Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2~17~03
1114-3
BICYCLE FRAME AND METHOD FOR ITS MANUFACTURE
The invention relates to a method of manufa~turing a bicycle
frame comprising at least one seat tube, a down tube, a top
tube and also a rear wheel fork, the frame having a pedal
bearing, a saddle mounting sleeve and a handle bar guide
sleeve.
Furthermore the invention is directed to a bicycle frame, in
particular a monoblock frame which is in particular
manufactured in accordance with the above mentioned method.
In addition to the manufacture of bicycle frames of metal
tubes it is also already known to manufacture such frames of
so-called composite materials, i.e. fibre and~or fabric
reinforced plastic material which is formed into tubes which
are then converted in heated dies into the respectively
desired shape. ~part from the fact that the manufacture in
accordance with the known method is frequen~ly costly, and
that the aesthetic ~shapes which can be achieved leave
something to be desiredj the necessi~y of manufacturing
dif~erent frame sizes causes a considerable additional
expense in manufacture and intermediate storage.
The object of the invention is to provide a manufacturing
method for the manufacture of bicycle frames which leads to
considerable savings in the manufacturing costs, which
- 2 - ~Ql ~ ~3
ensures high stability of the frame at low weight and which
leaves substantial freedom with regard to the precise shape
of the product. Furthermore, the invention is directed
towards shaping a bicycle frame which has a high strength, a
low weight and is o~ aesthetic appeal responsive, with the
bicycle frame being capable o~ being matched in extremely
simple manner to the different frame sizes which are
required.
The part of the invention which relates to the method is
solved in that a closed at l~ast substantially triangular
base ~rame comprising a seat tube, down tube and top tube is
formed with a ~ixedly attached rear wheel ~ork and an
integrated pedal bearing in such a way that, on the one
hand, the seat tube projects beyond the connection position
with the top tube in the form of the first section which can
be cut to lengt}l and, on the other hand, that the down tube
projects beyond the connection position with the top tube in
the ~orm of a second section which can ba cut to length: and
in that after the ~ixing of the respective frame siæe, which
takes place by the sections which can bè cut to length, a
connection is effected between these sections with the
handlebar guide sleeve and the seat mounting sleeve.
Through the provision of only two sections which are cut to
length it is possible to manufacture a basic fxame which is
identical for all frame sizes and which can be converted to
the respectively desired frame size by extremely simple
measures which are quickly carried out.
A bicycle ~rame formed in accordance with the invention
comprising a seat tube, a down tube, a top tube, a rear
wheel fork, an integrated pedal bearing mount, a handlebar
guide sleeve and also a saddle mounting sleeve is
characterized in that sections which can be cut to length
_ 3 - ~ ~17403
adjoin the connection positions between the seat tube and
the top tube and the top tube and the down tube
respectively, with the sections being intended for the
connection with a seat mounting sleeve and with a handlebar
guide sleeve respectively.
Particularly advantageous developments of the method of the
invention and particular layouts of the bicycle frame of the
invention are set forth in the subordinate claims.
The invention will now be described in more detail with
reference to an embodiment and to the drawing in which are
shown:
Fig. 1 a schematic illustration for explaining a possible
basic shape of a monoblock frame in accordance with
the invention,
Fig. 2 an illustra~ion of principle to explain the
attainment o different frame sizes with a frame
design in accordance with fig. 1,
Fig. 3 two different stages in the manufacture of a seat
tube with an integrated metal housing for receiving
the pedal bearing for use in a frame in accordance
with fig. 1,
Fig. 4 a schematic illustration to explain the manufacture
of a one-piece unit comprising a down tube and a
rear wheel fork,
Fig. 5 a schematic illustration to explain the fixation of
the top tube,
2~7~
Fig. 6 a schematic illustration of a frame which is
manufactured in accordance with a specific frame
size, and
Fig. 7 a like-wise schematic illustration of a finished
frame with integrated additional elements.
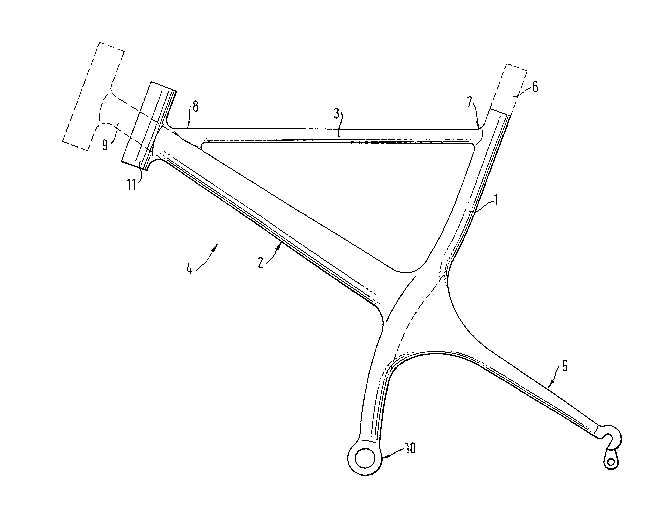
Fig. 1 shows the basic construction 4 of a possible variant
of a bicycle frame in accorance with the invention. This
frame comprises a seat tube 1 which is straight in the upper
region and is bent slightly forwardly from the center on in
the manner of a circular arc, with the end of the seat tube
being disposed in the extension of the axis of the straight
seak tube section. A metallic mounting sleeve for the pedal
bearing 10 is integrated into this lower end of the seat
tube 1. A diagonal tube or down tube 2 is provided at its
fxont end with a section 9 which can be cut to length and is
intended to receive a handlebar guide sleeve or head tube
11. The down tube 2 ~orks towards the rear so that a un~tary
arrarlgement of the rear wheel ~ork 5 and down tube 2 is
provided. The connection between the down tube 2 and the
seat tube 1 will be explained in more detail in the
following.
A horizontal tube or top tube 3 extends between a connection
position 8 disposed in the front xegion o~ the down tube 2
and a seat tube connection~position 7. A section 6 of the
seat tube 1 which can be cut to length extends beyond these
connection positions 7.
The schematic illustration of fig. 2 again shows the basic
concept of the frame of the invention comprising a seat tube
1, down tube 2 with rear wheel fork 5 and top tube 3. It can
be seen in this representation that the sections 6, 9 of the
_ 5 _ ~ ~17~03
seat tube 1 and the down tube 2 which can be cut to length
extend outwardly beyond the connection positions 7, 8 so
that, starting from the finished standard ~rame in the size
T3, the smaller sizes T2 and T1 can be provided by simple
shortening of the sections 6, 9 which can be cut to length.
After the respective cuttiny to length process the required
handlebar guide sleeve 11 and the saddle mounting sleeve 12
are attached and are preferably fixed by bonding.
The representations in fig. 3 show a preferred embodiment
for the manufacture of the seat tube 1 and its connection
with the mounting housing for the pedal bearing, i.e. the
bottom bracket. The seat tube 1 is manufactured from a
composite material in the form of a fibre and/or fabric
reinforced plastic, in particular while using carbon fibres,
and a tubular metal housing 14 with an internal thread which
is intend`ed to receive the pedal bearing is wound around
with the same material in such a manner that on the one hand
only the end face regions of this metal housing 14 are free
and, on the other hand, a radially projecting mounting
sleeve 22 is provided which is formed by the winding bandage
15 and can receive the end of the seat tube 1 which can be
inserted in the direction of the arrow.
The right-hand illustration in fig. 3 shows the arrangement
of a resilient hose 13 in the seat tube 1 and the finished
connection between the seat tube 1 and the metal housing 14.
The hose 13 which which can be set under pressure forms the
mould core for the seat tube material and is closed at its
lower end. When the seat tube 1 has been brought into the
associated position and has been fixed into the finally
desired shape the hose 13 is then pressurized. In order to
achieve an ideal transition from the point of view of the
strength between the metal housing 14, the winding bandage
15 and the seat tube 1 a curable foam 16 is introduced into
2 ~
-- 6
this transition region and can be positioned by the hose 13
in such a way that a cavity free transition is obtained.
Fig. 4 shows the construction of the down tube 2. This down
tube 2 comprises two individual tubes 23, 24 of comparable
construction to the seat tube 1. These individual tubes 23,
24 are provided in the region between th~ seat tube 1 and
the region of a handle bar guide sleeve 11 with a
bandage-like jacket 17, so that in this region an
arrangement is achieved which behaves as a strong single
tube.
The two individual tubes 23, 24 fork in the region o the
seat tube 1, so that the rear wheel fork 5 arises, and the
ends of the individual tubes can be fixedly bonded with
receiving claws 26 for the mounting of the rear wheel axle.
Elastic hoses 13 are again arranged in the individual tubes
23, 24, can be set under pressure and can, in the same way
as has already been described in connection with fig. 3,
also be used to press curable foam 16 into the transition
regions up to the two receiving claws, so that these claws
are, on the one hand, firmly anchored and, on the other
hand, ensure good continuity of the compression pressure
during moulding. The mounting claws 26 are preferably
provided with ring collars which favour the anchoring.
Fig. 5 shows in particular the connection of the top tube 3
with the seat tube 1 and with the down tube ~. The top tube
3 which can have a substantially smaller diameter in
comparison to the seat tube ~ and the down tube 2 is of the
same construction as the remaining tubes and likewise has a
hose which will be set under pressure.
In the region of the fxont end of the down tube the top tube
- 7 ~ 7 ~ ~
is so bent round that it runs parallel to the down tube over
a predeterminable length and can thus be fixedly connected
to the down tube 2 via a winding bandage 21.
The seat tube 1 is provided with an opening 25 through which
one end of the top tube is pushed and can then be preferably
arranged pointing upwardly in an angled manner in the seat
tube 1.
Fig. 6 furthermore shows a ~inished frame in which the
bandages 19, 20, 21 which are used to provide the connection
between the individual tubes are clearly characterized.
The handlebar guide sleeve 11 and the saddle mounting sleeve
12 are preferably connected with the corresponding tube ends
by adhesive bonding. The wound bandages 19, 20, 21
preferably comprise the same material as i.5 used for the
build-up of the tubes themselves and are preferably so
executed that a flu~h, aesthetically problem-free transition
always results between the dif~erent tubes while ensuring
the necessary strength.
With the final shaping of the ~rame into a unitary shape the
individual tubes which are intended to form the down tube 2
and the rear fork 5 are deformed in accordance with the
cross sectional represention S1, S2 and S3, i.e. upright
oval cross sections are used which are advantageous from the
point of view of strength and also from the external
appearance. In those regions in which the individual tubes
lie alongside one another a direct mutual bonding of these
tubes takes place in the mould via the plastic material.
Fig. 7 shows that additional members and elements can be
integrated and anchored without problem into the
construction of the frame of the invention such as is for
~ - 8 - 2~17~0~
example indicated for cable guides 27, chain thrower
carriers 28 and mountings 29 for bottles and the like.