Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~ 3 ~
The invention relates generally to a
continuous casting apparatus, especially an apparatus
for the continuous casting of steel.
More particularly, the invention relates to a
continuous casting mold and an associated support zone
for a strand formed in the mold.
A mold for the continuous casting of steel
slabs is generally made up of two pairs of spaced,
parallel copper plates which cooperate to define a mold
cavity. The plates of one pair are relatively wide
while the plates of the other pair are relatively narrow
and the narrow plates are disposed between the wide
plates. The plates are held together by clamping
elements which exert pressure on the wide plates.
In order to increase the versatility of the
mold, it has become known to insert one or more dividing
walls in the mold cavity. Such a dividing wall is
positioned parallel to the narrow plates and divides the
wide mold cavity into two narrower casting passages.
This makes it possible to simultaneously cast two
relatively narrow slabs instead of a single wide slab.
The dividing wall may be secured to the mold
at a fixed location. Although the narrow plates of a
slab mold are normally shiftable towards and away from
one another in order to change the width of the mold
cavity, the range of shifting is limited so that
mounting of the dividing wall at a fixed location limits
the mix of slab widths. Furthermore, the mold must have
provision for attachment of the dividing wall thereby
requiring fairly significant modification of the mold.
- 3 -
.
In addition, mounting of the dividing wall on the mold
and removal of the dividiny wall therefrom are
inconvenient.
A dividing wall which is shiftable along the
width of the mold cavity is also known. ~ere, the mold
is provided with separate clamping elements for the
dividing wall which are likewise shiftable along the
width of the mold cavity in order to be aligned with the
dividing wall. These elements require special structure
which again involves relatively significant modification
of the mold. Moreover, the dividing wall is
inconvenient to manipulate.
The mold of a slab casting machine is
generally followed by a series of support æones for a
slab formed in the mold. When a dividing wall is
inserted in the mold, it is desirable for the first
support zone to have a partition in register with the
dividing wall. In conventional machines, the partition
is formed as a unit with the first ~upport zone. Since
such support zone cannot be used for the casting of a
single wide slab, different first support zones must be
kept on hand. This not only increases equipment costs
but also increases the work required to convert the
machine from one which casts a single wide slab to one
which casts dual narrow slabs. Thus~ the first support
zone must be interchanged upon conversion of the
machine.
One aspect of the invention resides in a
continuous casting apparatus, especially an apparatus
for the continuous casting of steel. The apparatus
~ 3!~
comprises wall means defining a mold cavity having two
ends which are spaced from one another along a
predetermined direction (the casting direction). One
of these ends constitutes an inlet for molten material
while the other end constitutes an outlet for at least
one continuously cast strand of the materialO A
removable dividing wall i5 disposed in the mold cavity
and extends along the casting direc~ion so as to divide
the mold cavity into a pair of substantially parallel
casting passages. The apparatus further comprises
removable clamping means arranged to exert clamping
pressure on the wall means. The clamping means carries
the dividing wall and is designed to clamp the latter in
the mold cavity at a plurality of locations spaced
transversely of the casting direction.
According to the invention, the dividing wall
is mounted on the clamping means used to clamp such wall
in the mold cavity. The clamping means constitutes a
convenient device for manipulating the dividing wall
and, since the clamping means is removable, allows the
dividing wall to be easily removed from and inserted in
the mold cavity. Moreover, inasmuch as the clamping
means need not be secured to the wall means defining the
mold cavity, no significant modification of the wall
means is required in order to mount the dividing wall in
the mold cavity. In addition, due to the fact that the
clamping means can be positioned at different locations
along the mold cavity, a good mix of strand dimensions
can be obtained. This enhances the versatility of the
continuous casting apparatus.
-- 5 --
-
~ .
,
.
~ C.~
The apparatus may also comprise strand support
means downstream of the mold cavity. When the dividing
wall is present in the mold cavity, the strand support
means may accommodate a partition which is in alignment
with the dividing wall and, like the latter, extends
along the casting direction. In accordance with a
preferred embodiment of the invention, the partition is
removable and is mounted on the clamping means. This
not only provides the advantages outlined above for the
dividing wall but further makes it possible to use the
strand support means for both single-strand and
multiple-strand operation.
The novel eatures which are considered as
characteristic of the invention are set forth in
particular in the appended claims. The improved
continuous casting apparatus itself, however, both as to
its construction and its mode of operation, together
with additional features and advantages thereof, will be
best understood upon perusal of the following detailed
description of certain specific embodiments when read in
conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
FIG. 1 is a schematic horizontal sectional
view through a continuous casting mold with one
embodiment of a clamping mechanism according to the
invention;
FIG. 2 is a sectional view as seen in the
direction of the arrows 11-11 of FIG. 1 with parts of
the clamping mechanism broken away; and
FIG. 3 is a partly broken away, partly
sectional view similar to FIG. 2 but showing another
,
- : :
'' '
embodiment of the clamping mechanism.
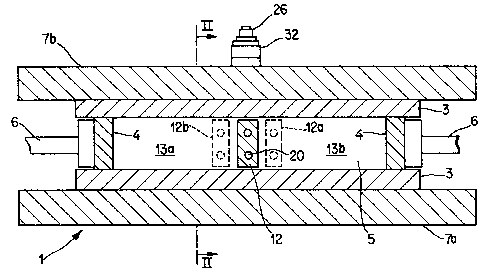
Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, the reference
numerals 1 and 2 generally identify respective
components of a continuous casting apparatus~ The
component 1 is a continuous casting mold while the
component 2 is a support zone for continuously cast
strands formed in the mold 1. The continuous casting
apparatus is here assumed to be of the vertical
straight-mold type or curved-mold type and is further
assumed to be designed for the continuous casting of
steel.
The mold 1 includes a pair of wide walls 3 in
the form of one-piec~ copper plates and a pair of narrow
walls 4 which are likewise in the form of copper plates.
The walls 3 are spaced from and parallel to one another
as are the walls 4 (as a rule, the walls 4 are not
exactly parallel but have a very slight inclination to
compensate for slab shrinkage). The narrow walls 4 are
disposed between the wide walls 3 and cooperate with the
latter to define a mold cavity 5 of rectangular cross
section. The narrow walls 4 are connected with
conventional drives 6 which allow the walls 4 to be
moved towards and away from one another in order to
change the width of the mold cavity 57
The wide walls 3 are mounted on respective
back-up plates 7a and 7b in the usual manner. The
back-up plate 7a is fixed whereas the back-up plate 7b
can undergo limited movement towards and away from the
back-up plate 7a in order to insert and remove tha
narrow walls 4. Furthermore, the wide walls 3 and
, ~, . , . ,. . ~ .
~ '
.
:, , '
.'J~ ~ ~
narrow walls 4 are cooled in a conventional fashion by a
circulating cooling fluid, typically water. The wide
walls 3 and narrow walls 4 are held in engagement with
one another by non-illustrated clamping bolts or the
like of known construction.
The preceding description of the mold 1
indicates that the latter is designed for the casting
of slabs, i.e., the continuous casting apparatus is a
slab casting apparatus.
The mold cavity 5 has an open first end 8a
which constitutes an inlet for molten steel and an open
second end 8b which constitutes an outlet for a
continuously cast steel slab formed in the mold cavity
5. The inlet end 8a and outlet end 8b are spaced from
one another along a predetermined direction 9 known as
the casting direction and steel moves through the mold
cavity 5 in such direction. In operation, the mold 1
has generally vertical orientation so that the inlet end
8a is located above the outlet end 8b and the casting
direction 9 is downwards.
The support zone 2 is disposed immediately
downstream of the mold 1 and constitutes the first of a
series of conventional slab support zones which follow
the mold 1 as considered in the casting direction 9.
The support zones downstream of the support zone 2 have
not been illustrated since this is not necessary for an
understanding of the invention.
The support zone 2 which, as indicated, is
conventional, includes a first row of rolls lOa in
alignment with one of the wide walls 3 of the mold 1 and
:
: ~ ', ' .
~ .fJi~
a second row of rolls 10b in alignment with the other of
the wide walls 3. The rolls 10a,10b serve to support
the wide faces of a slab issuing from the mold cavity 5.
Spray nozzles 11 for slab cooling may be disposed
between neighboring rolls 10a and neighboring rolls 10b.
A dividing wall 12 is disposed in the mold
cavity. The dividiny wall 12 is parallel to the narrow
mold walls 4 and extends in the casting direction 9.
The length of the dividing wall 12, as considered in the
casting direction 9, is similar to that of the mold
walls 3,4. The dividing wall 12 divides the mold cavity
5 into a pair of parallel casting passages 13a and 13b.
The dividing wall 12 is removable from the
mold cavity 5. In the absence of the dividing wall 12,
the mold 1 will produce a slab having a width equal to
the distance between the narrow mold walls 4. On the
other hand, when the dividing wall 12 is present in the
mold cavity 5, the mold 1 can generate two slabs of
lesser width. One of these slabs will have a width
equal to the distance between the dividing wall 12 and a
first one of the narrow mold walls 4 while the other
will have a width equal to the distance between the
dîviding wall 12 and the second narrow mold wall 4.
The dividing wall 12 is secured, e.g. bolted,
at 15 to a clamping device 14 located at the top of the
mold 1. The clamping device 14 resembles an inverted U
and embraces the mold 1. Thus, the clamping device 14
includes an elongated web 16 constituting a slab or
block and two arms 17a and 17b projecting downwards from
the respective ends of the web 16. The web 16 extends
. , .. . - . .
', ~ ....
transversely of the mold 1 from the back-up plate 7a to
the back-up plate 7b and the arm 17a is located
outwardly adjacent to the back-up plate 7a while the arm
17b is located outwardly adjacent to the back-up plate
7b. The web 16 is provided with recesses which are
designed to receive the upper ends of the wide mold
walls 3.
The clamping device 14 serves to clamp the
upper end of the dividing wall 12 in the mold cavity 5.
To this end, the clamping device 14 further includes a
clamping element 18, e.g., a clamping bolt, which is
mounted on the arm 17a and bears against the outer
surface of the bacX-up plate 7a. In addition, a
yieldable biasing element 19, which is here in the form
of a hydraulic cylinder, is mounted on the arm 17b and
bears against the outer surface of the back-up plate 7b.
The biasing element 19 functions to compensate for
thermal expansion and contraction of the dividing wall
12, i.e., the biasing element 19 contracts in response
to thermal expansion of the dividing wall 12 and vice
versa.
The dividing wall 12, which may consist of
copper like the mold walls 2,3, is formed with cooling
ducts 20 for circulation of a cooling fluid, typically
water. The clamping device 14 is provided with pipes
2la and 21b which communicate with the ducts 20. The
pipe 21a is connected to a non-illustrated source of
water and serves to admit water into the ducts 20 while
the pipe 21b serves to discharge water from the ducts
20.
-- 10 --
`'' ~ ' '
~ ' '~ ' .
~ 3 ~ ~ 3, ~
The clamping device 14 is located virtually
entirely outside of the mold cavity 5. This allows the
clamping device 14, and hence the dividing wall 12, to
be manipulated with relative ease.
The clamping element 18 and biasing element 19
of the clamping device 14 exert clamping pressure
directly on the back-up plates 7a,7b of the mold 1 a~d
indirectly on the wide mold walls 3 via the back-up
plates 7a,7b. Upon release of the clamping element 18,
the clamping device 14 is removable from the mold 1
together with the dividing wall 12.
The mold 1 and clamping device 14 are designed
in such a manner that the clamping device 14, and
therefore the dividing wall 12, can be situated at a
multiplicity of locations across the width of the mold
cavity 5. For instance, the clamping device 14 and
dividing wall 12 can be positioned at the center of the
mold cavity 5 as indicated by the full line showing the
dividing wall 12; somewhat to the right of center as
indicated by the phantom line showing 12a of the
dividing wall 12; or somewhat to the left of center as
indicated by the phantom line showing 12b of the
dividing wall 12. The design of the mold 1 and clamping
device 14 such that the dividing wall 12 can be
positioned at different locations across the width of
the mold cavity 5 enables a good mix of slab widths to
be obtained when casting dual slabs. This enhances the
versatility of the continuous casting apparatus.
A partition 22 is disposed in the support zone
2. The partition 22 essentially forms a continuation of
-- 11 --
the dividing wall 12 and divides the support zone 2 into
a pair of passages each of which is in register with one
of the casting passages 13a,13b in the mold 1. Thus,
the partition 22 is in alignment with the dividing wall
12 and, like ths latter, extends in the casting
direction 9. The partition 22 carries spray nozzles 23
which are arranged to spray the narrow faces of slabs
issuing from the mold 1 with a cooling fluid, typically
water.
The partition 22 is removable from the support
zone 2. When the dividing wall 12 is present in the
mold cavity 5 during a casting operation, the partition
22 should be present in the support zone 2. Similarly,
when the dividing wall 12 is removed from the mold
cavity 5 for a casting operation, the partition 22
should be removed from the support zone 2.
The partition 22 is secured, e.g., bolted, at
24 to a second clamping device 25 which is separated
from the clamping device 14 and is located at the bottom
of the mold 1. The clamping device 25 serves the dual
functions of clamping the lower end of the dividing wall
12 in the mold cavity 5 and holding the partition 22 in
position in the support zone 2. The clamping device 22
includes a clamping element which is here in the form of
a bolt 26. The bolt 26 extends transversely of the mold
1 from the back-up plate 7a to the back-up plate 7b.
The clamping device 22 further includes a block 27 which
is snugly received in a recess formed in the lower
surface of the back-up plate 7a and is secured to the
latter. The bolt 26 passes through the block 27 and has
- 12 -
: - --
' '
,:
an exposed end portion on the side of the block 27remote from the back up plates 7b. ~ clamping nut 28 is
mounted on the exposed end portion o~ the bolt 26.
The clamping device 22 additionally includes a
second block 29. The block 29 is received with
clearance in a recess formed in the lower surface of the
back-up plate 7b and is secured to the plate 7b. The
bolt 26 extends through the block 29 which can slide
relative to the bolt 26.
The bolt 26 has an enlarged head 26a which is
located near the external surface of the back~up plate
7b and cooperates with a ~ollar 30 of Z-shaped cross
section to define an annu]ar space circumscribing the
bolt 26. A blasting element 31, e.g., an elastomeric
ring, is accommodated in this space. The collar 30
carries a bearing ring 32 which abuts the external
surface of the back-up plake 7b and is confined between
the collar 30 and such surface.
Similarity to the biasing element 19 o~ the
clamping device 22 functions to compensate for thermal
contraction and expansion of the dividing wall 12.
A jacket 33 constituting a manifold
circumscribes the bolt 26 between the blocks 27 and 29
and a pipe 34 connected to a non~illustrated source of
cooling fluid, typically water, opens into the interior
of the jacket 33. The partition 22 is mounted on the
jacket 33 and is provided with conduits or passages
which connect the spray nozzle 23 with the interior of
the jacket 33. Thus, water enters the jacket 33 via the
pipe 34 and is discharged through the spray nozzles 23.
- 13 -
~ 3 ~
The clamping device 25 is again located
virtually entirely outside of the mold cavity 5.
Accordingly, the clamping device 25, and hence the
partition 22, can be manipulated with relative ease.
When the clamping nut 28 is tightened, the
block 27 and bearin~ ring 32 of the clamping device 25
ex~rt clamping pressure directly on the back-up plates
7a,7b, in turn, exert clamping pressure on the mold
walls 3. On the other hand, when the clamping nut 28 is
loosened and the blocks 27,29 are released from the
back-up plate 7b, the clamping device 25 is removable
from the mold 1 and support zone 2 together with the
partition 22. This allows the support æone 2 to be used
for the casting of a single wide slab as well as dual
narrower slabs.
As before, the mold 1 and clamping device 25
are designed so that the clamping devicQ 25, and
therefore the partition 22, can be mounted at various
positions across the width of the mold cavity 5.
When the dividing wall 12 is present in the
mold cavity 5, the dividing wall 12 in essence
constitutes a third narrow mold wall which functions to
form one narrow face of each of the two slabs generated
in the respective casting passages 13a,13b. The
partition 22 can support these narrow faces in the
support zone 2 if necessary.
In FIGS. 1 and 2, the clamping means for the
dividing wall 12 comprises two discrete clamping devices
14 and 25. FIG. 3, in which the same reference numerals
as in FIGS. 1 and 2 are used to identify similar
:
- 14 -
.
.- :
: ~ :
~ 3 ~
elements, illustrates a clamping device or means 35
which is in the form of a single uni~ and frames or
circumscribes the mold 1.
With referen~e now to FIG. 3, the clamping
device 35 includes a transverse upper strap or block 36
which extends across the top of the mold 1 from the
back-up plate 7a to the back-up plate 7b. The strap 36
has a first end portion 36a located outwardly of the
back-up plate 7a and a second end portion 36b located
outwardly of the back-up plate 7b. The dividing wall 12
is secured to the strap 36 and the latter has internal
cooling passages which communicate with the cooling
ducts 20 in the dividing wall 12. The end portion 36a
of the strap 36 is provided with a junction 36c for
connecting the strap 36 to a non-illustrated source of
cooling fluid, typically water, while the end portion
36b is provided with a nipple 36d for discharge of the
cooling fluid.
The upper surface of each of the back-up
plates 7a,7b is formed with a cutout which leaves the
top of the respective back-up plate 7a,7b with a narrow
upstanding rim adjacent to the associated wide mold wall
3. The strap 36 has a depending protuberance on eithsr
side of the dividing wall 12 and each protuberance
cooperates with the dividing wall 12 to define a recess.
The upstanding rim of the back-up plate 7a and the upper
end of the associated wide mold wall 3 are received in
one of these recesses with clearance while the
upstanding rim of the back-up plate 7b and the upper end
of the associated wide mold wall 3 are received in the
- 15 -
-,
~" 3 ~ s~
other recess with clearance.
The clamping device 35 further includes a
transverse lower strap or block 37 which extends across
the bottom of the mold 1 from the back~up plate 7a to
the back-up plate 7b. The strap 37 has a first end
portion 3~a located outwardly of the back-up plate 7a
and a second end portion 37b located below the back-up
plate 7b. The partition 22 is secured to the strap 37
and the latter is formed with a cooling passage 38 which
extends from the end portion 37a to the partition 22.
The end portion 37a of the strap 37 is provided with ,~
junction 37c for connecting the strap 37 to a source of
cooling fluid, typically water. The strap 37
constitutes a manifold at its connection with the
partition 22 to thereby establish communication between
the cooling passage 38 and the conduits or passages of
the partition 22 which lead to the spray nozzles 23.
The lower surface of each of the back-up
plates 7a,7b has a cutout which leaves the bottom of the
respective back-up plate 7a,7b with a narrow depending
rim adjacent to the associated wide mold wall 3. The
strap 37 has an upstanding protuberance on either side
of the dividing wall 12 and each protuberance cooperates
with the dividing wall 12 to define a recess. The
depending rim of the back-up plate 7a and the lower end
of the associated wide mold wall 3 are received in one
of these recesses with clearance while the depending rim
of the back-up plate 7b and the lower end of the
associated wide mold wall 3 are received in the other
recess with clearance.
- 16 -
.
': ~
: ::
.
-
.. . .
~ 3
The clamping device 35 additional]y includes afirst longitudinal strap or block 39 located to the
outside of the back-up plate 7a and extending lengthwise
of the latter, i.e., along the height of the back-up
plate 7a. The end portion 36a of the transverse upper
strap 36 passes through the upper end portion of the
strap 39 and such end portions are held together in any
suitable manner. Similarly, the end portion 37a of the
transverse lower strap 37 extends through the upper end
portion of the strap 39 with the portions again being
connected to one another.
The longitudinal strap 39 carries two spaced
clamping elements 40, here shown as being in the form of
bolts~ The clamping bolts 40 bear against the external
surface of the back-up plate 7a.
The clamping device 35 also includes a second
longitudinal strap or block 41 located to the outside of
the back-up plate 7b and extending lengthwise thereof,
i.e., along the height of the back-up plate 7b. ~he end
portion 36b of the transverse upper strap 36 passes
through the upper end portion of the strap ~1 so that
the end portion 36b has an exposed part on the side of
the strap 41 remote from the back-up plate 7b. The
exposed part of the end portion 36b is threaded and
mates with clamping nuts 42. A further clamping element
in the form of a screw 43 is mounted in the lower end
portion of the strap 41 and threaded into the end
portion 37b of the transverse lower strap 37. The screw
43 has an exposed part on the side of the strap 41
remote from the back-up plate 7b and nuts 44 are
- 17 -
~ .
,
J; ~ ~;
threaded onto such exposed part of the screw 43. The
clamping nut 42, screw ~3 and nuts 44 function to hold
the straps 36,37,39,41 together.
The longitudinal strap 41 carries two spaced
biasing devices 45. Each o~ the biasing devices 45
includes a housing 46 which is fixed to that side of the
strap 41 remote from the back-up plate 7b. A plunger 47
rides in each housing 46 and has an enlarged head 47a
which is arranged to bear against the external surface
of the back-up plate 7b. The biasing devices 45 serve
to compensate for thermal expansion and contraction of
the dividing wall 12.
Unlike the clamping means 14,25 of FIGS. 1 and
2, the clamping means or device 35 of FIG. 3 constitutes
a single unit during use. This unit resemblss a frame
which circumscribes the mold 1. On the other hand,
similarly to the clamping means 14,25 of FIGS. 1 and 2,
the clamping device 35 is located substantially entirely
outside of the mold cavity 5.
The clamping bolts 40 are tightened, the
clamping bolts 40 and biasing devices 45 exert clamping
pressure on the back-up plates 7a,7b which, in turn, act
on the wide mold walls 3. This zauses the dividing
wall 12 to be clamped in the mold cavity 5. Upon
loosening the clamping bolts 40 and nuts 42,44, the
clamping device 35 and dividing wall 12 are removable
from the mold 1 while the partition 22 is removable from
the support zone 2.
The mold 1 and clamping device 35 are designed
in such a manner that the clamping device 35, and
- 18 -
:
- . -
,
,
.
2 f,
accordingly the dividing wall 12 and partition 2~,can be
positioned at any desired location across the width of
the mold cavity 5. This may be achieved without
extensive modification of the mold 1.
- 1 9 -
.
, ~' ' :