Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
203~423
Fl~BRXC DUCT SYSTEM USING SEGMENTS WITH COUPLING MEANS
B~CKG~OUND OF TI~E INVENTION
This invention relates to flexible air ducts used in temporary
or semi-permanent air distribution. In particular, it concerns
flexible lightweight ducts used for distributing air, either
heated, cooled, or ambient, to buildings which have such a
requirement for air, including su~h structures as buildings under
construction, temporary ~helter areas, greenhouses, and the like.
It is also an eEficiellt means of distributing fresh air to areas
previously difficult to ventilate, such as mine shafts and
manholes. Similarly, these ducts can be used to exhaust
contaminated air, providing a safer working environment.
Even in northern climates, building construction is an
- activity which, in spite of limitations caused by harsh weather, is
no longer seasonal. Previously, once winter arrived, many
construction activities were halted.
Currently, buildings under construction are temporarily
enclosed using polyethylene or other similar materials, and heated
to a temperature that allows construction to continue. Maintaining
consistent temperatures is critical to the protection of materials
previously installed, and is essential in the curing and finishing
of materials during installation.
The building's permanent heating system is rarely available
for use in the construction stages, therefore temporary heating
units are installed and the tempered air is discharged into the
enclosure. This procedure does not allow for even distribution of
the tempered air. The expense of manufacturing, installing, and
removing shest metal duct work is too great to be cost effective on
a short-term or longer-term basis. Among the advantages of the
flexible air ducts of the present invention are ease of
-- 1 --
203~23
installation and removal, and durability. The ducts are effective
for temporary and/or semi-permanent installations, such as
installations with a lifetime of up to approximately ten years.
Air conditioners are frequently required on a temporary basis
in the event of permanent system failure or system revisions.
Further, auditoriums needing cooling or ventilation often lack an
air conditioning system. Additionally, show tents and other
temporary shelter areas often require ventilating and/or cooling.
To achieve these results, temporary air conditioning units ar~
often installed outside the structure and the tempered air is
ducted, using sheet metal ducts. Here, as with the heating system,
the sheet metal duct is expensive to manufacture, install and
remove on a short-term or temporary basis.
SUMM~RY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention reveals a temporary duct system that is
lightweight, low cost and easy to install and remove. This
invention will combine the advantages of a permanent heating,
ventilating, or cooling system, with the advantages of a portable
heating equipment, fans or cooling units in the transfer and
distribution of air. The system should prove especially beneficial
in the non-permanent air handling business, where either air
conditioners or heating units are employed on a short-term basis.
The flexible air duct system of the present invention provide
significant advantages over tubular polyethylene or the like,
particularly due to the light weight of the present ducts, with the
light weight being combined with durability during use.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
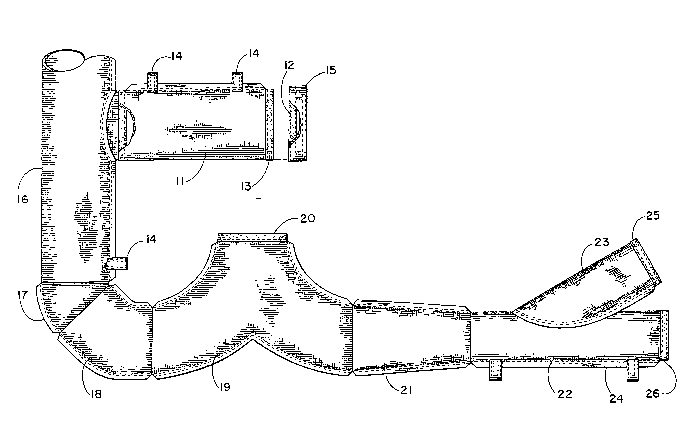
Figure 1 is an elevational view of all components which are
normally needed for use in connection with the present invention;
and
2~31~23
Figure 2 is a perspective cutaway view of the basic duct work
employed in the present invention.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
Referring to the drawings, the duct work is made up of a
series of one or more of the components depicted in Figure l.
These components are all composed of a woven Dacron~ polyester or
other suitable scrim-reinforced plastic film material. Dacron~
polvester is advantageous because of its strength, tear-resistance,
fle~ibility, and light weight. Figure 2 is a cutaway view of the
basic component ll utilizing the hook 12 and loop 13 fastening
system. Included are fabric support rings 14 for use in installing
the system. The most common method of installation is to suspend
the system from the ceiling.
A continuous, uninterrupted strip of the hook portion and loop
portion of a hook and loop fastening system (Velcro~) is employed,
the width being 1" for low static pressures and 2" for higher
pressures. This strip is secured flush to the inner and outer
surfaces of the cylinder member being joined. It has been found
that this magnitude of hook and loop fastening systems produce
desirable results in both allowing quick assembly and disassembly
of the duct work as well as a relatively air-tight seal at the
coupling sites. These joints are durable, and highly effective in
arranging an air-tight seal.
Referring to Figure 1, it can be seen that this invention is
composed of several different types of fittings. Virtually any
configuration can be assembled using these fittings to meet
construction needs. For even distribution, holes can be cut in the
straight sections of duct, allowing air to discharge uniformly. An
end cap 15 is available for maintaining back pressure, keeping the
duct system inflated, or for otherwise temporarily capping a line.
2031~23
This end cap is also effective in cutting off a supply of air that
is no longer needed. This concept can be perceived by noting
component 19, utilized when the user wishes to have the option of
branching a duct for distributing air to two separate areas. If
either branch of this "Y" component is no longer needed, an end cap
15 is used to stop the flow of air to the area no longer in use.
Components 17 and 18 are elbow-forming ducts used to provide
smooth, even air flow around corners or obstacles. As previously
stated, the most common method of installation is to suspend this
system from the ceiling. These components are also used to move
the air flow from ground level (at air handling unit) to the
ceiling, where the duct system will be suspended. Also, these
elbow-forming components fur~her reduce static pressure by allowing
air to flow effortlessly around corners, maintaining the blower
velocity of the air flow.
Furthermore, the duct work of the present invention possesses
substantial flow advantages over the wire-wound plastic tubing.
~he wire-wound material provides a series of rib-like depressions
which function on a cumulative basis to increase the pressure drop.
The lines of the present invention provide a much smoother interior
for flow purposes. Additionally, it will be noted from the views
that the flow direc-tion i5 arranged to flow from the female
connector to the male connector, providing further reduction of
discontinuous surfaces.
2~ Component 21 is a reducing fitting which gradually narrows.
This is generally used a-t the air handling unit to transition from
the square discharge of the air handling unit itself to a diameter
sufficient to meet the air handling needs.
The arrangement of the present invention provides for the
production o long and short elbows, reducers, and a large number
'2 ~ 2 ~
of other fittings. The material, particularly scrim-reinforced
Dacro~ polyester is durable, and is also washable. Typical
running lengths of straight sections of duct are 5' to 30', with
the light weight and ease of attachment providing for the overall
ease of installation. Also, the light weight characteristic of the
product renders it possible to utilize the support rings 14-14
which attach and/or are otherwise ~oined to the external surface of
the duct. For systems employing tubular polyethylene or the like,
the weight of the product renders it normally necessary to provide
a support ring which extends around the entire perimeter of the
tubular material.
The above described components, coupled with straight
sections, enable various configurations to be constructed and/or
modified simply and efficiently. It is to be understood that this
i~ for illustration purposes only and should not be limited
thereto, but only to the scope of the following claims.
What is claimed is: