Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
20~7S95
FIELD OF INVENTION
.
This invention relates to apparatus for operating gaseous
discharge tubes and particularly relates to neon sign
transformers for operating a neon tube from a mains frequency
alternating current by generating a high frequency high level
direct current.
BACKGROUND TO THE INVENTION
Gaseous discharge tubes such as florescent lamps or neon tubes
have generally been driven by alternating currents. In the case
of neon tubes the voltage applied to the neon tubes is generally
supplied at a high level in the vicinity of 5,000 to 15,000
vol's.
Various attempts have heretofore been made to drive said gaseous
discharqe tubes by a direct current.
For example, United States Patent No. 4,400,184 relates to
apparatus or operating gaseous discharge tubes such as
florescent lamps on a direct current from a source of alternating
current.
Moreover, United States Patent No. 4,745,342 teaches a signal
transformer which has a pair of secondary windings which are used
to drive a pair of tandem connected FET switches which, in turn,
are connected across a second direct current supply which has a
Z017595
high direct current voltage derived- from the input alternating
current voltage.
Furthermore, United States Patent No. 3,753,040 teaches a
strobing circuit for a florescent lamp where a triac connects the
lamp to a ballast winding, the triac being controlled by a two
transistor multi-vibrator supplied with direct current voltage
through a diode connected to a tap of the ballast winding. The
resistor is connected in parallel with the triac to conduct a
small amount of current when the triac is non-conductive and to
keep the lamp ionized.
Yet another apparatus is disclosed by United States Patent No.
3,120,347 which relates to apparatus and systems for dimming and
operating gaseous discharge lamps such as florescent lamps.
Finally, United States Patent No. 4,748,381 teaches a circuit
arrangement for alternating current operation of gas discharge
lamps.
These and other prior art devices present relatively complicated
structures which are generally ineffective to produce an
efficient device for energizing neon tubes with a high energy
direct current generated from an alternating current source.
Furthermore, many of the prior art devices have a general limited
utility as such devices operate gaseous discharge tubes within
~01759S
limited power capabilities and may not generally be utilized for
a wide range of tube characteristics.
It is an object of this invention to produce an improved
apparatus for operating gaseous discharge tubes.
It is a further object of this invention to produce a neon sign
transformer for operating neon tubes at a high voltage direct
current obtained by rectifying high frequency high voltage
alternating current. Such neon tube transformer is capable of
generating an output between 0 and 15 Kv depending on the neon
tubes which are connected thereto.
The broadest aspect of this invention relates to apparatus for
operating a gaseous discharge tube from an alternating current
comprising: a filter for filtering electro-magnetic interference
from said alternating current; a rectifier for rectifying said
filtered alternating current so as to produce a low level direct
current; electrical circuit driver for generating a high
frequency low level drive current; an electrical power circuitry
for generating a high frequency high level current for energizing
said gaseous discharge tubes.
It is another aspect of this invention provides a neon sign
transformer for operating a neon tube from a mains frequency
alternating current comprising: a filter for filtering electro-
magnetic interference from said alternating current; a first
rectifier for rectifying said filtered mains frequency
2017595
alternating current to a low level direct current; electrical
circuit driver for generating a high frequency low level
alternating current including, a first transistor for generating
said high frequency low level current, a drive transformer:
electrical power circuitry for generating a high frequency high
level alternating current for energizing said noon tube
inrluding, a second transistor for generating said high frequency
power, a high voltage transformer for generating said high level
voltage, and a second rectifier for generating a high frequency
high voltage direct current for energizing said gaseous discharge
tubes.
It is yet another aspect of this invention to provide a neon sign
transformer for operating a neon tube from a 60 Hz 120 v
alternating current source comprising: a filter for filtering
electro-magnetic interference from said 60 Hz 120 alternating
current source; an in rush current protection for protecting said
transformer from said in rush current; a first rectifier for
réctifying said 60 Hz 120 v alternating current to approximately
150 v direct current; electrical circuit driver powered by said
150 v direct current for generating approximately 20 KHz
alternating current signal including, a first transistor for
generating said 20 KHz signal, a drive transformer; and
electrical power circuitry for generating approximately a 20 KHz
alternating current signal and then transformed to a 0 and 15
Kv direct current in response to the characteristics of a neon
tube connected thereto including, a second transistor driven by
said drive transformer for generating said 20 KHz frequency, high
2017595
voltage transformer for generating an output between 0 and 15 Kv,
and a second rectifier for generating a direct current at a 0 to
15 Kv for energizing said neon tubes.
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
These and other objects and features shall now be described in
relation to the following drawings.
Figure 1 is a schematic drawing of the supply section showing the
filter and first rectifier of the neon sign transformer.
Figure 2 is a schematic drawing the driver stage and power stage
of the neon sign transformer.
Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of the drive transformer.
Figure 4 is a placement cross-section of the drive transformers.
Figure 5 is a side elevational cross-sectional view of the high
voltage transformer.
Figure 6 is a top plan view of the high voltage transformer.
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
Like parts have been given like numbers throughout the figures.
2017595
Figure 1 generally illustrates the supply section of the neon
side transformer and includes a plug having a Ground GND Neutral
N Load L wire. The supply for the plug will generally consist
of a 60 Hz 120 v alternating current or mains current. The
supply section also includes fuse 1 which will protect the
circuitry from an overload situation.
The filter for filtering electro-magnetic interference or noise
generally comprises Capacitors C8, Inductants L1 and Capacitors
Cs and C6 and C7.
Furthermore, a Resistor R2 is utilized as an in rush current
protector.
A Rectifier D7 and Capacitor 4 i8 utilized to rectify the 60 Hz
120 v alternating current to produce a low level direct current
voltage such as 150 v between points B and 0.
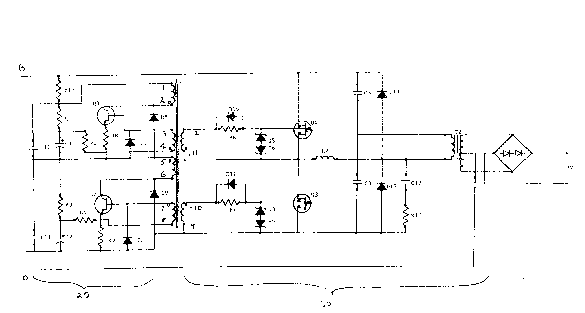
Figure 2 generally describes the driver stage 20 and power stage
30.
The driver stage is generally utilized to generate a 20 KHz
frequency from the direct current at points B and 0. The
transistors Q1 and Q2 generate the frequency and the drive
transformer T1 drives the output transistors Q4 and Q3 located
in the power stage section.
2017595
Figure 3 generally illustrates the drive transformer
specifications and in particular the following elements N
comprise the following turns having a AWG # at the following
start and finish points, namely:
Element Start Finish Turns AWG #
N 1 2 3 120 36
N 3 5 6 120 36
N 2 4 3 4 36
N 4 7 8 4 36
N 5 10 9 16 29
N 6 11 12 16 29
More particularly Figure 4 illustrates the physical separation
of the various elements of the drive transformer. In particular
a physical separation occurs between N 4 and N 6 as well as N 2
and N S. Furthermore each of the layers are insulated by a 1 mm
insulation of mylar or polyester.
Moreover the core of the drive transformer comprises a E F 20,
G A P of 0. In particular it has been found that favourable
results can be shown by using a Siemens (trade mark) having a
specification of B66311-G000-X127.
Good results have been achieved by using a Siemens (trade mark)
bobbin having specification B66206-A1012-T001.
2017595
Furthermore a Siemens (trade mark) yoke having a specification
of B66206-A2001-X00 has been used with favourable results.
Moreover it should be mentioned that the yoke is optional
although the core may not be loose.
The power stage 30 illustrated in Figure 2 comprises drive
transistors Q3 and Q4 which are driven by drive transformer T
so as to generate a high frequency power.
Furthermore a high voltage transformer T2 is utilized so as to
produce a high voltage output.
In particular good results have been achieved by using a high
voltage transformer having the following specifications:
- core-ferroxcub lF19 3C8
- gap-0.125mm spacer each leg
- windings - primary 28 turns A W G Symbolic form of
number 18
- secondary 3,700 turns AWG # 37, centre taped, connected
to the pin
Each layer of secondary winding is separated by a layer of mylar
which may be 2 mm minimum and each of the turns are to be
protected so as not to drop into the underlying layers.
2017595
Moreover the windings are to be vacuum-potted. The winding
capacitance is kept as low as possible and the spacing below the
high voltage terminals and the terminals themselves are to meet
regulations for 15 Kv working voltage device with a 7.5 Kv
terminal to ground.
Moreover an output rectifier is utilized having an operating
frequency of 18 KHz with an output voltage of 16.5 Kv maximum
working specified at least 20 Kv, with a reverse recovery of
250 ns or better.
Favourable results have been utilized by using diodes VG-lOXVAR0,
two in series for each branch of a full bridge output rectifier.
An alternate diode which may be utilized that has been found to
work favourably is DL 1000, edi.
In order to reduce leakage inductance ~which is to be in a range
of approximately 5%) both primary and secondary windings are
preferably located on the same column as shown in Figure 5.
Each layer of secondary winding is to be separated by a layer of
mylar and each of the turns are to be protected so as not to drop
into the underlying layers.
The second rectifiers or high voltage rectifiers may be located
in the high voltage transformer as best seen in Figure 5.
lo 201~759S
The driver stage 20 is independent of the power stage 30 and
therefore the driver stage 20 is independent of the load, and one
has devised, therefore, a circuit that withstands the open and
short circuit at output.
A coil ~ is located in the power stage and limits the current
in short circuit. Furthermore diodes Dl2 and Dl3 minimize damage
from a no load situation as they are utilized to dissipate
energy.
The output rectifier is capable of generating 0 to 15 Kv
depending on the load or neon tubes attached to the terminals of
the high voltage output transformer T2.
Accordingly the device takes little power when a small load is
applied thereto. This is achieved by the semi-resonate mode of
operation of the device by pic~ing the frequency and tuning the
circuitry for the high voltage transformer and coil.
Accordingly the device is very versatile as the device may be
used to drive or energize one or ten neon tubes attached thereto
or any number of tubes in between. In other words, the neon sign
transformer can be used for a wide range of tube lengths.
Furthermore the size and weight of the transformer is
dramatically reduced, the electronic transformer uses the
principles of high reactants to limited short circuit current.
-" ~017595
Moreover the electronic transformer can survive extended periods
of short circuit operation without damage.
The specifications of the resistors, transistors, diodes,
capacitors and inductors of the preferred embodiment are
specified in Figure 7.
Although the preferred embodiments as well as the operation and
use have been specifically designed in relation to the drawings,
it should be understood that variations in the preferred
embodiments could easily be achieved by a person skilled in the
art without departing from the spirit of the invention.
Accordingly, the invention should not be understood to be limited
to the exact form revealed in the drawings.