Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
332320
PRINTING APPARATUS
BACKGROUND OF TEIE INVENTION
The present invention relates generally to a
printing apparatus, and the invention more particularly
directed to a printer which can print color images
clearly without shifting between colors.
Printing apparatuses in which a paper sheet is
wrapped about a rotatable platen and a color image
printed thereon by a thermal head through a ribbon are
well known. An example of such a printer shown in Figs.
38 and 39, has a paper ejecting housing 202 and a paper
feeding portion 203. The ejecting housing 202 faces to
a printing station 201 and is located at the upper side
of a printer 200, while the feeding device 203 is
directed to the printing station 201 and is arranged
under the ejecting portion. A paper feeding roller 204
is provided above an upwardly opened box-shaped paper
feeding tray 207. The feeding tray 207 has a detachable
bottom plate 206 for receiving a stack of paper sheets
to be printed. When a paper sheet is fed to the platen
in order to be printed, as shown in Fig. 38, the bottom
plate 206 is lifted up by a lifting mechanism (not
shown) so that the reverse surface (non printed surface)
of the top sheet of the stack of paper sheets comes in
contact with the peripheral surface of the roller 204
under pressure. When the printed paper sheet is
transferred to the paper ejecting housing 202, as shown
in Fig. 39, the feeding roller 204 returns to the
initial position.
The paper sheet fed to the printing station by
the feeding roller 204 is wrapped about a rotatable
platen 208 by a pinch roller 209 or so forth. While the
platen 208 rotates three cycles, color image is printed
on the paper sheet by a thermal head through a ribbon.
~; When the printing is over, a guide plate 212 comes in
~: ~ . ,. . ;:
~ ~332320
-- 2
contact with the platen 208 so as to separate the
printed paper sheet from the peripheral surface thereof.
The printed paper sheet is carried out into the ejecting
housing 202.
In the above described conventional type paper
feeding system, since a feeding roller repeatedly comes
in contact with the reverse surface of the uppermost -~
paper sheet within the feeding tray and feeds it to the
platen, the agitated contact of the printing surface of
the lowermost paper sheet with the bottom of the feeding
tray tends to damage it. For the purpose of avoiding
damage, is is necessary to provide a protection sheet
between the bottom plate and the lowermost paper sheet,-
this results in inconvenience and relatively high
running cost.
Moreover, since new paper sheets are supplied
and removed from the top of the stack of sheets within
the paper feeding tray, the lowermost paper sheet tends
to remain longer.
-!;: :
Further, during printing, the edge of paper
sheet wrapped on the platen to collide with the pinch
rolI~r, the guide roller or so forth and position of the
; paper on the platen becomes shifted slightly each -~ -
; revolution which causes the printing start position of
25 ~ eàch of three colors~ to be shifted relative to the
SUMMARY OP IHE INVENTION ~
It i9 accor~dingly one object of the present
invention~to provide~a printing apparatus which has a
paper feeding system for feeding the lowermost printing
paper~sheet~of a stack of~ paper sheets within a paper
feeding~tray~without damaging the printing surface
théreo~f. ~ ~
Another object is to provide an improved color
35~;~ printing apparatus which enables the print starting
position to be maintained precisely without shifting
1332~2~
-- 3
between colors.
Accorting to one aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a printing apparatus for
printing an image on a sheet of printing medium
comprising a rotatable platen whose circumference is
less than the length of the sheet by a predetermined
value, first means for driving the platen about which
the sheet is wrapped so that the ends of the sheet
overlap each other during rotation, and second means for
printing an image on the printing paper during rotation
of the platen.
~;~ According to further aspect of the invention,
- there is provided a printing apparatus for printing an
image on a sheet of paper comprising a platen rotatable
in a predetermined direction, provided at a printing
station, about which the she~t is wound during a
printing operation, a tray, for storing a stack of
printing medium sheets, having an opening in its bottom
~; ; so as to expose the reverse surface of lowermost sheet
; 20 of the stack of the printing medium sheets, and feeding
means, provided under the tray, for feeding the
lowermost printing sheet exposed in the opening toward
the platen.
According to further aspect of the invetnion,
~, :
2~5 there is provided a multicolor printing apparatus for
pr~inting an~image on a sheet of printing medium
comprising a tray, for~storing a stack of the printing
shee~ts,~having an opening in its bottom from which the
reverse surface of lowermost sheet stored therein is
0 ~exposed, a rotatable platen, provided at a printing
stationj whereon the sheet is wound so that the ends of
the sheet overlap each other and a side edge thereof
p~rojects beyond an ehd of the platen during printing,
first means, for feeding the lowermost sheet exposed in
35 ~ the opening toward the platen, provided under the tray,
second means for driving the platen by a predetermined
rr,.~'~ . ~ ` - ....: . :" ~j .:, -: `: :~
~ . . 1 332320
number of rotations in each printing operation, third
means for printing an image on the sheet wrapped about
the platen during rotation of the platen, and fourth
means, associated with the third means, for sensing the
presence of the printing sheet wrapped about the platen
to determine printing start position each revolution of
the platen, provided in the vicinity of the third means.
According to another aspect of the invention,
there is provided a printing apparatus for printing an
image on a sh~et of printing medium comprising first
means on which the sheet is wound such that the ends
thereof overlap, for rotating a predetermined number of
revolutions in one printing operation and provided at a
printing station, second means for printing an image on
the printing medium through the predetermined
revolutions of the first means.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The present invention will be understood from
;~ the detailed description given hereinbelow and from the
accompanying drawings of the preferred embodiment with
is given explanation and understanding only and is not
intended to imply limitations to the invention.
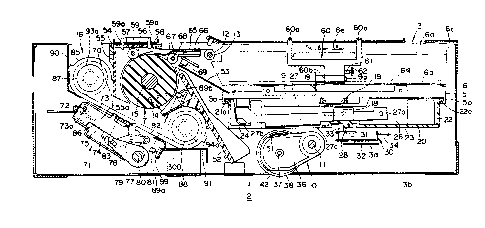
~ ~ Fig. 1 is a longitudinal sectional view of a
`~ printing apparatus of the present invention.
Fig. 2 is a perspective exploded view of a
color printing apparatus of the present invention.
Fig. 3 is a rear view of a color printing
apparatus of the invention.
Fig. 4 is a partially cutaway side view of a
color printing apparatus of the invention.
Fig. 5 is a top view of a paper feeding tray
` holder 5~
Fig. 6 is a section view taken along the line
A-A indicated in Fig. 5.
Fig. 7 is a perspective view of a paper
f-eding trey.
l ~
`.
~332320
-- 5 --
Fig. 8 is a partial perspective breakaway view
of a locking mechanism for a paper feeding tray
indicated in Fig. 7.
Fig. 9 is a perspective view of a paper
feeding mechanism.
Fig. 10 is a sectional view of a paper feeding
mechanism of Fig. 9.
Fig. 11 is a perspective view of a head moving
mechanism for lifting a thermal head up toward a platen.
Fig. 12 is a perspective view showing a
portion of a head moving mechanism of Fig. 11.
Fig. 13 is a partial side view of a head
moving mechanism of Fig. 11.
Fig. 14 is a rear view of the mechanism shown
Fig. 13.
Fig. 15 is a top view of a ribbon cartridge
driving system.
Fig. 16 is exploded perspective view of a
driving system of a color printing apparatus
Fig. 17 is a perspective view of a color
~; printing apparatus of the present invention.
Fig. 18 i9 a sectional side view showing a
~ paper feeding tray is in its loading state.
; Fig. 19 is a sectional side view showing a
paper feeding tray which is in the loading end position.
Fig. 20 is an explanatory view showing a
~; locking and releasing method for locking and releasing a
paper feeding tray.
Figs. 21 and 22 is an explanatory view showing
- , 30 a paper feeding meahanism.
~- Fig. 23 is an explanatory cutaway side of the
printer in a pre-printing mode.
Fig. 24 is an explanatory view which shows a
~,
paper sheet fed to a platen.
Fig. 25 is an explanatory view showing a paper
sheet being printed.
~' :
&~
- 6 _ 1332320
Fig. 26 is an explanatory view showing a
printed paper sheet which is ejected to an receiving
housing.
Fig. 27 is a bottom view of a driving
mechanism for a printer in an initial state.
Fig. 28 is a side view of a driving mechanism
for a printer when it is in an initial state.
Fig. 29 is a bottom view of a driving
mechanism for a printer while the leader section of a
ribbon is being aligned.
Fig. 30 is a side view of a driving mechanism
of a printer while the leader section of a ribbon is
being aligned.
Fig. 31 is a bottom view of a driving
mechanism for a printer when a paper sheet is fed to a
printing station.
Fig. 32 is a side view of a driving mechanism
` of the printer within a paper sheet is being fed to a
printing station.
Fig. 33 is a bottom view of a driving
mechanism for a printer when a paper sheet is wrapped
about a platen and is transferred to an ejecting
housing.
;~ Fig. 34 is a side view of a driving mechanism
,.
~ 25 for a printer which is in the same state as Fig. 33.
i~ Fig. 35 is a bottom view which shows a driving
mechanism for a printer while a paper sheet is being
printed.
Fig. 36 is a side view which shows a driving
~I 30 mechanism which is in the same state as Fig. 35.
i ~ Fig. 37 is a view in which a paper sheet is
jammed.
Fig. 38 is a schematically explanatory view
which shows a conventional printer in a paper feeding
~f~ 35 state.
Fig. 39 is a schematically explanatory view
.,,-~
.
! ~
1332320
-- 7 --
which shows a paper ejecting state in a conventional
printer.
Fig. 40 is an explanatory view which shows a
sheet of printing paper.
Fig. 41 is a view which shows the
relationship between the printing paper sheet in Fig. 40
and a platen according to the invention.
DESCRIPTION OF THE P~EFERRED EMBODIMENT
In order to facilitate better understanding
the present invention, a whole printing system of a
polychromatic printing apparatus according to the
present invention will now be described hereinbelow.
i
Referring now to the drawings, particularly to
Figs, l, 2 and 17, there is illustrated a printing
apparatus according to the present invention. A
polychromatic printing apparatus l has a printer cabinet
- 2. The cabinet 2 comprises a rectangular frame type
~ inner chassis 3 and an outer chassis 4 covering the
-~ front chassis. The cabinet 2 has a tray holder 5 for
receiving a feeding tray and a receiving tray housing 6
at the front side thereof. The tray holder 5 and the
, ~
receiving tray housing 6 are arranged on the right-hand
~ ~ side, in Fig. 2, of the cabinet 2 and the housing 6 is
!'''~, provided above the holder 5. A printing station 7 is
~provided~so as to face the tray holder 5 and the tray
housings 6 in the left-hand side of Fig. 2.
A feeding device 10 for feeding printing paper
sheets 8 one by one to the printing station 7 is
interposed between a front plate 3a and a rear plate 3b
; 30 of`the inner chassis 3. The device 10 is pivotally
supported by a driving shaft ll below the feeding holder
5.~ An~ejecting roller shaft 13 has a plurality of
ejecting rol~lers~12 for carrying the printing paper
sheet 8 towards the receiv~ing tray housing 6. The shaft
13~is rotatably supported~between the front plate 3a and
t he rear plate~3b and is disposed between the printing
- 8 _ 1 3 3 2 3 20
station 7 and the receiving tray housing 6. A platen
shaft 15 having a platen 14 is disposed above the
printing station 7 and is rotatably supported between
the front plate 3a and the rear plate 3b. A ribbon
cartridge housing 16 for storing a ribbon cartridge is
defined by the printing station 7.
As shown in Fig. 17, the receiving housing 6
opens forwardly from the upper right side in front of
the outer chassis 4 of the cabinet 2. The tray holder 5
is covered by an openable lid 4a. The ribbon cartridge
16, similarly to the tray holder 5, is covered by an
openable lid 4b.
With reference to Figs. 2, 5, and 6, a feeding
system will be described hereinbwlow.
The rectangularly shaped tray holder 5 is made
;~ of a synthetic resin. The tray holder 5 is disposed
-` between the front plate 3a and the rear plate 3b of the
inner chassis 3 and is fixed by clamps at the upper end
of an opening portion 3c which i5 formed at right middle
side of the front plate. A hook portions 5a are
integrally formed with the tray holder 5 at each side
~ thereof. The hook portions 5a extend downwardly and the
7 ends thereof oppose each other for detachably receiving
i~ a feeding tray 20, to be described hereinafter.
r ~ 25 A rectangular recess portion 5b is formed at
;~ the middle portion of the tray holder 5. A pair of
~ parallel elongated guiding openings 5c which extend in
t~ the longitudinal direction, or in the direction
perpendicular to the rear plate 3b of the inner chassis
3 is provided in the recess portion 5b. An ejecting
member 18, as shown in Fig. 8, which is made of a
; synthetic resin, is arranged at the underside of the
recess portion 5b so as to slide in the pair of openings
5c. This member 18 is operable to unload the feeding
tray 20 to project partly from the cabinet 2 towards
outside thereof. The member 18 is essentially U-shaped
, ~
; ~
;
~ . ~
9 ~332320
cross section. Both side walls 18a of the member 18
extend upwardly and are received in the pair of
elongated openings 5c. A pair of L-shaped portions 18b
project laterally at the upperside of the holder 5 so as
to slidably retain the ejecting member 18 on the holder
5. The pusher portion 18c which comes in contact with
the end of the feeding tray 20 extends downwardly from
the end of the ejecting member 18. It will be
appreciated that the eject member 18 can reciprocate
slidably along the pair of elongated openings 5c.
L-shaped cut out portions 18d are formed in
portion 18b of the ejecting member 18. A pair of holes
Sd provided in which the ends of a pair of tension
springs are installed which urge the ejecting member 18
away from the rear plate 3b.
; With reference to Figs. 7, the feeding tray
and a locking mechanism therefor will be described
hereinbelow.
. ~ ~
The feeding tray 20 is made of a synthetic
resin and is generally in the form of an upwardly
opening box for receiving a stack of paper sheets 8. In
a bottom of the tray 20, an opening 24 which is half the
size of the tray bottom is provided so as to expose a
half of the back surface, or the reverse side of the
25 ~ paper of the lowermost sheet of a stack of paper shèets
8~. Flange portions 21a and 22a are provided on side
walls 2~1 ànd 22 respectively so as to allow the feeding
tray 20~to~be slidably supported by holder portions 5a ~-
(see Fig. 6).
A handIe 25 is formed in the front of the tray -~
20. ~A pai~r of feeding levers 27 are provided which
supply the lowermost paper sheet 8 of the stack of paper
sheets within the tray 20 to the printing station 7.
Each;end of the levers 27 is pivotally supported by pin,
35 ~ one of which is connected to the inner side of the
handle 25 and other of which is connected to the rear
~332320
wall 26. The lever 27 has a barb section 27b for
receiving a corner of paper sheet on a corner of the
opening 24 of the tray 20.
An engaging member 28 is provided so as to
project downwardly from the bottom 23 of the tray 20 at
the rear wall 26 side (see Fig. 8~. The engaging member
28 is in the form of a triangle member defined by a
surface 2&a angled approximately fortyfive degrees
relative to the rear plate 26, a V-shaped cut-out
surface 28b, and a tapered surface 28c. A locking
mechanism 30 is provided at the rear plate 3b of the
inner chassis 3. The mechanism 30 is engageble with the
engaging member 28 of the feeding tray 20 to fix the
feeding tray 20 within the tray holder 5 and also can
release the engagement therebetween.
The locking mechanism 30, as shown in Fig. 8,
comprises a V-shaped locking member 32, a locking pin 33
which is secured on the end of the locking member at the
feeding tray side, and a tension coil spring 34 which is
hung on the other end of the locking member and the rear
plate 3b. The locking member 32 is pivotally supported
by an axle 31 on tab 3d which is formed with a section
of the rear plate folded so as to project horizontally.
The spring 34 urges the locking member 32 such that a
hooking portion 32b is urged toward the rear plate 3b.
With this arrangement, the insertion of the feeding tray
20 into the tray holder 5 causes the surface 28a of the
engaging member 28 to come in contact with the locking
~; pin 33 so as to rotate the locking member 32 in the
direction indicated by arrow in Fig. 8 against the
-;~ tensioning force of the spring 34, as can be seen in
t ~ Figs~. 20(a) to 20(c), and thereby allow the engagement
of the locking pin 33 with V-shaped surface of the
engaging member 28 to lock the tray. By pushing the
handle backward, th~ engagement between the locking pin
33 and the engaging member 28 is released, as can be
#'~
~"
- 11 133232(~
seen in Fig. 20(d) and 20(e). The feeding tray 20 is
partially ejected via ejecting member 18 to project
partly forward from the tray housing 6.
With reference to Figs. 9 and 10, a paper
feeding system will be described hereinbelow.
A paper feeding mechanism comprises the
driving shaft 11, a supporting shaft 37 which is
pivotally supported on the shaft 11 by a pair of arm
members 36, a rubber feeding roller 38 provided on the
shaft 37, and a pair torque limiters 39 disposed between
the shafts 11 and 37 at the ends of the feeding roller
for feeding the lowermost sheet 8 of the stack of paper
sheets within the feeding tray 20 toward the printing
station 7. The drive shaft 11 is rotatably mounted
between the front plate 3a and the rear plate 3b of the
inner chassis 3. The rotation of the shaft 11 causes
the feeding roller 38 to rotate via a driving gear 40
and a driven gear 42, thereby feeding a paper sheet to
the printing station 7. A pair of retaining rings 50 is
installed in grooves provided in the shaft 11 so as to
prevent the arm member 36 from moving outward due to the
force of the compression spring of the limiter.
The torque limiter 39 for controlling the ~,~
torque outputted by the driving shaft 11 comprises a
~first limiter 41 and a second limiter 43. The first
limiter 41 is provided with a compression spring which ~,
is interposed between the arm member 36 and the driving
~s ~n~ gea~r 40~fixed on the shaft 1. and always urges the arm
,member outwardly against the retaining ring to restrict ~,~
~30 the,rotati,on of thei arm member around the shaft 11. It
;Y~will be appreciated that the-arm member 36 can be - ' -
rotated by~the drivlng shaft 11 within the predetermined
range of tor~q~ue defined by the compression force of the
spring. The second limiter 43 comprises a limiter shaft
45~, a spring stopper 46, an engaging ring 48, and a
compression spring 49. The second limiter 43 is '~
- 12 ~33~320
arranged between the arm member 36 and a gear 42 which
engages with the driving gear 40. The shaft 45 is fixed
on the shaft 37 and supports the gear 42 via a felt ring
47 therebetween. The sprin~ stopper 46 is rotatably
mounted on the end of the shaft 45. The engaging ring
48 engages the felt ring 47 placed on the gear 42 and is
rotatably supported on the limiter shaft 45. The
compression spring is interposed between the spring
stopper 46 and the engaging ring 48 and urges the
engaging ring 48 into engagement with the gear 42 via
the felt ring 47.
It will be appreciated that torque is
outputted from the driving shaft 11 through the first
limiter 41, comprised of the spring so that the pair of
arm members lifts up the feeding roller 38 50 as to
engage the bottom sheet of the stack of paper sheets
within the feeding tray 20. The second limiter 43
supplies torque to the feeding roller so that the roller
separates one sheet from the bottom of the stack of
paper sheets so as to feed it to the printing station 7.
A pair of leaf springs Sl which contact a bottom edges
27c of the pair of levers 27 is mounted on the the pair
of arm members. Spring force of the leaf spring 51
causes the barbed sections 27b of the pair of feeding
~;~ 25 levers 27 to come in contact with the paper sheet 8 with
a predetermined pressure.
As shown in Fig. 1, synthetic resin middle
guiding plate 52 for paper is disposed between the
platen 14 and the feeding roller 38. The guiding plate
~, ~ 30 52 guides the paper sheet withdrawn within the tray 20
toward the upper peripheral surface of the platen 14.
In addition, a metal upper guiding plate 53 is disposed
between the tray holder 5 and the platen 14 above the
guiding plate 52.
A synthetic resin frame 54 defining an opening
is installed in the inner chassis 3 above the platen 14.
, -~
::
,~:
;`:
- 13 - 1332320
A synthetic resin paper guiding plate 55 mounted
detachably on the frame 52 so as to cover peripheral
surface of the platen 14 from the upper side of the
platen. The guiding plate 55 has a plurality of ribs
55a. Each ribs 55a has a section which is curved so as
to correspond to the outer peripheral surface the platen
14. A pinch roller 56 which comes in contact with the
outer surface of the platen 14 is rotatably supported by
a shaft 57 at the middle portion between the plurality
of ribs 55a.
A metal lid 58 is engageble with upper edges
of the front plate 3a and the rear plate 3a of the inner
chassis 3 to cover the upper side of the guiding plate
55. The end of the lid 58 can be inserted into a pair
of holes 3e provided in the rear plate 3b, while other
end thereof is fixed by a U-shaped synthetic resin
fastener 59. The fastener 59 has a pair of barbed
sections 59a on its legs. The engagement of the barbed
sections 59a with the upper edge of the front plate 3a
serves to fix the lid 58 to the cabinet 2.
As shown in Fig. 17, a rectangular opening 4c
is formed in a position on the outer chassi3 4 beneath
the lid 58. The opening 4c is accessable by opening a
lid 4d.
The paper ejecting system and the paper
receiving tray will be described hereinbelow.
As shown in Figs. 1 and 2, the receiving
housing 6 takes the form of a rectangular synthetic
resin box which has openings in the front and upper side
respectively. The housing 6 is provided at of the
printer upper right side between the front and the rear
pIates 3a and 3b of the inner chassis 3. The bottom of
the housing comprises an upper step 6a and a lower step -~
6b. The step 6a is located at the rear plate 3b side
~; 35 and defines "a first ejecting position", while the step
6b is positioned below the step 6a at the front plate 3a
,
:' :
14 1332320
side and defines "a second ejecting position".
A pair parallel of elongated openings 6d is
formed in the middle portion of the step 6a of the
receiving tray housing 6. The openings 6d extend to the
upper end of a rear wall 6c extending upwardly from the
rear end of the step 6a. A pair paper pushers 60a for
pushing the printed paper sheet up is formed on the end
of a U-shaped arm 60. The arm 60 can swing the paper
pushers from rear to front. The base portion 60b of the
arm 60 is rotatably supported by a pin 9 installed on an
L-shaped mounting plate 9 arranged between the front
plate 3a and the rear plate 3b. A pin 61 is anchored in
the base portion 60b so as to extend in the horizontal
direction. The arm 60 can therefore rotate about the
pin 9a of the mounting plate with the result that the
pair of paper pushers 60a projects upwardly above the
bottom plate 6a. Moreover, a guiding flange 6e for
guiding ejected paper sheets 8 onto the step 6a of the --
first ejecting position extends laterally from the rear
wall 6c. The laterally projected pin 61 cooperates with
an actuating plate 125 to be described hereinafter via a
sliding plate 62 and a plate 63 rotatable about a pin
200 anchored in the actuating plate (see Fig. 3).
Lateral displacement of the actuating plate 125 along
with the surface of the rear plate 3b causes the sliding
plate 62 to move perpendicularly to the surface of the
rear plate 3b, thereby allowing the arm 60 to swing
about the pin 9a, which causes the pair of paper pushers
to eject the paper from the ejecting roller into the
tray 64.
The receiving tray 64 is, as shown in Fig. 1,
stored on the lower step 6b within the receiving tray
housing 6. A pair of rectangular paper guiding plates
65 and 66 for guiding the printed paper sheet to the
receiving tray housing 6 is disposed along the
peripheral surface of the platen 14 above the guiding
' ~
- 15 ~ ~33232~
plate 53. Both ends of the pair of the plates 65 and 66
is fixed on the edges of the front and the rear plate 3a
and 3b. Under the lower side guiding plate 66, a pinch
roller 67 which contacts the peripheral surface of the
platen 14 is rotatably supported by a shaft 68. A paper
edge optical reflex-type sensor 69 is disposed between
the paper guiding plate 66 and the guiding plate 53 at
the platen 14 side. The sensor 69 senses an edge of the
paper sheet 8 to be printed. In addition, a sensor 300,
to be described hereafter, similar to the sensor 69 is
installed at a position in the vicinity of the end
surface of the platen 14 and is directed to the ribbon.
The sensor 300 detects the edge of the paper sheet
wrapped on the platen 14 to whether it is in an initial
position.
A head moving mechanism will be described
hereinbelow.
As can be seen in Fig. 1, a head moving
mechanism 71 is provided under the platen 14 of the
printing station. The mechanism 71 is adapted for
moving a flat-type thermal head (a printing head) 70
into contact with the periphery of the platen or to be
released therefrom.
With reference to Figs. 11, 12, and 14, the
head moving mechanism 71 comprises a head supporting
member 73, a sub-head supporting member 75, a pair of
linkage plates 77, a pair of driving arms 79, a driving
sha~ft 80,~and a ribbon roller 82. The head supporting ~`
member 73 is movably supported by a shaft 72 disposed `~
0 between the front and the rear plates 3a and 3b of the
inner chassis 3 and is adapted for fixing the thermal
head 70. The sub-head supporting member 75 includes a
pair of~side wall portions 75b and a pair of elongated
bottom ~plate 75a connected between the side wall
~portions and is~in the form of rectangular frame. The
ends of each of the side wall portions 75b is pivotally
s, ~ ~ ,
.,
~33232~
- 16 -
supported by the shaft 72 and the head supporting
members 73 are disposed between the pair of side wall
portions. A pair of coil springs 76 (only one is shown)
interposed between the bottom plate 75a positioned at
the driving shaft side and the heat sink plate on which
the radiating fins 74 are formed. One end portion of
pair of linkage plates 77 is rotatably connected to the
side wall portions 75b of the supporting member 75 by a
pin 201, while other portion thereof engages a cut-out
portion 79a formed in the driving arm 79 via a pin 78.
Also, an L-shaped sub-arm 81 is installed on the pin 201
at its corner and has the ribbon roller 82 at its end.
The driving arm 79 is fixed on the driving shaft 80
which is rotatably supported between the rear and the
front plate 3a and 3b of the inner chassis 3 and is
rotatable according to the rotation of the driving
shaft. It will be appreciated that with this
arrangement, the rotation of the driving arm 79 about
~ the driving shaft causes the head supporting member 73
;~ 20 and the sub-head supporting member 75 with the thermal
head 70 to be lifted up toward the platen 14.
With reference to Fig. 12, the head supporting
member 73, as described above, generally defines a
U-shaped. A pair of side plates 73b has through holes
-~ 25 73a for receiving the shaft 72. The holes 73a are
elongated vertically relative to a bottom plate 73c so
~; as to allow the head supporting member 73 to move a
little within the opening. Therefore, when the thermal
head 70 is driven contact with the platen 14 by the
compression force exerted by the spring 76 so the play
allows the contact pressure of the surface of the head
with the peripheral surface of the platen to be equal
;~~ along the entire length. The engaging pressure of the
thermal head 70 is supplied by the pair of coil springs
76 when the head supporting member 73 is thrust toward
the platen 14 by the driving arm 79.
, .
~ ,
.~
- 17 _ , 1 3 3 2 32 0
When the thermal head 70 is not in contact
with the platen 14, the location of the head is
determined by a barbed portion 75b provided on the
sub-head supporting member 75 against which the head is
thrust by the thrusting force exerted by the springs 76.
The ribbon roller pressure of the ribbon
roller 82 for thrusting the roller against the platen 14
is provided independently from the head pressure by a
tension spring 83 hung between the sub-head supporting ~ -
member 75 and the sub-arm 81.
A ribbon cartridge housing will be described ~ -
, hereinbelow.
As can be seen in Fig. 1, the ribbon cartridge
~ housing 16 is adapted for storing a ribbon cartridge 85.
''` 15 The ribbon cartridge 85 includes a supply reel 87 and a
take-up reel 88. The supply reel 87 is provided with a
,, , ribbon 86 having continuous printing areas formed with
yellow (Y), magenta (M), and cyanogen (C). The take-up
reel 88 is rotatably mounted within the cartridge so as
to take up the ribbon withdrawn from the supply reel.
The leader of the Y color section of the ribbon 86 is
detected by a light transmission type optical sensor 89,
which comprises a light emitting element and a light '~
receiving~element.
;25 ; ~ 'The ribbon cartridge housing 16 includes~an '',~
upper holding plate 90 and a~lower holding plate 91.
The holding plate 90 is arranged~within the housing 16
so~as~to hold the~supply~reel side~8~7 of the~cartridge. -~,,
The holding plate 91 is adapted for holding the take-up
30 ree,l side 88. ,An opening for inserting the ribbon ~
cartridge 85 into the housing 16 is, as shown in Fig. 2, -~'
ormed~in~the front plate 3a. As shown in Fig. 15, a
supply~reel~ table 93 for the supply~reel 87 and a
,take-up reel table 94 for the take-up reel 88 are
; ; 35~ ~'arranged d~iagonally on the~rear plate 3b. The reel
tables 93 and 94~p~roject inwardly from the rear plate 3b
`` 1332320
- 18 -
and are rotatably supported by shafts 96 and 97
respectively fixed on the mounting plate 95 which is in
the form of substantially L-shaped plate. Limiting
gears 98 and 99 are disposed between the mounting plate
95 and the rear plate 3b. In additionr reel hubs 93a
and 94a for engaging with the supply reel 87 and the
take-up reel 88 are provided on the shafts 96 and 97.
The driving system will be described
hereinbelow.
Referring to Figs. 1 and 16, a paper feeding
driving gear 100 and a paper ejecting roller driving
gear 101, and a platen driving gear 102 are disposed at
the outside of the rear plate 3b. The gear 100 is
installed on the end of the driving shaft 11. The gear
101 is installed on the end of the shaft 13 on which a
plurality of ejecting rollers 12 are supported. The
- platen driving gear 102 is installed on the shaft 15 on
which the platen 14 is supported.
The paper feeding driving gear 100 engages
with an intermediate pinion 104 through an intermediate
gear 103. A first shifting gear 107 is urged toward the
outside by a compression spring 106. The inwardly
shifting (rear plate side) of the gear 107 which is
, -
carried out by a driving force changing mechanism 140
~25 against the force due to compression of the spring
; ~causes the pinion 104 and the shifting gear 107 to be
engaged each other. The first shifting gear 107 is
adapted for being shifed among three positions (outside,
middle, and innerside) by the changing mechanism 140 and
engages with a gear 108a of an intermediate gear
assembly 108 which comprises the gear 108a and a pinion
108b.
The gear 108a of the intermediate gear
assembly 108 engages with a small gear llla of a second
, ~35 shifting gear assembly 111. The second shifting gear
assembly 111 comprises a gear 111 engageble with a worm
~, .. ~,
~ 1332320
lg --
113 and the small gear llla and is urged toward the
outside on a shaft 109 due to spring force of a
compression spring 110 via a second driving force
changing mechanism 150. Inward movement (rear plate 3b
side) of the second gear assembly 111 by the second
changing mechanism 150 causes the gear lllb to engage -~
with the worm 113 connected to a stepping pulse motor
112 provided as a second driving source. The gear llla
of the second gear assembly 111 engages with a driving
gear 101 for the ejecting roller 12 via a pinion 114.
The outward shifting of the first shifting
~ gear 107 due to compression force of the coil spring 106
-~ during a changing operation of the changing mechanism
140 causes the take-up reel table 94 to engage with the
limiting gear 99 provided thereon to rotate.
A thermal head gear 120 engages with a small ~;
gear 121b of a head idler gear assembly 121 which ~ `
comprises a gear 121a and the small gear 121b. The gear
121a of the head idler gear assembly 121 engages with a
small gear 124b of an intermediate gear assembly 124 ;
ncluding the small gear 124b and a gear 124a engageble
with a worm 123 provided on the stepping motor 122
provided as a first driving source. It will be -~
appreciated that the driving force outputted from the
stepping motor 122 causes the gear 121a to rotate.
;~ A pin 126 is fixed on the end of the actuating ~`
plate 125 and is inserted into one of three recess
portions~divlded by ribs~(not shown) provided in the
thermal head gear 120. The rotation of the gear 120
therefore causes the rib to come in contact with the pin
126 so as to be pushed laterally, thereby displacing the
actuating~plate 125.
The actuating plate 125 is operable for
swinging the U-shaped arm 60 which pushes the printed
35 ~ paper sheet forwardly within the receiving housing 6.
The actuating plate 125 is in the form of a long
` ~33232~
- 20 -
generally L-shaped plate and has three elongated
openings for receiving pins 127, 128, and 129 fixed on
the rear plate 3b. As described above, with this
arrangement, the actuating plate 125 can move in the
longitudinal direction thereof within the range defined
by the length of the elongated openings. The L-shaped
plate 63 is rotatably supported by the pin 200 fixed on
a folded plate 125d provided on the end of an extending
portion of the actuating plate 125. Lateral
displacement of the actuating plate 125 in the direction
of head driving gear 120 causes the pair of paper
pushers 60a of the arm 60 to enter the pair of openings
6d, indicated in Fig. 2, provided in the receiving
housing ~. On the other hand, lateral displacement in
the opposite direction causes the pair of paper pushers
60a to project upwardly from the pair of openings Çd.
An ejecting stopper 130 is pivotally supported
by the pin 127 fixed on the rear plate 3b via the
actuating plate 125 and adapted for engaging with a
L-shaped hook plate 32b cooperating with a plate 32.
The ejecting stopper 130 has an elongated opening 130a
for receiving a pin 131 fixed on the actuating plate 125
in its middle portion. Therefore, the lateral
displacement of the actuating plate 125 causes the
ejecting stopper 130 to rotate about the pin 127 in the
direction indicated by a two-dot chain line in Fig. 3.
The complete insertion of the feeding tray 20 into the
' ; tray holder 5 causes the hook plate 32b to projectoutwardly from the rear plate 3b. Lateral displacement
of the actuating plate 125 causes it to engage with the
~ hook plate 32b preventing the feeding tray from being
-~ withdrawn during the feeding of a paper sheets to the
I ~ printing station.
A cam having a projecting portion 121c and a
V-shaped surface 121d is provided on the gear 121a of
the head idler gear 121 which has a recess 121e. Coil
I :: ~:
I .
I
I ;~
..i:
.,,.~ . ~ . ,~,", .
~ ., " :,.. ". ,, ,: ,
1332320
- 21 -
springs 137 and 138 are connected between the ends of
braking arms 132 and 133 and a shaft 135 of the head
idler gear 121. The end surfaces of braking arms 132
and 133 are thrust by the springs 137 and 138 toward the
peripheral surface of the cam so as to come in contact ~ -
therewith, while the other end portions take the form of
barbs for engaging the limiter gears 98 and 99
respectively. It will be appreciated that the
engagement between the barbs and the gears 98 and 99 due
to the rotation of the cam causes the supply reel table
93 and the take-up reel table 94 to be stopped.
The driving force changing system will be
described hereinbelow.
The driving force changing mechanism 140
comprises a cam gear assembly 143 and a shifting lever
145. The cam gear assembly 143 includes a small gear
141 for engaging the head idler gear 121 and a cam 142
having a cam surface 142a which is in the form of a
recess. The shifting lever 145 functions as a cam
follower and is pivotally mounted on a U-shaped mounting
plate 144 via a shaft 145. One end of the lever 145
comes in contact with the cam surface 142a of the cam -~
gear assembly 143~ A leaf spring 146 for engaging the
upper surface of the shifting gear 107 is connected to
the other end thereof. The rotation of the cam gear
assembly 143 causes the~shifting lever 145 to rotate
about the shaft 145 according to the configuration of
the cam surface 142a and thereby the leaf spring 146
shifts the shifting gear 107 between its three positions
30 (outside, middle,~ and innerside). ~ ~-
A pair of pins 141a is fixed on the end
- surface o the small gear 141 of the cam gear assembly
~G ~ 143. A baoe plate portion 149a of an L-shaped locking
arm 149 is adapted for engaging the pair of pins 141a.
35~ The locking arm~has a`hollow cylindrical portion at its
~rner lnto wh1ch a shaft is inserted snd pivotally
: ` ~
`~ 133232~
- 22 -
supported by a U-shaped mounting plate 147, indicated in
Fig. 15, via a coil spring 148. It will be noted that
the rotation of the cam gear assembly causes the pin 141
to come in contact with the base plate portion 149a and
thereby the locking arm 149 rotates to release a barbed
portion 149b from an engaging portion 98a of the limiter
gear 98 against the repulsing force of the spring 148.
The supply reel table 93 can therefore rotate.
The second driving force changing mechanism
150 comprises an operating lever 151, an intermediate
operating lever 152, and a shifting lever 153. The
operating lever 151 is provided with a barbed portion
151a, at one end, for engaging with, and being released
from, the recess 121e of the head idler gear 121, a
curved portion 151 at its middle portion, and a pin 151c
secured on the other end. The intermediate lever 152
has a pin 152b projecting vertically from its middle
portion and an elongated opening 152a. One end of the
pin 152b is inserted into a hole formed in the operating
lever 151, while the other end thereof is rotatably
mounted in the mounting plate 95, as shown in Fig. 3.
The shifting lever 153 includes a supporting shaft 153c,
~; an engaging shaft 153a, and a leaf spring 153b. The
lever 153 is pivotally supported by the shaft 153c on a
bracket portion 95a of the mounting plate 95. The
engaging shaft 153a is inserted into the elongated
opening 152a of the intermediate operating lever 152.
The leaf spring 153b is in contact with the surface of
~ the shifting gear 111. It will be appreciated that
- ~ 30 swinging the operating lever 15~ causes the shifting
gear 111 to be shifted to an inside or outside position
by the leaf spring 153b.
The printing operation of the printer
according to the present invention will be described
hereinbelow.
In an initial state before printing, (or when
~2,~ ::
' ~
- 23 - 1332320
the feeding tray 20 is loaded or unloaded, the ribbon
cartridge 85 is installed or removed, or a paper sheet 8
is jammed) the feeding roller 30 of the feeding -~
mechanism 10 is spaced downwardly from the bottom of the
feeding tray 20. The U-shaped arm 60 for pushing out
the ejected paper sheet projects upwardly from the upper
step 6a of the receiving housing 6 and is inclined
forwardly. In this state, as shown in Figs. 27 and 28,
the first shifting gear 107 is located in the middle
position on the shaft 105 as described above, while the
second shifting gear 111 is released from the worm 113
of the stepping motor 112. Thereafter, as shown in ~-~
Figs. 18 and 19, when the feeding tray 20 is loaded into
the tray holder 5, the feeding tray 20 is locked, as
shown in Figs. 20 (c), by the locking mechanism 30. At
this time, the hook plate 32b projects outwardly from ~-
the rear plate 3b, as shown in Fig. 29. A print start
button (not shown) is pressed to operate the stepping
motor 122, thereby causing the head driving gear 120 to
rotate. As shown in Figs. 16, 29, and 30, the rotation
of the head driving gear 120 causes the driving force
changing mechanism to shift the first shifting gear 107
to the outside position, allowing the the first shift
gear 107 to engage with the limiter gear 99 of the
take-up reel table via the intermediate gear 115. The
driving operation of the take-up driving reel table 94
causes the leader of the ribbon 86 to be aligned at an
initial position, while the second shifting gear 111
engages with the worm 113 of the stepping motor 112 due
to the changing operation of the driving force changing
mechanism 150, so that the platen 14 and the ejecting
roller 12 rotate (the second shifting gear 111 maintains
engagement with the worm until the ejecting operation of
the printed paper sheet begins). When the ribbon is
aligned at its initial position, a braking arm 132,
locking arm 149 of the supply reel table 93, and the
,
,
1332320
- 24 -
braking a~m 133 of the take-up reel table 94 are
released so as to allow the ribbon to move freely. The
driving of the head driving gear 120 causes the
actuating plate 125 to be displaced laterally with the
result that the eject stopper 130 engages with the hook
portion 32b of the locking mechanism, thereby preventing
the feeding tray 20 from being withdrawn from the tray
holder 5. It will be appreciated that the removal of
the feeding tray 20 is prevented during feeding of the
paper sheets and during printing. Moreover, the lateral
displacement of the actuating plate 125 causes the pair
of paper pushers 60a of the arm 60 to swing rearwardly
within the opening 6d provided in the higher step of the
receiving housing 6, maintaining this state until the
ejecting operations begins.
The rotation of the stepping motor 122 causes
the first shift gear 107, as shown in Fig. 31, to be
shifted to the innerside position, engaging with driving
gear 100 for the feeding roller through the intermediate
gear 103 and 104. As shown in Figs. 22 and 24, the
rotation of the driving gear 100 causes the the feeding
roller 38 to be lifted up so as to come in contact with
the back ~urface of the lowermost paper sheet 8 in the
stack of paper sheets within the feeding tray 20. The
rotation of the paper feeding roller 38 causes a paper
sheet 8 to be fed to the printing station 7. During
this feeding, the braking arm 132 and the locking arm
~ 149 engage with the engaging portion 98a and the limiter
-` gear 98 respectively, while the braking arm 133 engages
with the limiter gear 99.
The paper sheet 8 fed from the feeding tray 20
,-
then is wrapped so that its back surface contacts the
periphery of the platen 14 and rotates therewith in the
direction indicated arrow in Fig. 24. During feeding
this paper sheet 8, the first shi~ting gear is located
at its middle position as shown in Fig. 33.
. ~
- --- 133232~
- 25 -
The rotation of the head driving gear 120 by
means of the stepping motor 122 causes, as shown in Fig.
25, the head moving mechanism 71 -to lift the thermal
head 70 up toward the platen 14, pushing the ribbon 86
against the platen. At this time, as shown in Fig. 35,
the first shifting gear 107 is positioned at its outside
position similar to alignment of the leader of the
ribbon 86 and drives the driving take-up reel table 94.
The braking arm 133 and the locking arm 149 are released
from the limiter gear 99 and the engaging portion 98 of
the limiter gear 98 respectively, while the braking arm
132 engages the limiter gear. During printing, the
brakes of the supply reel table 93 are applied,
preventing it from running idle with the result that a
back tension is applied to the ribbon. Thereafter,
printing begins.
As shown in Figs. 40 and 41, the width (Wp =
89mm) of the platen 14 is less than the width (Ws =
lOOmm) of the paper sheet 8 by a predetermined value
(llmm) so that the sensor 300 can easily detect marks
(M) printed on the edge of reverse surface of the paper
sheet 8. The circumference ~D (D = diameter of the
platen) of the platen 14 is less than the length (L) of
the paper sheet 8 by a predetermined value. It will
thus be appreciated that the end of the paper sheet 8
when wrapped on the platen 14 overlap by the
predetermined length.
;~ In conventional printers, when a platen with
sheet of paper wrapped thereon rotates, the leading edge
of the sheet tends to collide with the pinch roller or
the guide roller and this results in the position of the
sheet shifting about the periphery of the platen.
~; Therefore, the print starting positions of the
~ respective colors Y, M, and C therefore tend to be
;~ 35 shifted causing the printed image to be unclear.
~ By overlapping the both ends of the paper
'',, ~
., .
: ~
- 26 _ 133~
sheet as in the present invention however, the paper
sheet is prevented from colliding with the pinch roller
57 or so forth and therefore the initial printing
positions of the three colors do not become shifted.
When the paper sheet 8, as shown in Fig. 41,
is fed to the platen 14 and the mark M passes under the
sensor 300, the sensor detects it and provides a signal
to a printing controller (not shown). The sensor 300
is, as shown in Fig. 1, located a position adjacent to
the end surface of the platen 14 and near the contact
surface of the platen with the thermal head 70 so as to
sense the mark M printed on the edge of the sheet which
protruds beyond from the platen. Thereafter, according
to a signal outputted from the printing controller, the
thermal head 70 generates heat to begin printing yellow
from the mark or a predetermined position on the paper
sheet 8 according to a signal outputted from the
printing controller.
After the platen 14 rotates one cycle, the
paper sheet 8 overlap. The mark M printed on the paper
sheet 8 passes under the sensor 300 again to be detected
thereby. The C color is then printed on the paper sheet
8 in the same manner as the previous printing. After
the C color is printed, the M color is printed on the
paper sheet 8.
When the printing is finished, as shown in
Fig. 26, the rotation of the platen 14 reverses and the
platen rotates in the clockwise direction. The printed
~ paper sheet 8 is carried toward the receiving tray
`~ 30 housing 6 by the ejecting roller 13 and is guided onto
the step 6a by the rear wall 6c and the guiding plate
6e. During ejecting of the paper sheet 8, as shown in
Fig. 33, the first shifting gear 107 is positioned at
its middle position. Only the platen 14 and the
ejecting roller are operable to rotate by means of the
stepping motor 112. Thereafter, the actuating plate 125
~: :
~,
~::
-~ ~ .... ...
i"` ?~ " ~ :
- 27 - 133232~
turns back to the initial position to swing the pair of
paper pushers 60a in the forward direction. The printed
paper sheet on step 6a is ejected onto the receiving
tray 64.
As described above, in the printer according
to the present invention, the paper feeding roller 38 is
contacts the lowermost paper sheet exposed by the
opening 24 of the feeding tray 20 to feed it to the
platen 14. The paper sheet wraps on the peripheral
surface of the platen with its reverse surface in
contact therewith. Therefore, the sheets of paper are
stored within the feeding tray with the printing
surfaces up and this prevents the printing surfaces from
being damaged.
When the platen rotates one cycle, the ends of
the paper is overlap. Thereafter, printing is performed
as the platen is rotated and since the ends of the sheet
overlap shifting of the paper on platen due to
collisions of the edges of the sheet of paper with
obstacles is avoided.
:~ While the present invention has been described
~ with respect to specific embodiments thereof, it is
; evident that many alternatives, modifications, and
-~ variations will be apparent to those skilled in the art.
~ 25