Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
FIELD OF THE INVENTION ~ 3 ~ ~ 74 7
This invention relates to an apparatus and method for
re~oving fluid from a fibrous web. More particularly, this
invention relates to an apparatus and method in which a formed
web is subjected for an extended period to increased pressure
and temperature such that fluid within the web is removed.
INFORMATION DISCLOSURE STATEMENT
In the papermaking art, as much water as possible is
removed from the formed web in the pre~s section because
mechanical removal of fluid at this stage is more economical
than subsequent removal of fluid in the drying section of the
papermaking machine.
In copending Canadian patent application No. 541,259,
filed ~uly 3, 1987, so-called "high temperature pressing
apparatus and method" is disclosed in which the paper web is
subjected to a press drying operation for removing most of the
water from the fibrous web. The high temperature pressing
technique involves the application of high temperatures and
pressure to the paper web for an extended period of time. In
one embodiment of the high temperature pressing (HTP) process,
the web to be dried extends through a press which includes
JL 3 ~ ~ 7 ~ ~
an elongate shoe and a cooperating backiny roll. A
blanket extends, together with the web, through a pressing
section defined between the shoe and the backing roll (or
pressing member). The pressing member is inductively, or
otherwise, heated such that during passage of the web
through the pressing section, fluid within the web is
vaporized to force fluid remaining in the liquid phase
away from the web.
Because of the very high temperatures employed in the
aforementioned HTP process coupled with the extremely high
pressures, delamination of the formed web has been
experienced Such delamination occurs primarily as the
result of the rapid evolution of vapor within the pressing
section with such vapor blowing the web apart as the web
exits from the pressing section.
The present invention seeks to overcome the afore-
mentioned problem by providing the peess member (or
backing roll) with a porous layer such that the high
pressure vapor within the pressing section diffuses into
the porous layer. Additionally, the porous layer tends to
reduce thermal transfer between the press member and the
web which further inhibits delamination of the pressed
~eb
Therefore, it is a primary objective of the present
invention to overcome the aforementioned problems associ-
ated with the aforementioned press drying apparatus and
techniques and to provide an apparatus and method which
contributes significantly to the press drying art.
Another object of the present invention is the
provision of an apparatus for removing fluid from a
fibrous web in which the press member defines a pressing
surface which is porous.
--2--
13~7~7
Another object of the present invention is the
provision of an apparatus for ~ernoving fluid from a
fibrous web in which the press member includes a first and
a second coaxial layer with the second coaxial layer
extending around the first layer, the second layer de-
fining a cylindrical pressing surface.
Another object of the present invention is the
provision of an apparatus for removing fluid from a
fibrous web in which the second layer is sintered and has
a pore size of at least 2 microns.
Another object of the present invention is the
provision of an apparatus for removing fluid from a
fibrous web in which the second layer has a thickness of
at least .005 inches.
Another object of the present invention is the
provision of an apparatus for removing fluid from a
fibrous web in which the sintered layer is spray-coated
onto the first layer which is a backing roll of an
extended nip press.
Another object of the present invention is the
provision of an apparatus for removing fluid from a
fibrous web in which a fiber metal felt is disposed
between the press member and the web such that in
operation of the apparatus, the metal felt passes with the
web through the press section and in which the metal felt
is heated immediately prior to the passage of the felt
through the pressing section.
Another object of the present invention is the
provision of an apparatus for removing fluid from a
fibrous web in which a cleaning means is provided for
passing a cleaning medium through the metal felt towards a
surface of the metal felt contacting the web so that
13~7~7
contaminants picked up by the metal felt during operation
of the apparatus are ejected from the metal felt.
Another object of the present invention is the
provision of an apparatus for removing fluid from a
fibrous web in which the first layer of the p~ess member
is vented.
Other objects and advantages of the present invention
will be apparent to those skilled in the art by consider-
ation of the detailed description contained hereinafter
taken in conjunction with the annexed drawings.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an- apparatus and
method for removing fluid from a fibrous web. The appara-
tus includes a press member and a blanket means which
cooperates with the press member for defining therebetween
an elongate pressing ~section such that the web is pressed
between the press member and the blanket means during
passage through the pressing section. An elongate means
urges the blanket means towards the press member such that
when the web passes through the pressing section, fluid is
removed from the web. A heating means is disposed adja-
cent to the press member for transferring heat to the web
so that when the web passes through the press section, the
web is subjected for an extended period to increased
pressure and temperature so that water vapor generated
within the pressing section during passage through the
pressing section forces the fluid in the liquid phase away
from the web. The press member defines a pressing surace
which is porous such that delamination o the web is
inhibited.
In a more specific embodiment of the present in-
vention, the pressing surface is cylindrical and the press
~31~7~7
member includes a first coaxial layer and a second coaxial
layer which extends around the first layer with the second
layer defining the cylindrical pressing surface.
The second layer is sintered and has a pore si~e of
at least 2 microns and a thickness of at least .005
inches. The second layer may be spray-coated onto the
external surface of the first layer which may be an
extended nip press backing roll.
In an alternative embodiment of the present in-
vention, the apparatus includes a fiber metal felt which
is disposed between the press member and the web such that
in operation of the apparatus, the metal felt passes with
the web through the press section, the metal felt being
heated immediately prior to passage through the press
section.
In the alternative embodiment of the present in-
vention, the apparal:us also includes cleaning means for
cleaning the metal felt. ~he cleaning means includes
means for passing a cleaning medium through the metal felt
towards a surface of the metal felt contacting the web so
that contaminants picked up by the metal felt during
operation of the apparatus are ejected from the metal
felt.
In another embodiment of the present invention, the
first layer is vented such that fluid entering the porous
layer passes through the second layer into the first
layer.
In a urther embodiment of the present invention, the
hot roll includes a fi~st, or inner, solid surface, a
second, or outer, layer having a porosity of 20 microns
and an intermediate third layer of 100 microns porosity
_, ,_
~ 3 ~
disposed between the first and second layers such that the
third layer assists in the ventilation of the roll.
Although the present invention has been described
with a certain degree of particularity, it is to be
understood by those skilled in the art that the present
invention is not limited to the embodiments described in
detail hereinafter.
Those skilled in the art will appreciate that many
variations and modifications of the present invention may
be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the
present invention as defined by the appended claims. More
specifically, although the present invention provides a
porous second layer for inhibiting delamination, it will
be apparent to those skilled in the art that in the
alternative embodiment of the present invention, the
provision of the fiber metal felt may be sufficient to
inhibit delamination of the formed web without the need of
a porous outer layer on the press member.
Additionally, it will be appreciated by those skilled
in the art that the second, or outer, layer may not
necessarily be a separate layer but may be etched onto the
first layer or otherwise provided by mechanically working
the surface of the first layer.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
_ . _ ... . _ _ _
Figure 1 is a side-elevational view of an apparatus
for removing fluid from a fibrous web according to the
present invention.
Figure 2 is a side-elevational view of a second
embodiment of the present invention showing the provision
of a first and second layer of the press member.
~31~ 7
Figure 3 is a side-elevational view of a third
embodiment of the present invention showing a fiber metal
felt.
Figure 4 is a side-elevational view of a fourth
embodiment of the present invention in which the first
layer is vented.
Figure 5 is a sectional view taken on the line 5-5 of
figure 4,
Figure 6 is a side-elevational view of a fifth
embodiment of the present invention in which the first
layer is grooved, and
Figure 7 is a side-elevational view of a sixth
embodiment of the present invention including a third
intermediate layer.
Similar reference characters refer to similar parts
throughout the various embodiments of the present in-
vention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
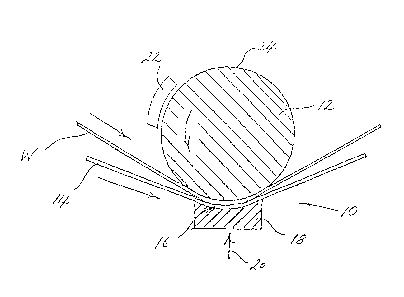
~ igure 1 is a side-elevational view of an apparatus
generally designated 10 for removing fluid from a fibrous
web W. The apparatus 10 includes a pr~ess member 12 and a
blanket means generally designated 14 which cooperates
with the press member 12 for defining therebetween an
elongate pressing section generally designated 16 such
that the web W is pressed between the press member 12 and
the blanket means 14 during passage through the pressing
section 16. An elongate means 18 such as an extended nip
press shoe, urges the blanket means 14 towards the press
member 12 as indicated by the arrow 20 such that when the
web W passes through the pressing section 16 fluid is
removed from the web W. Heating means generally
designated 22 is ~isposed adjacent to the press member 12
for transferring heat to the web W such that when the web
W passes through the press section 16, the web W is
subjected for an extended period to increased pressure and
temperat~re so that water vapor generated within the
pressing section 16 during passage through the pressing
section 16 forces the fluld in the liquid phase away from
the web W. The press member 12 defines a pressing
surface 24 which is porous for inhibiting delamination of
the web W. More specifically, as shown in figure 1, the
pressing surface is cylindrical
Figure 2 is a similar view to that shown in figure 1
but shows a second embodiment of the present invention in
which an apparatus lOA for removing fluid from a fibrous
web WA includes a press member 12A in which the press
member 12A has a first coaxial layer 26 and a second
coaxial layer 28 extending around the first layer 26. The
second layer 28 defines a cylindrical pressing surface
24A. The second layer 28, as shown in figure 2, may be a
sintered layer having a pore size of at least 2 microns.
The second layer 28 has a thickness of at least .005
inches. Such second layer 28 may be applied to the first
layer 26 by a spray-coating technique. The second layer
28 in the aforementioned spray-coating technique, is
spray-coated onto the external surface 30 of the first
layer 26, the first layer 26 being an extended nip press
backing roll.
Preferably, the second layer 28 is applied to the
first layer 26 by the aforementioned spray-coating tech-
nique in which the specification and performance of the
resultant second layer 28 is equivalent to the
7 ~ 7
specification and per~ormance of a plate having a pore
size of at least 2 microns and a thickness of at least
.005 inches.
Figure 3 iS a side-elevational view of a third
embodiment of the present invention and shows an apparatus
lOB for removing fluid from a fibrous web WB. The appara-
tus lOB includes a fiber metal felt 32 which is disposed
between a press member 12B and the web W8 such that in
operation of the apparatus lOB, the metal felt 32 passes
with the web WB through the press section 16B. The metal
felt 32 is heated as indicated by the heaker 22B immedi-
ately prior to passage of the metal felt 32 through the
press section 16B. The porosity, void volume and heat
transfer specification of the metal felt 32 iS equivalent
to the specification and performance of a sintered plate
having a pore size of at least 2 microns and a thickness
of at least .005 inches.
Figure 3 also shows cleaning means generally desig-
nated 34 disposed downstream relative to the press member
12B for cleaning the metal felt 32. The cleaning means 34
includes means 36 such as a pump for passing a cleaning
medium through the metal felt 32 towards a surface 24B of
the metal felt 32 contacting the web WB so that contami-
nants picked up by the metal felt 32 during operation of
the apparatus lOB are ejected from the metal felt 32.
Figure 4 is a side-elevational view of a fourth
embodiment of the present invention and shows an apparatus
lOC in which the first layer 26C of the press member 12C
is vented such that fluid entering the pressing surface
24C passes through the second layer 28C into the first
layer 26C. As shown in figures 4 and 5, the first layer
26C is grooved as shown particularly in figure 5 which is
a section on the line 5-5 of figure ~ Figure 5 shows a
plurality of axially-spaced grooves 38,39 and 40 defined
by the external surface 30C of the fist layer 26C.
~ igure 6 is a similar view to that shown in figures
and 5 but shows a fifth embodiment of the present in-
vention in which the first layer 26D is blind-drilled as
indicated by the holes 41,42 and 43.
In a further embodiment of the present invention as
shown in figure 7, the heated roll, or press member 12E
includes a first layer 26E which is solid and an outer, or
second, porous layer 28E having a pore size within the
range 5-50 microns and preferably of 20 microns. An
intermediate third layer 44 is disposed between layers 26E
and 28E, the third layer 44 having a pore size within the
range 50-100 microns and preferably of 100 microns such
that ventilation of the second layer and the web WE is
assisted.
In operation of the apparatus 10, as shown in figure
1, the web W is conducted through the press section 16 and
heat is applied, for example by induction heating, through
the heater 22 such that the press member 12 is heated.
Pressure is applied as indicated by the arrow 20 such that
the blanket 14 is pressed towards the pressing member 12
thereby exerting pressure on the web W as the web W passes
through the pressing section 16. The combination of high
pressure and high temperature for an extended period
results in fluid from within the fibrous web W being
vaporized such that this vapor forces fluid in the liquid
phase away from the web W Although there exists a
tendency for the aforementioned force of such pressurized
vapor to cause delamination in the pressed web, the
present invention overcomes this problem by the provision
-10-
7 ~ 7
of a porous layer 2~ on the ou~er surface of the press
member 12 such that the vapor pressure is relieved and the
amount of heat transferred throu~h the press rnember 12 to
the web W is reduced thereby inhibiting delamination of
the web.
The operation of the embodiment shown in figure 2 is
similar to that shown in figure 1, however, figure 2 shows
a simple means of applying a porous layer 28 to the
external surface of a conventional backing roll of an
extended nip press.
In operation of the embodiment shown in figure 3, a
fiber metal felt 32 is used to convey thermal energy from
the heater 22B towards the pressing section 16B such that
the web WB is subjected to heat and pressure during
passage through the pressing section 16B. The advantage
of the embodiment shown in figure 3 is that the pressing
surface which effectively is the surface 24B of the metal
felt 32 may be cleaned by means of the cleaning means 34.
Also, the metal felt can be replaced more easily ~han a
porous surface roll. Another advantage derived from use
of a metal felt is that the press member or roll will run
significantly cooler thereby alleviating problems associ-
ated with heating a controlled crown type roll.
The operation of the embodiment shown in figures 4,5,
6 and 7 is similar to that of the embodiment shown in
figures 1 and 2, however, the provision of a grooved (or
blind-drilled) first layer permits further reduction in
the force applied by the vapor in removing fluid in the
liquid phase away from the web in the case of the embodi-
ments of figures 4-6. Similarly, with the embodiment of
figure 7, the third layer 44 assists in the ventilation of
--11--
7 ~ 7
the outer layer 2~ and the web WE. Although this may
reduce the overall amount of fluid removed frorn the web,
such arrangements avoid the problem of delamination and
thus provides a very practical and economic rneans for
press drying a fibrous web.
-12-