Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
THE EMBODIMENTS OF THE INVENTION IN WHICH AN EXCLUSIVE
PROPERTY OR PRIVILEGE IS CLAIMED ARE DEFINED AS FOLLOWS:
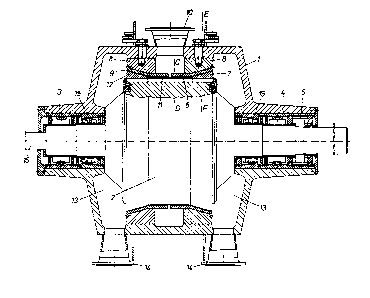
1. A drum refiner for the grinding of fibrous material
comprising:
an engine-driven drumshaped rotor having a
horizontally supported rotor axis and two front faces;
at least one material feed directed radially to the
rotor axis and having a cross-axial median plane;
a rotor shell with two rotation surfaces inclined
to the rotor axis and which increase in inclination in a
direction away from said at least one material feed, said two
rotation surfaces of said rotor shell being provided with
grinding elements;
a housing receiving said rotor, said housing having
inner walls opposing the two rotation surfaces of said rotor
shell with grinding surfaces arranged thereon;
grinding gaps being formed between said grinding
elements of said rotor shell and said grinding surfaces of
said housing, said grinding surfaces having means to adjust
the spacing between the grinding surfaces and the grinding
elements so as to provide said grinding gaps, said grinding
gaps being inclined to the rotor axis, said opposing grinding
surfaces of the housing being provided on two stator rings
which are generally horizontally displaceable within the
housing;
said grinding elements of said rotor shell being
equipped with ribs of essentially axial extension;
13
said at least one material feed being arranged
approximately in the center of said housing, said grinding
elements extending on the shell of said rotor and said
opposing surfaces of the inner walls of the housing being on
both sides of said at least one material feed, said surfaces
of said inner walls being arranged to form an angle with the
axis of the rotor which is open to the front faces of the
rotor, additional grinding clements being provided on the
shell of the drumshaped rotor said grinding elements being
situated between said at least one material feed and said
inner walls, said parallel grinding surfaces and grinding
elements including said additional elements all having outer
regions that form an angle with the axis of said rotor and
the grinding surfaces and grinding elements including said
additional elements all having inner regions which are
parallel to and adjacent with said at least one material
feed, said outer regions of all of said grinding surfaces and
grinding elements including said additional elements forming
an angle which continuously increases in inclination in both
directions away from said at least one material feed, said
grinding and additional surfaces of said inner walls being
spaced apart from corresponding said grinding and additional
elements of said rotor so as to form said grinding gaps;
said grinding gaps having central and outer regions
with the central regions being parallel to the axis and the
outer regions increasing in angle in a direction away from
said at least one material feed as said outer regions
continuously incline away from the axis of said rotor,
wherein said grinding surfaces and elements including said
additional elements are arranged symmetrically to the median
plane of said at least one material feed and have associated
outer regions which incline away from the axis and which
immediately follow and merge with associated central regions
which are parallel to the axis;
14
an annular material feed gap is provided by an
annular space enclosing the outside of the rotor within the
housing, said annular space being provided approximately in
the cross-median plane of the drum refiner between the
grinding surfaces of said stator rings and the grinding
elements of said rotor that extend parallel to the axis of
the rotor, said annular feed gap accepting the material that
empties from said at least one material feed;
said housing receiving said rotor being provided
with two front walls on both sides of the rotor each of which
walls lodging a shaft bearing for the rotor, said housing
also having cavities into which the material reduced within
the grinding gaps immediately empty, said cavities being
provided in the area of the two housing front walls in the
vicinity of the shaft bearings, said cavities being provided
on both sides of the rotor, said cavities being sealed steam-
tight against said shaft bearings by means of special sealing
units inserted in the bearing housings and placed between the
rotor and bearing on the side of the rotor, said cavities
being provided with discharge openings for the ground
material that is created by the operation of all of said
grinding surfaces and elements.
2. The drum refiner according to claim 1, wherein the
outer regions associated with all of said grinding surfaces
and grinding elements including said additional surfaces and
elements enclose an angle of approximately 5 to 45 degrees
with the rotor axis.
3. The drum refiner according to claim 1, wherein the
additional grinding surfaces on said inner walls include
grinding surfaces located at the outer regions that are
inclined by an angle which is increased relative to the angle
of the remainder of said grinding surfaces and similaryly,
the additional grinding elements on said rotor include
grinding elements located at the outer regions that are
inclined by an angle which is increased relative to the angle
of the remainder of said grinding elements.
4. The drum refiner according to claim 3, wherein the
increased angle of said additional grinding surfaces and
grinding elements at said outer regions is approximately 90
degrees inclined to said rotor axis.
5. The apparatus according to claim 1, wherein at least
two horizontal displaceable stator rings are provided both of
which cooperate with each other to provide said adjustable
gaps.
6. The drum refiner according to claim 5, wherein the
two stator rings are displaceable independently of one
another.
7. The drum refiner according to claim 1, wherein the
rotor is displaceably supported by bearings on both sides of
said rotor.
8. The drum refiner according to claim 7, wherein the
rotor is axially displaceably and floatingly supported in
hydrostatic sliding bearings and each of which has a sealing
unit enclosing the rotor shaft in a bearing located in a wall
of said housing and which unit is positioned between said
sliding bearing and the interior of the housing receiving the
rotor.
9. The drum refiner according to claim 1, wherein the
grinding elements provided on said drumshaped rotor have
diameters with dimensions which increase in a direction away
from the at least one material feed, said rotor being
supported in sliding bearings by means of a rotation shaft
fixedly connected to the rotor, said rotor being provided
16
with a special starting engine for the starting operation and
wherein the main engine of the drum refiner is designed to
operate at about 3000 to 3600 rpm at full load.
10. A drum refiner for grinding of wet fibrous
material, having an engine-driven rotor with frustoconical
surfaces provided with at least grinding elements, said
grinding elements having diameters with dimensions which
increase in the direction away from an at least one material
feed, said rotor having a horizontal rotation shaft which is
received by a housing, said housing having inner walls
corresponding to said frustoconical surfaces of said rotor
and having grinding surfaces arranged on said walls to
correspond to and have the same increasing dimensions as said
grinding elements, said housing receiving the rotor, said
horizontal rotation shaft of said rotor being received by
bearings located within said housing, said at least one
material feed being directed approximately radially to the
rotor axis and disposed approximately in the center of said
housing, said grinding surfaces enclosing an angle with
respect to the rotor axis on both sides of the cross medium
plane of the drum refiner which is open to the front faces of
the rotor, the improvement comprising (1) said rotor being
received by said bearing located within said housing, (2)
that grinding surfaces and elements extend approximately
parallel to the rotor axis on a jacket of the drum shaped
rotor and corresponding opposing grinding surfaces on the
housing are provided with increasing diameters in a direction
away from the at least one material feed, (3) that the
grinding surfaces and grinding elements are arranged parallel
to the axis and inclined to the axis of the rotor as well as
being arranged symmetrically to the median plane of the at
least one approximately radial material feed, and (4) that
the grinding surfaces and grinding elements arranged parallel
to the axis are followed immediately mergingly by the
17
grinding surfaces and grinding clements which are inclined
toward the axis of the rotor.
11. A drum refiner for the grinding of wet fibrous
material comprising:
an engine-driven drumshaped rotor having an
approximately horizontally supported rotor axis and two front
faces;
at least one material feed directed approximately
radially to the rotor axis and having a cross-axial median
plane;
a rotor shell with two frustoconical rotation
surfaces which continuously increase in inclination in a
direction away from said at least one material feed, said two
rotation surfaces of said rotor shell each having an opposed
inclination away from the rotor axis, and said rotation
surfaces being provided with grinding elements;
a housing receiving the rotor, said housing having
inner walls opposing the two rotation surfaces of said rotor
with opposing grinding surfaces arranged thereon, said
housing lodging at least one stator ring which is
horizontally displaceable within the housing, said stator
ring having grinding surfaces which are opposed said grinding
elements of said rotor;
grinding gaps being formed between said grinding
elements of said rotor shell and said grinding surfaces of
said housing, said grinding surfaces having means to adjust
the spacing between the grinding surfaces and the grinding
elements so as to provide said grinding gaps, said gaps being
inclined to the rotor axis;
18
said grinding elements of said rotor shell being
equipped with ribs of essentially axial extension;
said at least one material feed being disposed
approximately in the center of said housing, said grinding
elements on said rotor and said opposing grinding surfaces on
said housing are both arranged to form an angle which
increases in inclination in both directions away from said at
least one material feed, said opposing grinding surfaces of
said housing enclosing an angle with respect to the rotor
axis on both sides of the cross-median plane of the drum
refiner which is open to the front faces of said rotor;
additional grinding elements in said rotor and said
opposing grinding surfaces in said housing being provided
which are adjacent to said at least one material feed, said
grinding surfaces and said grinding elements including said
additional surfaces and elements having outer regions which
form an angle which continuously increases in inclination in
both directions away from said at least one material feed,
said grinding and additional surfaces of said inner walls
being spaced apart from corresponding said grinding and
additional elements of said rotor so as to form said grinding
gaps;
said grinding gaps having central and outer regions
with the central region being parallel to the axis of the
rotor and the outer regions increasing in angle in a
direction away from said at least one material feed as said
outer regions continuously incline away from the axis of the
rotor and wherein all of said grinding surfaces and elements
including said additional surfaces and elements are arranged
symmetrical to the median plane of said at least one material
feed and have associated outer regions which incline away
from the axis and which immediately follow and merge with
19
associated inner regions which are parallel to the axis of
the rotor;
an annular material feed gap is provided by an
annular space enclosing the outside of the rotor within the
housing, said annular space being provided approximately in
the cross-axial median plane of the drum refiner between the
grinding surfaces of said at least one stator ring and the
grinding elements of said rotor that extend parallel to the
axis, said annular feed gap accepting the material that
empties from said at least one material feed;
said housing receiving said rotor being provided
with two front walls on both sides of the rotor each of which
walls lodging a shaft bearing for the rotor, said housing
also having cavities into which the material reduced within
said grinding gaps immediately empty, said cavities being
provided in the area of the two housing front walls in the
vicinity of the shaft bearings, said cavities being provided
on both sides of the rotor, said cavities being sealed steam-
tight against said shaft bearings by means of special sealing
units inserted in the bearing housings and placed between the
rotor and bearings on the side of the rotor, said cavities
being provided with discharge openings for the ground
material that is created by all of said grinding surfaces and
elements.
12. The drum refiner according to claim 11, wherein the
grinding surfaces and gaps enclose an angle of approximately
5 to 45 degrees with the rotor axis.
13. The drum refiner according to claim 11, wherein the
additional grinding surfaces on said inner walls include
grinding surfaces located at the outer regions that are
inclined by an angle which is increased relative to the angle
of the remainder of said grinding surfaces and similarly, the
additional grinding elements on said rotor include grinding
elements located at the outer regions that are inclined by an
angle which is increased relative to the angle of the
remainder of said grinding elements.
14. The drum refiner according to claim 13, wherein the
increased angle of said additional grinding surfaces and
grinding elements at said outer regions is approximately 90
degrees inclined to said rotor axis.
15. The drum refiner according to claim 10, wherein the
grinding gaps are inclined toward the axis of the rotor and
are adjustable for the purpose of providing variable grinding
operations, said adjustable gaps being provided by at least
one stator ring that is approximately horizontally
displaceable within said housing.
16. The drum refiner according to claim 11, wherein at
least two displaceable stator rings are provided.
17. The drum refiner according to claim 16, wherein the
stator rings are displaceable independently of one another.
18. The drum refiner according to claim 11, wherein the
rotor is supported displaceably on both sides in its
bearings.
19. The drum refiner according to claim 18, wherein the
rotor is axially displaceably and floatingly supported in a
hydrostatic sliding bearing and has a sealing unit enclosing
the rotor shaft in a bearing located in a wall of said
housing and which unit is positioned between said sliding
bearing and the interior of the housing receiving the rotor.
20. The drum refiner according to claim 10, wherein an
annular material feed gap is provided by an annular space
21
enclosing the outside of the rotor within the housing, said
annular space being provided approximately in the cross-axial
median plane of the drum refiner between the grinding
surfaces and grinding elements that extend parallel to the
axis, said annular feed gap accepting the material that
empties from said at least one material feed.
21. The drum refiner according to claim 10, wherein
said housing receiving said rotor is provided with two front
walls on both sides of the rotor each of which wall lodging a
shaft bearing for the rotor, said housing also having
cavities into which the material reduced within the grinding
gaps immediately empty, said cavities being provided in the
area of the two front walls of the housing in the vicinity of
the shaft bearings, said cavities being provided on both
sides of the rotor, said walls of the housing having grinding
surfaces arranged to be parallel to the axis of the rotor,
said cavities being sealed steam-tight against the shaft
bearings by means of special sealing units which are inserted
in the bearing housing and placed between rotor and bearings
on the side of the rotor, said cavities being provided with
discharge openings for the comminuted material reduced by the
operation of all of the crushing and grinding surfaces.
22. The drum refiner according to claim 11, wherein the
drumshaped rotor is provided on its shell with grinding
elements which are approximately parallel to its axis, said
grinding elements having diameters with dimensions which
increase in a direction away from the material feed, said
grinding elements with increasing diameter being adjacent on
both sides of said at least one material feed, said rotor
being supported in sliding bearings by means of a rotation
shaft fixedly connected to the rotor, said rotor being
provided with a special starting engine for starting
operation and the main engine of said drum refiner being
22
provided for an operation of said drum refiner at
approximately 3000 to 3600 rpm at full load.
23. A drum refiner for grinding of fibrous material
sometimes mixed with water, said drum refiner having an
engine-driven drumshaped rotor with at least two rotation
surfaces provided with grinding elements having diameters
with dimensions which increase in a direction away from an at
least one material feed, said rotor having a horizontal
rotation shaft which is received by a housing, said housing
having inner walls with grinding surfaces corresponding to
said grinding elements of said rotor, said at least one
material feed extending approximately tangentially to the
rotor and being provided approximately in the center of said
housing, said grinding surfaces enclosing an angle with
respect to the rotor axis on both sides of the cross medium
plane of the drum refiner which is open to the front faces of
the rotor, said grinding surfaces and grinding elements all
having central regions which are parallel to and adjacent
with said at least one material feed, said grinding surfaces
and grinding elements all having outer regions which are
inclined to the axis of the rotor and which immediately merge
with said central regions, the improvement comprising: (1)
said rotor having a horizontal rotation shaft which is
received by said housing, (2) that grinding surfaces extend
approximately parallel to the rotor axis and also extend
between the at least one material feed and the grinding
elements and are of increasing diameters on a jacket of the
drumshaped rotor and corresponding opposing grinding surfaces
are provided on the housing, (3) that the grinding surfaces
and grinding elements are inclined to the axis of the rotor
as well as all being arranged symmetrically to the medium
plane of the at least one approximately tangential material
feed, and (4) that the grinding surfaces and grinding
elements which are parallel to the axis are immediately
23
mergingly followed by the grinding surfaces and grinding
elements which are inclined to the axis.
24. A drum refiner for the grinding of fibrous
materials comprising:
an engine-driven drumshaped rotor having an
approximately horizontally supported rotor axis and two front
faces;
at least one material feed;
a rotor shell with at least two rotation surfaces
with grinding elements inclined to the rotor axis, said two
rotation surfaces increasing in inclination in a direction
away from said at least one material feed, wherein said
rotation surfaces have an opposed inclination away from the
rotor axis;
a housing receiving said rotor, said housing having
inner walls opposing the two rotation surfaces of said rotor
with opposing grinding surfaces provided thereon, said
housing lodging at least one stator ring which is generally
horizontally displaceable within the housing, said stator
ring having grinding surfaces which are opposing said
grinding elements of said rotor;
said grinding elements of said rotor sheel being
equipped with ribs of essentially axial extension;
grinding gaps being formed between said grinding
elements on said rotor sheel and said opposing grinding
surfaces on said housing, said grinding surfaces having means
to adjust the spacing between the grinding surfaces and the
grinding elements so as to provide said grinding gaps, said
gaps being inclined to the rotor axis;
24
said at least one material feed having a cross-
axial median plane which extends approximately tangentially
to the rotor shell and is approximately in the center of said
housing, said grinding surfaces of said housing being
arranged to provide an angle which increases in both
directions away from said at least one material feed;
said grinding surfaces of said housing enclosing an
angle with respect to the rotor axis on both sides of the
cross median plane of the drum refiner which is open to the
front faces of the rotor;
additional grinding elements being provided on the
shell of the drumshaped rotor and correspondingly opposing
grinding elements being provided on said housing, said
grinding surfaces and grinding elements including said
additional surfaces and elements all having central regions
which are parallel to the rotor axis and adjacent to said
material feed, said grinding surfaces and grinding elements
including said additional surfaces and elements all having
outer regions that form an angle which continuously increases
in inclination in both directions away from said feed, said
grinding and additional surfaces of said inner walls being
spaced apart from corresponding said grinding and additional
elements of said rotor so as to form gaps;
said grinding gaps having central and outer regions
with the central regions being parallel to the axis of said
rotor and the outer regions increasing in angle in a
direction away from said at least one material feed as said
outer regions incline away from the axis;
said grinding sufaces and elements including said
additional surfaces and elements being inclined away from the
axis of said rotor and arranged to be symmetrical to the
median plane of said at least one material feed and all such
surfaces and elements having associated outer regions which
are inclined away from the axis of the rotor and which
immediately follow and merge with associated central regions
which are parellel to the axis;
an annular material feed gap is provided by an
annular space enclosing the outside of the rotor within the
housing, said annular space being provided approximately in
the cross-axial median plane of the drum refiner between the
grinding surfaces of said at least one stator ring and the
grinding elements of said rotor that extend parallel to the
axis, said annular material feed gap accepting the material
that empties from said at least one material feed;
said housing receiving said rotor being provided
with two front walls on both sides of the rotor each of which
wall lodging a shaft bearing for the rotor, said housing also
having cavities into which the material reduced within said
grinding gaps immediately empty, said cavities being provided
in the area of the two housing front walls in the vicinity of
the shaft bearings, said cavities being provided on both
sides of the rotor, said cavities being sealed steam-tight
against said shaft bearings by means of special sealing units
inserted in the bearing housings and placed between the rotor
and bearings on the side of the rotor, said cavities being
provided with discharge openings for the ground material that
is created by all of said grinding surfaces and elements.
25. The drum refiner according to claim 24, wherein the
grinding surfaces and gaps enclose an angle of about 5 to 45
degrees with the rotor axis.
26. The drum refiner according to claim 24, wherein the
additional grinding surfaces on said inner walls include
grinding surfaces located at the outer regions that are
inclined by an angle which is increased relative to the angle
26
of the remainder of said grinding surfaces and, similarly,
the additional grinding elements on said rotor include
grinding elements located at the outer regions that are
inclined by an angle which is increased relative to the angle
of the remainder of said grinding elements.
27. The drum refiner according to claim 26, wherein
said increased angle of said additional grinding surfaces and
grinding elements at said outer regions is approximately 90
degrees inclined to said rotor axis.
28. The drum refiner according to claim 23, wherein the
grinding surfaces and grinding elements which are inclined
toward the axis are adjustable for the purpose of providing
variable grinding operations, said adjustable grinding
surfaces and grinding elements being provided by at least one
stator ring that is approximately horizontally displaceable
within said housing.
29. The drum refiner according to claim 24, wherein at
least two displaceable stator rings are provided.
30. A drum refiner for the grinding of fibrous
materials comprising:
an engine-driven drumshaped rotor having an
approximately horizontally supported rotor axis and two front
faces;
at least one material feed;
a rotor shell with at least two rotation surfaces
with grinding elements inclined to the rotor axis, said two
rotation surfaces increasing in inclination in a direction
away from said at least one material feed, wherein said
27
rotation surfaces have an opposed inclination away from the
rotor axis;
a housing receiving said rotor, said housing having
inner walls opposing the two rotation surfaces of said rotor
with opposing grinding surfaces provided thereon, said
housing lodging at least two stator rings which are generally
horizontally displaceable within the housing, said stator
rings being displaceable independently of one another, said
stator rings having grinding surfaces which are opposing said
grinding elements of said rotor housing;
said grinding elements of said rotor shell being
equipped with ribs of essentially axial extension;
grinding gaps being formed between said grinding
elements on said rotor shell and said opposing grinding
surfaces on said housing, said grinding surfaces having means
to adjust the spacing between the grinding surfaces and the
grinding elements so as to provide said grinding gaps, said
gaps being inclined to the rotor axis;
said at least one material feed having a cross-
axial median plane which extends approximately tangentially
to the rotor shell and is approximately in the center of said
housing, said grinding surfaces of said housing being
arranged to provide an angle which increases in both
directions away from said at least one material feed;
said grinding surfaces of said housing enclosing an
angle with respect to the rotor axis on both sides of the
cross median plane of the drum refiner which is open to the
front faces of the rotor;
additional grinding elements being provided on the
shell of the drumshaped rotor and correspondingly opposing
28
grinding being provided on said housing, said grinding
surfaces and grinding elements including said additional
surfaces and elements all having central regions which are
parallel to the rotor axis and adjacent to said material
feed, said grinding surfaces and grinding elements including
said additional surfaces and elements all having outer
regions that form an angle which continuously increases in
inclination in both directions away from said feed, said
grinding and additional surfaces of said inner walls being
spaced apart from corresponding said grinding and additional
elements of said rotor so as to form said grinding gaps;
said grinding gaps having central and outer regions
with the central region being parallel to the axis of said
rotor and the outer regions increasing in angle in a
direction away from said at least one material feed as said
outer regions incline away from the axis;
said grinding surfaces and elements including said
additional surfaces and elements being inclined away from the
axis of said rotor and arranged symmetrical to the median
plane of said at least one material feed and all such
surfaces and elements having associated outer regions which
are inclined away from the axis of the rotor and which
immediately follow and merge with associated central regions
which are parallel to the axis;
an annular material feed gap is provided by an
annular space enclosing the outside of the rotor within the
housing, said annular space being provided approximately in
the cross-axial median plane of the drum refiner between the
grinding surfaces of said at least one stator ring and the
grinding elements of said rotor that extends parallel to the
axis, said annular material feed gap accepting the material
that empties from said at least one material feed;
29
said housing receiving said rotor being provided
with two front walls on both sides of the rotor each of which
walls lodging a shaft bearing for the rotor, said housing
also having cavities into which the material reduced within
said grinding gaps immediately empty, said cavities being
provided in the area of the two housing front walls in the
vicinity of the shaft bearings, said cavities being provided
on both sides of the rotor, said cavities being sealed steam-
tight against said shaft bearings by means of special sealing
units inserted in the bearing housings and placed between the
rotor and bearings on the side of the rotor, said cavities
being provided with discharge openings for the ground
material that is created by all of said grinding surfaces and
elements.
31. The drum refiner according to claim 24, wherein
only one said at least one stator ring is provided and said
rotor is supported displaceably in its bearings on both
sides.
32. The drum refiner according to claim 31, wherein
the rotor is axially displaceably and floatingly supported in
a hydrostatic sliding bearing and has a sealing unit
enclosing the rotor shaft in a bearing located in a wall of
said housing and which is positioned between said sliding
bearing and the interior of the housing receiving the rotor.
33. The drum refiner according to claim 23, wherein an
annular material feed gap is provided by an annular space
enclosing the outside of the rotor within the housing, said
annular space being approximately in the cross-axial median
plane of the drum refiner between the grinding surfaces and
grinding elements that extend parallel to the axis of the
rotor, said annular material feed gap accepting the material
from said approximately tangential material feed.
34. The drum refiner according to claim 23, wherein
said housing receiving said rotor is provided with two front
walls on both sides of the rotor each of which walls lodging
a shaft bearing for the rotor, said housing also having
cavities into which the material reduced within the grinding
gaps immediately empties, said cavities being provided in the
area of the two front walls of the housing in the vicinity of
the shaft bearings, said cavities being provided on both
sides of the rotor, said walls of the housing having grinding
surfaces some of which are arranged to be parallel to the
axis of the rotor, and some of which are arranged to be
inclined to the axis of the rotor, said cavities being sealed
steam-tight against the shaft bearings by means of special
sealing units which are inserted in the housing and placed
between rotor and bearings on the side of the rotor, said
cavities being provided with discharge openings for the
comminuted material reduced by the operation of all of the
grinding surfaces and elements.
35. The drum refiner according to claim 24, wherein the
drumshaped rotor has a shell provided with grinding elements
which are approximately parallel to the axis of the rotor and
adjacent to, on both sides, said at least one material feed,
said grinding elements having diameters having dimensions
which increase in a direction away from the material feed,
said rotor being supported in sliding bearings by means of a
rotation shaft that is fixedly connected to said rotor, said
rotor being provided with a special starting engine for the
starting operation of said drum refiner, said drum refiner
having a main engine which is provided for an operation of
3000 to 3600 rpm at full load of said drum refiner.
36. A drum refiner for the grinding of fibrous material
comprising:
31
a drumshaped rotor, driven by an engine at a
rotational speed of 3000 to 3600 rpm and having a
horizontally supported rotor axis and two front faces;
at least one material feed directed radially to the
rotor axis and having a cross-axial median plane;
a rotor shell with two rotation surfaces inclined
to the rotor axis and which increase in inclination in a
direction away from said at least one material feed, said two
rotation surfaces of said rotor shell being provided with
grinding elements;
a housing receiving said rotor, said housing having
inner walls opposing the two rotation surfaces of said rotor
with grinding surfaces arranged thereon;
said grinding elements of said rotor shell being
equipped with ribs of essentially axial extension;
grinding gaps being formed between said grinding
elements of said rotor shell and said grinding surfaces of
said housing, said grinding surfaces having means to adjust
the spacing between the grinding surfaces and the grinding
elements so as to provide said grinding gaps, said opposing
grinding surfaces of the housing being provided on two stator
rings which are generally horizontally displaceable within
the housing, said grinding gaps being inclined to the rotor
axis;
said at least one material feed being arranged
approximately in the center of said housing, said grinding
elements extending on the shell of said rotor and said
opposing surfaces on the inner walls of the housing being on
both sides of said at least one material feed, said surfaces
of said inner walls being arranged to form an angle with the
32
axis of the rotor which is open to the front faces of the
rotor, additional grinding elements being provided on said
shell as well as additional grinding surfaces being provided
on said inner walls all of which extend approximately
parallel to the rotor axis, said parallel grinding surfaces
being situated between said at least one material feed and
said grinding surfaces of said inner walls, said grinding
surfaces and grinding elements including said additional
surfaces all having outer regions which form an angle with
the axis of said rotor and the grinding surfaces and grinding
elements including said additional surfaces all having inner
regions which are parallel to and adjacent with said at least
one material feed, said outer regions forming an angle which
continuously increases in inclination in both directions away
from said at least one material feed, said grinding and
additional surfaces of said inner walls being spaced apart
from corresponding said grinding and additional elements of
said rotor so as to form said grinding gap;
said grinding gaps having central and outer regions
with the central region being parallel to the axis of the
rotor and the outer regions increasing in angle in a
direction away from said at least one material feed as said
outer regions continuously incline away from the axis of the
rotor, wherein all of said grinding surfaces and elements
including said additional surfaces and elements are arranged
symmetrically to the median plane of said at least one
material feed and have associated outer regions which incline
away from the axis and which immediately follow and merge
with associated central regions which are parallel to the
axis;
said housing receiving said rotor being provided
with two front walls on both sides of the rotor each of which
wall lodging a shaft bearing for the rotor, said housing also
having cavities into which the material reduced within said
33
grinding gaps immediately empties, said cavities being
provided in the area of the two housing front walls in the
vicinity of the shaft bearings, said cavities being provided
on both sides of the rotor, said cavities being sealed steam-
tight against said two bearings by means of special sealing
units inserted in the bearing housings and placed between the
rotor and bearings on the side of the rotor, said cavities
being provided with discharge openings for the ground
material that is created by all of said grinding and crushing
surfaces and elements.
37. The drum refiner according to claim 36, wherein
said two stator rings are displaceable independently of one
another.
38. A drum refiner for the grinding of wet fibrous
material, comprising:
a drumshaped rotor, driven by an engine at a high
number of revolutions and having a horizontally supported
rotor axis and two front faces;
at least one material feed directed approximately
radially to the rotor axis and having a cross-axial median
plane;
a rotor shell with two frustoconical rotation
surfaces which continuously increase in inclination in a
direction away from said at least one material feed, said two
rotation surfaces having an opposed inclination away from the
rotor axis, and said rotation surfaces being provided with
grinding elements;
a housing receiving the rotor, said housing having
inner walls opposing the two rotation surfaces of said rotor
with opposing grinding surfaces arranged thereon;
34
said grinding elements of said rotor shell being
equipped with ribs of essentially axial extension;
grinding gaps being formed between said grinding
elements of said rotor shell and said grinding surfaces of
said housing, said grinding surface having means to adjust
the spacing between the grinding surfaces and the grinding
elements so as to provide said grinding gaps, said grinding
gaps being inclined to the rotor axis;
said at least one material feed being disposed
approximately in the center of said housing, said grinding
elements on said rotor and said opposing grinding surfaces on
said inner walls being arranged to form an angle which
increases in inclination in both directions away from said at
least one material feed, said opposing grinding surfaces of
said inner wall enclosing an angle with respect to the rotor
axis on both sides of the cross median plane of the drum
refiner which is open to the front faces of said rotor;
additional grinding elements in said rotor and said
opposing grinding surfaces in said housing being provided
which are approximately parallel to the rotor axis and
adjacent to said at least one material feed, said grinding
surfaces and said grinding elements including said additional
surfaces and elements all having outer regions which form an
angle which continuously increases in inclination in both
directions away from said at least one material feed, said
grinding and additional surfaces of said inner walls being
spaced apart from corresponding said grinding and additional
elements of said rotor so as to form said grinding gaps;
said grinding gaps having central and outer regions
with the central regions being parallel to the axis of the
rotor and said outer regions increasing in an angle in a
direction away from said at least one material feed as said
outer regions incline away from the axis of the rotor and
wherein all of said grinding surfaces and elements including
said additional surfaces and elements are arranged
symmetrically to the median plane of said at least one
material feed and have associated outer region which incline
away from the axis and which immediately follow and merge
with associated central regions which are parallel to the
axis of the rotor;
said housing receiving said rotor being provided
with two front walls on both sides of the rotor each of which
wall lodging a shaft bearing for the rotor, said housing also
having cavities into which the material reduced with said
grindings gaps immediately empty, said cavities being
provided in the area of the two housing front walls in the
vicinity of the shaft bearings, said cavities being provided
on both sides of the rotor, said cavities being sealed steam-
tight against said shaft bearings by means of special sealing
units inserted in the bearing housings and placed between the
rotor and bearings on the side of the rotor, said cavities
being provided with discharge openings for the ground
material that is created by all of said grinding surfaces and
elements.
39. The drum refiner according to claim 38, wherein the
grinding gaps inclined away from the axis of the rotor are
adjustable for the purpose of providing variable operations,
said adjustable gaps are provided by at least one stator ring
which is generally horizontally displaceable within said
housing.
40. The drum refiner according to claim 39, wherein at
least two displaceable stator rings are provided.
41. The drum refiner according to claim 39, wherein two
stator rings are displaceable independently of one another.
36
42. A drum refiner for the grinding of fibrous material
comprising:
a drumshaped rotor, driven by an engine at a high
number of revolutions and having a horizontally supported
rotor axis and two front faces;
at least one material feed;
a rotor shell with at least two rotation surfaces
with grinding elements inclined to the rotor axis, said
surfaces increasing in inclination in a direction away from
said at least one material feed, wherein said rotation
surfaces have an opposed inclination away from the rotor
axis;
a housing receiving said rotor, said housing having
inner walls opposing the two rotation surfaces of said rotor
with opposing grinding surfaces provided thereon;
said grinding elements of said rotor shell being
equipped with ribs of essentially axial extension;
grinding gaps being formed between said grinding
elements of said rotor shell and said grinding surfaces of
said housing, said grinding surfaces having means to adjust
the spacing between the grinding surfaces and the grinding
elements so as to provide said grinding gaps, said gaps being
inclined to the rotor axis;
said at least one material feed having a cross-
axial median plane which extends approximately tangentially
to the rotor shell and is approximately in the center of said
housing, said grinding surfaces of said housing being
arranged to provide an angle which increases in both
directions away from said at least one material feed, said
32
grinding surfaces of said housing enclosing an angle with
respect to the rotor axis on both sides of the cross median
plane of the drum refiner which is open to the front faces of
the rotor, additional grinding elements being provided on
said rotor shell which are approximately parallel to the
rotor axis, and correspondingly opposing grinding surfaces
being provided on said housing, said grinding surfaces and
grinding elements including said additional surfaces and
elements all having central regions which are parallel to the
rotor axis and adjacent to said at least one material feed,
said grinding surfaces and grinding elements including said
additional surfaces and elements all having outer regions
that form an angle which continuously increases in
inclination in both directions away from said feed, said
grinding and additional surfaces of said inner walls being
spaced apart from corresponding said grinding and additional
elements of said rotor so as to form said grinding gaps;
said grinding gaps having a central and outer
regions with the central region being parallel to the axis of
the rotor and the outer regions increasing in angle in a
direction away from said at least one material feed as said
outer regions incline away from said axis;
said grinding surfaces and elements including said
additional surfaces and elements being inclined away from the
axis of the rotor and being arranged symmetrically to the
median plane of said at least one material feed and all
having associated outer regions which are inclined away from
the axis of the rotor and which immediately follow and merge
with associated central regions which are parallel to the
axis;
said housing receiving said rotor being provided
with two front walls on both sides of the rotor each of which
wall lodging a shaft bearing for the rotor being, said
38
housing also having cavities into which the material reduced
within said grinding gaps immediately empty, said cavities
being provided in the area of the two housing front walls in
the vicinity of the shaft bearings, said cavities being
provided on both sides of the rotor, said cavities being
sealed steam-tight against said two bearings by means of
special sealing units inserted in the bearing housings and
placed between the rotor and bearings on the side of the
rotor, said cavities being provided with discharge openings
for the ground material that is created by all of said
grinding surfaces and elements.
43. The drum refiner according to claim 42, wherein the
grinding gaps are inclined away from the axis of the rotor
and are adjustable for the purpose of providing variable
grinding operations, said adjustable gaps being provided by
at least one stator ring which is generally horizontally
displaceable within said housing.
44. The drum refiner according to claim 43, wherein at
least two stator rings are provided.
45. The drum refiner according to claim 43, wherein two
stator rings are displaceable independently of one another.
46. A drum refiner for the grinding of wet fibrous
material comprising:
a drumshaped rotor, driven by an engine at a high
rotational speed of up to 3600 rpm and having a horizontally
supported rotor axis, two rotation surfaces and two front
faces;
a housing receiving said rotor, said horizontal
shaft of said rotor being received and supported by bearings
located within said housing, said housing having two inner
39
walls opposing each of the rotation surfaces of said rotor,
said opposing surfaces being provided by a stator ring
arranged on each of said inner walls;
at least one material feed arranged approximately
in the center of said housing and directed approximately
radially to the rotor axis and having a cross-axial median
plane;
said rotation surfaces of said rotor being located
on both sides of said at least one material feed and
symmetrically disposed to the median plane of the at least
one material feed, said rotation surfaces being equipped with
precrushing elements with crushing surfaces that extend
parallel to the axis of the rotor and which are adjacent to
the at least one material feed, said precrushing elements
being provided for precrushing the wet fibrous material and
distributing it symmetrically in both directions away from
said at least one material feed, said rotating surfaces
further having grinding elements with grinding surfaces
inclined to the axis of the rotor and with diameters having
dimensions which increase in a direction away from the at
least one material feed, said inclined grinding surfaces of
said rotor being provided for further refining the material
that was precrushed by the precrushing elements and allowing
such precrushed and refined material to be discharged as
refined pulp along with generated steam;
said stator rings of the inner walls of the housing
being located one on each side of and symmetrically to the at
least one material feed, said stator rings being equipped
with precrushing surfaces with crushing surfaces that extend
parallel to the axis of the rotor and arranged so as to be
opposite to corresponding precrushing elements on the rotor,
precrushing surfaces of said stator rings being inclined to
the axis of the rotor;
grinding gaps being formed between said precrushing
elements on the rotor and said precrushing surfaces on the
stator rings, said precrushing surfaces of said stator rings
having means to adjust the spacing between the precrushing
elements and precrushing surfaces so as to provide said
precrushing gaps, said precrushing gaps having central and
outer regions with the central regions being parallel to the
axis of the rotor and the outer regions immediately followed
by and merging with said central regions; said outer regions
being inclined to the axis;
said stator rings of the inner walls of the housing
being horizontally displaceable independently of each other,
said stator rings providing said means for adjusting the
precrushing grinding gaps;
said precrushing elements of said rotor being
equipped with ribs of essentially axial extension;
said housing receiving said rotor being provided
with two front walls on both sides of the rotor each of which
wall lodging a shaft bearing for the rotor, said housing also
having cavities into which the material reduced within said
grinding gaps immediately empty, said cavities being provided
in the area of the two housing front walls in the vicinity of
the shaft bearings, said cavities being provided on both
sides of the rotor, said cavities being sealed steam-tight
against said shaft bearings by means of special sealing units
inserted in the bearing housings and placed between rotor and
bearings on the side of the rotor, said cavities being
provided with discharge openings for the ground material that
is created by all of said precrushing and grinding surfaces
and elements.
47. The drum refiner according to claim 46, wherein
there is an annular material feed gap provided by an annular
41
space enclosing the outside of the rotor within the housing,
said annular space being provided approximately in said
cross-axial median plane between the precrushing surfaces of
said stator rings and the precrushing elements of the rotor
all of which extend parallel to the axis, said annular
material feed gap accepting the material that empties from
said at least one material feed.
48. The drum refiner according to claim 47, wherein
said at least one material feed comprises a plurality of
feeds which are individually arranged at approximately equal
distances measured along the periphery of said housing.
49. The drum refiner according to claim 46, wherein
said precrushing surfaces of said stator rings are equipped
with ribs.
50. A drum refiner for the grinding of wet fibrous
material comprising:
a drumshaped rotor driven by an engine at a high
rotational speed of up to 3600 rpm and having a horizontally
supported rotor axis, two rotation surfaces and two front
faces;
a housing receiving said rotor, said housing having
at least one bearing for supporting said rotor, said housing
having two inner walls opposing each of the rotation surfaces
of said rotor, said opposing surfaces of each said two inner
walls being provided by a stator ring arranged on each of
said inner walls;
at least one material feed arranged approximately
in the center of said housing and directed approximately
tangentially to the rotor axis and having a cross-axial
median plane;
42
said rotation surfaces of said rotor being located
on both sides of said at least one material feed and arranged
symmetrically to the median plane of the feed, said rotation
surfaces being equipped with precrushing elements with
crushing surfaces that extend parallel to the axis of the
rotor and which are adjacent to the at least one material
feed, said precrushing elements being provided for
precrushing the wet fibrous material and distributing it
symmetrically in both directions away from said at least one
material feed, said rotation surfaces further having grinding
elements with grinding surfaces inclined to the axis of the
rotor and with diameters having dimensions which increase in
a direction away from the at least one material feed, said
inclined grinding surfaces being provided for further
refining the material that was precrushed by the precrushing
elements and allowing such precrushed and refined material to
be discharged as refined pulp along with generated steam;
said stator rings of inner walls the housing being
located one on each side of and symmetrically to the at least
one material feed, said stator rings being equipped with
precrushing surfaces with crushing surfaces that extend
parallel to the axis of the rotor and arranged so as to be
opposite to corresponding precrushing elements on the rotor,
said precrushing surfaces of said stator being inclined to
the axis of the rotor, said precrushing surfaces of said
stator having outer regions which are inclined to the axis of
the rotor;
grinding gaps being formed between said precrushing
elements on the rotor and said precrushing surfaces on the
stator rings, said precrushing surfaces of said stator rings
and said rotor having means to adjust the spacing between the
precrushing elements and precrushing surfaces so as to
provide said gaps, said precrushing gaps having central and
outer regions with the central regions being parallel to the
43
axis of the rotor and the outer regions immediately followed
by and merging with said central regions, said outer regions
being inclined to the axis;
said stator rings of the inner walls of the housing
being horizontally displaceable independently of each other
and providing said means for adjusting said precrushing gaps;
said precrushing elements of said rotor being
equipped with ribs of essentially axial extension;
said housing receiving said rotor being provided
with two front walls on both sides of the rotor each of which
wall lodging a shaft bearing for the rotor, said housing
having cavities into which the material reduced within said
grinding gaps immediately empty, said cavities being provided
in the area of the two housing front walls in the vicinity of
the shaft bearings, said cavities being provided on both
sides of the rotor, said cavities being sealed steam-tight
against said shaft bearings by means of special sealing units
inserted in the bearing housings and placed between rotor and
bearings on the side of the rotor, said cavities being
provided with discharge openings for the ground material that
is created by all of said precrushing and grinding surfaces
and elements.
51. The drum refiner according to claim 54, wherein
there is an annular material feed gap provided by an annular
space enclosing the outside of the rotor within the housing,
said annular space being provided approximately in said
cross-axial median plane between the precrushing surfaces of
said stator rings and the precrushing surfaces of the housing
all of which extend parallel to the axis, said annular feed
gap accepting that material that empties from said at least
one material feed.
44
52. The drum refiner according to claim 51, wherein
said at least one material feed comprises a plurality of such
feeds which are individually arranged at approximately equal
distances measured along the periphery of said housing.
53. The drum refiner according to claim 50, wherein
said precrushing surfaces of said stator rings are equipped
with ribs.