder 40. This
means for opening the valve is similar in structure
and operation to the structure described above in
connection Figs. 2-4. A plunger 170 is housed in a
~01204
-15-
bore 172 and is engageable with the ball 162. Fluid
pressure from the return side of cylinder 1~0 is
supplied through a port 178 to a cylinder 174 housing
a piston end 176 of the plunger 170. Means are also
provided for permitting an operator to cause manual
movement of the plunger. This means includes a pin
182 having an end 184 accessible through a central
opening in a plug 186. The pin 182 also includes an
opposite end engageable with the piston end 175 of
the plunger 170 such the pin 182 can be used to force
the plunger 170 into engagement with the ball 162.
Illustrated in Fig. 7 is another
alternative embodi~ent of the invention and wherein a
shuttle valve 200 and poppet valve 202 are employed
to control the supply of air under pressure to the
clamp cylinder 240 and to lock the air pressure in
the advance side of the clamp cylinder 240 in the
event of a ~ailure of the air pressure source
supplying air to the air cylinder. In the
construction shown in Fig. ~, the cylinder base 24Z
includes a valve bore 256 having one end connected to
an air supply line 246. A second passage 260
provides fluid flow between the valve bore and the
advance side of the pneumatic cylinder 240. The
valve bore 256 includes a valve seat 258 between the
air supply line 246 and the second passage 260, and
the shuttle valve 200 is selectively engageable with
the valve seat 258 to control air flow past the valve
~30~2(34
-16-
seat. A compression spring 266 housed in the valve
bore 256 engages a pin 201 of the shuttle 200 to
resiliently bias the shuttle 200 against the valve
seat. The valve bore 256 also includes a second
Yalve seat 259 in spaced relation to the first valve
seat 258 and engaged by the shuttle 200 when the
spring 266 is compressed. The valve bore 256 also
includes a pressure reLief valve assembly 265
comprised of a third valve seat 267 in the valve bore
256 and the poppet valve 202 selectively ~ngageable
with the third valve seat 269. A compression spring
269 selectively biases the poppet valve 202 into
engagement with the third valve seat 267. In the
illustrated arrangement, the compression spring 266
is substantially smaller than the compression spring
269 such that a smaller axial force on the shuttle
200 is required to effect movement of the shuttle 200
than is required on the relief poppet 202 to cause
movement of the relief poppet 202 to an open
position.
In operation of the apparatus
illustrated in Fig. 6, when air pressure is supplied
to the advance port 50, the shuttle 200 will move
against the force of the spring 266 to an open
position and the shuttle will engage the valve seat
259. Air pressure will be supplied to the advance
side of the cylinder 240. In one common application,
the air pressure supplied to the advance side of the
~0~;~04
cylinder will be 80 psi. When the air pressure to
the advance port is interrupted and air pressure is
supplied to the return port 252 of the cylinder, the
compression spring 266 will move the shuttle 200 into
engagement with the valve seat 258. Air in the
advance side of the cylinder 240 can then force the
poppet 202 away from the valve seat 267 and to
thereby provide for exhaust of air from the advance
side of the cylinder to the atmosphere and permit
retraction of the piston 230.
In the event air pressure is being
supplied to the advance side of the cylinder 240 and
there is a sudden failure of the air pressure source,
the spring 266 will force the shuttle 200 against the
valve seat 258 to preclude exhaust of air through air
line 246 and poppet 202 will be forced into
engagement with the valve seat by the compression
spring 26'3. A portion of the air in the advance side
of the cy;Linder may be exhausted through the poppet
ie the air pressure on the poppet 202 exceeds the
eorce of t:he compression spring 2~9 on the poppet but
the poppet will lock the remaining air in the advance
side of the cylinder. In one form of the invention,
the compression spring 202 will apply sufficient
force on the poppet 202 to maintain a 40 psi pressure
in the advance side of the cylinder.
In other embodiments of the inventiGn
valve assemblies of the type described above can be
13C~2~
-18
operably connected to both ends of a pneumatic
cylinder so as to lock the piston in any selected
position and against movement in either direction.
Various features of the in~ention are
set forth in the following claims.