Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
- OIV. II
132923~
Th-is application is a division of application
serial number 531,143 filed March 4, 1987.
This invention relates to clothes washing
machines of the type having a cabinet in which an
agitator is mounted on a vertical axis and is oscillated
back and forth within a perforated spin tub which in turn
is mounted within a water tight container, the spin tub
and the agitator rotating continuously in one direction
to give a spin action, said cabinet containing an
electric motor and driving means for the agitator and
spin tub and/or clothes washing machines incorporating
such drives.
It is an object of the present invention to
provide an electric motor of the type described which
will at least provide the public with a useful choice.
Accordingly in one aspect the invention
consists in an electric motor comprising an electric
motor comprising, a stator carrying energizable windings
on poles thereof, a rotor, a motor frame having a single
pair of bearings mounted in a central disposition, said
frame having stator locating means arranged to hold an
outer cylindrical surface of said stator concentric with
said bearings, and a single shaft rotatably mounted in
said bearings and carrying said rotor wherein said rotor
comprises a backing ring of a magnetic material, a series
of permanent magnets spaced apart on an inner surface of
;
- 1 -
1329~3~
said backing ring said backing ring and magnets being
rotatable exteriorly of said stator windings, a hub
mounted on said shaft, and a backing ring support holding
` inner faces of said permanent magnets concentric with
said shaft.
In a still further aspect the invention
consists in an electric motor comprising a stator formed
as an annular helical yoke edgewise wound from a strip of
magnetic material and having an inner face and an outer
face, said strip having pole pieces formed integrally
therewith, the pole pieces extending from one edge of
said strip and said strip being edgewise wound whereby
said pole pieces coincide in stacked groups to form a
plurality of poles arranged at equally spaced intervals
extending radially outwardly from the outer face of the
yoke, energizable stator windings wound directly on said
poles of said stator and adapted to be energized through
an electronic commutation circuit, and a rotor mounted
for rotation exteriorly of the relative to said stator,
. said rotor comprising a backing ring of magnetic material
and a series of permanent magnets held at spaced-apart
intervals on an inner surface of said surface of said
backing ring and opposing the poles of said stator.
To those skilled in the art to which the
invention relates, many changes in construction and
widely differing embodiments and applications of the
-- 2 --
`:
~, . .
- : . :
:,..
1329~33
invention will suggest themselves without departing from
the scope of the invention as defined in the appended
- claims. The disclosures and the descriptions herein are
purely illustrative and are not intended to be in any
sense limiting.
The invention consists in the foregoing and
also envisages constructions of which are the following
gives examples.
One preferred form of the invention will now be
described with reference to the accompanying drawings, in
which:
Figure 1 is a cross sectional elevation of a
clothes washing machine constructed according to the
invention, with some parts shown at 45 in plan to other
parts,
Figure 2 is an enlarged view part in cross
section of a water container, spin tub, agitator, drive
and electric motor, and
Figures 3 and 4 are respectively a plan view
and cross section of preferred motor frames incorporated
in the invention in the preferred form,
Figure 5 is a further enlarged view of a seal
shaft and bearings being part of Figure 2,
Figure 6 is a part cross section of an
alternative embodiment of the invention.
132973a
Flgure 7 ls a part cross sectlon of a further
alternative embodiment of the inventlon,
Figure 8 ls a scrap elevatlon at 45 to the view ln
Figure 1, and
Figure 9 ls a rear Yiew of a motor agltator forming
part of the lnventlon.
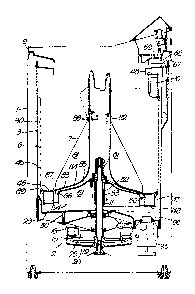
Referring to the drawings, a clothes washing machine
comprises a cabinet l of square cross section which has
mounted in it an electric motor 2 constructed accordlng to
the present invention as will be descrlbed further later.
A water container 3 is su~pended within the cabinet 1 by
suspension rods 4 and sprlngs 5 and for example four
springs and rods are provlded, and the motor and other
mechanism are attached to the container 3. The springs are
lS provided in the corners of the square cross section cabinet
; l accordlngly parts of the rod are shown in sectlonal view
in Figure 8 which is at 45 to the other sectional ~iew of
Figure 1. By water is meant washlng liquid, e.g. water and
- detergent. Contained within the water contalner 3 there is
a perforated spin tub 6 and within the spin tub is an
agitator 7. An opening lid 9, shown only partlally is
provided through which clothes may be inserted into the
- container and within the spin tub 6 and the spin tub is
partly balanced by upper balancing ring 10 shown only in
the rear one side in Figure 1. The springs terminate in
hooks 12 which engage in apertures`13 in the container base
,
-- 4 --
.
~, ~
132g23tj
moulding 29. The agltator 7 l~ mounted on a hollow drlve
shaft 11 so as to rotate therewlth but Is slldable axlally
thereon, The spin tub 6 ls coaxlally mounted on the shaft
11 so as to be rotatably and also ~lidable axlally thereon.
` S The motor 2 is constructed as follows. A rotor 15 has
a backing ring 16 (Fig 2) and the backlng rlng is formed
from a strip of magnetic material for example a slllcon
steel alloy and the strip of steel ls colled on edge wlth
adjacent surfaces lightly insulated and touching each other
to provide a short hollow cylinder or annular helix.
Inslde the helix there is provided a series of magnets 17,
the backing ring 16 being expanded sllghtly before being
placed over the magnets placed in a mould. The magnets are
permanent magnets of a material capable of being magnetlsed
to a high flux ~alue e.g. Neodinium iron made by
Magnaquench Inc. and the annulus and the magnets are held
in place by a plastlcs member 18 which has a hub 1~, a dlsc
or spoked connector portion 20, and substantlally
cylindrlcal element 21, the member being moulded over the
2~ backing ring and magnets so as to maintain the inner faces
of the magnets 17 concentric with the axis of the hub 16.
me stator 25 of the motor has a magnetic core whlch
comprises a strip of magnetic material again preferably a
silicon steel alloy or other low hysteresis steel which is
preformed to provide spaced apart pole pieces and again
this strip is formed by bending on edge to form an annular
helix in the form of a hollow cylinder with the poles 8
~..
~ '' , , .
. :
` 132923a
formed by the stacked pole pieces polnting outwardly. As
may be seen in Figure 9 the poles B are connected together
by a narrow band 14 so that bending on edge i3 relatively
easily effected. To provlde insulation for windlngs on the
poles of the core a top lnsulatlng moulding 22 is placed on
one Qlde of the poles and a bottom lnsulating mouldlng 23
placed on the opposlte side, meeting at a ~olnt llne 24
~indings are placed on the mouldings wound around each hole
and such windlngs 26 are effected on the poles dlrectly.
It ls preferable that the stator be wound ln a three
phase star connected mode and the wlndlngs are made and
connected using known techniques.
The stator 25 and the rotor 15 are mounted as will
shortly be descrlbed.
15 - The water container 3 is preferably an in~ection
moulding and the base 29 has motor support columns 30
preferably braced ~ith stiffening webs 31. These webs
extend to the outer perimeter of the contalner 3 and are
moulded integrally with the container.
The motor 2 includes two bearing frames 32 and 33 which
comprise injection mouldings of a die cast metal or
plastics material or preferably steel pressings or plastics
material. Preferably the frames 32 and 33 are produced
from the same mould or set of dies, thus enduring equality
of dimensions between the two frames. The frames are
carefully designed and made so that the bearing mouldings
21 and ~8 are concentrlc wlth locatlng plna or dlmple:l 34
,,:
' . ,
1329~3a
and corresponding holeq 35 at the perlphery of the frames
and wlth the external angle 36 ln whlch the lnner corner 37
of the stator 25 fits with an interference bit.
Stiffening depressions 49 are provlded to stlffen the
frames and on assembly one frame ls assembled rotated 45
relative to the other frame to provlde correct matchlng of
hole~ and dimples.
Bearings 38 and 39 fit in the bearing mountings 27 and
28 and the bearings are spaced apart by a spaclng tube 40
which encircles the drlve shaft 11. The hub 19 is fixed to
the shaft 11 by a bolt 41 en8aging a nut 42 held in the
hollow of the shaft 11 by the shaft 11 being swaged down to
provide splines which engage corresponding spline spaces 42
in the hub 11. For transport purposes a further nut 43
holds the assembly ~upported by suspension rods and fixed
to a cabinet member 44.
~ he spin tub 6 comprises a stainless steel perforated
hollow cylinder 45 ~ixed to a plastics extruded base 46
e.g. by spinning the lower edge of the cylinder 45 on to
the perlphery of the plastics base 46. If desired a lower
balancing ring 47 is provlded and the balancing rings each
comprise as a hollow ring with baffles and liquid container
therein and the rings are each closed by an annular disc
48. One balancing ring preferably the ring 10 were found
to give reasonable balance while spinning.
A plurality of bridges 50 are provided at spaced
intervals with gaps between them and the bridges connect
.
- 1~2923~
the balancing ring 47 (if fitted) to an alr cha~ber in the
form of a bell 51 havlng an open mouth directed downwardly
and a tube 52 integral therewlth which surrounds the qhaft
11. A low friction plastics bearing 53 enables the
plastics base 29 and consequently the spln tub 6 to rotate
and slide axially on the drive shaft 11.
A series of downwardly directed dog clutch teeth 55
(Fig 2) of a high impact duty materlal e.g. a high lmpact
duty plastics material are carried by a carrier 56 riveted
screwed or otherwise fixed to the air chamber 51 e.g. by
screws 57. A ring 60 carries coacting dog clutch teeth 61
also of a high impact duty material and the ring 60 is
rotatable by and axially slidable on the drive shaft 11
e.g. by engagement of splines on the ring 60 with splines
on the drive shaft 11. The agitator 7 has a bo~s 62 with
inner splines 63 engaging outer splines 6~ on the ring 60
so that rotation of shaft 11 results in rotation of the
teeth 61 and the agitator 7, and the boss 62 slides axially
on the drive shaft 11 as may be seen by conforming the up
position of elements on the left hand side of figures 1 and
2 with the 'down' position on the right hand side..
The air chamber 51 is designed to provide a flotation
or buoyancy force resulting from the entrapment of air in
the air tight air chamber 51 when water closes the
perimeter of the lower edge of the air chamber 51. In the
event that water enters the air chamber 57, e.g. because of
turbulance during agitation, the lower face could be closed
- 8 -
~' '. '` ' ' ~': "
132923~
off with a disc 54.
The buoyancy force is at least sufflcient to lift the
~pin tub 6, and the agitator 7 when a substantially
predetermined volume of water is provided in the contalner
3, and the spin tub and agitator 7 is shown in the nup"
posit~on on the left hand side of Figures 1 and 3 and in
the "down" position on the right hand side. When the spin
tub 6 is in the up position, i.e. supported by floatation
of the air chamber 51, the teeth 55 and the teeth 61 are
disengaged from each other and the agitator may be rotated
freely over any desired rotational movement independent of
the spin tub 6. When water is absent or substantially
absent from the container 3 the spin tub 6 sinks until the
teeth 55 and 61 are engaged. The spin tub 6 and agitator
will then be rotated as one unit and this rotation wlll be
effected continuously in one direction to spln clothes in
the spin tub to a drier condition in the known way. To
assist in freeing frictional contact between the axially
sliding parts during up and down movement of the spin tub
during filling with, and emptying of water, control meana
are provided controlling motor 2 to give a slow agitating
action i.e. forward and reverse rotation over a s~all arc
of movement. At each reversal the dogs will reverse
contact and be free of each other for a short time due to
clearances a~ between the dogs and spaces between the dogs.
To assist in fixing the spin tub against rotation
` dur~ng agitation, i.e. when the agitator is in the up
_ g _
13~9~3~
position, the upper edge 67 of the spin tub may contact a
frictional surface 68 on the underQide of a top member 69
of the container 3.
The agitator 7 haq external blades 81 thereon which
extend from the surface of both column 82 and the upper
surface of an upper coned disc 83. There is a space 84
between the disc 83 and the upper surface 85 of the air
chamber 51 this space may be divided with radial vanes (not
shown) since the purpose of the space arrangement is to
provide a centrifugai impeller. Such an lmpeller may be
otherwise provided e.g. an independent centrifugal pump
could be provided.
Outlet openings 86 are provided from the space 84 at or
near the outer edge of the disc 83 the outer edge 87 of
which is turned downwardly and operates ln close proximity
to the inner edge of the balance ring 46. As a result of
this construction a pumping action iq given, pumping water
from the centre of column 82 from apertures 88 through
space 84 below balance ring 46 to space 86 between the spin
tub 6 and the container 3 and lint is restrained in this
space before the water re-enters the spin tub through the
holes 90. If desired a container may be mounted on the
column 82 such container holding a clothes conditioner in
the known way.
Electronic commutation equipment 65 is provided on an
annular printed circuit board in an annular container 66
mounted below the stator 25 and the electronic commutation
-- 10 --
~, ~ ?, ``::
132923~
. ,
1 equip~ent is preferably enclosed in a compound for
protection and heat sinking, and is such as to enable the
electric motor 2 to move in a backward and forward motion
thus causing the shaft 11 to be oscillated backward and
forth resulting in the agitator 7 being also rotated in a
back and forth motion to give the well known washing
motion. The electronic commutation equipment 65 is also
arranged to drive the motor continuously to give a spin
action, and to drive the spin tub with the agitator, the
absence of water rom the container 3 results in
engagement of teeth 55 and 61 as above described.
-. However~ when the agitator is preferably given a
-
slow agitation motion and the container 3 has water in it
; ~
~-3~ at least to a predetermined level the flotation force of
air in air chamber 51 causes the air chamber spin tub and
agitator to rise~ The teeth 55 are then raised out of
.~
contact with the teeth 61 and the agitator may now move
-~ independently of the spin tub and thus may be oscillated
back and forth at a desired rate and over any desired
angle of rotation to give a washing action without
material movement of the spin tub.
. .
~ To provide seals between the drive shaft 11 and the
~;
, ~
-- 11 --
' .. . ~ `
. . .. ,, . - . ,
132923~
base 29 of the water contalner, a qhort cyllnder Or e.g.
steel 70 (Flg 50) ls flxed to the upper frame 32 by a screw
71 and a flange 72 holds the bearlng 38 ln place. The
short cylinder 70 supports a seal 72 agalnqt the wall 73 of
an apperture in the water contalner base 29 and a dlsc 74
holds a further seal 75 against the shaft 11, belng
reinforced by a backing rlng 76. A played disc 77 holds a
further seal 78 against the shaft 11 reinforced also by a
spring 79, the flange 80 sltting withln a short cyllnder 81
integral with disc.
The seal 72, short cylinder 81 disc 74 and seal 75 are
integral with each other and the played disc 77 seal 78 and
flange 80 are integral with each other. Both unit~ are
made of Neoprene or other known flexlble sealing material.
A pump 95 is provided for the purpose of drainlng the
container 3 and the pump 95 is mounted directly about an
opening 96 in a lower part of the container 3 and thus a
single flexible tube can run from the pump outlet through
the back o~ the cabinet to the user draln connectlon polnt.
~ 20 It is to be noted that the bearlngs 37 and 38 are a
`~ slip fit on the drive tube 11 and tightening of the bolt 41
-~ and a cap 91 by a screw 92 clamps both bearings into
position. Removal of the rotor securement screw 92 and the
bolt 41 can result ln the drlve tube 11 being removed from
above and the motor rotor 16 being removed from below. The
motor 2 is removable as a unit after removing also the
screws 93 holding the frames 32 and 33 ln posltion. Thus
-- 12 --
.
,~ .
,
~', `'~
1329 3~
for malntenance purposes thls removal can be readlly
effected. Furthermore followlng removal of the securement
screw 92, the agitator and aBitator hub can be removed and
the spin tub assembly then lifted off from above. Thu9
maintenance is very simple.
It is alao to be noted that because the spin tub and
its contents float during the agitation phase no thrust
bearing is required. Also the bearing 53 operates under
water and only under low speed condition i.e. the agitator
speed relative to the substantially stationary spin tub and
therefore the bearing need only be a light duty bearing.
An alternative form of interconnection means is
provided as follows:
The agitator 7 has associated with it a bell 100 both
~eing fixed to the shaft 101 by a bolt 102. The shaft 101
corresponds to the shaft 11 and is driven by an electric
motor as abo~e described.
, ~ithin the bell 100 is a rise and fall member 103 which
; is a plastics moulding sealably attached by a flexible
bellows 105 eg. of neoprene to the outer edge 106 of the
plastic member 103 and to the edge of the bell 100. A
further flexible bellows 107 is sealably attached to the
member 103 and to the hub of the bell 100. The member 103
has prongs or dogs 108 spaced at intervals thereon and such
prongs or dogs 108 engage in the spaces between
castellations 109 in the bottom of the spin tub 6. A
~pring (not shown) is provided which exerts a downward
- 13 -
- 1329~
force from the hub 108 on the member 103 and the cavlty 110
is open to atmosphere through a cros~ hole or notch 111 ln
the hub 104 and a series Or holes ln the shaft or drlve
tube 101. Thi~ arrangement is such that when the container
3 is emptyng, the spring moves the member 103 downwardly 50
that the prongs or dogs 108 engage in the spaces between
the castellations and thus the spin tub wlll move with the
agitator and be rotated with that agitator continuously for
the purpose of spinning. However, when t.he container 3 has
water in it to a predetermined level the hydrostatic water
- pressure on the undersurface of the member 103 causes that
member to rise against the pressure of the spring air
venting through the air holes abovementioned and the prongs
or dogs 108 are then raised out of contact with the spin
tub and the agitator may now move indpendently of the spin
tub and thus may be oscillated back and forth to give a
~ashing action.
In a further alternative arrangement of spin tub to
agitator interconrecting means shown in figure 7 the
agitator 7 is combined with a hub 110 fixed by a bolt 111
to a solid splined shaft 112. An air chamber in the form
` of a bell member 115 is a slideable fit on the shaft 112
and has air entrapment spaces 116 in which air is trapped
by rising water in the container 3 when the latter is being
filled preparatory to agitation occurring. The bell 115
then acts as a float raising detents or dogs 113 from
engagement with castellations 107 as shown on the right
- 14 -
13~923~
hand ~lde of flgure 7 to a disengaged po31tlon as shown on
the left hand slde of figure 7.
At least in the preferred forms the lnvention provldes
the following advantages:
1. The electric motor assembly and construction is
ntegrated with the drive system in that a slmple shaft
and pair of bearings supports the rotor at one end of
the agitator and spin tub at the other end advocating
the need for separate shafts and bearings for the motor
and for the agitator and spin tub drive~
2. The mounting of the stator and the rotor outboard of
the lower motor frame enable ready replacement of the
stator and/or rotor.
3. The mounting of the electronics in an annular disk
associated with the stator of the motor reduces the
length of interconnecting wiring and enables a compact
factory wired unit to be provided.
` 4. The floating spin tub concept eliminates the need for
springs bearings and enables ready maintenance to be
carried out.
5. The complete freedom of the agitation to rotate through
-` an unlimited angle of rotation during agitation enables
any desired angle of rotation.
- 15 -
.~ . .
'