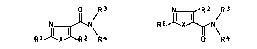Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~ v ~
O.Z. 0050/41126
Oxazole- and thiazolecarboxamide~
The present invention relates to oxazole- and
thiazolecarboxamides of the formulae Ia and Ib
O R3 ~ R2 R3
NJI`N~ R ~
RI~X~R2 R4 R4
Ia Ib
wher~
X i8 oxygen or Rulfur;
Rl is hydrogen; halogen; Cl-C6-alkyl which can carry
from one to five halogen atoms and/or one or two of
the following: C3-C~-cycloalkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, C1-C4-
haloalkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkylthio or
cyano;
benzyl which can carry fro~ one to three of the
following: Cl-C4-alkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy,
Cl-C4-haloalkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkylthio,
halogen, cyano or nitro;
C3-C~ cycloalkyl which can carry from one to three of
the following: Cl-C4-alkyl or halogen;
C2-C6-alkenyl which can carry from ons to three of
the following: halogen, Cl-C3-alkoxy and/or one
phenyl which in turn can carry from one to three of
the following: Cl-C4-alkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-
alkoxy, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy, Cl C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-
haloalkylthio, halogen, cyano or nitro;
C2-C6-alkynyl which can carry from one to three of
the following: halogen, Cl-C3-alkoxy and/or one
phenyl which in turn can carry from one to three of
the following: Cl-C4-alkyl, C,-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C~-
alkoxy, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-
haloalkylthio, halogen, cyano or nitro;
Cl-C~-alkoxy; Cl-C4-alkylthio; Cl-C4-haloalkoxy; Cl-C4-
haloalkylthio;
2026131
- 2 - O.Z. 0050/41126
phenoxy or phenylthio, which can carry from one to
three of the following: Cl-C~-alkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkyl,
Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-
haloalkylthio, halogen, cyano or nitro;
a 5- to 6-membered heterocyclic radical containing
one or two hetero atoms selected from the group
comprising oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen, it being
possible for the ring to carry one or two of the
following: Cl-C3-alkyl, halogen, Cl-C3-alkoxy or
Cl-C3-alkoxycarbonyl;
phenyl which can carry from one to three of the
following: Cl-C6-alkyl, C~-C6-haloalkyl, Cl-C6-alkoxy,
Cl-C6-haloalkoxy, Cl-C6-alkylthio, Cl-C6-haloalkylthio,
halogen, nitro and cyano;
R2 is formyl, 4,5-dihydro-2-oxazolyl or -CoYR5;
Y is oxygen or sulfur;
Rs is hydrogen;
Cl-C6-alkyl which can carry from one to five halogen
atoms or hydroxyl groups and/or one of the follow-
ing: Cl-C4-alkoxy, C2-C4-alkoxy-Cl-C4-alkoxy, cyano,
trimethylsilyl,C1-C3-alkylthio,C1-C3-alkylamino,di-
Cl-C3-alkyl~mino, C3-C7-cycloalkylamino, Cl-C3-alkyl-
sulfinyl,C1-C3-alkylsulfonyl,carboxyl,Cl-C3-alkoxy-
carbonyl, di-Cl-C3-alkylaminocarbonyl, di-Cl-C3-
alkoxyphosphoryl, alkaneiminoxy, thienyl, furyl,
tetrahydrofuryl, phthalimido, pyridyl, benzyloxy or
benzoyl, it being po~3ible for the cyclic radicals
in turn to carry from one to three of the following:
C1-C3-alkyl, C1-C3-alkoxy or halogen;
benzyl which can carry from one to three of the
following: Cl-C3-alkyl, Cl-C3-alkoxy, Cl-C3-haloalkyl,
halogen, nitro and cyano;
C3-Ca-cycloalkyl;
phenyl, which can carry from ono to three of the
following: Cl-C4-alkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-haloalkyl,
C1-C4-haloalksxy,C1-C4-alkoxycarbonyl,halogen,nitro
and cyano;
2026~31
_ 3 - O.Z. 0050/41126
C3-Cg-alkenyl, C5-C~-cycloalkenyl or C3-C8-alkynyl, it
being possible for these radicals to carry one of
the following: hydroxyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, halogen or a
phenyl ring which in turn can carry from one to
three of the following: Cl-C4-alkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy,
Cl-C4-haloalkyl, halogen, nitro and cyano;
a 5- to 6-membered heterocyclic radical containing
one or ~wo hetero atom~ selected from the group
comprising oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen or a benzo-
triazolyl radical;
phthalimido; tetrahydrophthalimido; succinimido;
maleimido;
one equivalent of a cation from the group compri~ing
the alkali metal~ or alkaline earth metals, man-
ganese, copper, iron, ammonium and substituted
ammonium;
-N=CR6R7;
R5 and R7 are hydrogen; Cl-C4-alkyl; C3-C6-cycloalkyl;
phenyl or furyl, or together form a methylene chain
-(CH2)~- with ~ = 4 to 7;
R3 is hydrogen; Cl-C6-alkyl which can carry from one to
three of the following: hydroxyl, halogen, Cl-C4-
alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio or di-Cl-C3-alkylamino;
C3-C~-cycloalkyl which can carry from one to three of
the following: Cl-C4-alkyl, halogen and C1-C4-halo-
alkyl;
R4 is hydroxyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy;
Cl-C8-alkyl which can carry from one to three of the
following: Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy, Cl-C4-
alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkylthio, di-Cl-C4-alkylamino,
halogen, C3-C8-cycloalkyl or phenyl which in turn can
carry from one to three of the following: halogen,
cyano, nitro, Cl-C4-alkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-
alkoxy, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy, Cl~C4-alkylthio or Cl-C4-
haloalkylthio;
C3-C8-cycloalkyl which can carry from one to three of
the following: Cl-C6-alkyl, Cl-C6-haloalkyl, Cl-C~-
202~131
- 4 - O.Z. 0050/41126
alkoxy, C~-C4-haloalkoxy, halogen, nitro or cyano;
C3-C6-alkenyl or C3-C6~alkynyl, which can be sub-
stituted from once to three times by halogen and/or
once by phenyl which in turn can carry from one to
three of the following: Cl-C4-alkyl, C,-C4-haloalkyl,
C~-C~-alkoxy, C~-C4-haloalkoxy, C~-C4-alkylthio, C~-C4-
haloalkylthio, halogen, cyano or nitro;
a 5- to 6-membered heterocyclic radical which
contains one or two hetero atoms selected from the
group comprising oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen, and
which can carry from one to three of the following:
C~-C4-alkyl or halogen;
phenyl which can carry from one to four of the
following: C~-C4-alkyl, C1-C4-haloalkyl, C1-C4-alkoxy,
Cl-C4-haloalkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalXylthio,
halogen, nitro, cyano, formyl, Cl-C4-alkanoyl, Cl-C4-
haloalkanoyl or C1-C4-alkoxycarbonyl;
naphthyl which can be sub~tituted from once to three
time~ by C,-C4-alkyl or halogen,
or
R3 and R4 together form -(CH2)n-Yp-(CH2)q- where n and
q are each 1, 2 or 3, p is 0 or 1 and Y is oxygen,
sulfur or N-methyl, or -(CH2)3-CO-, and the environ-
mentally compatible salts thereof,
where X in the formula Ib is not sulfur when R1 is
3-pyridyl, R2 is CO2CH2CH3 or R3 i~ hydrogen, and where X
in the formula Ia is not sulfur and R1 i5 not 2-thienyl
when YR5 i8 OH and R3 is hydrogen and R4 is methyl.
The invention also relates to processes for
preparing these compounds, and to herbicides which
contain at least one compound Ia' or Ib' in which the
substituents have the abovementioned meanings and ~ can
be sulfur when R1 is 3-pyridyl, R2 i5 CO2CH2CH3 and R2 is
hydrogen, or when R1 is 2-thienyl, YR5 is hydroxyl, R3 is
hydrogen and R4 i~ methyl.
Oxazole- and thiazolecarboxylic acids and deriva-
tives thereof ara known (DE-A 2,254,944, Bnll. Soc. Chim.
2026131
- 5 - O.Z. 0050/41126
Fr., 1969, 2152 and DE-A 2,221,647). Possible uses of
these ~ubstanc~s as herbicides have not been described.
It is an object of the present invention to find
and synthesize novel herbicidal compounds.
We have found that this object is achieved by the
oxazole- and thiazolecarboxamides Ia and Ib defined in
the first paragraph.
We have alse found processeq for preparing them
and herbicides which contain oxazole- and thiazole-
carboxamides Ia' and Ib' in which the substituent~ have
the abovementioned meanings
The oxazole- and thiazolecarboxamides Ia and Ib
according to the invention can be prepared in a variety
of ways. They are obtained, for example, by the following
processes:
1. Process for preparing compounds Ia and Ib where
R2 is Co2R5 and R5 is Cl-C5-alkyl
Rll~ `R4 R tl~,R 3
Ia Ib
(R5 = C~-CB_a1kY1 )
These oxazole- and thiazolecarboxamides Ia and
Ib are obtained by hydrolyzing a die~ter of the formula
II in a conventional manner with one equivalent of an
aqueous base to give the monoesters IIIa and IIIb and
then separating IIIa and IIIb or initially converting the
mixture to the halide or another active form of the
carboxylic acid and subsequently amidating these deriva-
tives with an amine IV.
o o o
NJ~OR 5 A . NJ~OH NJ~OR S
Il 11 . Il 11' 11 11
Rl~X~RS Rl~X~ORS Rl~X~OH
O O O
II IIIa IIIb
1~ U ~ ~J ! ~ i
- 6 - O.Z. OOSOt41126
O R3 o
HhR3R~ Rll~R5 Rll~o~R3
O O
IV Ia Ib
The individual steps A and B in this reaction
sequence can be carried out as follows:
Step A:
The partial hydrolysis of the diester II to the
monoesters IIIa and IIIb is normally carried out at from
-20 to 60CC~ preferably -10 to 30C, in an inert organic
solvent which is miscible with water, in the pre~ence of
from 1.0 to 1.2 mole eguivalent~ of a base.
Particularly quitable ba~es are alkali metal
hydroxides. The ba~e is generally added as an aqueous
solution which is from S to 20% strength.
Examples of preferred solvents for this reaction
are dioxane or the alcohol corresponding to the ester
component in the formula II.
The reaction mixture i5 normally worked up by
acidification, when the desired product separates out as
a solid or oil. Isola$ion is carried out in a conven-
tional manner by filtration or extraction.
The mixture of the two isomeric monoesters IIIa
and IIIb can be separated by fractional cry3tallization
or chromatography, or it can be reacted further without
separation.
Step B:
The compounds Ia and Ib are obtained from the
monoesters IIIa and IIIb by initially converting the
~ V r~.l J ~
- 7 - O.Z. OOS0/41126
latter in a conventional manner into the halide or
another active form of the carboxyl group and sub-
sequently amidating these derivatives with an amine IV.
Examples of active forms of carboxylic acidq are,
5 besides the halides such as, in particular, the chlorides
and bromides, also the Lmidazolides. The halides are
generally preferred.
They are obtained by reacting the carboxylic
acids IIIa and IIIb with a halogenating agent such as
thionyl chloride or bromide, phosphorus oxychloride or
oxybromide, ~richloride or trib~omide or pentachloride or
pentabromide, phosgene and elemental chlorine and
bromine.
From 1 to 5 mole equivalents, preferably from 1
lS to 2 mole equivalents, of halogenating agent are used.
The reaction is carried out at from ODC to the
boiling point of the halogenating agent or, if an inert
organic solvent is used, the boiling point thereof,
preferably at from 20 to 120C.
Examples of suitable solvent~ are hydrocarbons
and halohydrocarbons such as tetrachloroethane, methylene
chloride, chloroform, dichloroethane, chlorobenzene,
1,2-dichlorobenzene, benzene, toluene and xylene.
The active carboxylic acid derivatives are
normally isolated, for example by removing the halogenat-
ing agent and, where present, the solvent by distillation
and only then reacting them with the amines IV.
In this case, the amidation is carried out from
-20 to 100C, preferably at -10 to 20C, in an inert
aprotic polar organic solvent.
Particularly ~uitable solvents for thi~ reaction
are halohydrocarbon~ such as dichloromethane, and ether~
such as diethyl ether and tert-butyl methyl ether.
Since hydrogen halide is formed in the amidation
of acid halides, it is advisable to add the amine IV in
an excess of from 2 to 5 mole equivalent~, preferably 2
to 3 mole equivalen~s. If the amine i3 u~ed in equimolar
- 8 - O.z. 0050/41126
amount (from 1 to 1.2 mole equivalents), a base should be
added, especially a tertiary amine such as triethylamine
or pyridine, to bind the hydrogen halide.
When a mixture of the monoesters IIIa and IIIb i~
used as starting material, the reaction results in a
mixture of the isomeric carboxamide~ Ia and Ib. This
mixture can be fractionated into the individual com-
ponents in a conventional manner, for example by
fractional crystallization or chromatography.
The precursors II required for this synthesis are
known (Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1974, 2079) or can be ob-
tained by known methods (Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1969, 1762;
J. Chem. Soc., 1953, 93).
2. Process for preparing compounds Ia and Ib where
X is sulfur and R2 is CO2H
R 11~2H R 1 ~N~HRR 43
Ia Ib
These thiazolecarboxamide~ Ia and Ib are obtained
particularly advantageously by reacting a dicarboxylic
anhydride of the formula V in a conventional manner with
an amine of the formula IV to give the isomers Ia and Ib
and subsequently fractionating the mixture to give the
isomers
O O
N ~ o /1 ~ N~R4 + 1 ~ co2HR3
~ \R4Rl C02H Rl ~ N~
V IV Ia Ib
The reaction i~ normally carried out at from -10
to 150C, preferably 20 to 120C, in an inert aprotic
- 9 - O.Z. 0050/41126
polar organic solvent.
Particularly suitable solvents are halohydro-
carbons, eg. tetrachloroethane, methylene chloride,
chloroform, dichloroethane, chlorobenzene and 1,2-di-
chlorobenzene; ethers, eg. diethyl ether, methyl tert-
butyl ether, dimethoxyethane, diethylene glycol dimethyl
ether, tetrahydrofuran and dioxan; dipolar aprotic
solvents, eg. acetonitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethyl-
acetamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, N-methylpyrrolidone,
1,3-dimethyltetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidinone and 1,3-di-
methylimidazolidin-2-one; aromatic compounds, eg. ben-
zene, toluene, xylene, pyridine and quinoline; ketones,
eg. acetone, methyl ethyl ketone or mixtures thereof.
The amine IV is generally used in equimolar
amounts or in an excess, preferably in amounts of from
1.0 to 5.0 mole equivalents based on V.
The dicarboxylic anhydrides required for this
process as known or can be prepared by known methods
(Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1969, 1762; CS-A-195,369;
CS-A-195,370).
3. Proce~s for p~eparing compounds Ia and Ib where
Rl is not halogen and R2 is carboxyl or formyl
O R3 N ~R2 R3
NJ~N\ R l~X~N
Rl~X~R2 R4 R4
Ia Ib
(Rl ~ Hal; R2 = CO2H, CHO)
These isomeric oxazole- and thiazolecarboxamides
are obtained by activating and amidating a carboxylic
acid IIIc or IIId under the conditions described in lB,
and then reacting the resulting amides VIa and VIb in a
conventional manner in the presence of a carboxylating or
formylating reagent.
20261~
- 10 - O.Z. 0050/41126
~ R .1~
IIIc IIId VIa
R11~ ~ R3
VIb Ia Ib
Step A in this reaction sequence is generally
carried out under the conditions described in Section B
in Proces~ 1.
Step B.
The carboxylation or formylation of the oxazole-
and thiazolecarboxamides VIa and VIb is usually carried
out at from 0 to -100C, preferably -50 to -80C, in an
inert aprotic polar organic solvent in the pre ence of a
base with exclusion of moisture.
The preferred carboxylating agent is gaseous or
solid carbon dioxide, and dimethylformamide or N-formyl-
morpholine is used, in particular, as formylating
reagent.
Suitable ~olvent~ are, in particular, ethers, eg.
diethyl ether, methyl tert-butyl ether, dLmethoxyethane,
dLethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran and
dioxan.
The ba3es which ars preferably used are organo-
metallic compound~, eg. methyllithium, n-butyllithium,
s-butyllithium, t-butyllithium or phenyllithium.
The reaction is normally carried out by first
adding up to 3 mole equivalents of the dissolved base to
a solution of the oxazole- or thiazolecarboxamide VIa or
VIb, resulting in a derivative which i8 metalated on the
heterocycle and i~ then converted into the desired
~ v ~ ~ 1
~ O.Z. 0050/41126
product Ia or Ib by addition of the electrophilic
carboxylating or formylating reagent.
When R3 is hydrogen, correspondingly more mole
equivalents of the base are required because, in this
case, the amide nitrogen is initially deprotonated.
Hence, from 2 to 2.5 mole equivalents of the base are
preferably used for the reaction of carboxamides VIa or
VIb where R3 is hydrogen.
Compounds VIa and VIb where Rl is hydrogen react
with the base initially to metalate the 2-position of the
heterocycle ring.
In order to introduce the carboxyl or formyl
radical adjacent to the carbamoyl group in this case, it
is necessary to start from oxazole- or thiazolecarbox-
amides VIa or VIb where R3 is hydrogen.
Oxazole- and thiazolecarboxamides Ia and Ib where
R1 is hydrogen and R3 is not hydrogen are obtained from
the compounds which can be obtained by $he abovementioned
process and in which Rl and R3 are hydrogen in a conven-
tional manner by subsequent alkylation or cycloalkyl-
ation.
The carboxylic acids IIIc and IIId required for
the abovementioned process are known from the literature
(Beilstein, Volume 27, Supplements 1-53 or can be pre-
pared by conventional methods, for axample by oxidationof the corresponding alcohols or aldehyde~ or by hydro-
lysis of the corresponding nitriles (J.V. Metzger in "The
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds, Vol. 34, Part 1,
Thiazole and it~ Derivatives", Arnold Wei~sberger and
Edward C. Taylor (Editors), John Wiley and Sons, page~
519 et sec., I.J. Turchi in ~'The Chemistry of
Heterocyclic Compounds, Vol. 45, Oxazoles", Arnold
Weissberger and Edward C. Taylor (Editors), John Wiley
and Sons).
4. Process for preparing compounds Ia and Ib where
R2 is carboxyl
- 12 - O.Z. 0050/41126
R 1 ~2H R 1 J~o'N~HRR 3
Ia Ib
These oxazole- and thiazolecarboxamides Ia and Ib
are obtained, for example, by hydrolyzing an appropriate
carboxamide Ia or Ib where R2 is Co2R5 and R5 is Cl-C6-alkyl
in a conventional manner with one equivalent of an
aqueous base. The reaction is shown in the following
diagram only for the carboxamides Ia. It takes place
similarly with the corresponding carboxamides Ib.
N~N'R 3 R 11~ 2H
Ia (R5 = Cl-C6-alkyl) Ia
This synthesis is generally carried out under the
condition~ described in Section A in Proces~ 1.
5. Process for preparing compounds Ia and Ib where
R2 ig CoYR5
Rl~rRS Rl~o RR3
Ia Ib
These carboxamides Ia and Ib are obtained by
activating a corresponding carboxylic acid Ia or Ib
(R2 = CO2H) and subsequent reaction in a conventional
manner with a compound VII.
~ ù ~
- 13 - O.Z. 0050/41126
or Rl l ~ `R4 + HYR
Rl X C02H O
Ia Ib VII
R 1 1~YR 5 ~;~Y R 5 3
Ia Ib
The reaction can be carried out at from -20C to
the reflux temperature of the solvent or mixture thereof,
preferably at from 0 to 60C.
Solvents expediently used for these reactions are
halohydrocarbons, eg. tetrachlorosthane, methylene
chloride, chloroform, dichloroethane, chlorobenzene and
1,2-dichlorobenzene; ethers, eg. diethyl ether, methyl
tert-butyl ether, dimethoxyethane, diethylene glycol
dimethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran and dioxan; aromatic
compounds, eg. benzene, toluene or xylene; or mixtures
thereof.
Suitable condensing agents are dicyclohexylcarbo-
diimide or propanephosphonic anhydride.
The molar ratios of the starting compounds in the
reaction are generally from 0.5:1 to 2:1 for the ratio of
carboxylic acid VIa to alcohol or thiol and from 1:1 to
1;3 for the ratio of carboxylic acid IVa to condensing
agent.
The concentration of the precursor3 in the
solvent is generally from 0.1 to 5 mol/l, preferably 0.2
to 2 mol/l.
It is particularly preferred to use ethers such
as die~hyl ether, tetrahydrofuran or dioxan with propane-
phosphonic anhydride as condensing agent at from 20 to
2026~31
- 14 - O.Z. 0050/41126
60C.
6. Process for preparing compounds Ia and Ib where
R2 is 4,5-dihydro-2-oxazolyl
R~ 4 ,~ ~3
o
Ia Ib
These compound~ are obtained by reacting an
appropriate carboxylic acid derivative Ia or Ib where R2
is CO2R' or COOH and R' i5 Cl-C4-alkyl in a conventional
manner with an amino alcohol of the formula VIII.
R 1~2H or 1 ~ ,R 3
10 Ia Ib VIII
R1~4 or Rl ~ 13
Ia Ib
The reaction is carried out at from 0 to 180C,
preferably at the reflux temperature of the mixture with
an amino alcohol VIII, in the pre~ence or absence of an
inert solvent. The ratio of ester or carboxylic acid Ia
or Ib to amino alcohol VIII in this reaction is from 1:1
to 1:2.5, preferably 1:1 to 1:1.5.
The ~olvents expediently used arQ halohydro-
carbons such as chlorobenzenH and 1,2-dichlorobenzene,
ether~, eg. methyl tert-butyl ether~ 1,2-dimethoxyethane,
diethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran and
~J IJ r~ v ~
15 ~ O~ Z ~ 0050/41126
dioxan; alcohols such a~ methanol, ethanol, propanol or
ethylene glycol, dipolar aprotic solvents, eg. aceto-
nitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethylacetamide, dimethyl
sulfoxide, N-methylpyrrolidone, 1,3-dimethyltetrahydro-
2(1H)-pyrimidinone and 1,3-dimethylimidazolin-2-one, or
aromatic compounds, eg. benzene, toluene and xylene. The
concentration of the precurqors in these solvents is
generally from 0.1 to 5 ~ 0 mol/l, preferably 0.2 to
2.0 mol/l.
The reaction is generally complete after
14 hours; the carboxamides Ia and Ib are then precipi-
tated, where appropriate by adding water, filtered off
with suction or extracted with an organic solvent, and
purified by conventional methods such as recrystal-
lization or chromatography.
Compounds of the formula VIa where R1 is _ZR8 are
obtained in a conventional manner (Xelv. Chim. Acta, 37
(1954) 2059) by reaeting a 2-halothiazole-4-carboxamide
VIa (DE 2,241,035) with an alcohol or thiol H-ZRa in the
presence of a base in an inert organic solvent.
1~ \ + H--ZRa , 1~ ~
VIa (R1 = Hal) YIa'
Hal in formula VIa is a halogen sueh as fluorine,
ehlorine, bromine or iodine; particularly suitable
compounds VIa are those where Hal i~ chlorine or bromine.
R8Z in formula VIa' is Cl-C~-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkyl-
thio, each of-which can be substitu~ed up to three time~
by halogen, in particular methoxy, ethoxy, l-methyl-
ethoxy, 1,l-dimethyletho~, trifluoromethoxy, methylthio,
ethylthio~ difluoromethylthio; or phenoxy or phenylthio,
eaeh of whieh ean be substitute~ up to three time~ by
Cl-C4-alkyl, Cl-C"-haloalkyl, Cl-C~-alkylthio, Cl-C4-halo-
- 16 - O.Z. 0050/41126
alkylthio, halogen, cyano or nitro, in particular 2,4-di-
chlorophenoxy, 2,4-difluorophenoxy, 2,4,6-trifluoro-
phenoxy, p-trifluoromethylphenoxy, 2-chloro-4-trifluoro-
phenoxy, 3-cyanophenoxy, 4-cyano-2-methoxyphenoxy,
4-nitrophenoxy, 2-fluorophenylthio, 4-trifluoromethyl-
phenylthio and 3-cyanophenylthio.
The solvents expediently used for these reactions
are halohydrocarbons, eg. tetrachloroethane, methylene
chloride, chloroform, dichloroethane, chlorobenzene and
1,2-dichlorobenzene; ethers, eg. diethyl ether, methyl
tert-butyl ether, dLmethoxyethanè, diethylene glycol
dimethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran and dioxan; dipolar
aprotic solvents, eg. acetonitrile, dimethylformamide,
dimethylacetamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, N-methylpyrrol-
idone, 1,3-dimethyltetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinone and
1,3-dimethylimidaæolidin-2-one; aromatic compounds, eg.
benzene, toluene, xylene, pyridine and quinoline;
ketones, 2g. acetone, methyl ethyl ketone; alcohols, eg.
methanol, ethanol, iso-propanol and tert-butanol or mix-
tures thereof.
The reaction can be carried out at from -100C to
the reflux temperature of the solvent or mixture thereof,
preferably at from -60~ to 150C.
The bases used are hydrides and alkoxides of
alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, in particular
NaH, RH, CaH2, LiH and RO-tBu. It is also beneficial on
occasion to use combinations of the bases listed.
The molar ratios of the starting compounds in the
reaction are generally from 3:1 to 1:1 for the ratio of
alcohol or thiol to 2-halothiazole-4-carboxamide VIa and
from 1:1 to 1:3 for the ratio of alcohol or thiol to the
base.
The concentration of the precursor~ in the
solvent is generally from 0.1 to 5 mol/l, preferably 0.2
to 2 mol~l.
It is particularly preferable to use aprotic
dipolar solvents such as acetonitrile~ dimethylformamide,
- 17 - O.Z. 0~50i41126
dimethyl sulfoxide, N-methylpyrrolidone, 1,3-dimethyl-
tetrahydro-2(1~I)-pyrimidinone and 1,3-dLmethylimidazo-
lidin-2-one or ethers such as 1,2-dimethoxyethane,
diethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran or
dioxan at from 50C to 150C with NaH or RO-tBu as base.
The 2-halothiazole-4-carboxamides of the formula
- VIa required for the reaction can be obtained by methods
known from the literature from the corresponding carbonyl
halides by reaction with amines (DE-A 2,241,035).
10The alcohols or thiols which are used are com-
mercially available in many cases or thPy can be prepared
in a conventional manner.
Furthermore, the compounds of the formula Vlb are
obtained in a conventional manner (Helv. ChLm. Acta, 37,
15(1954) 2Q59) by reacting a 2-halothiazole-5-carboxamide
VIb with an alcohol or thiol in an inert organic solvent
in the presence of a base a~ shown in the scheme:
N~ R3 N~ R3
Il 11 ~ ~ H-zR8 . Il ll
Ha I~X~N\ . . R8;~X~N~
Q R~ o R~
VIb VIb'
Hal in VIb is a halogen such a~ fluorine,
chlorine, bromine or iodine; particularly uitable
compounds VIb are those where Hal is chlorine or bromine.
R9Z in formula VIb' is Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C~-alkyl-
thio, each of which can be substitutad up to three time~
by halogen, in particular methoxy, ethoxy, 1-methyl-
ethoxy, 1,l-dimethylethoxy, trifluoromethoxy, methylthio,
ethylthio, difluoromethylthio; or phenoxy or phenylthio,
each of which can be=~ubstituted up to three times by
Cl-C4-alkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-alkylthio,
C1-C4-halo-alkylthio, halogen, cyano or nitro, in par-
ticular 2,4-dichlorophenoxy, 2,4-difluorophenoxy,
2,4,6-trifluorophenoxy, p-trifluoromethylphenoxy,
~ J ~
- 18 - O.Z. 0050/41126
2-chloro-4-trifluorophenoxy, 3-cyanophenoxy, 4-cyano-2-
methoxyphenoxy, 4-nitrophenoxy, 2-fluorophenylthio, 4-
trifluoromethylphenylthio and 3-cyanophenylthio.
The solvents expediently used for these reactions
are halohydrocarbons, eg. tetrachloroethane, methylene
chloride, chloroform, dichloroethane, chlorobenzene and
1,2-dichlorobenzene; ethers, eg. diethyl ether, methyl
tert-butyl ether, dimethoxyethane, diethylene glycol
dimethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran and dioxan; dipolar
10 aprotic solvents, eg. acetonitrile, dimethylformamide,
dimethylacetamide, dLmethyl sulfoxide, N-methylpyrrol-
idone, 1,3-dimethyltetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinone and
1,3- dimethylimidazolidin-2-one; aromatic compounds, eg.
benzene, toluene, xylene, pyridine and quinoline;
lS ketone~, eg. acetone, methyl ethyl ketone; alcohols, eg.
methanol, ethanol, iso-propanol and tert-butanol or mix-
tures thereof.
The reaction can be carried out at from -100C to
the reflux temperature of the solvent or mixture thereof,
20 preferably at from -60C to 150C.
The ba es used are hydrides and alkoxide~ of
alkali metals and alkaline earth metal~, in particular
NaH, KH, CaH2, LiH and KO-tBu. It i~ also beneficial on
occasion to use combinations of the bases listed.
The molar ratios of the starting compounds in the
reaction are generally from 3:1 to 1:1 for the ratio of
alcohol or thiol to 2-halothiazole-5-carboxamide VIb and
from 1:1 to 1:3 for the ratio of alcohol or thiol to the
base.
The concentration of the precursors in the
solvent i~ generally from 0.1 to 5 mol/l, preferably 0.2
to 2 mol/l.
It is particularly preferable to use aprotic
dipo~ar solvents such as acetonitrile, dimethylforma~ide,
35 dimethyl sulfoxide, N-methylpyrrolidone, 1,3-dimethyl-
tetrahydro-2(lH)-pyrimidinone and 1,3-dimethylimidazo-
lidin-2-one or ethers such a~ 1,2-dimethoxyethane, di-
- 19 - o.z. 00~0~41126
ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran or dioxan
at from 50C to 150C with NaH or KO-tBu a~ base.
The 2-halothiazole-5-carboxamides of the formula
VIb required for the reaction can be obtained by methods
known from the literature from the correspondin~ carbonyl
halides by reaction with amines (US-A-4,001,421
Compounds of the formula Ib can be obtained by
reacting dicarboxylic esters of the formula II with
amines in a conventional manner, and hydrolyzing the
resulting amides Ib as shown in the scheme:
~1 l~R 5 + -- R 1 l~R 3 b ~ R 3
I I ( R2 = Co2R5 ) Ib ( R2 =C02H )
The procedure for this is expediently to dissolve
the diester II in an inert organic solvent and react with
an amine.
The solvents used for these reactions are ethers,
eg. diethyl ether, me~hyl tert-butyl ether, dLmethoxy-
ethane, diethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran
and dioxan; aromatic compounds, eg. benzene, toluene,
xylene or mesitylene; alcohols, eg. methanol, ethanol,
iso-propanol and tert-butanol, or mixtures thereof.
The reaction can be carried out at from -100C to
the reflux temperature of the solvent or mixture thereof,
preferably at from -60 4C to 150C.
The molar ratio of diester II to amine is from
1:1 to 1:2, preferably from 1:1 to 1:1.2.
The concentration of the precursors in the
solvent is generally from 0.1 to S mol/l, preferably 0.2
to 2.0 mol/l.
It i~ particularly preferable to use alcohols
- 20 - O.Z. 0050/41126
such a~ ethanol in the presence of one equivalent of
amine at from ~0 to 100C. The diester~ II required for
the reaction are known from the literature or can be
prepared by conventional methods (Bull. Soc. ChLm. Fr.,
1969, 1762; J. Chem. Soc., 1953, 93).
Beside~ Processes 1-6 which have been described
above for preparing compounds Ia and Ib, there are
further po~ible syntheses which can be found in the
following references:
Beilstein, main serie~ and supplement3 1-5,
volume 27; R.W. Wiley, The Chemistry of Heterocyclic
Compounds, Five- and Six-Membered Compounds with Nitrogen
and Oxygen, Interscience Publisher~, New York, London
(1962), Heterocyclic Chemistry, Vol. 6, ~ive-Membered
Rings with Two or More Oxygen, Sulfur or Nitrogen Atoms,
Pergamon Press, 1984, J. March, Advanced Organic
Chemistry, third edition, John Wiley and Sons, 1985,
Houben-Weyl, Methoden der organischen Chemie, 4th
edition, Thieme Verlag, volumes IV, VI, VII, VIII and X.
With a view to the intended use of the compounds
Ia' and Ib', the following sub3tituents are preferred:
X i9 oxygen or sulfur
R1 is hydrogen;
halogen such a~ fluorine, chlorine, bromine and
iodine, especially fluorine and chlorine;
Cl-C~-alkyl, such ~8 methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, iso-
propyl, n-butyl, ~ec-butyl, i~o-butyl and tert-
butyl, pentyl, l-methylbutyl, 2-methylbutyl,
3-methylbutyl, l,l-dimethylpropyl, 1,2-dimethyl-
propyl, 2,2-dimethylpropyl, l-ethylpropyl, hexyl,
l-methylpentyl, 2-methylpen~yl, 3-methylpentyl,
4-methylpentyl, l,l-dimethylbutyl, 1,2-dimethyl-
butyl, 1,3-dimethylbutyl, 2,2-dLmethylbutyl, 2,3-
~ dimethylbutyl, 3,3-dLmethylbutyl, l-ethylbutyl,
2-ethylbutyl, 1,1,2-trimethylpropyl, 1,2,2-tri-
methylpropyl, l-ethyl-l-methylpropyl and l-ethyl-2-
met~ylpropyl, e~pecially methyl, ethyl, propyl and
1~ V r~ ~ ~ JL
- 21 - O.Z. 0050/41126
iso-propyl, which can carry from one to five halogen
atoms, in particular fluorine and/or chlorine or one
or two of the following: cycloalkyl such as cyclo-
propyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl,
especially cyclopropyl; alkoxy ~uch a~ methoxy,
ethoxy, n-propoxy, 2-methylethoxy, n-butoxy,
l-methylpropoxy, 2-methylpropoxy and 1,l-dimethyl-
ethoxy, especially methoxy, ethoxy, 1-methylethoxy
and 1,1-dimethylethoxy; haloalkoxy such as difluoro-
methoxy, trifluoromethoxy, chlorodifluoromethoxy,
dichlorofluoromethoxy, 1-fluoroethoxy, 2-fluoro-
ethoxy, 2,2-difluoroethoxy, 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoro-
ethoxy, 2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy, 2-chloro-1,1,2-
trifluoroethoxy and pentafluoroethoxy, especially
trifluoromethoxy and pentafluoroethoxy; alkylthio
such as methylthio, ethylthio, propylthio, 1-methyl-
ethylthio, butylthio, 1-methylpropylthio, 2-methyl-
propylthio and 1,1-dimethylethylthio, especially
methylthio and ethylthio; haloalkylthio such as
difllloromethylthio, trifluoromethylthio, chlorodi-
fluoromethylthio, l-fluoroethylthio, 2-fluoroethyl-
thio, 2,2-difluoroethylthio, 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl-
thio, 2-chloro-2,2-difluoroethylthio, 2,2-dichloro-
2-fluoroethylthio, 2,2,2-trichloroethylthio and
pentafluoroethylthio, especially difluoromethylthio
and pentafluoroethylthio or cyano;
benzyl which can carry from one to three of the
following: alkyl as mentioned above, especially
methyl, ethyl and i~o-propyl; haloalkyl as mentioned
above, especially trifluoromethyl and chlorodi-
fluoromethyl; alkoxy as mentioned above, especially
methoxy and ethoxy; haloalkoxy as mentioned above,
especially trifluoromethoxy, pentafluoroethoxy and
trichloromethoxy; alkylthio as mentioned above,
especially methylthio and ethylthio; haloalkylthio
ac mentioned above, e~pecially difluoromethylthio,
pentafluoroethylthio and trifluoromethylthio;
~ V r~ V ~ c~ 1
- 22 - O.Z. 0050/41126
h~lo~en as mentioned above, especially fluorine and
chlorine; cyano or nitro;
cycloalkyl such as cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclo-
pentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl and cyclooctyl,
especially cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl,
which can carry from one to three of the following:
alkyl as mentioned above, especially methyl, or
halogen as mentioned above, especially chlorine and
fluorine;
alkenyl such as ethenyl, l-propenyl, 2-propenyl,
l-methylethenyl, l-butenyl, 2-butenyl, 3-butenyl,
l-methyl-l-propenyl, l-methyl-2-propenyl, 2-methyl-
l-propenyl, 2-methyl-2-propenyl, 1-pentenyl,
2-pentenyl, 3-pentenyl, 4-pentenyl, l-methyl-l-
butenyl, 2-methyl-1-butenyl, 3-methyl-2-butenyl, 1-
methyl-2-butenyl, 2-methyl-2-bu~enyl, 1-methyl-3-
butenyl, 2-methyl-3-butenyl, 3-methyl-3-butenyl,
1,1,-dimethyl-2-propenyl, 1,2-dimethyl-1-propenyl,
1,2-dimethyl-2-propenyl, l-ethyl-l-propenyl,
1-ethyl-2-propenyl, 1-hexenyl, 2-hexenyl, 3-hexenyl,
4-hexenyl, 5-hexenyl, l-methyl-l-pentenyl, 2-methyl-
l-pentenyl, 3-methyl-1-pentenyl, 4-methyl-1-
pentenyl, l-methyl-2-pentenyl, 2-methyl-2-pentenyl,
3-methyl-2-pentenyl, 4-methyl-2-pentenyl, l-methyl-
3-pentenyl, 2-methyl-3-p~ntenyl, 4-methyl-2-
pentenyl, l-methyl-3-pentenyl, 2-methyl-3-psntenyl,
3-methyl-3-pentenyl, 4-methyl-3-pentenyl, l-methyl-
4-pentenyl, 2-methyl-4-pentenyl, 3-methyl-4-
pentenyl, 4-methyl-4-pentenyl, 1,1-dLmethyl-2-
butenyl, 1,1-dLmethyl-3-butenyl, 1,2-dLmethyl-l-
butenyl, 1,2-dLmethyl-2-butenyl, 1,2-dLmethyl-3-
butenyl, 1,3-dLmethyl-l-butenyl, 1,3-dLmethyl-2-
butenyl, 1,3-dLmethyl-3-butenyl, 2,2-dLmethyl-3-
butenyl, 2,3-dLmethyl-l-butenyl, 2,3-dLmethyl-2-
butenyl, 2,3-dLmethyl-3-butenyl, 3,3-dLmethyl-l-
butenyl, l-ethyl-l-butenyl, l-ethyl-2-butenyl, 1-
ethyl-3-buten~l, 2-ethyl-1-butenyl, 2-ethyl-2-
~ ~ r.~
- 23 - O.Z. 0050/41126
butenyl, 2-ethyl-3-butenyl, 1,1,2-trLmethyl-2-
propenyl, l-ethyl-l-methyl-2-propenyl, 1-ethyl-2-
methyl-l-propenyl and l-ethyl-2-methyl-2-propenyl,
especially allyl which can carry from one to three
s of the following: halogen as mentioned above,
especially fluorine and chlorine; alkoxy as
mentioned above, especially methoxy and ethoxy,
and/or one phenyl which in turn can carry from one
to three of the following: alkyl as mentioned above,
especially methyl, ethyl and iso-propyl; haloalkyl
as mentioned above, especiall`y trifluoromethyl and
chlorodifluoromethyl; alkoxy as mentioned above,
especially methoxy and ethoxy; haloalkoxy as
mentioned above, especially trifluoromethoxy,
pentafluoroethoxy and trichloromethoxy; alkylthio as
mentioned above, especially methylthio and ethyl-
thio; haloalkylthio as mentioned above, especially
difluoromethylthio, pentafluoroethylthio and tri-
fluoromethylthio; halogen as mentioned above,
especially fluorine and chlorine; cyano or nitro;
alkynyl such as ethynyl, l-propynyl, propargyl,
l-butynyl, 2-butynyl, 3-butynyl, 1-methyl-2-
propynyl, l-pentynyl, 2-pentynyl, 3-pentynyl, 4-
pentynyl, l-methyl-3-butynyl, 2-methyl-3-butynyl,
1-methyl-2-butynyl, 3-methyl-1-butynyl, l,l-di-
methyl-2-propynyl, 1-ethyl-2-propynyl, l-hexynyl, 2-
hexynyl, 3-hexynyl, 4-hexynyl, 5-hexynyl, l-methyl-
2-pentynyl, 1-methyl-3-pentynyl, 1-methyl-4-
pentynyl, 2-methyl-3-pentynyl, 2-methyl-4-pentynyl,
3-methyl-1-pentynyl, 3-methyl-4-pentynyl, 4-methyl-
l-pentynyl, 4-methyl-2-pentynyl, 1,1-dimethyl-2-
butynyl, 1,1-dimethyl-3-butynyl, 1~2-dimethyl-3-
butynyl, 2,2-dLme-~hyl-4-butynyl, 3,3-dLmethyl-l-
butynyl, 1-ethyl-2-butynyl, 1-ethyl-3-butynyl, 2-
ethyl-3-butynyl and 1-ethyl-1-methyl-2-propynyl,
especially propargyl, which can carry from one to
three of the following: halogen as mentioned above,
~ V rJ ;J ~
- 24 - o.Z. 0050/41126
especially iodine; alkoxy as mentioned above,
especially methoxy and ethoxy, and/or one phenyl
which in turn can carry from one to three of the
following: alkyl as mentioned above, especially
methyl, ethyl and iso-propyl; haloalkyl as mentioned
above, especially trifluoromethyl and chlorodi-
fluoromethyl; alkoxy as mentioned above, especially
methoxy and ethoxy; haloalkoxy as mentioned above,
especially trifluoromethoxy, pentafluoroethoxy and
trichloromethoxy; alkylthio a3 mentioned above,
e~pecially methylthio and ethylthio; haloalkylthio
a~ mentioned above, especially difluoromethylthio,
pentafluoroethylthio and trifluoromethylthio;
halogen as mentioned above, e~pecially fluorine and
chlorine; cyano or nitro;
Cl-C4-alkoxy as mentioned above, e~pecially methoxy
and ethoxy;
Cl-C4-haloalkoxy as mentioned above, especially
trifluoromethoxy, pentafluoroethoxy and trichloro-
methoxy;
Cl-C4-alkylthio a~ mentioned above, especially
methylthio and ethylthio;
C1-C4-haloalkylthio as mentioned above, especially
difluoromethylthio, pentafluoroethylthio and tri-
fluoromethylthio;
phenoxy or phenylthio, each of which can carry from
one to three of the following: alkyl aæ mentioned
above, especially methyl, ethyl and iso-propyl;
haloalkyl as mentioned above, especially trifluoro-
methyl and chlorodifluoromethyl; alkoxy as mentioned
above, especially methoxy and ethoxy; haloalkoxy as
msntioned above, e~pecially trifluoromethoxy,
pentafluoroethoxy and trichloromethoxy; alkylthio as
mentioned above, e~pecially methylthio and
ethylthio; haloalkylthio as mentioned above, especi-
ally difluoromethylthio, pentafluoroethylthio and
trifluoromathylthio; halogen a~ mentioned above,
~ v l ~ ~
- 25 - O.Z. 0050/41126
especially fluorine and chlorine; cyano or nitro;
a 5- to 6-membered heterocyclic radical containing
one or two hetero atoms selected from the group
. comprising oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen, such as 2-
S tetrahydrofuryl, 3-tetrahydrofuryl, 4-tetrahydro-
pyranyl, 2-tetrahydropyranyl, 3-tetrahydropyranyl,
3-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-furyl, 3-tetra-
hydrothienyl, 2-tetrahydropyranyl, 5-isoxazolyl, 3-
isoxazolyl, 4-iscxazolyl, 5-isothiazolyl, 4-isothia-
zolyl, 3-isothiazolyl, 2-oxazolyl, 4-thiazolyl, 4-
oxazolyl, 2-thiazolyl, 5-oxazolyl, 5-thiazolyl, 2-
imidazolyl, 4-imidazolyl, 5-imidazolyl, 3-pyrrolyl,
2-pyrrolyl, 3-pyrazolyl, 4-pyrazolyl, 5-pyrazolyl,
4-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl and 2-pyridyl, it being pos-
sible for this ring to carry one or two of the
followings alkyl as mentioned above, especially
methyl; halogen a~ mentioned above, especially
fluorine and chlorns; alkoxy as mentioned above,
especially methoxy and ethoxy, or alkoxycarbonyl
such a methoxycarbonyl and ethoxycarbonyl,
especially methoxycarbonyl;
phenyl which can carry from one to three of the
following: alkyl a-~ mentioned for Rl, especially
methyl, ethyl and iso-propyl; haloalkyl ac mentioned
above, especially trifluoromethyl and chlorodi-
fluoromethyl; alkoxy as mentioned above, e pecially
methoxy and ethoxy; haloalkoxy as mentioned above,
especially trifluoromethoxy, pentafluoroethoxy and
trichloromethoxy; alkylthio as mentioned above,
especially methylthio and ethylthio; haloalkylthio
as mentioned above, especially difluoromethylthio,
pentafluoroe~hylthio and trifluoromethylthio;
halogen as mentioned above, especially fluorine and
chlorine; cyano or nitro;
R2 is formyl, 4,5-dihydro-2-oxazolyl or -CoYR5
and
Y i~ oxygen or ~ulfur;
- 26 - O.Z. 0050/41126
R5 i B hydrogen;
alkyl as mentioned for Rl, especially methyl, ethyl,
n-propyl, iso-propyl, and n-hexyl, which can carry
from one to five halogen atoms as mentioned for Rl,
especially fluorine and chlorine, or hydroxyl groups
and/or one of the following: alkoxy as mentioned for
Rl, especially methoxy and ethoxy; alkoxyalkoxy such
as methoxyethoxy, ethoxyethoxy, propoxyethoxy,
especially methoxyethoxy; cyano; trimethylsilyl;
alkylthio as mentioned for R1, especially methylthio
and ethylthio; alkylamino such as methylamino,
ethylamino, propylamino, iso-propylamino, especially
methylamino and ethylamino; dialkylamino such as
dimethylamino, diethylamino, dipropylamino, diiso-
lS propylamino, methylethylamino, especially dimethyl-
amino and methylethylamino; cycloalkylamino such as
cyclopropylamino,cyclobutylamino,cyclopentylamino,
cyclohexylamino and cycloheptylamino, espeeially
cyclopropylamino; alkylsulfinyl such as me~hyl-
sulfinyl, ethylsulfinyl, propylsulfinyl, iso-propyl-
sulfinyl, e~pecially methylsulfinyl and ethyl-
sulfinyl; alkylsulfonyl such as methylsulfonyl,
ethylsulfonyl, propylsulfonyl, iso-propylsulfonyl,
especially methylsulfonyl and ethylsulfonyl;
carboxyl; alkoxycarbonyl as mentioned for R1,
especially methoxycarbonyl; dialkylaminocarbonyl
such as dim~thylaminocarbonyl, diethylaminocarbonyl,
dipropylaminocarbonyl, diisopropylaminocarbonyl,
dicyclopropylaminocarbonyl, methylethylamino-
carbonyl, especially dimethylaminocarbonyl and
diethylaminocarbonyl; dialkoxyphosphoryl such as
dimethoxyphosphoryl, diethoxyphosphoryl, dipropoxy-
phosphoryl, diisopropoxyphosphoryl, especially
dimethoxyphosphoryl and diethoxypho~phoryl;
alkaneLminoxy ~uch as, in particular, 2-
propaneiminoxy; thienyl, furyl, tetrahydrofuryl,
phthalimido, pyridyl, benzyloxy; benzoyl, it b~ing
2026~31
- 27 - O.Z. 0~50/41126
possible for the cyclic radicals in turn to carry
from one to three of the following: alkyl as
mentioned for R1, especially methyl and ethyl; alkoxy
as mentioned for Rl, especially methoxy and ethoxy,
or halogen as mentioned for Rl, especially fluorine
and chlorine;
benzyl which can carry from one to three of the
following: alkyl as mentioned for Rl, especially
methyl and ethyl alkoxy as mentioned for Rl, aspeci-
ally methoxy and ethoxy; haloalkyl as mentioned for
Rl, especially trifluoromethyl; halogen as mentioned
for R1, especially fluorine and chlorine, nitro and
cyano;
C3-Ca-cycloalkyl a~ mentioned for Rl, especially
cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl;
phenyl which can carry -from one to three of the
following: alkyl as mentioned for Rl, especially
methyl and ethyl; alkoxy a~ mentioned for R1,
especially methoxy and ethoxy; haloalkyl as
mentioned for R1, especially trifluoromethyl; halo-
alkoxy a~ mentioned for Rl, especially trifluoro-
methoxy; alko~ycarbonyl a~ mentioned above,
e.?ecially methoxycarbonyl; halogen as mentioned for
R1, especially fluorine and chlorine and bromine,
nitro and cyano;
C3-C6-alkenyl as mentioned for R1, especially allyl
and methallyl, C5-Cs-cycloalkenyl such as 2-cyclo-
pentenyl and 2-cyclohexenyl, especially 2-cyclo-
hexenyl, or C3-CB-alkynyl a~ mentioned for R1,
especially propargyl, it being po~sible for these
radical~ to carry one of the following: ~ydroxyl;
alkoxy as mentioned for Rl, especially methoxy and
ethoxy; halogen a~ mentioned for Rl, especially
iodine, or phenyl which in turn can carry from one
to three of the followinq: alkyl a~ mentioned for
Rl, e3pecially methyl and ethyl; alkoxy a~ mentioned
for Rl, especially methoxy and ethoxy; haloalkyl a~
~ ~ . J J ~
- 28 - O.Z. 0050/41126
mentioned for Rl, especially trifluoromethyl;
halogen as mentioned for Rl, especially fluorine and
chlorine, nitro or cyano;
a five- to six-membered heterocyclic radical con-
S taining one or two hetero atoms selected from the
group comprising oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen as
mentioned for Rl, especially tetrahydrofuryl and
tetrahydropyranyl or a benzotriazolyl radical;
phthalimido; tetrahydrophthalimido; succinimido;
maleimido;
one equivalent of a cation of an alkali metal or
alkaline earth metal, manganese, copper, iron,
ammonium or substituted ammonium
or -N=CR6R7 where R~ and R7 are, independently of one
another, hydrogen, alkyl as mentioned for Rl,
especially methyl, ethyl and iso-propyl; cycloalkyl
as mentioned for R1, especially cyclopropyl; phenyl
or furyl, or together form a methylene chain -(CH2)~-
with m = 4 to 7,
20 R3 i~ hydrogen,
Cl-C~-alkyl as mentioned for Rl, especially methyl,
ethyl or iso-propyl, which can carry from one to
three of the following: hydroxyl; halogen as men-
tioned for Rl, especially fluorine and chlorine;
alkoxy a~ mentioned for Rl, especially methoxy and
ethoxy; alkylthio a~ mentioned for Rl, especially
methylthio and ethylthio, or dialkylamino as men-
tioned for R5, especially dimethylamino;
cycloa~kyl as mentioned for R1, especially cyclo-
propyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl,
which can carry from one to three of the following:
alkyl as mentioned for Rl, especially methyl, ethyl
and isopropyl; halogen as mentioned for Rl, especi-
ally fluorine and chlorine, or haloalkyl as
mentioned for R1, especially trifluoromethyl;
R4 is hydroxyl;
alkoxy as mentioned for Rl, especially methoxy and
J ;~
- 29 - O.Z. 0050/41126
ethoxy;
alkyl as mentioned for R~, especially methyl, ethyl,
n-propyl, i~o-propyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl, iso-butyl
and tert-butyl, which can carry from one to three of
the following: alkoxy as mentioned for R1, especially
methoxy and ethoxy; haloalkoxy as mentioned for Rl,
especially trifluoromethoxy; alkylthio as mentioned
for Rl, especially methylthio and ethylthio; halo-
alkylthio as mentioned for Rl, especially
trifluoromethylthio; dialkylamino as mentioned for
Rl, especially dimethylamino and diethylamino;
halogen as mentioned for R1, especially fluorine and
chlorine; cycloalkyl as mentioned for Rl, especially
cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl, or phenyl
which in turn can carry from one to three of the
following: halogen as mentioned for R1, especially
fluorine and chlorine; cyano; nitro; alkyl as
mentioned for R1, especially methyl and ethyl;
haloalkyl as mentioned for Rl, especially trifluoro-
methyl, alkoxy as mentioned for R1, e pecially
methoxy and ethoxy; haloalkoxy as mentioned for Rl,
especially trifluoromethoxy; alkylthio as mentioned
for Rl, especi lly methylthio and ethylthio, or
haloalkylthio as mentioned for R1, especially tri-
fluoromethylthio;
cycloalkyl as mentioned for Rl, especially cyclo-
prspyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl,
which can carry from one to three of the following:
alkyl as mentioned for Rl, especially methyl, ethyl
and isopropyl; haloalkyl as mentioned for Rl,
especially trifluoromethyl; alkoxy as mentioned for
Rl, especially methoxy and ethoxy; haloalkoxy as men-
tioned for Rl, especially trifluoromethoxy; halogen
as mentioned for R1, e~pecially fluorine and
chlorine, nitro or cyano;
alkenyl or C3-Cs-alkynyl as mentioned for Rl,
especially allyl, methallyl, propargyl and 1,1-
202613~
_ 30 - O.Z. OOS0/41126
dimQthyl-2-propynyl, which can be substituted from
once to three time~ by halogen as mentioned for R1,
especially fluorine and chlorine, andJor once by
phenyl which in ~urn can carry from one to three of
S the following: alkyl as mentioned for Rl, especially
methyl and ethyl; haloalkyl a~ mentioned for R1,
e~pecially trifluoromethyl; alkoxy a~ mentioned for
Rl, especially methoxy and ethoxy, haloalkoxy a~ men-
tioned for Rl, e4pecially trifluormethoxy; alkylthio
as mentioned for R1, e~pecially methylthio and
ethylthio; haloalkylthio as mentioned for R1,
especially trifluoromethylthio; halogen as mentioned
for R1, especially fluorine and chlorine, cyano or
nitro;
a 5- to 6-membered heterocyclic radical which
contains one or two hetero atoms selected from the
group comprising oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen as
mentioned for R1 and which can carry from one to
three of the following: alkyl as mentioned for Rl,
especially methyl, ethyl and iso-propyl, or halogen
as mentioned for R1, especially fluorine and
chlorins;
phenyl which can carry from one to four of the
following: alkyl a~ mentioned for R', especially
methyl, ethyl and iso-propyl; haloalkyl as mentioned
for Rl, especially trifluoromethyl; alkoxy a~ men-
tioned for R1, e~pecially methoxy and ethoxy; halo-
alkoxy as mentioned for R1, e~pecially trifluoro-
methoxy; alkylthio as mentioned for Rl, especially
methylthio and ethylthio; haloalkylthio a~ mentioned
for R1, especially trifluoromethylthio; halogen as
mentioned for R1, especially fluorine and chlorine;
nitro; cyano; formyl; alkanoyl such a acetyl,
propionyl, butyryl, especially acetyl; haloalkanoyl
such a~ trifluoroacetyl, trichloroacetyl, penta-
fluoropropionyl, e~pecially trifluoroacetyl, or
alkoxycarbonyl a~ mentioned for R1, especially
2026131
- 31 - O.Z. OOS0/41126
methoxycarbonyl;
naphthyl which can be substituted from once to three
times by alkyl as mentioned for R1, especially methyl
and ethyl, or halogen as mentioned for R1, especially
fluorine and chlorine,
or
R3 and R~ can together form -tcHz)n-yp-(cH2)q-~ where
n and q are each l, 2 or 3, p i~ 0 or 1 and Y is
oxygen, sulfur or N-methyl, su~h as -(CH2)3-,
-(CH2)4--, -(CH2)5-r -(CH2)6-- -CH2-O-CH2-,
-CH2-CH2-O-CH2-CH2-, -CH2-S-CH2-, -CH2-CH2-S-CH2-CH2-,
-CH2-CH2-N ( CH3 )-CH2-CH2-, especially -(CH2) 5- and
-CH2-cH2-o-cH2-cH2-, or -( CH2)3-CO-;
and the environmentally compatible salt~ thereof.
Particularly preferred compounds Ia~ and Ib' are
those in which R3 is hydrogen and those in which:
Rl is hydrogen;
methyl, ethyl, propyl, 1-methylethyl, butyl, 1-
methylpropyl, 2-methylpropyl and 1,1-dimethylethyl;
methoxy, ethoxy, propyloxy, l-methylethoxy, butyl-
oxy, l-methylpropyloxy, 2-methylpropyloxy and 1,1-
dimethylethoxy;
difluoromethoxy and trifluoromethoxy;
methylthio, ethylthio, propylthio, 1-methylethyl-
thio, butylthio, 1-methylpropylthio, 2-methylpropyl-
thio and l,1-dimethylethylthio;
difluoromethylthio and trifluoromethylthio,
R2 i8 --Co~R5;
R5 is hydrogen; phthalimido; ~uccinimido; maleimido
or -N=CR6R7;
R~ and R7 are each hydrogen;
methyl, ethyl, propyl, l-methylethyl, butyl, 1-
methylpropyl, 2-methylpropyl and 1,1-dimethylethyl;
cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl and
cycloheptyl;
or together form a 4- to 7-membered alkylene chain
~uch as -CH2CH2CH2CH2-~ -CH2CH2CHzCH2cH2~~
~ U r~
- 32 - O.Z. 0050/41126
-CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2- and -cH2cH2cH2cH2cH2cH2cH2-;
R3 and R4are each methyl, ethyl, propyl, l-methylethyl,
butyl, l-methylpropyl, 2-methylpropyl and 1,1-
dimethyle~hyl;
5 `cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl and cyclo-
heptyl;
or together form a 4- to 7-membered alkylene chain
such as -CH2CH2CH2cH2-~ -CH2CH2CH2cH2cH2-
-CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2- and -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2-;
10Examples of very active compounds of the formulae
Ia and Ib are listed in the Tables which follow:
J ~
33 O.Z. 0050/41126
Table A
,R3
1 ~ N~R4 Ia (X = O or S)
R1 X-~
R2
R1 R2 R3 R4
H COOH H tert.-butyl
5 F COOH H tert.-butyl
Cl COOH H tert.-butyl
methyl COOH H tert.-butyl
ethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
n-propyl COOH H tert.-butyl
10 iso-propyl COOH H tert.-butyl
n-butyl COOH H tert.-butyl
iso-butyl COOH H tert.-butyl
sec.-butyl COOH H tert.-butyl
tert.-butyl COOH H tert.-butyl
15 cyclo-propyl COOH H tert.-butyl
cyclo-butyl COOH H tert.-butyl
cyclo-pentyl COOH H tert.-butyl
cyclo-hexyl COOH H tert.-butyl
cyclo-heptyl COOH H tert.-butyl
20 cyclo-octyl COOH H tert.-butyl
l-methylcyclopropyl COOH H tert.-butyl
trifluoromethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
chlorodifluoromethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
pentafluoroethyl COOH H tert.-buty~
25 methoxymethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
l-methylmethoxymethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
1-methylmethoxyethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
ethoxymethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
vinyl COOH H tert.-butyl
30 allyl COOH H tert.-butyl
methallyl COOH H tert.-butyl
crotyl COOH H tert.-butyl
ethynyl COOH H tert.-butyl
propargyl COOH H tert.-butyl
35 phenylethynyl COOH ~ tert.-butyl
methoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
ethoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
trifluoromethoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
methylthio COOH H tert.-butyl
2026131
34 O.Z. 0o5o/4ll26
Rl K2 R3 R4
trifluoromethylthio COOH H tert.-butyl
phenoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
5 4-CI-phenoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-(Cl,Cl)-phenoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
4-CF3-phenoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-F-phenylthio COOH H tert.-butyl
10 3-F-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-(F,F)-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-CI-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-CI-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-(Cl,CI)-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
15 2-CH3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-CH3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
4-CH3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-(CH3,CH3)-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4,6-(CH3,CH3,CH3)-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
20 2-CF3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-OCH3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-(OCH3,OCH3)-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
4-OCF3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
4-SCH3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
25 3-SCF3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-(NO2,NO2)-phenyt COOH H tert.-butyl
4-NO2-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-thienyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-thienyl COOH H tert.-butyl
30 2-furanyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-furanyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-tetrahydrofuranyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-tetrahydrofuranyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-pyridyl COOH H tert.-butyl
35 3-pyridyl COOH H tert.-butyl
4-pyridyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H tert.-butyl
4-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H tert.-butyl
40 iso-propoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
H COOH H cyclo-propyl
F COOH H cyclo-propyl
Cl COOH H cyclo-propyl
~ ù,~
O.Z. 0050/41126
Rl - R2 R3 R4
methyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
ethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
5 n-propyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
iso-propyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
n-butyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
iso-butyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
sec.-butyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
lQ tert.-butyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
cyclo-propyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
cyclo-butyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
cyclo-pentyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
cyclo-hexyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
15 cyclo-heptyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
cyclo-octyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
l-methylcyclopropyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
trifluoromethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
chlorodifluoromethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
20 pentafluoroethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
methoxymethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
1-methylmethoxymethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
l-methylmethoxyethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
ethoxymethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
25 vinyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
allyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
methallyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
crotyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
ethynyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
30 propargyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
phenylethynyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
methoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
ethoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
trifluoromethoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
35 methylthio COOH H cyclo-propyl
trifluoromethylthio COOH H cyclo-propyl
phenoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-CI-phenoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
2,4-(Cl,CI)-phenoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
40 4-CF3-phenoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-F-phenylthio COGH H cyclo-propyl
3-F-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2,4-(F,F)-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
202613~
36 O.Z. 0050/41126
Rl R2 R3 R4
2-Cl-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-CI-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
5 2,4-(Cl,CI)-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-CH3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-CH3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-CH3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2,4-(CH3,CH3)-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
10 2,4,6-(CH3,CH3,CH3)-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-CF3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-OCH3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2,4-(OCH3,0CH3)-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-OCF3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
15 4-SCH3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-SCF3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2,4-(N02,N02)-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-N02-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-thienyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
20 3-thienyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-furanyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-furanyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-tetrahydrofuranyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-tetrahydrofuranyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
25 2-pyridyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-pyridyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-pyridyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
30 4-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
iso-propoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
H COOH methyl tert.-butyl
F COOH methyl tert.-butyl
Cl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
35 methyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
ethyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
n-propyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
iso-propyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
n-butyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
40 iso-butyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
sec.-butyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
tert.-butyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
cyclo-propyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
cyclo-butyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
37 O.Z. 0050/41126
Rl R2 R3 R4
cyclo-pentyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
cyclo-hexyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
5 cyclo-heptyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
cyclo-octyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
l-methylcyclopropyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
trifluoromethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
chlorodifluoromethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
lO pentafluoroethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
methoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
l-methyImethoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
l-methylmethoxyethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
ethoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
15 vinyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
allyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
methallyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
crotyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
ethynyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
20 propargyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
phenylethynyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
methoxy COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
ethoxy COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
trifluoromethoxy COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
25 H COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
F COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
Cl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
methyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
ethyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
30 n-propyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
iso-propyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
n-butyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
iso-butyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
sec.-butyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
35 tert.-butyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
cyclo-propyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
cyclo-butyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
cyclo-pentyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
cyclo-hexyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
40 cyclo-heptyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
cyclo-octyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
1-methylcyclopropyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
trifluoromethyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
chlorodifluoromethyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
38 O.Z. 0050/41126
Rl R2 R3 R4
pentafluoroethyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
methoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
5 l-methyImethoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
l-methylmethoxyethyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
ethoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
vinyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
allyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
10 methallyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
crotyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
ethynyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
propargyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
phenylethynyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
15 methoxy COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
ethoxy COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
trifluoromethoxy COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
3S
39 O.Z. 0050/41126
Table B
R2
,R3 Ib (X = O or S)
R4
o
Rl R2 R3 R4
5 H COOH H tert.-butyl
F COOH H tert.-butyl
Cl COOH H ` tert.-butyl
methyl COOH H tert.-butyl
ethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
10 n-propyl COOH H tert.-butyl
iso-propyl COOH H tert.-butyl
n-butyl COOH H tert.-butyl
iso-butyl COOH H tert.-butyl
sec.-butyl COOH H tert.-butyl
15 tert.-butyl COOH H tert.-butyl
cyclo-propyl COOH H tert.-butyl
cyclo-butyl COOH H tert.-butyl
cyclo-pentyl COOH H tert.-butyl
cyclo-hexyl COOH H tert.-butyl
20 cyclo-heptyl COOH H tert.-butyl
cyclo-octyl COOH H tert.-butyl
1-methylcyclopropyl COOH H tert.-butyl
trifluoromethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
chlorodifluoromethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
25 pentafluoroethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
methoxymethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
l-methylmethoxymethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
1-methylmethoxyethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
ethoxymethyl COOH H tert.-butyl
30 vinyl COOH H tert.-butyl
allyl COOH H tert.-butyl
methallyl COOH H tert.-butyl
crotyl COOH H tert.-butyl
ethynyl COOH H tert.-butyl
35 propargyl COOH H tert.-butyl
phenylethynyl COOH H tert.-butyl
methoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
ethoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
trifluoromethoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
40 methylthio COOH H tert.-butyl
20261~1
O.Z. 0050/41126
Rl R2 R3 R4
trifluoromethylthio COOH H tert.-butyl
phenoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
5 4-Cl-phenoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-(Cl,CI)-phenoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
4-CF3-phenoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-F-phenylthio COOH H tert.-butyl
lO 3-F-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-(F,F)-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-Cl-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-CI-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-(Cl,Cl)-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
15 2-CH3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-CH3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
4-CH3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-tCH3,CH3)-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4,6-(CH3,CH3,CH3~-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
20 2-CF3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-OCH3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-(OCH3,0CH3)-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
4-OCF3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
4-SCH3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
25 3-SCF3-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2,4-(NO2,NO2)-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
4-NO2-phenyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-thienyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-thienyl COOH H tert.-butyl
30 2-furanyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-furanyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-tetrahydrofuranyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-tetrahydrofuranyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-pyridyl COOH H tert.-butyl
35 3-pyridyl COOH H tert.-butyl
4-pyridyl COOH H tert.-butyl
2-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H tert.-butyl
3-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H tert.-butyl
4-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H tert.-butyl
40 iso-propoxy COOH H tert.-butyl
H COOH H cyclo-propyl
F COOH H cyclo-propyl
Cl COOH H cyclo-propyl
methyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
~:~ v r~
41 O.Z. 0050/41126
Rl R2 R3 R4
ethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
n-propyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
5 iso-propyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
n-butyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
iso-butyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
sec.-butyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
tert.-butyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
10 cyclo-propyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
cyclo-butyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
cyclo-pentyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
cyclo-hexyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
cyclo-heptyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
lS cyclo-octyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
l-methylcyclopropyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
trifluoromethyl COOH H cyslo-propyl
chlorodifluoromethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
pentafluoroethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
20 methoxymethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
l-methylmethoxymethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
l-methylmethoxyethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
ethoxymethyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
vinyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
25 allyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
methallyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
crotyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
ethynyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
propargyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
30 phenylethynyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
methoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
ethoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
trifluoromethoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
methylthio COOH H cyclo-propyl
35 trifluoromethylthio COOH H cyclo-propyl
phenoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-CI-phenoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
2,4-(Cl,Cl)-phenoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-CF3-phenoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
40 phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-F-phenylthio COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-F-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2,4-(F, F ) -phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-CI-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
42 O.Z. 0050/41126
Rl R2 R3 R4
3-CI-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2,4-(Cl,CI)-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
5 2-CH3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propy1
3-CH3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-CH3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2,4-(CH3,CH3)-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2,4,6-(CH3,CH3,CH3)-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
10 2-CF3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-OCH3-phenyl COOH H ` cyclo-propyl
2,4-(OCH3,0CH3)-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-OCF3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-SCH3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
l5 3-SCF3-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2,4-(N02,N02¦-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-N02-phenyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-thienyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-thienyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
20 2-furanyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-furanyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-tetrahydrofuranyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-tetrahydrofuranyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-pyridyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
25 3-pyridyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-pyridyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
2-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
3-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
4-tetrahydropyranyl COOH H cyclo-propyl
30 iso-propoxy COOH H cyclo-propyl
H COOH methyl tert.-butyl
F COOH methyl tert.-butyl
Cl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
methyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
35 ethyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
n-propyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
iso-propyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
n-butyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
iso-butyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
40 sec.-butyl COOH ~ethyl tert.-butyl
tert.-butyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
cyclo-propyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
cyclo-butyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
cyclo-pentyl COOH methyl tert.-butyl
43 O.Z. 0050/41126
Rl R2 R3 R4
cyclo-hexyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
cyclo-heptyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
5 cyclo-octyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
1-methylcyclopropyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
trifluoromethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
chlorodifluoromethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
pentafluoroethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
10 methoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
1-methylmethoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
1-methyImethoxyethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
ethoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
vinyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
15 allyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
methallyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
crotyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
ethynyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
propargyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
20 phenylethynyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
methoxy COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
ethoxy COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
trifluoromethoxy COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
H COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
25 F COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
Cl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
methyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
ethyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
n-propyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
30 iso-propyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
n-butyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
iso-butyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
sec.-butyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
tert.-butyl COOH iso-propyl tert.-butyl
35 cyclo-propyl COO~ iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
cyclo-butyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
cyclo-pentyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
cyclo-hexyl COO~ methyl cyclo-propyl
cyclo-heptyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
40 cyclo-octyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
1-methylcyclopropyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
trifluoromethyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
chlorodifluoromethyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
pentafluoroethyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
~;~ v r~
44 O.Z. 0050/41126
Rl R2 R3 R4
methoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
1-methylmethoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
5 1-methyImethoxyethyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
ethoxymethyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
vinyl COOH i so-propyl cyclo-propyl
allyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
methallyl COOH iso-propyl cyclo-propyl
10 crotyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
ethynyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
propargyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
phenylethynyl COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
methoxy COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
15 ethoxy COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
trifluoromethoxy COOH methyl cyclo-propyl
~0
t~ ,L ~) i
~_ OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
_ O
~D _
C ._
~ ~_ o o ~E I~
o I~ o E E s ~
U-) I ~ 0 I ~ ~ I T I
o x ~ _ _ u E ~ _ Z ~ I C ~
~`J ' ~: ~ L "~ ~ S O ~ ~, ~ Z ~ ~ n 0~ 0 -- Z
~ ~ J o o I L T I I T I C_~ I T O T ~
0=~=0 U~ ~ 11 11 1 ~ ~ O I I I T I I I I I
Z=~
._
o
_ ,. _ _. _ _ _, _, _ ,_ _, . _ _, _
I~ ~ +~ ~ ~ ~ +~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
_. n n n ~ n ~ ~ D n n ~1 n 8 n n n n n ~
1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.
Y ~ + ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ + Y ~ ~ +- ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
LLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLL
t~ cu ~ cu cu ~ cu 0 0 cu cu 0 cu 0 ~
\Z~ I ~
=~,)= 1~ I I T I T T T T I I I I I I I I = I I
1~
_.
m _ ~ . . ~
_. ~ ~ ~. ~ ~.
~Q~C~
O O O O O O _ _ _ . ~ . _ LL~LLL
CLLLLL~Q
~- O O O O O O ~ '- ~ ~ S S I
_~ s ~- ~ s ~ ~ cu ~ ~ cU V 0 ~ v
~ ~ u c~ .) V E F E E E E E ~
20261S~l
~- o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
I a~ _
~, ~ _ a~ ~ ~
-- -- ~ -- -- ~, _ s _ ~ ~a _
S S ~ S S S ~ ~ ::~ L L ~,
n ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ o
O I G ~ O ~J> ~ E ~ ~ :,. ~ s o o ~
-- E E L E E _ o ~ ~ L L ro
OV -- -- ~ ~ O L~ ~ S
I S s ~ _ C~
~1 ~ I V ~) ~ O L t~ 3 .C~
O ~ I ~ ~ I L O I V V I ~ Il) a) S ~ L 1 3
~ L ~ z In o O z ~ ~ ~ ~ s c~ o n o CJ
n 3 3 8 3 8~ 3 D ~ D 3 la n n n 3 n n 3 ~ 3 ~ n
IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII11.1.1.1.1.1.1.
LLLL~LLLLLLLLtLLLLLLLLLLL
I T I I I I I T I I I T T'T I I I I I I I T I I T
_ _. _ _ _ _ _
_ c~ ~ ~ cL ~ n. c~
O O O O O O O
C L LtL - ~ x x x
-- v tJ ~ t~ t~ t~ q ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ v Q) v ~ ~ E E E
~- o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
+' ~ E ~ c
E O
~D E E _ _ ~, ,E ~-- E
_. ~ ~, ~ , _ c -- C
~ ~c X ,, ,, ~ .~ S ~~ I s ~ E :'~
o E ~ ~ ~ ~) E a~ . .) +~ c ~1 c
In -- '~' 8 ~ ~ ~ o E ~ o ~, ~ ~ o o ~ o
O ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ X ~ C ~ -- L ~ _ C ~ :-~
~ ~ O ~ X X O O E c a~ -- ~ E ~ ~-- E ~-- o x
1~i .a C L E o +C,, ~ ~ o T _ C _ S ._ C . ~:L OL
o o )C +~ o ~ _ rD :_~ ~ rO ~ ~-- ~-- O 1~
o L ~, ~, c 8 c n E ~ ~C ~ ~ ~ I +C, ~ ~ ~ ~ + + + (t) s'
~ ~ r~ r~ ~ ~ n -- -- ~ E ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ E ~ Z Y Z ~ ~
- - . - ~ . . - - - . - - - - , - - - . - - - - . .
n n ~. ~ I ~ n n n n 1~ n n 1~ ~ n n n n ~ ~ .o n n
L L L '~ L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L
3: ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ +~ IJ ~ ~ .~J +~ J ~ ~ +~
r~
I I I I I I I I I T I I I I I I I I I I I I I I T
.
C ~ ~
S ~ S S S S S
OOOOOOOOOOOOOO__,~
a a ~ Q~ s s c s s s c
s s s I I I I I I I '~
E E E E ~ ~ ~ ,~ s s s s
2026131
o o
, oo o oooooooooooooooooooo
~D _ cO
.
_. -- ~ -- O o _ I --
~ ~, ~ In ~ ~ C ~ '~ I
o '~,~ ~ ~ o E E." ~ ) u O I
O _n. I ~ I ~ c ~ I t_~0 11 I ~
O ~ ~ U- E X ~ I ~E _ + _ z -- Z ~ I ~.)
_ L ~I CL O I ~.> C ~ O -- Z 2 0 ~ ~ V~ O O -- Z
r~l _ O L O L ~ ~, (~ -- O C.) ~, ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ _ ~ ~ -- ~ O _
O ~ -- ~ I ~ C,~ ~ ~ ~ I ~ I I O I C"~
-- ~ ~ O ~-- S ~ ~ ~ ~ c_~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ r~ ~ ~ ~ ~ _ ~ =
In ~ E '`I o ~ ~ z z ~ ~ ~' Z ,~ I S ~ ~ I ~ I I I I I
00
_ _
+~ ~ ~ ~ O O Q ~ C~ I:L Q Q. ~ Q ~ ~ ~ O O O O o
3 3 ~ Q L L L L L L LO L LO LO LO L L L L L L
~----OOOOOOOOOOOOO_____
L L L L L o V _ _ _ _ _ -- -- -- _ _ _ _ _ ~ ~ ~ ~ V
~ V ~ ~
._ ~ L OL LLO _ _ _ _ _ _ o o o o O O o
,c r c O O O O O O S C S S ~: ' C O ~ O O O O O
E E E E E E ~
~ ~I J .~ ~i
~- o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
In
E c
I a
~D ~ ~ C
~1 ~ c _ ~ c ~
_. N _ _ ~ C _ ~ ~ _
_. ~1 C S ~ S S ~ _ i _ _ C ~
O I O (~ O ~ ~ E C ~ :~ ~ c O O N
1~-) ~ E E ~ E E O ~ ~
O -- I I ~ I I _ L C ~ ~ ~ I ~ ~ ._ _ _ ~,
O O -- ~ O CL ~ S S ~ :~ ~t L :.7 _ :., ~
_ ~ c ~ c ~ O ~ O _ ~ ~ n
1~1 ~ ~ . s ~ 7 ~ O y _ _ Q ~ ~> 3 n
O ~ ~ C I ~ O ~ ) a) r~
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Q a) ~ ~ z lo 0 0 z ~ ~ n ~ s ~ o ~ o ~ t
- - - - ~ . - - - - - -
~ L ~ o o LO OL O O ~O ~O O O O O O O O O
l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
OOO_OO__~OOOOOOOOOOO_O_OO
I T I I I I T T T T I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
_ _ _ ,_ _ _ _
O O O O O O O
L L L L C~, ~, L ~ ,, ~ X X o o
_ _ ~ _ _ _ _ ~ S S S S
~ > -- -- . -- -- -- -- C S S S S S S ~ ~ ~ ~
~ u ~ ~ ~ ~ E E E E
2026131
ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
._ s E
t-t- al
+~ E ~ c
EE -- -- E ~ E
-- E
_. ~ ~, ~ _ s -- ~ ~
~ ~ o ~. ~ ~ ~ s q~ ~ ~ c 8 _
o E +~ E a~ +~ ~ E
u~ -- -- ~ ~ ~ t- n o E ~, o -- Q~ o Q o -- +~
o ~ ~ s I E ~> ~ ~ o s o ~. -- ~ o o 1~ o ~,
o x ~ ~ ~ ~ n x ~ -- t ~ -- E
~ 8 X xo E C -- ~ E u +~ ~ ~-- ~, E ~-- ~ LXo
~ l~t--o~-~oI-t-.r~ - ~L
o - - o ~ ~ ~ 8 s c , ~ ~ , c L~ +~
~ t- E I I ~ +~ +~ -- ~ ~ +~ + + ~ -- t- _
U~ ~ ~ +~ ~ ,c ~ I T ~- l C (I~-_~--~+ I ~--I--
Cl: U ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ E ~ c~ ~ ~ r +~ E u~ c~ ~ z Y z ~ t~ ~
o
u~
_ _ _ _
___.~~__r~____~:~:~_r_______
3~Q~
OOOOOOOOOOOOLLLLOOOOOOOOO
LLLLLLLLLLLL~LLLtLLLLL
I I I I I I I I I I I I O O O O I I I I I I I I I
OOOOOOOOOOOO__~--OOOOOOOOO
U t.J t.t ~ J tJ t,~ t~ t~ t~ t~ tJ t~ .J V ~ (J
~Y ~ V ~ t~ ~ ~ t~ V ~
IIII~IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
_ _ _ _ _ _ _
C c c~ ~ c
C S S C c c t
X X X X X X X -- -- -- -- -- -- --
OOOOOOOOOOOOOO___.~__
a~ C -- -- ~ -- C C
x ~ x ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ n. ~ ~ -- ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
O O O
_ 8 E E ~ ~ ~ ~ s s s c s s
o o
~- o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
v~ In
~D
cn
O ~ L
~ O ~ L ~ ~ ~ <`~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~) ~ ` _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ L ~ I I I I T I I I I T T <`~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~) ~ ~ ('>
_ O L O ~ ~ C.~ 7 ~ O t_) I I T I I I T
Ir~ I L I Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z
l l l l l l l l l l
In
____
~._____________r~_.~_~_
L. L L L ~ ~ ~ ~ a ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
CL 0. ~ ~L D ~ D n ~ D D .R D D .1~ g n n D D D D D D
~ I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
_ O O _
~U~'~LLLLL_LLLLLLLLLLLLLL'
T T T I I I I I I ~- I I I I I I I I I T -r I I I I
~ ~ _
O
~ ~, O
O'-L~
_ ~ _. _. ~1 0 E
_ ~ D ~ O
-- ~ ~ O ~ C X ~ O ~ O
_~ ~L~L._~
. ~L~ D ~ ~ D~ s ~ -
-- ~ . o L~ ~ n I o o o o o o +~ . L~l
_ ~ _~~~~~ILS~
~ 1~ ~ T ~ ~ E
~ ~ ", ! ' i
~' OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
~O
o
o
____~____~_________________
I~J I I T I I I ~ I I I I I T I I I I I T I I I I I
O ______.___________________
U-11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 1~ 11 11 11
~ ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
U~
n n n D ~ ~ D/ D ~ n n n ~ n D ~ n ~ 8 n n ~ n n
~t ~v <v ~v ~v ~ ~v ~v ~v ~V ~v ~ ~ a~ ~v ~v ~ ~ ~V ~v ~v v ~> v a~ ~
r I -- I I I -- I I I -- I I -- T I I I I I I I I I I I
' :-, O
-- X
E ~v o
X X _ s ~ ~
~ E E ~ _ _ ~ E O E o _ ~ _
E -- , sv ~ _3 ~ L sV ~ ' CV V
X ' ~ > ' -- X :~. ~ _ ~ X " C.) I _ ' S 1~
O ~C E E C C ~ ~ O '' O a ~ ~ V ~ ;~ "' ~ ~ ~--
a~ <v I I ~ -- _ sv ~ S a~ ~ ~ ~ L, S
n: ~-- E ~ cv ~ E s~ sv ~ c~ E ~ ~ E ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
~V~ v,~i
~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
o
u~
1~1I I I I I I I :1: I I I I I I I I '' T I I I I
O___________,______________
U- ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
n
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ . . _ _ . . _ _ . . _ _ _. _
~ n n ~ n 8 8 n 8 5:1 ~ ~ n n 1~ n ~ n n ~ ~ ~ 8 ~
~ I I I I I 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ~ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
L t t t L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L ~ L L
1~: I I ~ I I T I II I I T I I I I I I I I I
a)
_ I ~ _.
~1 S C
C ~ O i C ~ ~
S ~ L L
-- I _ ~
I ~ ~ ~ O O
-- -- ^ ~ ~7 ~ O ~ ~ ~ O :'~ L L
C C 0 10 a ~ ~ ~ ~ t- t- ~ IIJ _ . r~ _ ~`, :~, _ _
O ~ ~ ~- t- ~ ~ ~I t~ t- t-
S S _ ~ ~ I ~ I I I ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ L L ~
~ 1~ T 1~ -- t~ L L ~ ~ L L L
O ~ ~ O t.~ O ~ O `J O ~ U) ~ Z ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ I:L ~ CL
t~ I t~ t I ~ , ~ ~ t~ ~ I ~ ~ ~ I t~ ~ I tr~ t I ~) t I C~ t I C~ ~
,. : ~ ' ~ '
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
~D
o
o
o r I r I r r ~ ~ I I ~ ~ r r r r I T r I r
~: ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
U~
D n D ~ ~ C~ Q. CL n. ~ n. C~ Cl. Q ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Q Q Q Q
l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
O _ O _ O O _ O O _ O _ _ _ O _ O _ _ _ _ O
L L L L~ t.l o ~ V t.~ ~ t~ V t J O O L~ tJ L~ ~ t.) L> O ~ O
V ~ ~ ~ t~ U V ~ t~ t~ ~ ~ t~ t.~
I ~r T I I '` = I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
_ _ _ -- :'~
~ ~ ~7 >~ S
~ t t O
L L L L ~ E
>, ~, ~ ~ ~ O
O t~
L L L , ':~, _ ~, _ ~, _ -- +~ O a~
_ :~ ~ ~') ~ ~t ~ ~ ~ E X
t - t _ ~ , ~ L -- L
L L L -- t'L :~ ~ n I I ' I I I , t- ~ o ~ L
:~ _ O ~ ~ ~ I O O O O O O ~ _ L q I t'
~ C~ L I ~ I ~ ~ ~ -- -- ~ ~ O
_. ~ '~ ' S ~ O ~ O t ~ ~ ~ I L t- ~ V~
~ 1~ t~ tJ ~ V ~ _ V t.~ ~ ._
2026131
~ ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
~o
.
o
o
o __~_____~_____
___________
~J I I I I ~ I I I I I I I I I I I T I I = I I I I I
O _________~________________
Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z 2 Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z ~ Z Z Z
U~
U~
--~----------------r~,________,,,~,
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
LLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLL ~LLL
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
_ _ _ _ _ _ . _ _ . - _ . _ .-- _. ~ _ _ _ . ~ _ _, _
UUU~UUUUUUUUUUUUUUU~)UUUUU
UUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUU
a:
.~
IIIIIIII T I T IIIIIIIIIIIIII
~,,
~, O
~, , X
E a
~, ~,
X X o ~, s o '-
o o _ -- C s ,~ ~ ._
-- ~ ~ ~ ~ . CU U X -- o ~ ~ _
u E E ~ _ _ c E O E o _ C ,~
E - - ~ ~ ~ ~ LC-C ~_ C~
E . -- V~ ~ ~ o ~ o ~ '- . Q a~
O ~ ~ X _ r ' 11~ 1-1 C~ ~ X ~ . ~ X Q O I . s s ~ Q
c ~ a~ o ~ :~ ~ ~ ~ Q ~ C o ~ -- ~ c . I LL ~ I I I --
~ E E s c -- ~ o c o a~ ~ c ~ -- ~ o ~ ~ a~ l. ~ ~ c
-- U ~ ~ E U a~ Q Q E ~L -- I
h V ~ ~
~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
o
o
o
~1I T I T T T T I T T I T I T I I T T ~: T I I T I I
O_________________________
~ ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
~O
U~
LLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLL
l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
O _ _ _ O _ O O _ _ O _ _ _ _ _ O O O _ O O _
~ V U ~ V ~ U ~ ~
1.~ T T T I I T I T T T T I T T T T I I I I T T I I I
_ ~ ~ ~
_ c ~ c L ~ ~ -
_ ~ LL
^I -I---~
I ~ , V ~ ~ ~7 ~ -- O O O
. _ c ~~ v ~ Z) z c
L v ~ ~IJ a> ~ T ~ S ~ S S C ~ Il) r :-~ :~'t --
S S '~ IV~~VIII~CCCC
~Vlllv~lI-~I~ I~L~L~LLL~
'lIVV~vO~O~x~Z~
~`J J ~
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
~D
_.
o
o
O _ _
1~1 I I
O _ _
~n Z Z
I I T I T I I I I T T I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
1~1
_ ,, -- ~
X :~,
~ ~ S
r _ O E o
~ _ ~ O
O O :~ _ ~ I O V C X ~ O t~
L L . C~ . _ . L ~ ~ ~ _ ~ I
I I -- ~ L ~, ~ ~ >~ ,~, ~ ,, ., ,, ~ ~ ~ ~ S ~, _
O ~ -- O C- ~ .0 1 ~ ~ C X X X ~ O O O O ~ ~
~ ~ C ~ O ~ O ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ C C E 1~ E ~ -- ~ O
T I -- I I I T I T I I . T I I T T T I T I I I I T
C C
L L
C~ ~
O O _ _ _ . _
L L ~, ~, ~, ~, ~,
c ~ ~ ~ ~ n. L L L L L
~ ~ _ _ _ _ _ o o o o o o ~ ~ ~ n. c~
L L L L L L ~ ~ ~ :r~ ~, ~ ~ CL C~ 1~. ~ ~ O O O O O
~ O O O O O _ ~C, .~C7 ,~C, .~ ,, ~ o o o o o o c >
_. I I C ~ C C C ~ ~ ~ /D a~ a~ o tn v) u) v~ ul v7
1~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ E E E E E E ~
r` ~ ` :
~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
~D
~n
o
o
~r
I I I I I I I I I T I I I I T I I I I I T I I I I
, S
~ ~ . I
~ ~
1~ ~ O ~ C I
I c :~ ~ s
E ~ s O
_ _ I
. _a~ r :~ s ~ I /1~ ~ r I O
r
S ~ G~ E C C <_~ ~ C ~ ~
-- c ~ . o x '~:J s ~ s c Q~ v ~ I O
~t C ~ L O I 1 ~ ~ T -- ~ ~ C S ~ -- S
L >~ s ~ ~ C S O s Z . I I ~ I I s n. ~ 1~ I ~ ~ O
~ ~ a ~ ~J C ~ s ~ Z C I I ~ I ~ L~l
o 8 ~ ~ C ~ E v E -- a~ v c ~ 7 v o ~
t~: I T I I I I I I T I I I I I I I I T I I I I I I I
_ ~
~ ~XXXXX
O ~ Oc ~ ~ c o
~ X X X X ~C X~ CS~ ~ S~ S S S
O _ ~ -- C C e ~ ~ ~ C) O O O O O I
-- ~ C C S S S S _ -- _ -- _ _
V ~ -- -- -- -- -- C 5: S ~ S
v ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ a~ E E E E E ;~ ~ ;~`
~v,.,~,_~i
~- o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
o
o
o
In
I T I I T I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
O~ ~ O
1~-) C _ N
S C
S "~ ,~C~ -- S
O C~l
_ ~ _ T . ~
~ ~ ~ ~ >~ . ~ . C C O O ~ I
~ ~ 0 ~ c z c s s _ _ o v v ~> s 8 _ ~ _
cL ~ n. s ~ s , , c s -- s s o, , _ ~ -. ~
~ "~ I z I T l,L S ~ L
~ ~ ~ ~ ~,) O ~ T O O '~ ~ I I S ~ '
o o ~n ~ v) z ~ ~ <.~ ~ c c ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~.) ~ s ~ o ~ o ~
s
CC I I I I I T I I I I I I I I I T I I I I I I I I ~
. - - . . .
ccc
s s s ~ ~c s
- - - - ~ -
o o o o o o -- .
S ~ S S S ~ ~ C
C~CCCCIIIIII~S1-SSS~
_~ S C S S S S
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
o
o
O ~ 1 t~l N ~J ~ ~ ~ 1 ~ N ~1 ~ ~ ~`J
_____~____~__~_____
~1 ~ -- S -- I I I I I I I I I I
O ___________________
~r zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz
I I T I T I l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l I
~D
. _ ~
~ E O
~ ~_ _ _ _
_ . ~ ''
_ _ __ ~ -- ~ _ _ _ I O ~' t X V
" ~ ~ ~ o _ ~ ~ L n s~
~ C ~ X X X ~ -- o ~ ~ ~ I C C C X X X ~ o o o o ~
Q Q c~ c c s ~ c Q o ~ o v ~- Q Q s c C E v v v v E
~1 C ~l ~ E ~ C ~-- c ~ c t~l ~ c ~ ~ ~ v v v v _~
1~:
. _ ,_ _ _ _
. ~.
~ a~ ~ ~> ~ ~
E E E E E E
-- ~ -- -- -- -- , _ _ _., _
~ ~ ~. ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ., ~, ~ o
o o o o o o o o o o o o
L L L L ~ ~ O O O O O O _ _ _ _ _ _ ~ L L L ' L
I I I I I I o o O O o o ~' ~' S ~ S~ s I I I ~ Q ~ --
OOOOOO--_____~OOOOOOV
_. u~ tn v- ~n c c c - s ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ a ~ u~
~r ~ v v v v v v E E E E E~ E -- -- ~ -- -- v
h U h~ U ~ ~) i
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
~D
o
u~
~J I T T T T T I T T I T 2 I T I I T I T
~ ___________~_____________
In 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 Z 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11t~ ZZZZZZZZZZZIZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
~ _ .
X S~ C
S ~ ~
O ~ S :~
'D V :-~ O . I ~D
I C :~ _ S
I E a) I
~, C ,, ~ S V -- --
s ~ _ Q ~
E -- 5~ ~ ~ o :~. s ~ . ` . ~ c~ _ s .
o ~ I s -- s ~ ~ ~. ~ I ~ ~. -- --
o ~ ~ ~ c
-- C ~ C ~ ,,, ~, O ~ S~ 5~ S~ ~ S Q~ 1~ C-)
0 _ L ~ S ~ _ C C O -- Z ~ I I C.) I I S ~ t~
L >, ~ ~ ~ ~ 0 ~ ~ S O C ~ S~
-- ~ o o n E G C C~ E v E -- 0 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ c~ ~ ;
I ~ I L L I I 1 0 1 1 1 1 I S
T T I T I I T I ~ I I I I I I , T I I I T I I I
_____
~7 ~. ~ ~ ~ X X
n. ~ o o
O O O O O C ~
G ~ _ _ _ _ r~ _ ~`, :~ ~, ~, ~. ~ S S
o o o o o _ ~ _ _ . ~ C C C~ ~ C~ o Xo o o o o ~ ~
, _ _ _ _ ~ ~ S S S S S S _ --
V V V V V -- -- -- ~ . _ S S S S ~ S ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ C~
_, v V V V u ~ ~ ~ ~ E E E E E E ~ ~
iJ ~3 l
~- o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
~>
o
o
T I I :1: I I X I I I I I I I
In 11 11 11 ~1 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 1~ Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z 2 Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z
l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
. _ ~
~ ~, ~ ~, O
D C I = --
c O ~ ~ ~
-- I ~' I s s
} O r_ S _ T ~
T
~.~ ~ I ~ ~ ~ ~ a ~ Z ~ s S ~ ~ ~ 8
c s~ V s 1~ ~ ~ s ~9 ~ ~ . ~ V
~9 1~. T O ~ X Cl. S ~ N S I I ~ S ._ ~ S O
~ I ~ I ~ I I Z I I 1.-- t- s -- t L ~ I I n.
I I-- 1-`1 LL 11_ T _ I.L N -- O V V C~ C~ L ~ ~ :~
Z I ` Vo o V~ :t tn Z ;t I V 8 ~ c Q ~ ~ ~ v v ~ s ~
~ t~l t~ t`~ t~ t~ ~ t~ t`J tr~ ~ ~ t~ ~ ~ ~ In ~ E ~9 ~
I I I T I T I I -- T T I I T I T I I I I I I I I I
~ . .- . .
~9 ~9 C9 ~9 ~9
S S S ~ ~- ~
X X X X -- -- -- ^ -- --
O O O O O O O O O O _ _
~9 ~9 ~9 ~9 -- S ~ t- S S
S ~ -- S ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ -- -- -- -- -- -- ~ ~ ~ C C C ~ ~
~ C~ _ ~_ _ _ _ _ ~ t.9 V V ~.) V ~9 ~9 .t9 ,~9 ._ ._ L L L
_ _ _ _ C ~ C ~ ~ ~ I I I I I I S t- _ S ~ '~
~ V V ~9 ~9 ~9 a~ ~9 ~9 ;1 ~ ;
_. I I I I S l= S S S s
202~131
~ oooooooooo~v)v~
D
~ C "
s t
~ , ,
$ t~, t . ~ ~ t, ~ ~
__________~,, ,. ~ .. ~, ..
I I T T I I T I I I -- ~ O ~ O
O ___________~_~,. :~,C~,~--'~,_~L--
u- Z z z 2 z z z z z z ~ I ~ ~ . ~ c~ .~
~7
D
____.__________
o -- ~ ,. ,. ~ _ _ _ n ~ D n n 8 8 8~ 8~ n 8~ ~8 8 8 ~8
8 I C C C X X X
o n o L Q L~ ~ _ C ~ L L L L L L L L L L L L L L
._ C ._ U~ C ~ ~ C ~ C~ ~ ~ +~
_ _ _ _ _ ~ _
C C C C S -- C
a ~ ~ a
E E E E E E E
~ ~, ~ f' ~ C~ ~ C~ C~ ~ C C C~ r. Q ~. ~. '
'J ~ ~ LO LO LO OL L _ _ _ _ _ _ L
L ~ L ~ ~ ~ O" ~ ~L ~. ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ D. L Q o
_ O O O O O O O ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ O O O O O O O J
~: '~ ~ -- E E E E E E E ~
'
;
2026131
~o
s s
l~J ~5 ~ s ~ ~, Q ~ Q ~ ~ s ~ ~, Q
O ~ ~ ~ O D O n ~ Q -- ~ O
~ C ~ s ~, ~ ~, ~ ~ s 5~ ~. s :~ ~
11~ L a1 1~ ~.J ~ ~ ~ O IJ L ~ ~ ~ O ~ L 11~ Il, ~ ~ Q tJ -- O
n ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 8 ~ .~ . E ~ V1 D ~ s ~
___,--________,______.______
n ~ ~ 1~ D ~ ~ ~ a ~ ~ 1~ ~ ~ ~ n ~ 1~ ~ 1~ ~ ~ ~
. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.'. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.
L L L L L ~ L L L L ' L L ~ L L L _ L L L l_ L L
" ~' ~ ~ ~ O O O O Q O
O O O O O O ~ ' ~ ~ ~ ~
_ X X X ~ X X ~ Q sQ s s C s
_ _ o o o o ,, ~ ~ ,, ,., ,., s s s r- I I I I I --
~: ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ E E E t~ E E E ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
~ vi~, 'J ~Ji
~D
_ `
~ s s s
o
g _ ,,~
c e~ ~ S; ~ I:L C S
I ~ L I _ ~ I t~ L I _ ~
O _ :>, ~ ~> -- L _ ~ _ :~ ~ '` -- ~ _ ~L -- ~ ~ '-7 -- L
u~ ~ L Q~ O ~ L ~ IL C) ~ O. S O ~ L ~ ~ S:L
u~
~o
- - - - - - - - - - -
L OL OL OL OL OL OL
l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
O O _ _ O O O O O O O
L L ~ L L L L L L L L L. C ~ o O ~) CJ O ~
l~ T T T I I I I T I I I I I ~' I I I I I I T I I I I
_ _ _ ~ _ _ _
~ a~ v v v a) v
C- S S S S ' S
X -- -- _ ~
O------____ ____
; - ;;; c~ c~ c~ ~ ~ ~ o o o o
O t,) O O O t.) O V V V ~ _ _ ~ _ L L L L
I ~ 'C 'S ~ S S C- C S S S
C_) ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 4' ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ O O O O
_ ~ ~ ~ C~l ~ ~ C~ ~ C~l C~l ~ ~r7 t~ t~7 E E V 8 E E E ~
r ' ' ' ' t
~D
_.
_. C C
O~ _ I _S
$ _ -- _ ~
~ o 8 ~ ~ . o n o D ~ ~;
-- I _ C I ~ ~
~ ~ ~ C I l,L I ~7 c ~, I ~ ~ C 1 1~ 1
U ~ C O ~ IL y ~ I C O ~ a) ~ c o ~ a~
E ~ -- 8 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ E Q) -- n ~ n. E ~ ~-- D ~ C
~D
Q Q C~ Q Q ~ C
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
1 ~ ~ ~ Q Q CL ~ C~ Q ~ n. Q Q Q C~
OOOOOOOOOOOOO010000000000
__~_______r~______________
r~ rJ v v ~ V r ~ U U r~ r~ u r~ v r~ u r~ u V u r~ r~
VVVUVV~VV~VV~UV~ V~U~
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ ~.
_ _ ~ Q ~ Q Q Q Q ~ O O
~ ~ O O O O O O O C C
Q D~ Q ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
O O O Q ~ n~ ~ Q Q Q ~ ~ S S
C~ Q ~ O O O O O O O _ _ _ _ _ r O O O O O O O I Q
I I I -- -- -- -- -- ~ S C C C C S C _ --
OOOVVUVVVV------------~+~
~ ._ ._ ._ v v v u ~ v . ~ ,~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 8 E E E E E E ~ ~
2026131
~- v~ ~n u~ V~ ~ (n ~ v~ ~ ~n ~ ~ ~ u~ ~ ~ V~ v) o o o o o o o
x ~ u~ O O O O o o o
.D _ ~
~, ~
.,. _ o o
O Q _ ~ I o E E
o _~, ~ c _ _
o ~ ~ o E ~ ~ u
1~ Q c S ` ~ oQ ~ a) Q O I ~ C ~ ~ '
O ,_ _ L _I ~ ) L -- Q -- ~ Q ~ ~ V ~J ~ g
In ~ ~ ' O ~ L ~11 1~ V ~ 1:~ C O ~ L a~ 1~ V ~ V V n ~ v
c~ ~I E Q~ ,_ Q ~ s ~ I ~ I ~ ~ n s
~D
__,___________.,__
LLLLLLLLLLLLoLLOOOO~y~
~Q~D n DDD~D
O O 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ~
VVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVLLLLLLL
VVVVV~VVVVCJVUVV~.>~V~
I I T I I I I I I T I T I I I T I I I T I I I I T
_______
~ C C C ~ C C
a~
~ S S ~
O O O O O _ _ _ _ _ _ _
CCCCC~t_~______
C C C -- C _ _ _ _ _ _ _ ~ C ~ ~
~ --oooooo--
_IiIIIIIC~C~ OOOOOOC
_. ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ V V v V E
20~6131
,. oooooooooooooooooooooooo
X oooooooooooooooooooooooo
~D O -- S :~
_. . ~ N N N -- n~ . , --
-- -- ~ 1`7 N ~ ~ ~1 L ~- ~ S
O ~ V N I -- D ~ ~ ~ ~
~ ~ -- -- O I I E E L E E O
o a I v v 11 T -- N .: I I V I I -- L I v ~
E V -- _-- z ~ ~ v . -- ~ -- -- ~ o 1~ ~ s
l~i~, N ~ ~ N N _ N N _ "I O _ <.) ._ 11~ L ~ -- -- s ~ I v
O L I I ~ I I V I T O I V :~ -- L -- ~J L L ~ N -- I
~ V V V ~ C_~ V ~ O ~ ~ I N I ~ C I L O I V
U- ~ ~ N N N N N N N ~ _ N ~ ~ ~ t~ G) ~ ~ Z U-) O
~ I T I I I I I I I I I T
D
_~_.~_.--.__~-.r____.r__.____
n n n ~ n ~ D D n 8 ~ ~ n n ~ n ~ n D n n n n ~ n
L~LLLLLLL~LLLLLLLLLLLLLLL
~: I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
~LLLLLLL
o o o o o o o ~ ~ n. D C~ n. cL
__..__LLL~LLLIIIIIII
~G~OOOOOOO-..--
S S ~C ~ ~C, ,S~ o o o 0 1 0 0 U
n: E E E E E E -- -- -- -- -- -- --
h J ~.~ v ~) .L
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
X OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
_ _c
, s a~
_ ~ ~ ~ E
:~- ` E E -- --
._c c
_.:~ L L :1~ S ~ O S
o o Q. ~-- ~o ~ ~ ~ ~ s a~
~ ~, s o o ~ E -- ~ ~ r~ a) E ~ .
O C ~ L L ~ . . . ~ al ~ C n o E ~ O ~
o s ~ ~ ~ X~ s,, ~ ~, n : ~ ~ _ s g ~,
s s ~ _ Q ~, ~ ~ ~ o a x X O O E s ~ --
~ I C~ ~ ~ O ~ O ~ ~ 8 -- ~ E O O E s ~-- ~ E u~ q~
O -- C~. ~ 8 1 0 o~ X~ ~ ~ L 1) ~ ~
t ~ I ~ 111 a) C :~ L I ~ I ~ ~ ~ O ~ 1`1 ~ E s s s ~ c
u~ O Z ~ ~ 8 ~ S CL O 8 O L r v S E _ I I ~ +~ ~ _
;~ ~ E ~ C ~-- c -- v~ ~ ~v ~J a) ~ 8 ~ ~ t~. E
al
~D
8 8 D n 8 8 D 8 n ~ 8 D 8 D 8 D D n 8 D 8 8 8 8 8
L ~ L L L L L L L L L L L L L t L L L S_ L L L L L
v~vv~vva)~vvvv~vvvvvvv
I I T I I S I I T T T I I -r I T I I I I I I I I I
~ ~7
X X X X X X X
OOOOOOOOO
a) v v v v v v s s
_ _ . - . r . . ~ S S S S S S S ~ ~
_ _ '~ ~ X X X X X X X C~ ~:L ~ ~ ~ 1~ s' _
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ S r- S S I
_--SSSS'~SS~J~C_)~t_~C.~VV
_~ -- -- ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ v a) v Q~ V V V I I I I I I I S
c~ 0 ~ v ~ a~ v a v ~ E E E E E E E
2026131
~ ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
X ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
_ E o --
~I E ~ E
_. -- -- E ~ _
_. _ ~ o I _ ~ ^ o o --
o ' ~ E ~ -- ~ .t3 I ~-- ~--
u~ ~ -- ~ s ~, c I ~ o E E
O ~ o ~ o _ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ C- ._ ._ ~
O ~ _L ~ ~-- C ~ ~ O :~ ^ O E ~ ~ U- E
1~ C E ~ _ E ._ LO O ~ L ~C~ O I c~ C a~ ~ CD .
O S ~ S -- C -- ~ L _ O LO L '`J ~ 1 S O
I - L ~ CJ 11) + CO ~ ' ~ D. O :>~ -- -- ~ -- -- I
11~1~ ~ ~ _ U C~ + + ~ -- --_ CJ O _ S ~ ~ C c C_~
;t c~. tJ E v~ ~ J z `' z ~ f~ ~ E '~ n. cr) ~t z z c~ z ~
_ ,- _ _ _ . _ _ _ ,~ _ _ _ ,~ _~ _ _ ~ ~.
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ +~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ +~ ~ ~ O O O O O O O O
n n ~ n ~ ~ ~ ~ n ~ ~ ~
. . 1. . . . 1. . . . . . . . . . . 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
y~y+~+l~________
LLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLCJVc~c~CJ~
<.~ I I I I I I I I I T I I T ~ T T
_ _ _ _ _, ,_
C C C C- C ~ C
~ ~ ~ ~ q> ~ ~
S ' S -- S S S
~ Q ~ n.
o O _ _ ~ ~ V
s s ~
_ _ _ _ ~ ) V O V ~ V /1~ ~ o o o o o o
C~C~CIIIIIIIsss soooooocs
c c s s s ~s s -- s c s ~ ~
` ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ C C V ' C E E
~.~ U ~`~ V ,~ J i
,_ O O o O o O o o o o o o O o o O o O O o o O o O
X OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO OOOO
_. I -- ~N -- -- ~ _ _ ~ _ S
~ ~ ~ I ~ ~a~ s s ~ s s s :~, Q
O ~ -- -- t ) ~ I --D ~ V ~ ~ ~ ~t) (I) --
~ _ ~7 ~ _ _ ~ InI ~ a~ o QJ G~ E s ~ ~,
$ ~ I I ~ u7 o ~_ E E L E E _ o Q. IL. c
~ _ _ Z N T ~ ~ O 1~ ~ S S
1~iZ Z t_~ C.)~ t/) O O -- Z ; ~ ~ ~ C ~ ~ -- ~ 11. 1
~ ~ ~7 ~ ~ _ ~ ~ -- ~ O ~ ~ L ~ . s
O I I 1~ I I C.) I I O I O :~ -- L -- ~ L L ~ t' --
m ~ I N I ~ s ~ ~ ~ ~ I O
t~: I T I I T I I S I I I ~ I I I I I s
~ c~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ n ~ ~r~ t~ ~ t~ t~ ~ ~ t~
_ _ _ _ ~ ~ _ _ ~ _ _ _ _ _ r l _ _ ~ _ _ _ _ _ _ '
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
LLLLLLLLLLLLLL~LLLLLLLLLL
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
~J ~ t~ ~> U t.~ ~ t~ U tJ t. ~ tJ ~J t~ t.~ ~ t.~ t~ tJ V
~ U U U C~ U ~ U ~
C~ I I I S -- I T I I I I I I I I T I I I I I I I I I
_. _ ~ _ _ _ _
-- -- -- ~ -- --' -- Q ~ '' ~ C~. ~ n
~LLLLLLL
o o o o o o o ~ ~ ~ ~ a. ~ o.
__~__LLLLLLLIIIIIII
S ~ S S S I I I I I I I _ -- -- ~ _ _ _
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ O O O O O O O V t~ t~ _ _ _ _ _ _
_. ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ u7 t~7 tn v~ t~ ~n vl ~, ~ ~ ~, ~, ~, ~ _ _ _ _ _ _
~ E E E E E -- -- -- ~ t~
2026131
ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
X ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
. ~. ~
~, s E
D _ _ ~ E --
_ E I _
. ~ al _ ~, ~, _ x ~, c
:~, L L ~, C X :'~ O C
C ~ ~ O ~ x ~1 ~ c a~
O ~ O O ~ S O C Q~ ~ I I S
Ir~ O. L L (1~ E ~ ~ ~ c D o E ~ o -- a1
o I ~ ~ -- ---- ~ ~ ~ c I E q~ o c o ~, --
~ ~ , L ~ . ~ X n. ~ ~ n >c
O L L ~ _:~ O _ ~ D ,C L E o o O L ~_ ~ o
O C-) ~ ~ ~ ~ -- O ~' ~ D I O O X ~ :~ L
I ~1) C ~ L I ~ I ~ -- O ~) ~ ~ E C S C O C
u z ~~ n ~ -- ~ on o ~ ~LV :~ ~ ~ E a1 ~ ~ s ~ I T S
~ ~ ~ ~ E ~ ~ ~ ~ u ~ a~ ~ D -- -- ~L E ~ ~
__________.__.____.__
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O Qll n.
LL LL~tLLLLLLLLLLLLLLOOOO
O O O O O O . O O O O
t.~ V t. V V V V U V V ~) ~ 1.~ V V U ~.J V C.) ) ~ ) ~ -- --
VVVVVVVVVVVVV~VVVVUV~
I T I I T I I I I I I I I I I T T I I I I I I I I
:., ~, ~
O O O O O O O O O O
~ ~ C ~
~ X X X X X X X ~ ~ ~ ~ ~L ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
_ ~ ~ ~ ~ C ~ ~ O O O O O O O I I I I I I I ~ ~7 ~
-- S c c ,c ,c ,c ,c .~,C, .~C, .~ ,C, ,~,C, ~ ~ -- _ _, C C C
_ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ a~ ~ ~ ~ ~ I I I I I I I C C C
~ a) ~ a ~ ~ a~ a~ E E E E E E E ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ n
V h~ V .L ~J 1
~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
x o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
E o
~CI E ~ EE
<~J ._ r-
~c E --
~ o ~ ~ s
In InO ~ O _ ~ --
o o ~ o o ~ o~ ~ -- C~
o~ oE ~ ~-- E ~--o x~ o ~, L '` ~ ~ ~) ~ -
'-- ~ E _ T~ L O _ S_ O) ~ I T I I T T I I T
1~1 _ S ~-- C ~-- Cl. ~ _ O ~_ O ~
O ~a ~ .-- ._ L O V . 1~] r ~ ~ -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
~ ~ _ t~) ~ + + ~ ~_ C _ ~ ~ O -- 1~ 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11
m C 'OJ ~ ~ ~ ~ + I ~ D I L I Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z
+~ E ~ Z Y Z ~ ~I ~ E
________________
O O O O LO O ,0 L L L L L L L L L ~ ~ ~ ~
n. ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ C ~' ~ ~ ';L ~ D ~ ~ n ~ n D n n
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
___.____.________~+,~+,
V V ' U U ' ' ' ' L L ' L ' ~ L t
~: ~ '~ ~ V ~ ' ~ ~ ~ +~ ~ +~ ~ ~ ~
I T I I I '- S I I I I T I I T I I I I T T I I I I
_ _ _ _ _
C ~
t- r ~ ~ S '
~ c~
l l l l l l l
O O O -- -- -- --
~ ~ S S ~ _;~; ~; :~ ~ ~ ~ t_ ~ O +~
_ _ _ _t~ ~J O~ ~ O O ~ JJ ~ ~ _ ~ L
C e C CI I I I I I I C S S S t- S ~-, L
s s s s ~ I I I I I _ a~ ~ I v~ I v~
_~ ~ ~ c~J T 1~ C_~ E Q~ ~ '-- C
202~131
, ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
X ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
~D
o
o _________________________
. II~I T I T III T IIIIIII T IIIIII
~ __-________~_____~__~______
U ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
_ _ _ ,~
n D S~ n n ~ ~ D n ~ n n ~ ~ J~ n Q ~ ~ ~ D n ~ n n
1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. ~. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.
LLLL L LLLLLLL~LLLLL-LLLLLL
I I I - I I I TIIIIII T III T I I I I I I
~, C ~
~ ~ ~ t_
o a) -- E
L~ E
~ ,, o s ~ x
OSL~ -00_
_ ~ ~ ~ $ :~ t ~
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ E - LX~
~, ~ o ~ c x c~ ~ E _ E ~ --
n ~ o ~, o ~ -- o ~
DIIlllllL-~O~LXSt-~ -.~L~X
I _____~LO~S~O~S~S
L)LL~ LJ LJ LJ L) ~ ) E ~-- -- c o ~ E E ~ c -- ~ o t- o ~ ~
_ ~ILC~II~-_.~L~LC~
~ U) ~ LJ LJ LJ LJ L,~ LJ _ ~ LJ ~ E ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ E LJ ~ Q ~ E
'.J ,~
~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
x o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
o
u~
o - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
I I I I I I T I T I
U ZZZZZZZ~ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
U~
I_
_________.__r~__._..__~__
n n ~ n n n n n ~ n n n 1~ ~ ~ n n 1~ n ~ n n n n n
L L L L L L L L r L L L L ~ L L L L L L L L L L L
I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I T T
O ~, -- I C
-- X _ C ~ S
S O
~ _ ~ ~, a.
O ~ S O C S I ~ ~
c s c~ :~ -- a) 1~ _ _ -- I _ I -- --
~ x -- o ~ Q ~ r~ C O C C
Eo ._ Eo C ~ O ~ c C.~ ~ ~ C C
L S t a) ~ ,C C C 1~ ~ C S C (~ S ~ I 1
o ~ o " s _ c~ s s _
:~ ~ -- ~ X l~ I -- S S 1~ ~ ~ t_) I I I C ~ I I ~ O <'7
~ I I I T
s ~ ~ ~ V~ I.L L~ ~ ~ c.) O ~ o tn
_, y L s I ` ~ ~
202~131
ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
~c ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
o
In
O NN~N~
O ~________________________
I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 li 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11
In ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
I~
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ ~ _ _
~ Q~Q
~OOOOOOOOOO
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ a ~ ~ LLLLLLLLLL
n n ~ n n n n n D n n n n n n ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ I ~ ~
L~LLLLLLLLLLLLL~V~
C~: = I I I I I I I T I I I I I I I I I I I I T T I I
_ _ _ .
~L LLL
I
_ _ ~ ~ ~ ~ C~
CO~ LL
O ~ C C C ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ O -- ~ ~
~ZI~LL~ --LLL _ ~L~ n
~-~----LL~LLLY~ ~-0~ n I
~Z~ ~ ~LI I
, ~ T 1~C.~ E ~ s~
h l l ~ u ~
~ o o ~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
x o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
o
I I I T I T I S I I I I I I I I I T I T I I I I T
~ _________________________
11 11 11 11 11 11 11 ll 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11
U- ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
_ _, . ~
OOOOOOoooOOOOOOooOOOOoooo
L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L ~ L L L L L
l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
O _ O O _ O _ _ _ _ _ O O O O O _ O _ O O _ _ _
~7
C T I I I T I I T T T
_ ~, s
a>
o ~ -- E a~
L ,- O ~ x x
_ _ o -- ~ ~ -- o o
E -- L X ~ ~ ~ '- ~,
O ~) C X Cl. ~ C~ ~ E E E ~ -- --
n f~ -- ~ o ~. o ~ _ o ~. ~, ~ E -- ~ cn a~ ~
O O O O O O ~ _ L ~ O ~ ~ X -- . ~ :~ C (1~ O X
-- -- -- _ -- -- ~ ~ o ~ ~ o :~ ~, s ~ ~ L ~ S O
~ O ~ O ~ ~ E ~-- -- C O ~ E E s L . ~ o s o a~ ~ s
-- r~ ~ ~, ,, ., ~, :~, ~ ,~L ,S~ E I 1 5> ~ 8 E ~ E
2026131
~ ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
X ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
C~
o
U~
O N~NN~NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
O _.________________________
I I I T I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
11 11 1~ 1~ 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 1' 1' 1' 1'
u- Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z 2 Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z
lY IIIIIIIIIIII~IIIIIIIIIIII
0~
_ _ _ _ _ _~ . . _ _, _ _ _ . _ _ _ . _ . _ _ _ _
OOOooooo~QoooQ~oooQoo~QQ
LLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLL
QQ~Q~QQ~QQ~QQ~QQQ
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
tY I I I I '~T I T I I I I I I I I I I T I I I T I I
,. ~ ~
O
-- X _ ~ .~ .
~ O :~ Q
X
C' Q
~D ~> X -- O ~ C~ -- ~ ~ ~ O
O EO _ ~ ~ ~ c ~ ~
` ' C S ~ ~ S S I S ~ _
O~ O ~ ~ _ Q ~ ~ ~ I-- -- _ Q Q QT- Q I L ~ I I I
X ~ C,~ l ~ C S ~ ~ ~Q ~ I I I ~ ~D ~ T--1~ I 1
~C ~ C -- I 1~. C I I I -- . I I I I
,- LL C I ~ I S
u ~
~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
~c o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
D
o
u~
o ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
o ~
I I I I I T I I ~' I I I
______________
O ~ C~
U~ ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
K I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
0-
I_
_ _ _ . - _ _ _, ~ . ~ _, _ _ _
L L L LO L LO O L L L L L C~
~ ~- Q ~ C~ S~. ~ 1~ C~. 1~ n. ~ n. ~' _ >~ O _ ~ 3 ,~ ,, ~ _
oooooooooooooo~.o~V~,CCCX
~ J V U ~ , ~, ~ S ~ L 1 3
~ ~ ~ V ~ ~ ~ E ~11 c ~_ c ~ c ~I ~ c
I I I I I I T T I I I I I I I I ~ I I I I I I I I
~, _ _ _ _
C C ~
~C L ~ ~ ~: c
Q ~ L L L L
I
~-- O O O C O
O ~ L L L L L
Z C _ _ _ V V V
~ ,c ~ , ~, C C '~, ~ C C
O ~' C ~ ~ C ~ ~ ~I ~ V
Z ~ V L L L L --L ~L ~L ~ ~ L L L L L ~
I O C C ~ ~ ~ 11 ~ O O O O O O C C S C ,C
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ E E E E E~
~J U i~ 'J 1 ~ i
~^ OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
X OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
~D
o
o
o
In
~: I I I I T I I I T T I I I I I I T I I I I I I I I
00 X
C~ ~, O
_ t,) ~ ._
:~ s ~ ~, I ~, E
s ~ s
Eo ~ ~ _. _ ~ . . " ~'
E -- ~ ~ ~. o :~. s Y -- _
c~co ~ ~ s -- s ~ E
I o ~ X ~ o ~rl _ ~ I I ~ t~ ~ ~ ~-- ~ o
-- '-- ~ ~ ~ -- ~ I >, I -- 1: -- -- o X ~ s s
S I I I I S ~ (1~ _ L ~ _ L S O ~ Z r f
X ~ O O O O ~ ~-- _ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ :~, ~ ~ . ~ ~ ~, ~ ~>
-- ~ u ~ J E ~ -- n o o 3 E Q E ~ E ~
`7
~: I I T I I T T I I I I I I I T I I I I I I I I I I
_ _ ~ . . _
_ ~
OOOOOO
1~ ~ ~ 1~ t
-- _ L _ L L L I I I I I I ~,
~ ~ ~ O O O O O O ' --' ~ -- -- --
_. ~ o o o o o o c c cJ _ _ _~ _ _ _ s s s ~ r
f~ V ~ ~j .. ~) i
~- o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
x o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
o
o
o
u~
Cl:I I I I I I I I I I I T T I I T I I I I I I I I I
:~ s
~ _~
0~ s ~, _ _ _
_ I ~r I C ,--
:~,-- Cc O -C
~ I I~ ~ _ ~ ~
s ~ _ ~ I s
~ __ I c
-- I a~ I O -- C _ I -- --
~ t.) _ s _ ~ c ~::
I ~ _ C O ~ C I c U~ C ~ O :~. ~ 0
I ~ :~ c c _; C s ~ c.~ C LL c ~ s ~ Z s s _ _ o
O s c ~ L ~) ~> Q I O ~ I ~ I ~ s ~ -- I I s s ~_
~ ~ s s ~ -- ,c I O I I ~ I ~ ~ I Z I I ~ C S
~ ~ ~, ~ o o ~ ~ o o ~ ~ o o v~z ;t o 8 8 c c ~
~ I I T T I I I I I I I I T I I II I I I I I I I I
______
C c ~ c C c
c -- s s C s
Q ~L Q ~ ~ t~
O O O O O O O O O O O O -- -- _ -- -- .
c c c ~ c ~ _ _ _ _ ~
~ ~ ~ ~ ' S S S ~~ S .~ .~,s~ ~s S s c;;
xxxxxx~1~n.~.-.___~.)~t~c~c)~
OOOOooIIIIII:":,~,~,:~,~,--_____._
s S s S S C -- . ~, --~ C C C C C C I I I I I I s
_. ~IIIIIISSSSSS
o~ E E E E E E ~ ~:t ~ J ~ ~ ~ c~ ~ ~ c ~ ~ c~
2~26~31
~ ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
X ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
9
.
o
In
o ~ ~ ~ .~,
_ _ _ _ _ _ _
I I I I I
O
m I I I I I I I I I I T I I T I I I I
C~J
o~ O
_ _ ~
~ ~ -- s
L L
I
o o al I
L-- -- O
~ ~ -- ~ ~ ~ --
S -- O I I ' C~ ~ ~ -- --' -- _ -- ~ ~ ~
L L ~ I I -- r. L. ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ _ r L :~ ~ n
~J ~ S I ~ ~ '~, L ~ V 'V iJ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~, L I
s c~ o .n o 1.~ ~ ~ ~ s s s ~ s ~ o D O 1.
t~7 ~ ~ E ~ ~ -- C -- ~ ~- C~l ~ ~ ~1 ~) E ~ C -- --
, _ _ _ _ _
<.~ ~ s s s ~ S --
~YT T I T I T T T I T I ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ I T I I I I I
E 8 E E E E E
c ~ ~ ' ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ o o o ~ o o o
~ ~ Q~ o o o o o o .
._ ._ ._ ._ -- L L L L L L ~ C~ C~ ~ n. Q L L L L L L
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Q Q. CL ~ ~ ~- O O O O O O O -- -- -- ~
(/~ S S f
V ~ J 1
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
X OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOoOOooO
tD
_.
o~
O ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ tvl t~ ttl t~ t~-~ t~ t~ ~ t~ t~ t~7 t~l tr~ tt~ tt~ t~
T T I I I I I I T I I I I I I I I I I I I ~r I I I
~ _________________________
~n ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
.
. ,
_
V ~
v E _ 9
_ ~ ~ o ~, ~ 8 I c o ~ s
~ Q ~ v
-- -- . I L ~ ~9 X V ~ ~ _ O X
~ ~:--) -- -- -- ~. Q 8 Q ~ ~ . ~ ~ t`- ~, :~ ~ ~ L O
C ~ e X X X ~ O O O O ~ ~ ~ L ~ ~ C :~ V ~ _ ~
v a~ ~ ~v ~v ~v 'J) _ ~ ~ ~ ~) L ~ l C- ~D C- V
I I I I I I I ~ I L O I I I V I I Y
cr~ ~ ~ ~ CJ c~ ~ L _~ t''l C` n c~
C
ct~
~: I I I T I I I T T I I I T I I I I I I I I I I I
_ .- _ _ _ _
O O O O O O
~' ~ ' ~ Cl. ~ L L L L L L
O LO L L L L
C C~ C~ C O O O O O O ~ _ _ _ -- =
O O O O O O V ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ .~ S~
~ E E E E E ~ u ~ ~ v
2026131
~ ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
X ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
o
In
o _________._______ _______
I = I I I T I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I ~' I
~ _______________________
O _ _
ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
a~
_ ~ ~ :>, ~ >~
O _ I ~ C T ~ _.
C :~7 ~ S ~ t~
E a I ~ S
S ~
S; ~ -- S -- I
-- ~ O ~ C I ~ ~ ~ ~ O
CC ~ C ~7 0 S 1~ ~ ~ S ~
-a S ~ O ~ C ~ a) 1~ 0 Q~ 1~. I O ~ I Q I C~ S ~ --
Z I I ~ I I c c~ ~ I n. ~ o I ~ ~ ~ ) ~ I Z I T
I ~Z o <r~ ~ o O V) ~ 5/~ Z
~:I I T II :1: I T I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
~ ~ W
~X~XXX ------
OOVOOOOOOOOO__--
~_ S S S ~ S S;
X X X X X X ~ ~ ~ ~ CL
~OOOOOOIIIIII~
s S S' S S ~ S S S S _
~a~ IIIIIIsssss~
c~ E E F E E E
~ IJ ' ~ ~
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o ~
x o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
~D
-~ s
cL
O _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
I I I I T T I I I I I I I I I I I --
~n ZZZZzZZZZZzZZZZZZZZZZz~I~
U~
OD O
_ _ ~
~, ~
C C _ ~
L L
,_ ~ ~ O ~
~ O O lU T
a) L L _ ._ O _ _ _
S r -- ~ ~ ~ .~ VO
I ~ -- -- s ~ o I I ~ n. :~ ~ -- -- --
~ ~ ~ ~ ,~ ~, O _ ~ ~ ,, ,, ~ _ _ _ ~ n n
t ~ ~ ` L ~ ~ _ ~ ~ ~ _ O ~ ~ ~ I C C C X X
o ~ ~ I T ~ 0 ~ IJ ~ ~
t_) C C ~ ~ ~ ~ O ~_) ~ ~ CL O ~ O ~J ~ Cl ~ ~ S S ~ L L
E a~ C .~n C .U~
s s s s s s s
C~ I I S I I I I I I I I T I I I ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ T T I
E E E E E E E
_ r _~
c, c'7 ~
~> ~ ~
C S S
l l l
_ _ _
~ ~ V ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Q) ~-- -- -- -- ._ _ L L L L L L L _ ~ --
I I I r ~ ~ , I I I I I I I c ~ ~
~- ~t ~ ~ I I I ~ ~ ~ ~ ~:L C~ ~ ~ ~ o o o o o o o ~ ~ ~
2026131
X ooooooooooooooooooooooooo
~ ~ `
;t s C
æ
O _ ~ _ ~ _ . ~ _ C _ _
O ~. ~ ~ ~ ., _ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ _
O n ~ ~, _ '' O ~ ~ s
I~J ~ i _ S I O ~ I _ ~ I O _ _ L I ~ _
O " ~ 7 _ L :>~ ,, C- " .~,~ S 1 1~ ~ ~ ,~,,~ >' o ~ L a1
u v~ ~ ~ c I I ~ ~ ~ C I I ~ I a) ~ u) ~ ~ ~ ~
~ ~-- 8 ~ c~ ~ ~ ~ ~E ~ ~-- 8 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ E ~ ~ n ~ ~ E
~D
~o
- - - - - - - - - - . - - - - - - . - -----------
~ ~ ~ n ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ D n n ~ n ~ ~ n D '~ n ~ ~ ~
1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.
LLLLLLLLL~LLLLtLLLLLLLLLL
I I I I I I I T I T I I I T I I I I I I I I I I I
_ _ ~,_ . _ _
~7 ~ .-- ~.
QQQ~QQQLLLLLLL
____~LLLLLLIIIIIII X
S S ' S I I I I ~ ~ S
~ V ~ ~ O O O O O O O ~J V 1,~ ~J ~.) ~ ) ~ -- -- -- -- -- _ ~
_. E E E E ~ 1 ~ E
h ~
x o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
` ~
._ ~ a~
u~ ~ ~
o ~ ~
,_ ~ ~, Q ~ c S ~ ~ CL ~ C
~J 0 8 ~ ~ _ 0 8 C -- ~ 0 8
O I 1~ 1 >~ S ~ C> ~ ~ _ ~ _ ~ _
s o ~ t ~ 1~ ~ ~ ~ ~ S O ~ ~ ~ O ~ ~ 0 1
u ~ V1 ~ ~D S I I ~ I ~ ~ V~ ~ ~ S I I ~ n ~ ~ s I
~: ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ E a~ ~-- n ~ c~ 8 ~ CL ;~
0~
______~____________.__._._
n ~ ~ n n n ~ 8 8 Dl n ~ D 8 .n D ~ ~ n 8 n ~ ~ n n
L L L L L L L L L L L L ~ ~ L L L L ~ L
I~C I I I I I I I I T T I T T I I I I I I I I I T I I
_ .~
C C C C
S S S C S S S
Q C~ ~ ~ Q. a.
o o o o o o o - - - - - - ~
x x ~ ~ s ~c ~ s s ~
O O O O O O I I I I I I I -- -- -- ~ -- L
C C S S S C ~ I I I I I I I C ~ S
~: E E E E E E ~ ~ ;t ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
2o26l3~
x o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
~o ~ - ~
_. c a~
~ s s s
_ Q _ CL _ Q
O C _ ~~, _ ~ _ _~ ~, _ _ _
o ~ ~.> _ ~~ ~ o C,~ . ~, ~ ~ o ~ _ ~,
s ~ ~ C s ~ ~- ~ Y ~ s ~ ~,
l~i I C.) _ L I _ S I O ~_ _ L I ~' I O -- _ L
O ~ _ L -- ~ S ~ ~ ~ L ~ ~ S O
In I ~ s I I ~ S I I ~ I
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~-- n ~ Q ~ ~ E o ~ ~ Q ~ ~ '`I ~I E ~ ~--
a)
o~
_________._______.__,____
~ , Q ~ ~ ~ ~ Q Q C~ a. Q ~ Q ~ Q Q ~ Q Q Q Q Q
~oooooooooooooooooooooooo
L L L L L L L L L L L L L ~ L L. L L L L L L L L
^ ~ ~ Q Q Q ~ n. Q.
oooooooooooooooooooooooo
~VV V~VVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVV
~: ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ V ~ ~ U ~ V ~ ~ ~- ~
t2: I T I I I ~ I T I I T I I I I I T - I I I T I T I
_ _ _ _ . _ _
_ _ . -- _ -- -- Q 1~ Q Q Q Q Q
_ ~ ~ ~ O O O O O O O
~ C~ t~ ~ Cl. r~ Q Q L L L L L L L
._ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ L LO L L OL L L Q Q Q Q Q O Q
L5~ ~ Q Q Q Q Q Q Q O O O O O O O -- --
:~ S S S ~ S S S ~
Q ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ o o o o o o o v v v v v v -- _ --
~ E E E E E E E ~
f.~ J ~
X OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
~D
_~ ~ S
In ~
O ~ . C _ _ -~ . C _ .
r~ n _ _ I _ s ~ ~, ,V _ I . s I ~ ._ L
O ~L~CO~L~O~SO~L~SO
u~ ~ a) c a~ ~ ~ c I I ~ I ~ ~ v) ~ Q~ ~ i I ~ I ~ ~
~ ~ E a) -- .Q ~ ~ ~ ~ ~I ~I e ~ -- n ~ CL ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ _
C~
__________________~_.____.
~Q~A~
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
LLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLL
~Q~Q
O _ _ O _ O 9 0 0 0 0 _ _ O _ O O _ O O O O O O O
V ~ U ~ > V V ~
IIIIIIIIII T IIIIIIIII T I T II
, _ _ _ _ _ ~
~ C C C C C C
S S S S S S S
OOOOOOO------------
C C C C C C C ~ ~ ~
~. ~ C S S S S S S ~ -- ; _ _ _ ~ C
x x ~ x x x x ~ ~ n. ~ v V c~ V ~
----~OOOOOOOIIIIIII--~
~ , S S C C S ~ C . . - _ _ _ ~ _ I I I I I I I S
C~ ~ ~ Rl E E E E E E E~ ;t ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~1 '`I '~I ~ ~ '`I C`
2026131
~ ooooo
D
. .
o ~ ~ ~
o ~ ~
n ~ n.
~ I _ ~ I
O
In ~ ~ L~ y
~ D ~ ~ ~ ~
_ _ . _ _
OOOOO
L L L C
l l l l l
O O _ _
C~
~ ~ ~ U
C~ I I I I I
. . _ _ _
V V V
a ~ .~
._ ._ L
~ ~ ~ ~'
,.
~ ù ~
91 O.Z. 0050/41126
The oxa~ole- and thiazolecarboxamides la' and Ib', or herbicidal agents
containing them, may be applied for instance in the form of directly
sprayable solutions, powders, suspensions (including high-percentage
aqueous, oily or other suspensions), dispersions, emulsions, oil dis-
5 persions, pastes, dusts, broadcasting agents, or granules by spraying,atomizing, dusting, broadcasting or watering. The forms of application
depend entirely on the purpose for which the agents are being used, but
they must ensure as fine a distribution of the active ingredients accord-
ing to the invention as possible.
For the preparation of solutions, emulsions, pastes and oil dispersions to
be sprayed direct, mineral oil fractions of medium to high boiling point,
such as kerosene or diesel oil, further coal-tar oils, and oils of vege-
table or animal origin, aliphatic, cyclic and aromatic hydrocarbons such
15 as toluene, xylene, paraffin, tetrahydronaphthalene, alkylated naphtha-
lenes and their derivatives, methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol, cyclo-
hexanol, cyclohexanone, chlorobenzene, isophorone, etc., and strongly
polar solvents such as N,N-dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide,
N-methylpyrrolidone, water, etc. are suitable.
Aqueous formulations may be prepared from emulsion concentrates, pastes,
dispersions, wettable powders or water-dispersible granules by adding
water. To prepare emulsions, pastes and oil dispersions the ingredients as
such or dissolved in an oil or solvent may be homogenized in water by
25 means of wetting or dispersing agents, adherents or emulsifiers. Concen-
trates which are suitable for dilution with water may be prepared from
active ingredient, wetting agent, adherent, emulsifying or dispersing
agent and possibly solvent or oil.
30 Examples of surfactants are: alkali metal, alkaline earth metal and
ammonium salts of aromatic sulfonic acids, e.g., ligninsulfonic acid,
phenolsulfonic acid, naphthalenesulfonic acid and dibutylnaphthalene-
sulfonic acid, and of fatty acids, alkyl and alkylaryl sulfonates, and
alkyl, lauryl ether and fatty alcohol sulfates, and salts of sulfated
35 hexadecanols, heptadecanols, and octadecanols, salts of fatty alcohol
glycol ethers, condensation products of sulfonated naphthalene and
naphthalene derivatives with formaldehyde, condensation products of
naphthalene or naphthalenesulfonic acids with phenol and formaldehyde,
polyoxyethylene octylphenol ethers, ethoxylated isooctylphenol, ethoxyl-
40 ated octylphenol and ethoxylated nonylphenol, alkylphenol polyglycolethers, tributylphenyl polyslycol ethers, alkylaryl polyether alcohols,
isotridecyl alcohol, fatty alcohol ethylene oxide condensates, ethoxylated
~ iJ
92 O.Z. 0050/41126
castor oil, polyoxyethylene alkyl ethers, ethoxylated polyoxypropylene,
lauryl alcohol polyglycol ether acetal, sorbitol esters, lignin-sulfite
waste liquors and methyl cellulose.
5 Powders, dusts and broadcasting agents may be prepared by mixing or
grinding the active ingredients with a solid carrier.
Granules, e.g., coated, impregnated or homogeneous granules, may be
prepared by bonding the active ingredients to solid carriers. Examples of
10 solid carriers are mineral earths such as silicic acids, silica gels,
silicates, talc, kaolin, attapulgus clay, limestone, lime, chalk, bole,
loess, clay, dolomite, diatomaceous earth, calcium sulfate, magnesium
sulfate, magnesium oxide, ground plastics, fertil kers such as ammonium
sulfate, ammonium phosphate, ammonium nitrate, and ureas, and vegetable
15 products such as grain meals, bark meal, wood meal, and nutshell meal,
cellulosic powders, etc.
The formulations contain from 0.1 to 95, and preferably 0.5 to 90, % by
weight of active ingredient. The active ingredients are used in a purity
20 of 90 to 100, and preferably from 95 to 100, % (according to the NMR
spectrum).
Compounds Ia and Ib according to the invention may be formulated for
instance as follows:
I. 90 parts by weight of compound no. 1.003 is mixed with 10 parts by
weight of ~-methyl-alpha-pyrrolidone. A mixture is obtained which is
suitable for application in the form of very fine drops.
30 II. 20 parts by weight of compound no. 1.010 is dissolved in a mixture
consisting of 80 parts by weight of xylene, 10 parts by weight of the
adduct of 8 to 10 moles of ethylene oxide and 1 mole of oleic acid-N-
monoethanolamide, 5 parts by weight of the calcium salt of dodecylbenzene-
sulfonic acid, and 5 parts by weight of the adduct of 40 moles of ethylene
35 oxide and 1 mole of castor oil. 8y pouring the solution into 100,000 parts
by weight of water and uniformly distributing it therein, an aqueous dis-
persion is obtained containing 0.02% by weight of the active ingredient.
III. 20 parts by weight of compound no. 1.004 is dissolved in a mixture40 consisting of 40 parts by weight of cyclohexanone, 30 parts by weight of
isobutanol, 20 parts by weight of the adduct of 40 moles of ethylene oxide
and 1 mole of castor oil. By pouring the solution ints 100,000 parts by
weight of water, an aqueous dispersion is obtained containing 0.02% by
weight of the active ingredient.
2026131
93 o.z. 0050/41126
IV. 20 parts by weight of compound no. 1.011 is dissolved in a mixture
consisting of 25 parts by weight of cyclohexanone, 65 parts by weight of a
mineral oil fraction having a boiling point between 210 and 280C, and
10 parts by weight of the adduct of 40 moles of ethylene oxide and 1 mole
5 of castor oil. By pouring the solution into 100,000 parts by weight of
water, an aqueous dispersion is obtained containing 0.02% by weight of the
active ingredient.
V. 20 parts by weight of compound no. 1.011 is well mixed with 3 parts by
10 weight of the sodium salt of diisobutylnaphthalene-alpha-sulfonic acid,
17 parts by weight of the sodium salt of a lignin-sulfonic acid obtained
from a sulfite waste liquor, and 60 parts by weight of powdered silica
gel, and triturated in a hammer mill. By uniformly distributing the
mixture in 20,000 parts by weight of water, a spray liquor is obtained
15 containing O.i% by weight of the active ingredient.
VI. 3 parts by weight of compound no. 1.003 is intimately mixed with
97 parts by weight of particulate kaolin. A dust is obtained containing 3%
by weight of the active ingredient.
VII. 30 parts by weight of compound no. 1.004 is intimately mixed with a
mixture consisting of ~2 parts by weight of powdered silica gel and
8 parts by weight of paraffin oil which has been sprayed onto the surface
of this silica gel. A formulation of the active ingredient is obtained
25 having good adherence.
VIII. 20 parts by weight of compound no. 1.010 is intimately mixed with
2 parts of the calcium salt of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid, 8 parts of a
fatty alcohol polyglycol ether, 2 parts of the sodium salt of a phenol-
30 sulfonic acid-urea-formaldehyde condensate and 68 parts of a paraffinic
mineral oil. A stable oily dispersion is obtained.
~he active ingredients or the herbicidal agents containing the~ may be
applied pre- or postemergence. If certain crop plants tolerate the active
35 ingredients less well, application techniques may be used in which the
herbicidal agents are sprayed from suitable equipment in such a manner
that the leaves of sensitive crop plants are if possible not touched, and
the agents reach the soil or the unwanted plants growing beneath the crop
plants (post-directed, lay-by treatment).
The application rates depend on the objective to be achieved, the time of
the year, the plants to be combated and their growth stages, and range
from 0.001 to 5, and preferably from 0.01 to 2, kg/ha.
2026131
94 O.Z. 0050/41126
In view of the number of application methods possible, the compounds
according to the invention, or agents containing them, may be used in a
large number of crops for eliminating unwanted plant growth.
5 To increase the spectrum of action and to achieve synergistic effects, the
oxazole- and thiazolecarboxamides Ia and Ib may be mixed wit~, each other,
or mixed and applied together with numerous representatives of other
herbicidal or growth-regulating active ingredient groups. Examples of
suitable components are diazines, 4H-3,1-benzoxazine derivatives, benzo-
10 thiadiazinones, 2,6-dinitroanilines, N-phenylcarbamates, thiolcarbamates,
halocarboxylic acids, triazines, amides, ureas, diphenyl ethers, triazin-
ones, uracils, benzofuran derivatives, cyclohexane-1,3-dione derivatives,
quinolinecarboxylic acids, thetero)-aryloxyphenoxypropionic acids and
salts, esters, amides thereof, etc.
It may also be useful to apply compounds Ia and Ib, either alone or in
combination with other herbicides, in admixture with other crop protection
agents, e.g., agents for combating pests or phytopathogenic fungi or
bacteria. The compounds may also be mixed with solutions of mineral salts
20 used to remedy nutritional or trace element deficiencies. Non-phytotoxic
oils and oil concentrates may also be added.
Synthesis examples
25 The directions given in the synthesis examples below were used, after
appropriate modification of the starting materials, to obtain further
compounds. The compounds thus obtained are given in the following tables
with their physical data.
30 1. Methods of manufacturing the intermediates
Example 1.1
4(5)-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-methyloxazole-5(4)-carboxylic acid
At -10C and under a nitrogen blanket, a solution of 6.0 g (0.15 mol) of
sodium hydroxide in 150 ml of water was dripped over a period of 4 hours
into 33.8 9 (0.15 mol~ of 2-methyloxazole-4,5-dicarboxylate in 300 ml of
ethanol, and the mixture was stirred at -10C for 2 hours. The solution
40 was evaporated down, the residue was taken up in 300 ml of water, the pH
was adjusted to 8 to 9 with hydrochloric acid and the solution was ex-
tracted twice, each time with 300 ml of diethyl ether. The mixture was
then acidified to a pH of 2 with concentrated hydrochloric acid and the
aqueous phase was extracted four times, each time with 250 ml of dichloro-
~ u ~
O.Z. 0o5o/4ll26
methane. The combined organic phases were dried over magnesium sulfate andthe solvent was removed under reduced pressure. There was obtained 26.4 9
(88%) of 4(5)-ethoxycarbonyl-2-methyloxazole-5(4)-carboxylic acid as a
white solid (isomer ratio: 3:1 ~lH-NMR, HPLC). Fractional crystallization
5 from cyclohexane/ethyl acetate (2:1) or column chromatography using silica
gel (toluene, THF, glacial acetic acid (7:3:1)) gave the pure isomer of 4-
ethoxycarbonyl-2-methyloxazole-5-carboxylic acid. lH-NMR (250 MHz,
D6-DMS0); main isomer: ~ = 1.28 (t; 3H), 2.52 (s; 3H), 4.30 (q; 2H), 14.00
(broad s; lH).
Example 1.2
4-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-methylthiothiazole-5-carboxylic acid
15 At room temperature, a solution of 1.10 9 (27.5 mmol) of sodium hydroxide
in 10 ml of water was added over a period of one hour to a solution of
7.00 9 (25 mmol) of diethyl 2-methylthiothiazole-4,5-dicarboxylate in
100 ml of ethanol/water (2:1). The mixture was stirred for one hour, the
solvent mixture was then removed under reduced pressure, the residue was
20 taken up in 100 ml of water, the solution was extracted once with 50 ml of
diethyl ether, and the aqueous phase was acidified with concentrated
hydrochloric acid. The precipitated product was filtered off and dried.
Yield: 4.50 9 (73%). Melting point: 104C.
The carboxylic acids given in the following table were obtained in accord-
ance with the above example:
202~131
96 O.Z. 0050/41126
Example Rl R5 X Physical data
1.9(b) phenyl CH3 S mp.: 127-137
5 1.4(a) n-butylthio C2H5 S 0.95 (t;3H), 1.40 (t;3H), 1.50 (sext;2H),
1.80 (quint;2H), 3.40 (t;2H), 4.35 (q;2H)
1.5(b) n-butylthio C2H5 S 0.95 (t;3H), 1.35 (t;3H), 1.50 (sect;2H),
1.80 (quint;2H), 3.30 (t;2H), 4.45 (q;2H)
2.6(b) iso-propylthio C2H5 S 1.50 (d;6H), 1.45 (t;3H), 3.90 (hept;lH),
4.55 (q;2H), 12.50 (s;lH)
1.7(a) iso-propylthio C2H5 S 1.45 (t;3H), 1.50 (d;6H), 4.05 (hept;lH),
IS 4.50 (q;2H), 12.50 (s;lH)
1.8(a) methylthio CH3 S 2.80 (S;3H), 4.05 (s;3H)
Example 1.9
s Diethyl 2-methylthiothiazole-4,5-dicarboxylate
At 0C, a solution of 2.1 9 (0.03 mol) of sodium methylthiolate in 10 ml
of ethanol was dripped into a solution of 9.2 9 (0.03 mol~ of diethyl
25 2-chlorothiazole-4,5-dicarboxylate in 30 ml of ethanol. The mixture was
allowed to heat up to 25C and was then stirred for two hours. The solvent
was then removed under reduced pressure, the residue was taken up in
100 ml of diethyl ether and the solution washed with 50 ml of 5% strength
sodium hydroxide solution and with 50 ml of water. Drying over sodium
30 sulfate and evaporating down gave 7.2 9 t87%) of the product as a color-
less oil.
1H-NMR (CDC13, 250 MHz, TMS as internal standard): 1.35 (t, I=7.0 Hz,
3H), 1.45 (t, I=7.0 Hz; 3H), 2.75 (s, 3H), 4.30 (q, 1=7.0 HZ; 2H), 4.50
35 (q, I=7.0 Hz; 2H).
~ . v ~.. ., ~. ~3 1
97 O.Z. 0050/41126
2. Process for manufacturing compounds ~Ia and VIb
R3 N R3
NI~N RlJ~ N~
R1 X R4 R4
Vla VIb
Example 2.1
5 2-Methoxythiazole-4-carboxylic acid-tert.-butylamide
At 25C, 8.90 9 of a 3~% strength solution (49 mmol) of sodium methanolate
in methanol was added to a solution of 12.00 9 (46 mmol) of 2-bromothia-
zole-4-carboxylic acid-tert.-butylamide in 150 ml of methanol. The mixture
10 was boiled under reflux for four hours, the clear solution was evaporated
down, the residue was taken up in 300 ml of diethyl ether and filtered,
and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. There was obtained
9.60 9 (98%) of the product as a yellow oil.
15 lH-NMR (CDCl3, 250 MHz, TMS as internal standard): 1.45 (s; 9H), 4.10 (s;
3H), 7.00 (s, broad, lH), 7.48 (s; lH).
Example 2.2
20 2-lsopropyloxa~ole-4-carboxylic acid-cyclopropylamide
At room temperature, 47.6 9 (0.40 mol) of thionyl chloride was dripped
into a solution of 31.0 9 (0.20 mol) of 2-isopropyloxazole-4-carboxylic
acid in 200 ml of toluene and 2 ml of dimethylformamide, and the mixture
25 was stirred for one hour at 80C. The solvents were stripped off under
reduced pressure, the residue was dissolved in 300 ml of dichloromethane,
and 24.0 9 (0.42 mol) of cyclopropylamine in 20 ml of dichloromethane was
dripped in at 0 to 10C. The mixture was stirred for 12 hours at room
temperature, 150 ml of water was added, the phases were separated, the
30 organic phase was washed once with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution
and dried over magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was removed under
reduced pressure. There was obtained 37.2 9 (96%) of 2-isopropyl-oxazole-
4-carboxylic acid-cyclopropylamide.
35 1H-NMR (CDC13, 250 MHz): ~ = 0.62 (m; 2H), 0.88 (m; 2H), 1.34 (d; 6H),
2.86 (m; lH), 3.09 (m; lH), 6.93 (broad s; lH; NH), 8.09 (s; lH).
The amides listed in the following table were obtained in accordance with
the above examples or analogously to the cited literature:
2026~31
TE v~
E ~ E
-- -- 0 o
u~ O~D ~ 00
o
i T ~) --
~ ~- I `-- I I I
_ ~~ _ Zv~ D Z
E I I I ~n I T _ T ~ I
C ` ` Vl O V~ o
._ -- ---- O -- C~) -- -- O --
~o o u~ ~ r~ o
_ o o~ r~
Cl:r~ r ~ -- r~ , T _~ _ T
~: I ~z T .~ .
E ~~ Z E~ E
,~ I TT :1: r I ~
~ _ a~ o ~o, o
o ~ _ -- -- -- -- -- r~ ~ ~ r~ -- -- m ~ -- -- o
u~ . r~
O~" . O U~ ~D ~ 00 ~ 0~ ~ O O I I I ~ ~ I I ~ O~
~ E~ u~ ~ I ~ I I ~ ~ ~ ~ D o ~ ~ r~ o o ~r) r~ r~ o r~
~ ~ _ r~ r~ o -- ~ o
o
x u> u~ o o o o o o o o o o o
o~
o~
_ _ _ _ _ _
a0 L OL ~a ~~ ~ ~ ~ o 0 ~ o ~ Q L ~
n ~ ~ ~ ~ D n ~ ~ n n. ~ n r o o Cl~ c
I O O ~ O ~ 0 1~ ~' O
t L C.~ V V S L L L L L V O L V O O V O
~r ~ ~ ~ v v ~ ~~ ~ ~ ~ v ~ ~ v ~-- -- v ~
I T T T I TT I I I I T I I T I I I
_ ~,
O o ., '~ :., o~ o O
C L Q. ~ Q L L L
~, ~ o o o ~
:~ O :~ O O >~ :~ O :~ O _ L L ~ o o o
c E C E C C c -~ C . ~ ~ ~ I I I ~ ~
~> o a) o ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ v C C ,C O O O v t~ V
~ n ~ n 8 E ~ E E v 0 ~ a> -- -- -- v v v
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ ,_ _ _ _ _
_ _____ _ n ~
~ o _ t~l ~ ~ ~~ ~ ----__
Z t~ t~ t~ t~ t~i t~i t~ ~ t~ t~ t~i t~ t~ t~ t~ t~
2026131
_ _ _
--
~ o ~ o
_
E _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Q ~ o ~ ~ ~ ~ '~ o
c u~ ~ V) tn ~ ~ v~
._ _ ,_ _ _ _ ,_ _ I~ _ _ _
~o o ~ u~ In o ~ o ~ ~D O (D
_ ~ _ ~ ~ ~ _ ~ _ ~ o o~
~ Z ~ E ` ~ ` E ` E
_. ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ O~ ~0 ~ O ~ _ ~ _
U~ . ~ ) O t~l I I I I
o v~ I I I I I I I I ~ I o o u~ oo In o) u~) oo ~'l ot) o ~ o o Ir
O :~. En. æ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ u~ ~ ~ ~ O ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
o
x O O o o
a~
___ _
~ O, L S L ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ V
8 o ~ ~ ~ n v n n n E n D D n n Q n
. C~ o I o 1. o 1. 1. 1. 1 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.
~t O ~ ~ L L ~ L L L L ~ ~
~: I I I I T I I I I I I ~' I I I I I I I
_ S_ _ . ~
N-- E ~ ~ ~ --
~:-, I ~ s ~ >,
a~ _. ~ ~, a~ ~ v ~ E
_ n ~,~ ~ O D I n~ ~ o
~ ~ n ~ o ~ ~ ~ n
_ . _ _ _ ~ _ I ._ I ~ c~, _ ~ _ ~ , I
a~ c> ~ E , J s s L
S S ~ ~ I ~ ~ I I I I ~ V I ~ I ~ V
~: c~ ~ ~ ~ E~ ~ ~ ~ c~ ~ ~ ~ n ~ ~ ~ E ~
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
-- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- ~
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 1-- oo ~ o ~ ~ ~ ~ In ~ O
o ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
z ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
h ~J r~ U ~ V 1
~ . ~ ` . ~
~r E I -- I
O ` ~ `
_~ ~ E~ t~l
E I I I T 0~ I OD
o ~ o ~
~ v, ~ ~ . v) n v~ _ . v7 _
._ ~ ~ ~ I~ ~ ~ ~ I (~I ~ I
~ O Z~ ~ Z
_U~ o ~~ _~ I_ Ir) I _ l~) I
I ~
~D Z~ E
~ I I T I I T I ~ T ~
_ ~ _ ~ Dt~1~) 00 ~ L1~ 0 ;t 0~ ~ L
. I I I I I I I I I ~ I
o u~ C~ o c~ In I I o ~ Irl ~ ~ ~ _~ ~ In ~ o C~ ~ o
o ~ c~ ~ ~ ~ ~ o r~ o In ~ ~ ~ O D ~ 0~ 0~ ~ ~ ~D ~ O
~ E ~ ~ <D o ~ ~D
o
X V~ oOoO~OOOOO OOOO
g ~
C
I. CL -- ~ o .
~,~, o ~ .~ O ~ ~ ~> C ~ ~ L O L
I~ ~ C~. .Q ~ C~ I C~ n o s ~
I I I I I I ~ I I L Q I I I V
O O -- _ ~ I _ ~ O
L V L L V ~ V L O ~ L L V -- V
~ v :~ ~ a :~, ~ ~. v- I ~ ~1) ~, I
tY I I T I I I I I I I T I I T I I
_~, _
C~C ~ C _ _
~ I x xc c c c ~ ~ ~ ~ al
E-- -- -- -- E E
X C I I ~ ~ ~ X I I I X
C ---- L I I I I
Q. V V Q n. Q ~ ~ ~ L L L ~
E--~ V ~ c c c ~t ~t ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ E
_ ____ ~______ ____
_ ____ _______ ____
O . . ... ....... ....
Z ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ C`J ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ f~ ~
o
101 O.Z. 0050/41126
3. Methods of manufacturing compounds Ia and Ib
Example 1
5 4-Cyclopropylaminocarbonyl-2-isopropyloxazole-5-carboxylic acid
At -70C and under a nitrogen blanket, 0.12 mol of n-butyllithium (80.0 ml
of a 1.5 molar solution in hexane) was dripped into a solution of 10.4 9
(0.054 mol) of 2-isopropyloxazole-4-carboxylic acid-cyclopropylamide in
lO 250 ml of tetrahydrofuran, and the mixture was stirred for 30 minutes at
this temperature. The reaction mixture was then`poured onto 500 g of solid
C2 and allowed to stand overnight. The residue remaining after evaporat-
ing down was taken up in 200 ml of water and 30 ml of 2N NaOH, the sol-
ution was extracted twice, each time with 100 ml of diethyl ether, the
15 aqueous phase was acidified to a pH of 2 with concentrated hydrochloric
acid and the solution extracted three times, each time with 200 ml of
ethyl acetate. Drying over magnesium sulfate and removal of the solvent
under reduced pressure gave 10.4 9 (81%) of 4-cyclopropylaminocarbonyl-
2-isopropyloxazole-5-carboxylic acid as a white powder of m.p. 109-112C
20 (active ingredient no. 3.007).
Example 2
4-tert-Butylaminocarbonyl-2-methoxythiazole-5-carboXyliC acid
At -70C, 65 ml of a 1.5 molar solution (97 mmol) of n-butyllithium in
n-hexane was dripped into a solution of 8.00 9 (37 mmol~ of 2-methoxy-
thiazole-4-carboxylic acid-tert-butylamide in 150 ml of tetrahydrofuran,
and the mixture was stirred for 30 minutes at this temperature. The
30 reaction mixture was then poured onto 500 9 of solid carbon dioxide and
allowed to warm up to room temperature over a period of 14 hours. The
solvent was removed under reduced pressure, the residue was taken up in a
mixture of 150 ml of water and 16 ml of 2N NaOH and filtered, the filtrate
was acidified with concentrated hydrochloric acid and the precipitated
35 carboxylic acid was filtered off.
There was obtained 7.80 9 (82%) of 4-tert-butylaminocarbonyl-2-methoxy-
thiazole-5-carboxylic acid as a white powder of m.p. 120-122C (active
ingredient no. 1.003).
) iy ~
102 o.Z. 0050/41126
Example 3
5-tert-Butylaminocarbonyl-2-methoxythiazole-4-carboxylic acid
5 At -70C and under a nitrogen blanket, 56 mmol of n-butyllithium (37.3 ml
of a 1.5 molar solution in hexane) was dripped into a solution of 5.4 g
(25.2 mmol) of 2-methoxythiazole-4-carboxylic acid-tert-butylamide in
150 ml of tetrahydrofuran, and the mixture was stirred for 30 minutes at
this temperature. The reaction mixture was then poured onto 500 g of solid
lO CO2 and allowed to stand overnight. After concentration the residue was
taken up in 150 ml of water and 10 ml of 2N NaOH, the solution was
extracted twice, each time with 50 ml of diethyl ether, and the aqueous
phase was acidified to a pH of 2 with concentrated hydrochloric acid and
extracted three times, each time with 100 ml of ethyl acetate. Drying over
15 magnesium sulfate and removal of the solvent under reduced pressure gave
3.9 g (60~o) of 5-tert-butylaminocarbonyl-2-methoxythiazole-4-carboxylic
acid as a white powder of m.p. 105-110C (active ingredient no. 2.001).
Example 4
a) 4-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-methyloxazole-5-carboxylic chloride
At 0C, 40 ml of thionyl chloride and 1 ml of dimethylformamide were
dripped into 12.2 g (61.3 mmol~ of 4-ethoxycarbonyl-2-methyloxazole-5-
carboxylic acid, and the mixture was refluxed for one hour. The excess
thionyl chloride ~as stripped off under reduced pressure and the
residue was distilled under an oil pump vacuum.
There was obtained 10.9 g (82%) of 4-ethoxycarbonyl-2-methyloxazole-5-
carboxylic chloride as a yellow oil of m.p. 103-105C/0.1 mm. lH-NMR
(250 MHz, CDC13): ~ 1.42 (t; 3H~, 2.66 (s; 3H), 4.66 (q; 2H).
b) 4-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-methyloxazole-5-carboxylic acid-tert-butylamide
At 0C, a solution of 11.0 9 1150 mmol) of tert-butylamine in 20 ml of
dichloromethane was dripped into 10.9 g (50.3 mmol) of 4-ethoxycarbon-
yl-2-methyloxazole-5-carboxylic chloride, and the mixture was stirred
at this temperature for 12 hours. The reaction mixture was taken up in
200 ml of water, the phases were separated, the organic phase was
washed once with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and once with
saturated sodium chloride solution and dried over magnesium sulfate,
and the solvent was stripped off under reduced pressure in a rotary
evaporator.
There was obtained 11.9 9 (93%) of the title compound as a white solid
of m.p. 152-155C (active ingredient no. 4.001).
103 O.Z. 0050/41126
Example 5
5-tert-~utylaminocarbonyl-2-methyloxazole-4-carboxylic acid
5 At 0C and under a nitrogen blanket, a solution of 1.2 9 (30.0 mmol) of
sodium hydroxide in 50 ml of water was dripped into 7.4 g (29.1 mmol) of
4-ethoxycarbonyl-2-methyloxazole-5-carboxylic acid-tert-butylamide in
150 ml of ethanol and 50 ml of THF. The mixture was stirred for 2 hours at
20C, the solvents were stripped off under reduced pressure in a rotary
10 evaporator, the residue was taken up in 300 ml of water, the pH adjusted
to 9, and the aqueous phase was extracted three times, each time with
100 ml of diethyl ether. Acidification was then effected to a pH of 2 with
6N HCI and extraction carried out four times, each time with 150 ml of
dichloromethane. The organic phase was dried over sodium sulfate and the
15 solvent stripped off under reduced pressure.
There was obtained 6.1 g (93%) of the title compound as a white solid of
m.p. 186-188C (actiYe ingredient no. 4.002).
20 Example 6
a) 4-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-methylthiothiazole-5-carboxylic chloride
3.40 9 (13.7 mmol) of.4-ethoxycarbonyl-2-methylthiothiazole-5-carbox-
ylic acid was dissolved in 50 ml of thionyl chloride, and the mixture
refluxed until no more gas evolved. Excess thionyl chloride was
removed under reduced pressure, leaving 3.55 9 (98~o) of the acyl
chloride as a colorless oil.
lH-NMR (CDC13, 250 MHz, TMS as internal standard): 1.50 (t, I=7.0 Hz;
3H), 2.75 (s; 3H), 4.60 (q, I=7.0 Hz; 2H).
b) 4-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-methylthiothiazole-5-carboxylic acid-tert~butyl-
amide
3.50 9 (13.2 mmol) of 4-ethoxycarbonyl-2-methylthiothiazole-5-carb-
oxylic acid chloride was dissolved in 20 ml of dichloromethane and
dripped, at 0C, into a solution of 3.20 9 (44 mmol) of tert-butyl-
amine in 50 ml of dichloromethane. The mixture was allowed to warm up
to room temperature and was then stirred for 14 hours. 100 ml of lO~o
strength hydrochloric acid was added and the organic phase was separ-
ated, washed with 50 ml of water and dried over sodium sulfate. The
solvent was removed under reduced pressure, leaving 4.00 g (lOOYo) of
product as a yellow crystalline slurry.
h~J1
104 o.Z. 0050/41126
lH-NMR (CDC13, 250 MHz, TMS as internal standard): 1.45 (t, I=7.0 HZ; 3H),
1.45 (s; 9H), 2.75 (s; 3H), 4.50 (q; I=7.0 Hz; 2H), 9.90 (s broad; lH).
(Active ingredient no. 2.007)
5 Example 7
5-tert-Butylaminocarbonyl-2-methylthiothiazole-4-carboxylic acid
0.82 9 (14.6 mmol) of potassium hydroxide in 10 ml of water was added to a
10 solution of 4.00 9 (13.2 mmol) of 4-ethoxycarbonyl-2-methylthiothiazole-5-
carboxylic acid-tert-butylamide in 50 ml of water/ethanol (2:1), and the
mixture was refluxed for 2 hours. The solvent mixture was then removed
under reduced pressure and the residue was taken up in 50 ml of water and
acidified with concentrated hydrochloric acid. The precipitated product
15 was filtered off and dried.
Yield: 3.40 9 (94%); m.p. 100C (active ingredient no. 2.005).
Example 8
4-tert-Butylaminocarbonyl-2-methoxythiazole-5-carboxylic acid acetoxime
ester
At room temperature, 4.4 9 (43.6 mmol) of 4-methylmorpholine and 1.5 9
25 (12.3 mmol) of 4-dimethylaminopyridine were dripped into a solution of
3.1 g (12.0 mmol) of 4-tert-butylaminocarbonyl-2-methoxythiazole-5-carb-
oxylic acid and 1.2 9 (16.4 mmol) of acetoxime in 100 ml of dichloro-
methane, and the mixture was stirred for 5 minutes. Subse~uently, 10.1 9
of a 50% strength solution of propanephosphonic anhydride in dichloro-
30 methane (= 15.9 mmol) was added and the mixture was refluxed for 7 hours.After concentration, the residue was taken up in 100 ml of ethyl acetate
and the solution was extracted twice with saturated sodium bicarbonate
solution, and once with 5% strength citric acid solution, once with
saturated sodium carbonate solution and once with saturated sodium chlor-
35 ide solution. The organic phase was dried over magnesium sulfate and thesolvent was stripped off under reduced pressure.
There was obtained 3.1 y (82%) of 4-tert-butylaminocarbonyl-2-methoxythia-
zole-5-carboxylic acid-acetoxime ester as a white powder of m.p.
40 128-131C (active ingredient no. 1.011).
105 O.Z. 0050/41126
Example 9
5-tert-8utylaminocarbonyl-2-methyloxazole-4-carboxylic acid acetoxime
ester
At room temperature, 3.46 9 (16.8 mmol) of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide in
20 ml of tetrahydrofuran was dripped into a solution of 3.80 g (16.8 mmol)
of 5-tert-butylaminocarbonyl-2-methyloxazole-4-carboxylic acid and 1.23 g
(1~.8 mmol) of acetoxime in 40 ml of tetrahydrofuran. The mixture was
10 stirred for 14 hours, the precipitate was filtered off, the solvent was
stripped off under reduced pressure and the residue was chromatographed
using silica gel (cyclohexane/ethyl acetate (1:1)). There was obtained
2.7 9 (57%) of 5-tert-butylaminocarbony~-2-methyloxazole-4-carboxylic acid
acetoxime ester as a white solid of m.p. 107-111C (active ingredient no.
15 4.003)-
The active ingredients listed in the tables below were prepared analogous-
ly to the above compounds:
E ~f ~ f f
.~
E frf ~ f ~,~f
_ _ _ _ _
u~f o o ~n
~O In f~ In f~
I~ ~ I~ f~O
D z ^~ T
I T .--f I I . f
~ f ~f~ f~f f~ f
O f~f C~f` ~ Vf ` ~ ~f
,n ~ f o~ f~f f ~' f l~ ,r) v~f E -- vf ~' -- 1-- ~ ~f
g _f f . f _ f o o _ ~ f
frf I I I I I o u~ ~Sf o m rf
,, fr~ ~f f~ O ~ ~f ~ ~ fXf f~O
O ~ Ef ~ ~ f f f ._ ,_ fs _,f ,~ ~D ~ O f~ f ~f
,_ o o o o o o o o o o o
_
~D I I I
_.
~ f_f f_~
U- Z Z Z
Y I I T T ~ I
\z/ / _ _ _
0~ _O :-, f ~-
= ~ f_ --f L ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~-
~f f f f ~ o f f f ~f f c~ rf
Z=~ ~ O ~ O ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ O
~ fV :~ fV ~ f~ fV fV ~ fD
fY fY ~ ~ ~ ~> ~ ~ ~ ~J ~ U ~
f~f
~Y T I T I -- I I I I I T
f~
f
O ~ O
f f
-- -- X X _ _ f . _ X ~'C
O O ~ ~ 1 ~7 ~. O O
fV fl f 'f ~ ~ ~ ~
~ E F E 8 f~ nL ~ E E E E
._f fv
fl'f f ~f ~f f ~f ~ 1~ frf fS-
f~ fEcf; o o o O f~ o o f~ o o o
~ ~L' ~f _'f . f ~f ~ ' . f ~f ~
~ V ~ ~ ~ ~J
_T I T
E ~ ~
LE m E
.__ _
~o~ _ a-
O ~ ~`J
Z~_~
I .` S
O ~ ~ .
O ~ _E u~ ~ ~ O O
O . ~ O
~n . ~ O 1~ ~ -- _ _ _ _ _ _
~ ~ 1~ $ o o ~ ~ ~ ~ o a~
O _ _ _ _ _. _ ~ _ _ _ _
:.' O
O OOOOOOOOOOO OOO
_ ~
1--
_. ~ ~
U~ Z Z
t~: I I I I I I X I I T I T I I I T
_
~ -- _ . . . ' _ _ ~ _ _ _ _ . _ _
I ~ n ~ ~ ~ n O S~ ~ .Q D ~ n n ~
L L L L L L L L L L L L L
Y ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
T I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
s
S ~ (D --
I ~ ~ 8 ~ X ~ ~I)
u~~, ~., E -- ~ " ~ I -- --
c ~ ~ ~ n n CL C o x
~,~. ~ ~ ~ q) o ~ c~ ~ o I ~ 8
0 1~ ~ ~ ~ ~ V ~ ~ O ~
C ~: E '' C ~ I E C~l ~ $ ~ ~ ~ E ~-- ~ ~ O
v
-
E _, _ ;t u-) ~) 1-- ~ a O _ C`J ~
. O O OOOOOOOOOOO OOO
X O
~ W Z _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
202~131
_
.
_ ~
o
_
I
._ i_
E
_ _ _ T
O ~ .
C ~` O` V~
-- CO
~O O
_ CO
Ir
~:
z ~ E --
;~ ~. ~ _ _ T
_ c~ --' I T
1~ ~ O
o _
U~ . I O
C~ -- ~ 0 U-)
~ c E O a~
o ~ _ _ _ I_ _ _ I_
O O O O o
oo
o
-
u
1~: I Z T T T
~ ~ ~ ~ n
1. 1. 1. ~. 1. .
L L L L
n T T T I
,-
r~ a~ I
S~
L .~ a~ --
I
_I
o
-
CO 0 0 _
E ~ ~ ~ ~
n ~ . o o o o o
x o
Ll~ z
~ V~
~r _
In o~
E
C U~ ~
O U~ O
_ 1~ 11~
~D ~r
Z .~ .
,~1. ~ I _ T
_ t~ I O~
O ~ o O
O _ ~ -- -- O ~I
O . ~
V~ I r~ U~ U~ O
~ ~ ~ D o 1~ , ~ O ~ O u ) ~0 J
O
~- OOOOOOO OO OOO OO
C~
C~
_. .~ :~
In ~
U') ~ '7 ~ T ~ E I I I a I I I T I I I
.-._____ __ ___ __
0=~ ~--O ~ :~ ~, ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~7 ~ ~.
al ~ ~ -- -- -- -- ~ --
l ~:1 ~ C Q ~ ~ .a ~ n n 1~ 8 D n
Z ~ ~ ~ ' I ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
L L ~ L L L L ' L L L ~ L
1~ T I T I T I I I T I I I I I
O
._
_ I ,, a~ ~ --
O ~ -- E ~
C ~ ~ ~ LO ~. 'L " E
~ ~ s ~ o ~ o ~ c ~n
~o _ _ .~ ~ o L u~ O
_. ~ V ~ ~ _) I D O O ~ ~ ~ L
E ~- n. ~ E ~ C -- ~ ~-- ~ O E
.~ o
E O O O O O O O O O ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
18. OOOOOOO OO OOO OO
X O
J ' ~ i
E ` ` E
I I
c~
.
E i
_ ~ o U~ ~
OD I I
_ ~
~ u~ I I I I I T
._ _ _ ~
~ ~ ,n ~ ~ ~ ~n u O
<DC~ '`'I a. I
z E ` ~ ` U7 ~ ` ` E
. ~ I I T T
_ oo Cr~ c.~ c.~
O ~ ~ O ` ` ` ~D ` ` ` 1~)
O _ U~ _~ _ _ _ O) _ _ _
O . ~
I Irl u ~ '1 OD ~ O ~) O
E ~ . . . . . . . .
-- o ~
~- O o o o O
U~ ~ s s
I
_- . . .
~ ~ ~ ~ :~
n n 8 3 n
i I 1. 1. 1.
L L L
~: ~ ~
~: I S
_
Q ~ a~ .
o E E
~,
_ I x x a~
~ o o o n
, .,,
~. ~ >, cv
L ~ n 0 E E
-
~ 0
n. ~
n ~ . o o o o o
x o
L~ z ~ ~ ~ c.~l c,~
o ~ O r~ o u~
o -- ~ ~ ~ ~`
o . ~ .~ . ~ O _- o
1~ ~, ~ U~ In O ~ O 1~ .~ D O ;t O ~
~- o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
~1 ~ ~ N ~ ~ t~l
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_. I I I I I I T
~ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
1~:I I I I T '-- I T I I I I I I I I I I
l-7 ~ U
\z/ / _ _ __ _ _ _
0=( ~=0 -- -- ~ C ~ ~, ~ C ~
~ ~ O 11) ~ ~ O :~ ~ O a~ ~ o ~ o
1~= ~ ~ S ~ ~ L 1:~. ~ L C ~ L 1~ ' L
Q 8 ~. ~ n n ~ OL ~ ~ ~ 8 I L I L L
z=( o ~ _ ~ _ ~ o n. ~ ~ _
L L V O L L V O L V O L ~ O L O O V
rl~ I I T I T T I I I T I I I I I I T T
_ _ _ _ r
O ~ O O O O
L t~ ~ C~ Q ~ ~ ' L L L
_ I L L L S_ L L
:~ r~ _ . ' O ~ ~ ~ _ _ _ ~ ~ ~ O O O O
_. +~CCCVOOO~CCOOO
c~ E ~ ~ ~ v ~ v v v
C~ ~ O 1~ o ~ o ~ 0;:~
E o o o o o o o o o ~
. oooooooooooooooooo
X o ~ ~ ~ ~ ~r) ~ ~ ~ C'~ ~ ~ ~ ~
hvi~,
~ o~
E ~ _
c~ I I
._ _ _,
~o ~ oo
_ n
Z __ _
~ 1~1 .~ T I
_.
O ~ ~ .~ .~
o ~ oo ul ~D o ~ E ~o ~D oo a~ `1 o o ~ ~1
tn IIIo7 1 ~IIIIIIIIIIII1~1
l~i ~ ~ O _. O ~ o ~ ~~ ~ ~ 1~ 1-- ~ O O .~ 1~ oo I o ~1
:~ O o o o o o o o O o o O o o O o o O o o O
~ ~ o ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
- . ~ ~ - l~
_. ~_ _ _ " y ~ _ _ _ __ _ _
IS') I T T I ¦ ~ ~T T T ~:t I I I I I I I I I I I
_ _ _ _ _
2 a> ~ c~ 2 ~ ~ ~ 2 ~ . ~ ~ ~ ~
C~ ~-- O 0 8 n 8 LI I ~ I o 1. o o t~ . . o
_ _ I I ~ ~ ~ I . ~ _ ~ _ ~ _ _ I ~ ~ ~ I c
O O O L ~ O L t_~ L L U O C L ~ a
T I T I I s T I I I I I I I I I T T
O O ~ ~ O X X X
L ~ Q ~ ~
CL rl _ _ _ L I _ _
O O -- -- -- C~ Q ~ ~ O Q O :-~ O O O O
-- ~ ~ I C C C I _ C C _ _ _ C L L L L
_. ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ S U~ ~ ~ C ~ S I I ~ I
c ~r ~ --V~D_V~CCCC
. Ooooo o Ooooooooooooooo
X O
., ~
~ U r~ `v
r_
E
c
._
_
z
~ ~ .
O -o o
O _ O r~
O ~ .
r E I~ ~
O O O O O O O
_ _ _
l- X T I
Q. O ~ ~ O
O L ~ O L
L 1~ I L C3.
n~ , , T O I I I O
O ~ -- O C~
. I U
L I :~ L u X :~
C~ ~ ~ ~ I ~ ~ I
c~:I I I I I I
c
~,
:~ 8 n 8 n D ~
X I I I 1. 1. 1.
V ~ L L L L L L
~ ~ ~ ~ al Q~
c ~Y E ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
u
a~
O ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~D
n ~ . o o o o o o o
X o ~ ~ ~ C~
~u~v . ~1
~ c~
~ z
o ~ ~
u~ ~ o
o _ u~
o ~n ~
:~, ~ ~ ~ O
,~ s E u~ ~ o u~ ~
o
,_ o O o o o
_ _ _
U7 ~ Z ~
u7 ~ ~ ~ I I 11>
\ \z/
0~ ~=0 -- _ r~ _
~ 8
z=~ L
_ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
~: I T I I I
S ~ C C C
_. ~ C~
Ir E E E c~.
L ~
E o o o o o
n ~5 o o o o o
~ x o ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
~ ~r~
115 O.Z. 0050/4~126
Use examples
The herbicidal action of the oxazole- and thiazolecarboxamides of the
formulae la and Ib' is demonstrated in greenhouse experiments:
The vessels employed were plastic flowerpots having a volume of 300 cm3
and filled with a sandy loam containing about 3.0~O humus. The seeds of the
test plants were sown separately, according to species.
10 For the preemergence treatment, the active ingredients, suspended or
emulsified in water, were applied to the surface of the soil immediately
after the seeds had been sown. The vessels were lightly sprinkler-
irrigated to induce germination and growth. Transparent plastic covers
were then placed on the vessels until the plants had taken root. The cover
15 ensured uniform germination of the plants, insofar as this was not
impaired by the active ingredients.
For the postemergence treatment, the plants were grown, depending on
growth form, to a height of 3 to 15 cm before being treated with the com-
20 pounds, suspended or emulsified in water. The application rate for post-
emergence treatment was 1.0 kg/ha.
The pots were set up in the greenhouse, heat-loving species at 20 to 35C,
and species from moderate climates at 10 to 25C. The experiments were run
25 for from 2 to 4 weeks. During this period the plants were tended and their
reactions to the various treatments assessed. The assessment scale was 0
to 100, 100 denoting nonemergence or complete destruction of at least the
visible plant parts, and 0 denoting no damage or normal growth.
The plants used in the experiments were Cassia tora, Chenopodium album,Chrysanthemum coronarium, Ipomoea spp., Triticum aestivum and Veronica
spp .
35 Active ingredients nos. 1.001~ 1.003, 1.004, 1.009~ 1~010~ 1.011~ 3.002
3. 005 and 3. 024, applied postemergence at a rate of 1.0 kg/ha, provide
excellent control of unwanted broadleaved plants. Compounds nos. 1.001~
1.003 and 1.00~ are also tolerated by wheat. Compound no. 3~005 is excel-
lently tolerated by Indian corn.