Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
This invention relates to a process for the protection
of a fat or a food, cosmetic or pharmaceu~ical product con-
taining a fat against oxidation and to the use of coenzyme
Q as an antioxidant in a food, cosmetic or pharmaceutical
product containing a fat.
It is known that the coenzyme Q ~CoQ3, or ubiquinone,
which has been isolated ~rom the lipids of mitochondria,
is involved in the basic mechanisms of energy production by
respiration, in the transport of electrons in mitochondria
lo and in oxidative phosphorylation. Its antioxidant activity
in biological media i5 known, cf. for example Littarru et
al., Fats and Perspectives, Drugs exptl. clin. Res. X (7),
491-496. However, in a different environment, such as a
food, cosmetic or pharmaceutical product cvntaining lipids,
the oxidized form, namely quinone, could be expected to
have no antioxidant activity because quinones are normally
considered to be deactivation products of antioxidants of
the hydroquinone type.
It has now unexpectedly been found ~hat ubi-
quinone in its quinone form has a significant antioxidantactivity in food, cosmetic or pharmaceutical products
containing lipids, more particularly in oils rich in
polyunsaturated fatty acids.
The process according to the invention is charac-
Z5 terized in that an ef~ective quantity of coenzyme Q isincorporated in the fat or in the food, cosmetic or pharma-
ceutical product.
In the context of the invention, the tenm llfood
product" is to be understood in a broad sense encompassing
products intended for human or animal consumption providing
~ they contain lipids susceptible to oxidation. Similarly,
a cosmetic or pharmaceutical product is to be understood in
a broad sense intended for topical application or for oral,
enteral or parenteral administration providing the product
in question c~ntains lipids susceptible to oxidation.
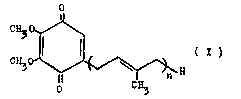
According to the invention, CoQ is understood to be a
~7~
quinone derivative corresponding to the following formula
C~O~
~ ~ H t I )
in which n = 6-10. The compound CoQ10, in which n = 10, is
preferred because it is the most common and, at present, is
the only industrially available derivative.
In the process or the use according to the invention,
the CoQ is incorporated in the lipid phase of the food,
comsetic or pharmaceutical product in a quantity of 0.1 to
5% by weight, based on the lipids present in the product.
If less than 0.1% is added or used, there is a risk that
the lipids of the product in question might not be ade-
quately protected. If more than 5% is added or used, the
level of protection obtained is not significantly greater
than can be obtained by adding quantities in the range
indicated.
In one preferred embodiment of the process according
to the invention, the CoQ, which is lipo~oluble, is used in
admixture with other antioxidants capable of producing a
synergistic effect, for example water-soluble ascorbic acid
(AA), in the presence of a natural emulsifier.
In the context of the invention, a "natural emulsi-
fier" is understood to be any of the naturally occurring
nonionic surfactants, for example saponins, or ionic
surfactants, for example phospholipids, of animal or
vegetable origin of milk, egg or soya ,. preferably lecithins,
for example commercial le.cithins, purified lecithins, soya
lecithin fractions. The nature of the emulsifier used has
only a secondary effect on the effect observed providing it
is capable of forming a stable dispersion of AA in an anhy-
2 ~ 7 7
drous product, for example a fat or a food containing a fat
or a cosmetic or pharmaceutical product containing a
fat. It is preferred to use soya lecithins or fractions
thereof which are abundant and economical.
The preferred antioxidant mixture suitable fox use in
accordance with the invention advantageously contains 2.5
to 10~ and preferably around 5~ of CoQ and 2.5 to 20% and
preferably 5 to 20% of AA, based on the weight of natural
emulsifier.
It is of course possible to use the mixture as such or
to incorporate the various components of the mixture sepa-
rately from the fat to be protected. In cases where, for
example, the fat is a vegetable oil already naturally
containining lecithin (LC), for example soybean oil, it is
sufficient to add the CoQ and the AA in effective quan-
tities.
In one advantageous embodiment of the preferred
variant described above, the mixture is prepared by combin-
ing LC and CoQ with stirring at a temperature below or
equal to 60C, preferably while an inert gas, for example
nitrogen, is bubbled through. The AA dissolved in a polar
solvent, preferably of low boiling point, for example
ethanol, is then progressively added to this premix, after
which the solvent is eliminated at a temperature of 60C,
for example in a light vacuum. The mixture obtained is in
the form of a transparent and viscous liquid. It may be
used in different ways, for example by incorporation in a
fat to be protected, preferably with heating, the mixture
being at approximately 60C, with vigorous stirring.
In another advantageous embodiment of the preferred
variant described above, the AA and the CoQ are incorpo-
rated in the fat to which the lecithin has previously been
added, preferably in the form of a solution in a polar
solvent, for example ethyl alcohol, after which the solvent
is eliminated.
2 ~ iJ ~
The fats to be protected in accordance with the inven-
tion are preferably those most sensitive to oxidation, for
example fats rich in unsaturated, particularly polyunsatu-
rated, fatty acids, such as vegetable oils, for example
wheat germ oil, grape seed oil, corn oil, soybean oil,
safflower oil, olive oil, evening primrose oil, borage oil
and, in particular, black currant seed oil. Animal fats
susceptible to oxidation include chicken fat, butter oil,
oils of marine animals, particularly fish oil.
The foods, cosmetic products or pharmaceutical prod-
ucts to be protected are preferably those containing such
fats.
The invention is illustrated by the following Examples
in which percentages and parts are by weight, unless
otherwise indicated.
~xample 1
Preparation of samples
Samples of 20 g oil stabilized by addition of ubi-
quinone CoQ10 (formula I, n = 10) in the quantity indicated
are prepared and mixed while stirring, after which the
samples are placed in lacquered, sterilized 200 ml tinplate
cans in a quantity of 0.5 g stabilized oil per hatch per
can. The cans are hermetically sealed and stored at 37C.
Accelerated oxidation test
The head space of the cans containing the samples are
analyzed after a certain time (in days) by d,eterminin~ the
contents of pentane and ethane as the respective degrada-
tion products of linoleic and ~-linolenic acid by oxidation
and also the residual oxvgen content. For comparison, the
same analyses are conducted with samples prepared without
2 ~ 7 ~
antioxidant. The pentane and ~thane contents are deter-
mined by gas-phase chromatography while the oxygen content
is determined by measurement of the paramagnetic suscep-
tibility.
The results of this test are set out in Tables 1 and
2 below.
2 ~ 7
~D
~ r-l ~ .
O o\O O ~ r-l O O OO 1~ O
O r~
rt
O O
a) O r l 11) r-l
j: r~
r-l ~ ~r ~) r;
O r-l O
~I r-l r-l
O O Q) O
r l r-l ~ r-l
a) . . ~ .
Pl t~) d' P~ r-l
~4 N 1~ U~ ~ -
O o~ O l~t r-l O :~ O O r-l ~ O
O
CO I I I ~' I I
O O O OO
a) ID O r-l r-l r1 0 a) r-( r-l
r~
r~ ~ ~ r-~ r~
r~ ,C Z ~ D ~ r~ ~ I O O
r; ~ N r;ID ~ r;r;
O
r-l ~ Or-l
O r-l ~ r~
O a) O r-l I O O ~L) OO
r-l I O
~ o .. o ~
r-lt~ C~) r~ I ~r-l
. . ~ .. . ~1
t`I`
~1
~ ~In ~D ~ ~ r~
O o~r-l ~I r-l r l OO d'r-l O
r-lr-l ~ O OO r~
r~lrl r-l r I r-lr~
ta
O O O O OO Q)
~1) r-l r-l r1 r1 a) r-l r-l C)
o
a5a~CO tn ~ r-lr~ Ql
tn r-l ~ X IU)
~ t~ ~tn ~
~ ~ o o a~
r~ 1 r-l r~r-l ~
r-l I I Ir-l -~1
~3 o I o o ~ oI ,q
~:r-l O r l r~ r-l0 ~1
r-l ~ ~1 IL)
n t~ ~ ~ ~
~: X t~ ~ ~ tn :: X I ~`1 ~ I
O O ~
r-l r-1 0
Or-l r-l r-l O ~Ir~ r-l
C,~Ot 01 O~ O~Ot C~
O OO ~ OO O O
r l r U U \ UC.) U U3
r-l r l ~ 0\ \~ 5-~ o\o\ .
o a) o r-~ tn~ ,a O ~ O,~
~ r-l ~ ~ ~ R~~ ~1 ~ ~ ~
r ~~) O U~ ~ ~) ~ ~ ~ O
/~1 .~ r~ rl ~ .rl r~ .rl O (D
E-l 1~ Ul 3 3 3 3 _ ~ tn
~2 1~7i7
r~
.
o o~o o o o o:~
In I u~
~ o
x
~ o
a) ~ ,
~-1 0
Q)aJ o
o
a) u~
~ o ~o
.~l o'
~ o ~~
~ c~
o o o o o l
~ ~ vc)
~ ~ . o\o o\o ,~
o a) o
~ ~ o ~ ~
R ~ 3 ~ ~ ~ ~ O
~ ~ U) 3 ~:3 3 --
2 ~ ~ ~ 6 7 ~
o o o ~ o
oo ~
o o
,. .
~ ~ In ~
. ~ ~ , .. ..
CO ~
o o
,. ..
X
o , ~ ~ o~
,.. .. . . ..
o o o Ul ~
Q~ O ~ ~ ~ ~ O
,I r ~ ~ o~ ~
. . . . o o
N ~d ' ~ (U
'I -I E3 ~: . .
~1 0 ~ 0~ ~1 0 ~ U~ t`
O I O O ~
O a) o o ~-1
X
~d ~ o
o ~
` ! I O O ~1 . ~ ~1 ~ ~1
O o ~
I O C~ O Ul
, c~ ~1 a) o_I ~1 ~1 0
O
r~ X
O ~ O ~
~d ~1 o
J~ ~ ~1 a~ o ~ c~ Q)
X ~' o I I o o
~ Q ~1 ~1
Q) ^ a~
o o
o ~ o olo o C:) O O
O ~ 1 ~ 0~Ir l
O O~:) O o o O
O Q~ O ~1In~ ~ O a~ o ~
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ s ~ ~
RUl ~3 ~ ~ ~ ~ O M E~ ~ ~ ~ ~I t~
E-~ 1~ 3 3 3 ~ 3 3
~ a 2 i~
?
~ .
U~ o o~ o O ~ O :~
,~
~a
o
a
O C~
Q~ 1:4 In
~ o
.~ ~ o o o
O ~ ,~
O ~ 01 0~
O o o o O
U ~\o
,1 ~
o\ o\O .
O q) o ,~
,1 o
~ ~ ,~
E~ e4 ~ ~ 3
2 ~ 2 ! ~ 6 7 7
The above results clearly demonstrate the antioxidant
activity of CoQ10 in fish oil and black currant seed oil by
comparison with the same oils without CoQ10.
Example 2
The procedure described in Example l is again used to
measure the pentane, ethane and oxygen contents of the head
space of 200 ml cans containing 0.5 g fish oil stabilized
with
2.1 0.1% CoQ10
2.2 0.1% CoQ10 and 1% purified soya lecithin (Topcithin~,
LC)
2.3 0.1% CoQ10, 1% Topcithin~ and l,oO0 ppm (parts per
million) ascorbic acid (AA)
and stored at 37C for the period indicated (days).
The pentane, ethane and oxygen contents of the head
space of the cans containing the fish oil without stabili-
zer (Cl), with 1,000 ppm AA (C2) and finally with l,000 ppm
AA + 1% LC (C3) are determined for comparison.
The results obtained are shown in Table 3 below.
2 ~ 7 ~
o o~o o o oo o o o
o
~r ~ ~ I i .
.
a~ o
,,
~ X
P~ ,,
N ~r
U~
In .
o
C~
I I I CO CO
~n oo ~ olo
o
In o co 1`
. . . . . .
CO ~ o o
~3 o~I o
~1 '1 'I ~I'~
I I r~ ~I
oo ~ o o I la
~I ~I ~~ ~ o
I I
~ ~ O ~D O ~
O ~ . . . . . ..,1
~n
o 0\o ~ ~ ~I ~ ~I ~I ~
~I ~I ~ o ~( ~l
o Ul
~1 ~n
o o o o o I a
~I ~I~I o
. . . . . ,~ ~e
o L~
.
w a~ ~ ~~1 ~ O
~ ~l
a) o o o o
~l ~ ~l ~l ~l o s~
~ x ~ ~ u~ o ~l co
a) ......
;. ~
o a~
~ u~
~ ~1 ,a ~1
E~ ~ ~~ ~ U C~ U
12 2~ 7
The above results clearly show that the combination of
CoQ1O, AA and LC in the quantities used affords fish oil
effective protection against oxidation, even after storage
for 41 days, whereas without stabilizer (C1) fish oil
oxidizes rapidly from the 12th day. In addition, the use
of AA alone (C2) or in admixture with LC (C3) no longer
affords fish oil protection against oxidation from the l9th
day.