Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
A 7453
.
55~
Metallgesellschaft AG February 209 1990
Reuterweg 14
6000 Frankfurt on-Main 1
Case No. 890030
Method for the Automatic Control of the Rate of Supply
of Oxygen to a Claus ~'rocess Plan-t
. .
DESCRI~ION
~his invention relates to a method for.-
operatin~ a
plant for producing elemen,tary sulfur in
a process in which an H2s-containing feed gas i5 partly
combusted with an oxygen-containin~ gas in a combustion ~ :
: chamber of a Claus process plant and a gas mixture that !~
oonta1ns H25 and S02 is~thus produced, from which elemen-
tarD sulfur is produced by a reaction of H2S with S02 and
: is separated, wherein the reactio~ of the gas mixture
coming from the combustion chamber is effected in one or
more catalytic processing ska~es and optionally in after- :.
....
treatinPi meansO .:
: In laus proce~s pl~nts~ a 6as which contains
:
; H2S is converted in known manner -to a mixture of H2S and
2 gase~ by a partial combustion and eleme~tary sulfur
~: :
~ .
:
.
:
~ : ~ .,, :
; '
-2- 2 ~ 3 ~
is produced from that mixture in accordance with the
simplified reaction equation 2 H2S + SO2 = 3 S ~ 2
H20. Details of the process have been described in
Published German Application 34 15 722 and the corres-
ponding U.S. Patent 4,632,819 and in Ullmanns Encyklopa-
die der technischen Chemie, 4~h edition (1982), volume 21,
on pages 8-26. The catalysts employed in th~ catalytic
processing stages of the Claus process plant usually
consist substantially of alumina or titanium dioxide.
The gas mixture coming from the Claus process plant is
usually subjected to an aftertreatment by which the con-
tents of sulfur compounds, particularly of H2S and SO2,
in the gas mixture are decreased further. In known after-
trea~ing processes, elementary sulfur is formed by the
reaction of H2S with SO2 or 2 on catalysts which also
consist substantially of A1203 or TiO~. The gas mixture
obtained by the aftertreatment contains residual H2S and
52 in a total of about 500 to 1500 ppm. That gas may be
combusted and then discharged into the atmosphere.
It is an object of the invention to
effect an automatic control of the rate of supply of oxygen
to the combustion chamber of the Claus process plant with
sufficient accuracy and in a manner which is as simple as
possible. In the process described first hereinbefore
this is accomplished in accordance with the invention in
that the concentrations K and P of H2S and SO2 in the ~as
. , .
~mixture are measured upstream or downstream of one of the
catalytic processing stages or upstream or downstream of
the after-
- - ~
2 ~ 3 ~
--3--
treating means or in such aftertreating meansi, the rate
of feed ga~ flowin~ to the combustion chamber and the
rate of supply of the oxygen-contâinin., ~,~s to the com-
bustion chamber ~re me~suredt the results of said
measurements are indicated -to a controller and u~ed to
calculate the correction rate by which the rate of oxy-
gen-ccntaining gas must be corrected ~o adjust the
dif erence D- ~ - a -~ P to zero, ~,vherein a is !~ factor
that is specific to the process and lies between 0.1
and 10, and the rate of supply of oxygen-containing gas !;
to the co~bustion ~hamber is changed by the correction
rateO : '
~ ccordi~g to a further feature of the
invention the stream OI~ oxygen-contair.ing gaS supplied
to the combustion chamber is formed from a main stream
and a supplemen~al stream, the rates of the main stream
and of the supplemental stream are au~cmatically con- ~ :
trolled in dependence on the measurement of the rate of
the feed gas~ and the xa-te of the supplemsntal stream
is increased or decreased by the calculated correction
rateO
~he correction rate L (in sm3/h, ~here :
sm3 is standard cubic meter) of the oxygen-containing
gas is preferably calculated in a¢cordance with the
formula :~
~'
. , .
. '
5 ~
wherein
V = a factor that is speclfic to the process ~nd
lies between 0~01 and 2.0,
D = the concentra-tion diffelence ~L ~ a x P, me~sured
in mole percent,
E = rate of feed ~as measured in sm~/h,
= percentage (in mole percent) of oxygen in the
oxygen containing ~as,
M = total rate (measured in sm3/h) of supply of the
oxygen-containing gas to the combustion chamber.
The factor a which is specific to
the process and i~uded in tne difference ~ = I`L ~ a x P
is determined by the desired ratio a = K/P of ths concen-
. .
trations o~ H2S and S02 in the gas flowin~ through the
;~analyzer for mea~urlng~the concentrations, i.e~, bythat value o~ that ratlo which is regarded as an optimum.
AS a result, the fq~r a will depend on the ~reatment
which succeeds the conce~tration measurement. If it is
deslred to react H28 a~d S02 bv the reaction S02 ~
~ H2S to elementary sulfur also after the concentration
a~nalysis5 a~will be 2~ The fa~tor V whLch is speci~7ic
to the~process i~ determined by ~ trial operation of the
plantO If the oxggen-con~aining gas ;Fed to the combustion
hamber oons~i9t8 of pure air, S will be 21. If pure
` oxygen is used~or the combustion in the combustion
chamber, S will be lO0.
, : : :
:: :
. 2~35~4
Detail~ of the automatic control in ac-
cordance with the invention ~i.ll be ex~ained with
reference to the illustrative embodiment of the process
shown on the drawing~
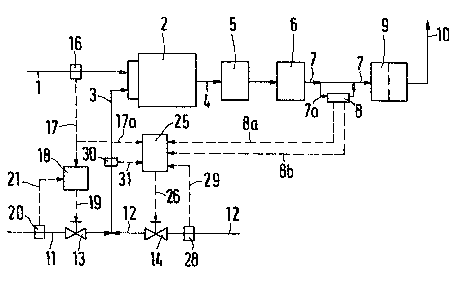
The H2S-containing feed gas which is to
be desulfurized is ~ed in line 1 to the combustion
chamber 2 of a alaus process plantO Oxygen-containing
gas is supplièd in line 3. '~he Claus process plant usu-
ally comprises a plurallty of catalytic processi~g sta-
ges, in which elementary sulfur is produced in accord- -.
ance with the (simplified) reaction equation 2 H2S ~
S2 = 3 S + 2 H20 from the gas mixture coming in line
4 from the combustion chamber 2. ~he sulfur i9 separated
in a known manner, whlch is not shown hereO The drawing
shows two catalytic ~rocessin~ stages 5 and 60 Part o~
the~elemen-tary sulfur Qay have been separated before the .`
catalytic stages by condensation from the gas mi~tuxe .. `:
coming from the combustion chamber 2. That ~as mixture
flows -through the catalytlc processing stages 5 and 6
and then flows in line 7 to an analyzer 8, ~Jhich is incor- ` :
,
porated in a branch line 7aO
he analyzer 8 detects the concentrations
K and P of H2S and SO2 in the arrivi~ gas mixture, which :
is subseque~tly fed to the aftertreating means 9. In the
aftertreating means the content o~ sulfur compounds in
: ~: the~6as mixture is further decreased. The aftertreatment
.
2 L3 3 ~
is not required in all cases and may be effected in
known manner and in a plur~lity of parts or in a plula-
lity of stages. The gas mixture is subsequently passed
through afterburning means and is then discharged
through a chimney 10 into the atmosphere.
il'he oxygen-containin~ ~as in line 3 is
formed from a main stream supp~Lied in line 11 and of a
supplemental stream supi)lied in line 12 and consisting
of that ga;. ~he rates of said streams are
cont~led by the flo~l control valves 1~ and 14. 'rO con-
trol the rate of the maln stream in line 11, the rate of
the feed gas in line 1 is measured b~ the flow meter ~
16 and -the rate signal is delivered via the signal line ~:
17 to a firs~ controller 18, w~lich acts on the flow
oontrol valve 13 via the signal line 19. The same ra~e
signal is delivered via à signal line 17a to a second
controller 25 for adJusting the rate of the supplemental
: stream of oxygen~containin; gas by means of the ~low
c:ontrol valve 140 ~he flow meter 20 in line 11 indicates
: ~ via the signal line 21 to the controller 18 the actual
flow rate in line ll.
'l'he rate of the main stream of ~he
oxygen-containing g~ fad to the combustion chamber 2 is
~::
co~trolled by means of the first controller 18. The
secorld controller 25 serves also to e~ctly adjust the
:~rate of supI)ly of oxygen to the combustion chamber 2 to
- ,
:~ , ' '
'~:
: ~ "
2 ~ 5
~7--
the required value by a change of the rate of the
supplementary s-tream comin from line 120 ~he control-
ler 25 influences via the si~nal line 26 the flow
control valve 14. In order -to determine the correction
rate L by which the rate of the supplemental stream
of oxygen~containing gas is to be chan~ed~ t~ correct- -
ion rate ~ is calculated in the controller 25 i~ accord-
ance with the formula
~ = D
S . .
The various parameters of said formula have been ex-
plained hereinbefore. For the calculation of the cor-
rection rate ~ the second controller 25 receives from
the analyzer 8 via the signal li~e 8a the co~centration
K of H2S and via the signal line 8~ the concen~ration -
, . .~
P of S02 in the gas mixture which flo~ through -the
anaIyzer. The -to~al rate ~i of oxygen-containing gas
flowing in line 3 to the combustion chamber 2 is de-
:~ ~te~mined by the meter 30 and the measured value is indi-
cated via the signal line 31 to the controller 25, ~he
flow meter 28 ln line 12 in~icates via the signal line
29~ to the oontroller 25 the rate at wbich oxygen-contain-
ing g~s actually Elows through line 12
In a modification of the example illus-
trated on the drawing the analy~er ~ :Eor measuring the
~ ,
concentrations of H2~ and S02 in the gas mixture may be
~arranged at different locations. ~he concentrations may
,, ,
::, ~: : ' ''
~al3~
be analyzed upstream or do~vns-tream of any of ~he
catalytic processin~ stages 5, 6 and upstr~am or
downstream of a processin~ s~age which oelon~s to the
aftertreatin~ means 9 or in such stage~ In -the embodi-
ment of the process which is shown in the drawing the
analyzer 8 is provided downstxeam of the last catalytic
stage 6 of the Claus process I~lantO
.~xample
In a processing s~stem as shown on the
drawing, an H2S-containing feed ~a~ composed of
H2S 7' mole ,'0
H2o 5.7 mole ,6
~2 23.3 mole ~0 .
2H6 3r~0 mole ,~ -
is fed at a rate of 8520~sm3/h to the combustion chamber
2 and is partly combusted therein with air supplied
from~line 3 at a ra-te o~ 13793C:sm3/h. A main stream
of th~ air is supplie:d at a rate of 12,510 sm3~h f~om
: ~ . r
: ~ : line 11 and a supplemental stream is supplied at a r~te
of 1420 sm~/h from line 12. The Claus process plant con-
tains arl A1203 catalyst in t~ro catal~tic sta~es 5 and 60
: Th~ analyzer 8 measures an H2S concentration I; of 0084
: mole percent: aDd an S0z concentratio~ P of 0.42 mole
percentr. ~he desired value a:of the ratio K/~ is 2.00
~: ~ '.'
: ` ~
: ~ ; ~: :
., . . , . . . ..... , , - :: ; .: . . .
cj ,~
~ fter a ch~n~e of the concentratiion o~'
H2S in the feed gas in J.ine 1 to 72 mole ~ercent, the ana-
lyzer 8 will detect v.alues of E~ = 1049 mole percent and
P - 0,32 mole percent. From a factor a = 2, S = 21 and
a factor V = 0.412, which has been determined by a trial ::
operation, ~he controller 25 calculates the correction
rate of air as ~ollows: ~
L = -Zl- (0.412 x 13,930 ~ 0.5 x 8520) = 404 sm3/h. ..
'~''
3~ an adjustment of the flow control valve
14 the rate of air flowing in lines 12 and 3 is increased
by that rate. .~s a result, an H2S concentration of 0~84
mole percent and an S02 concentration of 0~418 mole per-
cent are rees~ablished in line 7 so that the desired
ratio a = K~P = 2 is approxi~ated with ~ufficient accuracyD
The aftertreatment in 9 is pexformed by
the Sulfreen ~rocess of Lurgi GmbH in Frankfurt on an
A1203 catalyst by a re~ction of 2 H2S ~ S02 to 2 H2S +
3 SxO 600 p~m H2S and 300 ~rJm S02 are still found in the
aft;ertreated gas. ~uel gas and air are added to~at gas,
w~ich is then combusted and discharged into the atmos- .
phere O
, .
:: :
,~.',
; '
,.';
~ '
. .
, . . . , ,, . " , ...