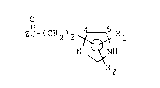Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
13lo96o
~his invention relates to novel compounds having useful
pharmacological properties, to pharmaceutical compositions
5 containing them, to a process and intermediates for their
preparation, and to their use as pharmaceuticals.
EP-A-242973 (Glaxo Group Limited) discloses a class of
indole derivatives which are 5-HT3 receptor antagonists.
EP-A-291172 (Glaxo Group Limited), published 17th November
1988, discloses a further group of 5-HT3 receptor
antagonists wherein the indole moi~ty is replaced by another
function, designated 'A' in formula (I) therein.
A class of novel, structurally dis~inct compounds has now
been discovered which compounds have 5-HT3 receptor
antagonist activity.
20 Accordingly, the present inventlon provides a compound of
formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acc-ptaoie salt Lhe~eof:
ZC-(CH2)2 ~ R
N ~ NH
R2 (I)
30 wherein
R1 and R2 are independently hydrogen or C1_6 alkyl;
Z is a group of su~-formula (a), (b), (c) or td):
Z~
1310960
R (a)
R6 R4
X NH-
~( OR7 (b)
2 s X ( c )
~ (d)
Rlo g
131096~
01 _ 3 _
02 wherein
03 xa to Xd are selected from hydrogen, halogen and
04 hydroxy;
05 R3 is hydrogen and R4 is hydrogen or Cl_6 alkyl, or R3
06 and R4 together are a bond;
07 Rs to Rlo are independently selected from hydrogen or
08 C1_6 alkyl; and R6 together with R4 may be C2_7
09 polymethylene when R3 is hydrogen, or R g and
Rln may together be C2_7 polymethylene.
11
12 Examples of moieties in alkyl or alkyl containing
13 groups in Rl, R2 and R4 to R10 include methyl, ethyl,
14 n- and iso-propyl, n-, iso-, sec- and tert-butyl,
preferably methyl.
16
17 Suitable examples of R4 and R6 or Rg and R1o when
18 joined include C2, C3, C4, C5 or C6 polymethylene,
19 preferably C2, C3, C4 or C5 polymethylene.
21 xa to Xd are preferably selected from hydrogen, fluoro,
22 chloro and hydroxy, most preferably hydrogen.
23
24 Preferably the ZC0-~CH2)2- moiety is attached to the
imidazole ring at the 4-position. Preferably R1 is
26 hydrogen or methyl, attached at the 5-position and R2
27 is hydrogen.
28
29 When Z is of sub~formula (a), R3 and R5 are preferably
both hydrogen and one or both R4 and R6 (most
31 preferably both) are alkyl groups, such as methyl, or
32 are ~olned to form C2_7 polymethylene.
33
34 When Z is of sub-formula (b), R7 is preferably methyl.
36 When Z is of sub-formula (c)~ one of C0-(CH2)2- and R8
37 is attached at the 1-position and the other is attached
38 at tlle 3-position as depicted in sub-formula (C), and R8 is
~ preferably methyl or ethyl.
13~6Q
When Z is of su~-formula (d), one or both of Rg and R1o
(most preferably both) are alkyl groups, such as methyl or
are joined to form C2_7 polymethylene.
s The pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds of
the formula (I) include acid addition salts with
conventional acids such as hydrochloric, hydrobromic, boric,
phosphoric, sulphuric acids and pharmaceutically acceptable
organic acids such as acetic, tartaric, lactic, maleic,
o citric, succinic, benzoic, ascorbic, methanesulphonic,
a-keto glutaric, ~-glycerophosphoric, and
glucose-1-phosphoric acids.
The pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds of
5 the formula (I) are usually acid addition salts with acids
such as hydrochloric, hydrobromic, phosphoric, sulphuric,
citric, tartaric, lactic and acetic acid.
Preferably the acid addition salt is the hydrochloride salt
Examples of pharmaceutically acceptable salts include
quaternary derivati~es of the compounds of formula (I) such
as the compounds quaternised by compounds Ra-T wherein Ra is
Cl_6 alkyl, phenyl-C1_6 alkyl or C5_7 cycloalkyl, and T is a
25 radical corresponding to an anion of an acid. Suitable
examples of Ra include methyl, ethyl and n- and iso-propyl;
and benzyl and phenethyl. Suitable examples of T include
halide such as chloride, bromide and iodide.
30 Examples of pharmaceutically acceptable salts of compounds
of formula (I) also include internal salts such as
pharmaceutically acceptable N-oxides.
The compounds of the formula (I), their pharmaceutically
35 acceptable salts, (including quaternary derivatives and
131~ 0
01 N-oxi~es) may also form pharmaceutically acceptable
02 solvates, such as hydrates, which are included wherever a
03 compound of formula (I) or a salt thereof is herein referred to.
05
06 It will of course be realised that some of the
07 compounds of the formula (I) have chiral or prochiral
08 centres and thus are capable of existing in a number of
09 stereoisomeric forms including enantiomers. The
invention extends to each of these stereoisomeric forms
11 (including enantiomers), and to mixtures thereof
12 irlcludin~ racemates. The different stereoisomeric
13 forms may be separated one from another by the usual
14 methods.
16 It will be appreciated that the imidazole ring in
17 formula ~I) can exist as tautomers i.e. the hydrogen
18 atom can be on either of the imidazole nitrogen atoms.
19 The invention extends to both tautomers and mixtures
thereof.
21
22 The invention provides process for the preparation of a
23 compound of formula (I) wherein Z is of formula (a) or
24 (b), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof,
which process comprises reacting a compound of formula
26 (II):
27
28 ZlH (II)
29
31
32
33
34
36
~ 3 ~ 0
01 - 6 -
02 wherein zl is of sub-formula (a) or (b), with a
03 compound of formula ( III ):
04
05
06 O
08 ~C-(CH2)2 ~ R
09 ~IH
R2
11 (III)
12
13 wherein Q is a leaving group and the remaining
14 variables are as deflned in formula (I); and thereafter
lS optionally forming a pharmaceutically acceptable salt
16 thereof.
17
18 Examples of leaving groups Q, displaceable by a
19 nucleophile, include halogen such as chloro and bromo;
Cl_4 alkoxy, such as CH30 and C2H5O-; PhO-;
21 activated hydrocarbyloxy, such as C15C6O- or C13CO-;
22 succinimidyloxy; and imidazolyl. Preferably Q is
23 halogen, most preferably chloro.
24
If a group Q is a halide or imidazolyl, then the
26 reaction is preferably carried out at non-extreme
27 temperatures in an inert non-hydroxylic solvent, such
28 as benzene, dichloromethane, toluene, diethyl ether,
29 tetrahydrofuran ~THF) or dimethylformamide (DMF). It
is also preferably carried out in the presence of an
31 acid acceptor, such as an organic base, in particular a
32 tertiary amine, such as triethylamine, trimethylamine,
33 pyridine or picoline, some of which can also function
34 as the solvent. Alternatively, the acid acceptor can
be inorganic, such as calcium carbonate, sodium
36 carbonate or potassium carbonate. Temperatures of
37 0-100C, in particular 10-80C are suitable.
38
~2 ~
~S~IJ~O
01 ~ 7 ~
02 If a group Q is Cl_4 alkoxy, phenoxy, activated
03 hydrocarbyloxy or succinimidyloxy then the reaction is
04 preferably carried out in an inert solvent, such as
05 toluene or dimethylformamide. In this instance, it is
06 preferred that the group Q is C13CO- or succinimidyloxy
07 and that the reaction is carried out in toluene at
08 reflux temperature.
09
When the compound of formula (III) has an imidazolyl NH
11 moiety wherein Rl/R2 is hydrogen, adjacent to the point
12 of attachment of the QCO(CH2)- group, the compound of
13 formula (III) may be of formula (III)':
14
~1
16 N/
18 ~ N ~
19 R2 (III)'
21 i.e. a cyclic anhydride.
22
23 The conditions for this reaction are similar to those
24 used when Q is C1_4 alkoxy.
26 The present invention also provides a process for the
27 preparation of a compound of formula (I) wherein Z is
28 of sub-formula (c) or (d) or a pharmaceutically
29 acceptable salt thereof, which process comprises
reacting a compound of formula tIV):
31
32 Z2COCH3 (IV)
33
34 wherein z2 is of sub-formula (c) or (d)
with a compound of formula (V):
36
1 310~0
01 -- 8 --.
02
0 3 0
05 HC ~ R
06 V~
P' 2 ( V )
0`8
09 in the presence of a base (Claisen-Schmidt) reaction
followed by reduction of the resulting compound of
11 formula ~VI):
12
13 o
145 Z CCH--CH ~ R
16 N ~NH
17 R2
18 (VI )
19
wherein the variable groups are as deflned in formula
21 (I); and thereafter optionally forming a
22 pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
23
.24 The Clalsen Schmidt reaction takes place in the
presence of a base, preferably containing alkoxide or
26 hydroxide ion, for example sodium hydroxide in ethanol
;27 as solvent, at ambient temperature.
28
.29 The reduction is preferably carried out by catalytic
hydrogenation using hydrogen-platinium although it may
31 also be carried out using reducing agents, such as
32 sodium borohydride in pyridine.
33
34 It will be appreciated that these reduction conditions
Will probably also reduce the carbonyl group in formula
36 (VI) and therefore it will be necessary to oxidise the
T~ .
D~3
1 3 ~
01 -- 9 --
02 resulting alcohol using a appropiate oxidising agent,
03 such as sodium dichromate.
04
05 Alternatively, the reduction may be carried out using
06 sodium borohydride in methanol, which reduces only the
07 carbonyl group in formula (VI); the resulting a~
OB unsaturated alcohol is then heated under reflux in
09 ethanolic potassium hydroxide to produce the rearranged
product of formula ~I).
11
12 The compounds of formula (II), ~III), (IV~ and (V) are
13 known or are prepared analogously to, or routinely
14 from, known compounds.
16 As regards zl and z2 in the compounds of formulae (II) and
17 (IV), reference is hereby made to the following:
18
19 ~a) ~P-A-297266
21 (b) E~-A-235878
22
23 ~C) EP-A-255297 and EP-A-289170.
24
26 (e) UK Patent 2125398 and EP-A-289170
27
.2~
.,~ g
31 (All European Patent References are in the name of
32 seecham Group p.l.c.).
33
34 Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds of
this invention may be formed conventionally. The acid
36 addition salts may be formed for example by reaction of
37 the base compound of formula (I) with a
~,
1310~0
01 - 10 -
02 pharmaceutically acceptable organic or inorganic acid.
03
04 The compounds of the present invention are 5-HT3
05 receptor antagonists and it is thus believed may
06 generally be used in the treatment or prophylaxis of
07 emesis, migraine, cluster headaches, trigeminal
08 neuralgia and visceral pain. Compounds which are 5-HT3
09 antagonists may also be of potential use in the
treatment of CNS disorders such as anxiety and
11 psychosis; drug withdrawal syndrome; arrhythmia;
12 obesity and gastrointestinal disorders such as
13 irritable bowel syndrome.
14
Antiemetic activity includes in particular that of
16 preventing cytotoxic agent or radiation induced nausea
17 and vomiting. Examples of cytotoxic agents include
18 cisplatin, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide.
19
The invention also provides a pharmaceutical
21 composition comprising a compound of formula (I), or a
22 pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and a
2 3 pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
24
Such compositions are prepared by admixture and are
26 suitably adapted for oral or parenteral administration,
27 and as such may be in the form of tablets, capsules,
28 oral liquid preparations, powders, granules, lozenges,
29 reconstitutable powders, injectable and infusable
solutions or suspensions or suppositories. Orally
31 administrable compositions are preferred, since they
32 are more convenient for general use.
33
34 Tablets and capsules for oral administration are
usually presented in a unit dose, and contain
36 conventional excipients such as binding agents,
37 fillers, diluents, tabletting agents, lubricants,
38 disintegrants, colourants, flavourings, and wetting
B-~
~31~0
. 0 1 ~
~02 agents. The tablets may be coated according to well
03 known methods in the art, for example with an enteric
04 coating.
05
06 Suitable fillers for use include cellulose, mannitol,
07 lactose and other similar agents. Suitable
08 disintegrants include starch, polyvinylpolypyrrolidone
og and starch derivatives such as sodium starch
glycollate. Suitable lubricants include, for example,
11 magnesium stearate.
12
13 Suitable pharmaceutlcally acceptable wetting agents
14 include sodium lauryl sulphate. Oral liquid
preparations may be in the form of, for example,
16 aqueous or oily suspensions, solutions, emulsions,
17 syrups, or elixirs, or may be presented as a dry
lB product for reconstitution with water or other suitable
19 vehicle before use. Such liquid preparations may
contain conventional additives such as suspending
21 agents, for example sorbitol, syrup, methyl cellulose,
22 gelatin, hydroxyethylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose,
23 aluminium stearate gel or hydrogenated edible fats,
24 emulsifying agents, for example lecithin, sorbitan
monooleate, or acacia; non-aqueous vehicles (which may
26 include edible oils)~ for example, almond oil,
27 fractionated coconut oil, oily esters such as esters of
28 glycerine, propylene glycol, or ethyl alcohol;
29 preservatives, for example methyl or propyl
p-hydroxybenzoate or sorbic acid, and if desired
31 conventional flavouring or colouring agents.
32
33 Oral liquid preparations are usually in the form of
34 aqueous or oily suspensions, solutions, emulsions,
syrups, or elixirs or are presented as a dry product
36 for reconstitution with water or other suitable vehicle
37 before use. Such liquid preparations may contain
~2
)
~10~3
01 - 12 -
02 conventional additives such as suspending agents,
03 emulsifying a~ents, non-aqueous vehicles (which may
04 include edible oils), preservatives, and flavouring or
05 colouring agents.
06
07 The oral compositions may be prepared by conventional
08 methods of blending, filling or tabletting. Repeated
09 blending operations may be used to distribute the
active agent throughout those compositions employing
11 large quantities of fillers. Such operations are, of
12 course, conventional in the art.
13
14 For parenteral administratlon, fluid unit dose forms
are prepared containing a compound of the present
16 invention and a sterile vehicle. The compound,
17 depending on the vehicle and the concentration, can be
18 either suspended or dissolved. Parenteral solutions
19 are normally prepared by dissolving the compound in a
vehicle and filter sterilising before filling into a
21 suitable vial or ampoule and sealing. Advantageously,
22 ad~uvants such as a local anaesthetic, preservatives
23 and buffering agents are also dissolved in the
24 vehicle. To enhance the stability, the composition can
be frozen after filling into the vial and the water
26 removed under vacuum.
27
28 Parenteral suspensions are prepared in substantially
29 the same manner except that the compound is suspended
in the vehicle instead of being dissolved and
31 sterilised by exposure of ethylene oxide before
32 suspending in the sterile vehicle. Advantageously, a
33 surfactant or wetting agent is included in the
34 composition to facilitate uniform distribution of the
compound of the invention.
36
37 The invention further provides a method of treatment or
!IB '
~lQ~
01 - 13 -
02 prophylaxis of emesis, migraine, cluster headache,
03 trigeminal neuralgia, visceral pain, gastrointestinal
04 disorders and/or CNS disorders in mammals, such as
05 humans, which comprises the administration of an
06 effective amount of a compound of the formula (I) or a
07 pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
08
09 An amount effective to treat the disorders herein-
before described depends on the relative efficacies of
11 the compounds of the invention, the nature and severity
12 of the disorder being treated and the weight of the
13 mammal. However, a unit dose for a 70kg adult will
14 normally contain 0.05 to lOOOmg for example 0.1 to
500mg, of the compound of the invention. Unit doses
16 may be administered once or more than once a day, for
17 example, 2, 3 or 4 times a day, more usually 1 to 3
18 times a day, that is in the range of approximately
19 0.0001 to 50mg/kg/day, more usually 0.0002 to 25
mg/kg/day.
21
22 No adverse toxicological effects are indicated at any
23 of the aforementioned dosage ranges.
24
The invention also provides a compound of formula (I)
26 or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof for use
27 as an active therapeutic substance, in particular for
28 use in the treatment of emesis, migraine, cluster
29 headache, trigeminal neuralgia, gastrointestinal
disorders and/or CNS disorders.
31
32 The following Examples illustrate the invention.
33
~S
~,. ~1
1 3 ~
01 - 14 -
02 Example 1
03
04 N-(3,3-Dimethylindolin-l-vl)-3-(4-imidazol~l)Propion-
05 amide monohvdrochloride (El
06
07
08 CIOCH2CH2
09 ~ N ~
~ N V NH
12 (El)
13
14 A suspension of 3-(4-imidazolyl)propionic acid
monohydrochloride (2.og) (Chem. Ber. 66, 156 [1933]) in
16 thionyl chloride (10ml) and DMF (3 drops) was stirred
17 at room temperature for 3h. The excess thionyl
18 chloride was removed by rotary evaporation and the
19 residue re-evaporated with 2 x 50ml of dry toluene.
The residue was suspended in CH2C12 (1o0ml) and a
21 solution of 3,3-dimethyl indoline (1.7g) and
22 triethylamine (4ml) in CH2C12 (50ml) was added with
23 stirring and cooling. The reaction mixture was stirred
24 overnight, washed with saturated NaHCO3 and the lower
organic layer dried ~Na2SO4). Concentration of the
26 organic extracts afforded the crude product which was
27 purified by column chromatography on silica, eluting
28 with CHC13 containing increasing quantities of
29 methanol. The title compound free base was converted
to the hydrochloride salt by standard procedures.
31 m.p. 226-8C.
32 lH Nmr (D6-DMSO) 6:
33 9.11 (s, lH)
34 8.15 (d, lH)
7.58 (s, lH)
36 7.36 (d, lH)
37 7.27 (t, lH)
~s'
131~6~
01 -15-
02 7.13 (t, lH)
03 3.99 (s, 2H)
04 3.05 (br.s, 4H)
05 1.40 (s, 6H)
06
07 Following the procedures outlined in Example 1, the
08 following compounds were prepared.
09
Examples 2 to 5
11
12 N-(3.3-DimethYlindolin-1-vl)-3-~5-methYl-4-imidazolYl)-
13 propionamide (E2)
14
16 COCH2CH2 CH3
7 ~ N NH
(E2)
21
22m.p. 151-3C
231H Nmr (CDC13) ~:
248.22 (d, lH)
257.42 (s, lH)
267.26-7.00 (m~ 4H)
273.71 ~s, 2H)
282.95 (t, 2Hj
292.71 (t, 2H)
302.20 ts, 3H)
311.31 (s, 6H)
32
~.~
0
-16~
02 N-(2-Methoxvphenyl)-3-(5-methyl-~-imidazolyl)propion-
03 amlde [E3)
04
05
0 6 NHCOCH 2CII 2 CH 3
og ¢~OCH
3 ~E3)
11
12 m.p. 149-151C
13 lH_Nmr ~d6-DMS0) 6
14 8.65 ~brs, lH)
8.13 ~d, lH)
16 7.37 ~s, lH)
17 7.05-6.80 ~m, 3H)
18 3.82 ~s, 3H)
19 ~ 2.84 (t, 2H)
2.71 (t, 2H)
21 2.13 (s, 3H)
22
23 N-(2-Methoxy~henyl)-3-~4-imidazolyl)propionamide (E4
24
26 /NHcocH2cH2
27 ~ ~ ~
28 ~ OC~I3 N~"NH
(E4)
31
3~ m.p. 98-9C.
33 lH Nmr (CDC13) 6:
34 8.32 (d, lH)
7.90 (brs, lH)
36 7.52 ~s, lH)
37 7 .10-6 . 80 ~m, 4H)
3.84 (s, 3H)
3.01 (t, 2H)
2.78 (t, 2H)
131~60
ol -17-
02 Pharmacoloqv
03
04 Antaqonism of the von Bezold-JarisCh reflex
05
06 The compounds were evaluated for antagonism of the von
07 sezold-Jarisch reflex evoked by 5-HT in the
08 anaesthetised rat according to the following method:
09
lo Male rats 250-350g, were anaesthetised with urethane
11 (1.25g/kg intraperitoneally) and blood pressure and
12 heart rate recorded as described by Fozard J.R. et al.,
13 J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2, 229-245 (1980). A
14 submaximal dose of 5-HT (usually 6yg/kg) was given
repeatedly by the intravenous route and changes in
16 heart rate quantified. Compounds were given
17 intravenously and the concentration required to reduce
18 the 5-HT-evoked response to 50% of the control response
lS (EDso) was then determined.
21 The results are as shown in Table 1.
22
23 Table 1
24
ComPound ED~n ~q/k~ i.v.
26
27 E1 4.2
28
æ~
I