Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2 ~
WH-7533-90 - 1 - 3454H/~080F
TITLE: VEHICLE ~RAKE
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
This application relates to the subject matter of
earlier application Serial No. 07-02512 filed 03-09-87 which
was a continuing application of application Serial No.
06-792213 filed 10-28-85.
The present invention relates to vehicle braking
systems and in particular to vehicle braking systems having
associated therewith an air flow for removing heat from the
braking system.
There are a host of different braking arrangements
for vehicles which have been proposed, with the most popular
braking system being either the Drum Brake or more recently
the Disk Brake. In addition to these two types of braking
systems there is also what is referred to as a Ring ~rake as
generally shown in the United States patent 3,170,542 where
braking can occur on both sides of the ring brake member.
Common to all of these braking systems is the "`-
dissipation of energy by means of heat which is generated at
or on the braking surface. This heat is dissipated to the
surrounding air environment by means of convection, however,
due to the placement of the brake generally in a confined
region under a vehicle, the circulation of air is relatively
poor and the convection coefficient of heat transfer is
relatively low. This problem of heat build-up is
particularly acute where the brake must be operated
frequently over a long period of time and thus the braking
system does not have an opportunity to dissipate the heat
when the brake is not in use. Such circumstances commonly
occur with truck braking systems, particularly in
mountainess regions, and the possibility of brake failure is
quite acute. For example, there are often run-off regions
where vehicles that are out of control (i.e. where braking
system is substantially lost) may exit into these regions
which are designed to stop the vehicle.
, . ... . . .
2 0 ~
WH-7533-90 - 2 - 345~iH/0080F
~ost conventional car braking systems operate
satisfactorily, however, braking systems used to maximum,
say eight times in a row, result in the effective braking
power to be less than 50%. The principle reason -For the
reduction in braking power is heat build-up within the
braking system.
Another problem associated with vehicle braking
systems is in the transmission of the heat generated in the
braking system to the wheel bearing of the vehicle. ~heel
bearings have generally been protected from transfer of heat
from the braking system, as the life of the wheel bearing
would be substantially reduced if exposed to the heat
generated in the braking system. Therefore, the prior
practice has been to isolate the wheel bearing from a direct
heat transfer path of the braking surface to the wheel
bearing.
There remains a need for a simple effective braking
system where heat can be efficiently removed from the
braking surface to improve both the life and performance of
the braking system.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
A vehicle brake and hub according to the present
invention comprises a ring braking member having braking
surfaces to both the interior and the exterior of the
member. A cast hub is provided which includes centrally
disposed aligned bearing ports for receiving bearings, in
combination with an outwardly exposed securing surface which
cooperates with the ring braking member to effect securement
of the ring braking member to the casting and in a manner to
accommodate heat transfer therebetween. The cast hub
includes intermediate the securing surface an~ the alignea
ports, fan blades which cause, with rotation of the brake
and hub, an axial flow of air to move across the bearing
ports and to extract heat from the fan blades of the
securing surface. The fan blades collectively interconnect
2 ~ 9
WH-7533-90 - 3 - 3454H/U080F
and s-tructurally secure the securing surface to the bearing
ports.
The ring braking member, the securing surface and
the fan blades collectively cooperate such that, under high
heat load generation at the ring braking member, heat is
efficiently dissipated from the ring brake member by means
of convection heat transfer to the surrounding air and by
means of conduction heat transfer to the securing surface
and to the fan blades which is subsequently removed by
convection from the fan blades to the air flow passing over
the fan blades during the rotation of the vehicle brake and
hub.
The present invention recognizes that heat can not
be effectively dissipated by the ring braking member alone
and this heat can be advantageously removed by means of the
cast hub acting as a heat sink. In addition, the invention
recognizes that the cast hub cannot solely act as a heat
sink, and the hub has been adapted to dissipate heat from
the hub to the surrounding air. The normal heat transfer by
means of convection would not be sufficient, therefore, the
hub is modified to provide an air flow which serves to
dissipate or remove heat from the fan blades as the air
flows through the hub. This air flow serves to remove heat
and protect the bearing ports provide~ at the center of the
hub. Thus, although the hub itself is designed to act as a
heat sink, the resulting air flow through the hub maintains
the center of the hub cool and, similarly, the ring braking
member is relatively cool due to the heat transferred to the
hub.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The preferred embodiments of the invention are
shown in the drawings, wherein:
Figure 1 is a perspective view of the vehicle brake
and hub;
2 9 ~
WH-7533-90 - 4 - 3454H/0080F
Figure 2 is a perspective view of the vehicle brake
and hub from a differen-t angle;
Figure 3 is a sectional view through the hub of
Figure 2; and
Figure 4 is a plan view of the cast hub and ring
brake.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED E~BODI~ENTS
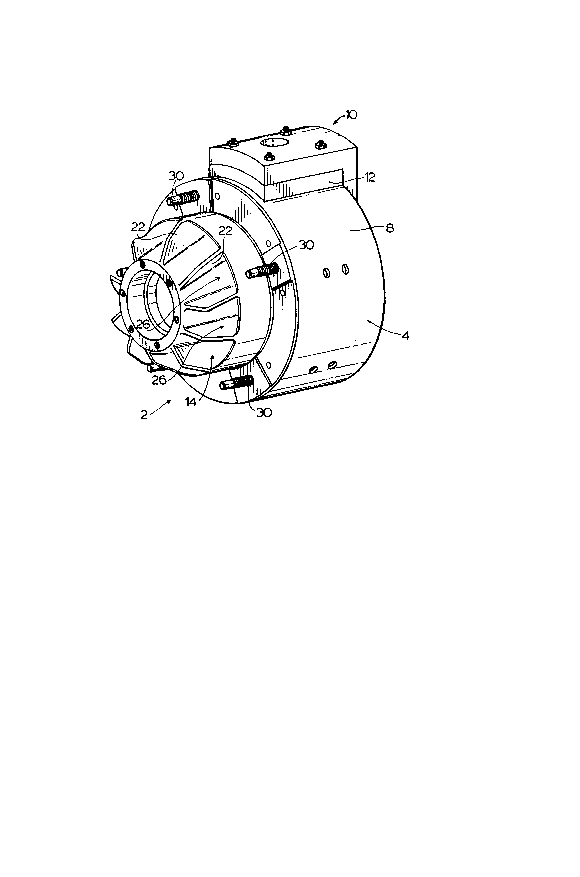
The vehicle brake and hub is generally shown as 2
in the drawings and comprises a ring braking member 4 having
interior braking surface 6 and exterior braking surface 8.
The caliper 10 can slide over one end or edge of the braking
member to position braking pads 12 directly opposite the
braking surfaces 6 and 8.
A cast hub 14 is shown having centrally disposed
aligned bearing ports 16 for receiving axle bearings. The
cast hub 14 has, at an exterior edge thereof, a securing
surface 18 in the form of an annular ring. This securing
surface 18 cooperates with the corresponding inwardly
directed radial flange 20 of the ring brake member 4. Fan
2û blades 22 form the connection between the outwardly disposed
securing surface 18 and the centrally disposed aligned
bearing ports 16.
The location of the mating of the radial flange 20
in securing surface 18 is generally intermediate the two
bearing ports 16 and as such, heat would have to move
outwardly to these bearing ports. Intermediate the fan
blades 22 and the securing surface 18 are air conduits 26
which with rotation of the hub produce an air flow generally
indicated as 24 through the air conduits which remove heat
3û from the blades. This heat is removed by convection and is
transferred to the forced air flow 24. Securement of the
ring brake member 4 to the cast hub 14 is accomplished by
means of the nut and bolt arrangement generally shown as 28
in the drawings. In addition, the securing surface 18
includes wheel rim studs generally shown as 30 by means of
2 ~
WH-7533-90 - 5 - 3454~/0080F
which the wheel rim can be secured to the vehicle brake and
hub 2.
When heat is generated on the braking surfaces 6
and 8 by means of the braking pads 12 being brought into
pressure contact with the braking surfaces 6 and 8, the heat
can be dissipated from the ring brake member 4 by means of
conduction through the ring braking member into the cast hub
14. The cast hub 14 acts as a heat sink to receive the heat
from the ring braking member 4. Heat received by the cast
lG hub will be transferred to the remaining portion of the cast
hub and will tend to migrate towards the bearing ports 16,
however, with rotation of a hub, the air flow 24 flows over
the fan blades 22 and over the bearing ports 16 whereby heat
can be removed from the cast hub member by means of forced
convection. It has been found that it is beneficial to
provide an efficient thermal transfer from the ring braking
member 4 to the cast hub 14, eventhough this cast hub will
be associated with the wheel axle bearing. It is more
efficient to provide this excellent heat transfer which will
2û allow the ring brake member to perform more consistently and
more dependably and to provide an efficient means for
dissipating the heat load resulting from braking by
transferring it to the air flow forced through the hub. The
air flow also serves to maintain the bearing at a cool
operating temperature in spite of the fact that the cast hub
acts as a heat sink for the ring braking member 4.
In considering assembly of the vehicle brake and
hub, it can be appreciated from Figure 3 that the ring
braking member 4 can be sleeved over the cast hub 14 to
bring flange 20 into abutting contact with securing surface
18. At this point, the nut and bolt arrangements 28 can
secure the two components. This arrangement allows each of
the separate components of the vehicle brake and hub to be
manufactured separately and then assembled in the particular
manner described. This particular brake and hub is suitable
for many applications from stock cars to large vehicle
2~9~9
WH-7533-90 - 6 - 3454H/008UF
brakes used, for example, in trucks which require a large
braking surface due to the relatively large loads. As can
be appreciated, the braking surfaces 4 and 6 are generally
at the same distance from the axis of rotation and do not
have a decreasing net effect as found in a disc brake. It
can also be appreciated that the size of the ring braking
surface can be married to the particular braking application
and the only limitation to date is in the aesign of the
caliper generally shown as 10, as the far end of the caliper
is effectively cantilever.
Although various preferred embodiments of the
present invention have been described herein in detail, it
will be appreciated by those skilled in the art, that
variations may be made thereto without departing from the
spirit of the invention or the scope of the appen~e~ claims.
, .