Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02036903 2000-O1-25
- 1 -
Method and apparatus for setting a wire in a plastic film
10
The present invention relates to apparatus for setting a wire in
waveform in contact with a plastic film applied on a base structure.
The present invention is particularly useful in the production of
heatable laminated glass, wherein a plastic film or an intermediate film,
fitted with waveformed wires, is typically laminated between glass sheets,
the assembly being intended for use e.g. as a motor vehicle windscreen.
Methods for setting a wire in a plastic film used particularly as an
intermediate film in laminated glass are prior disclosed e.g. publications
GB 1,392,736 and US 3,522,651. In the method described in publication GB
1,392,736, the simultaneous heat-assisted setting of a plurality of wires
on a plastic film travelling horizontally on a base structure is carried
out by means of an eccentric-controlled guide rod, which is in a transverse
reciprocating motion relative to the plastic film advancing direction.
During said reciprocating motion, the guide rod creates a waveform in the
wires running through a set of grooves formed in the guide rod. Setting
the wires in a desired waveform on the surface of a plastic film is
effected by means of a press roll, located downstream of the guide rod in
the plastic film advancing direction and having the same width as the
plastic film. In order to set the wires permanently in a plastic film, the
cited publication further discloses a number of different heating
variations either for wires, a press roll or a plastic film. The
publication US 3,522,651 discloses a method, wherein a rotating frame
assembly is fitted with resistance wires adjacent to each other. At the
following stage of the method, the wires carried by said frame assembly are
all waved in a single operation by means of a cylindrical toothed roller.
At the following separate operating stage, the waved wires removed from
said frame assembly are secured to a glass surface by means of a sprayable
chemical.
A useful wire is characterized by being thin and prone to breaking
as well as inconvenient to handle. Therefore, in a method disclosed in the
CA 02036903 2000-O1-25
_ 2 _
publication GB 1,392,736, the simultaneous handling of a plurality of wires
leads to a number of practical problems. For example, breaking of an
individual wire or its running out on a particular supply reel is difficult
to notice. The wires must be synchronized and arranged according to the
width and/or desired resistance characteristics of a plastic film in each
individual production series. Thus, the application of the above-described
method requires considerable preliminary work and continuous monitoring
during the manufacturing process. An apparatus used in the method
disclosed in the publication US 3,522,651 requires a lot of space
particularly due to independent stages of operation. It is of course
obvious that production involving several stages of operation is not
efficient. The manufacture of high-quality laminated glasses with the
technique described in the cited publication is very tedious and
inconvenient. Particularly due to the spraying of a chemical agent, the
method also involves environmental hazards and, thus, application of the
method requires labour protective measures.
An object of a method and apparatus here described is to provide a
decisive improvement on the above drawbacks and, thus, to advance the
2o available prior art.
The most important benefits gained by a method herein include
simplicity and operating reliability since a wire is set in a plastic film
in a single operation, the progress of which can be readily monitored. An
apparatus for the application of this method requires very little space
indeed, and yet the obtainable productive capacity is of the same order or
even better than what is achieved by the prior art methods.
By using an apparatus disclosed it is possible in a simple and
reliable manner to set a wire in a waveform in contact with a plastic film,
said plastic film being particularly intended for use as an intermediate
film in laminated glass.
CA 02036903 2000-O1-25
-3-
In accordance with the invention there is provided an apparatus for setting a
wire in contact
with a plastic film comprising a base block, a base structure receiving the
plastic film to be provided
with the wire, said base structure comprising an endless surface rotatable
about a centre axis of an
axle assembly, first elements comprising a gear assembly for creating a
waveform in the wire, the
waveform being produced by means of said gear assembly by working the wire
mechanically into a
waveform defined by a cross-sectional shape of the gear assembly, a second
element for setting the
wire in waveform into and in contact with the plastic film, means for shifting
said first and second
elements and said endless surface relative to each other substantially in the
longitudinal direction of
said axis over that section of the width of the plastic film to be provided
with wire, and means
providing an electric potential difference between said first elements and
said second element for
heating that section of wire between said first and said second elements.
Embodiments of the invention will now be described with reference to the
accompanying
drawing which is a schematic perspective view of one embodiment of an
apparatus embodying the
invention.
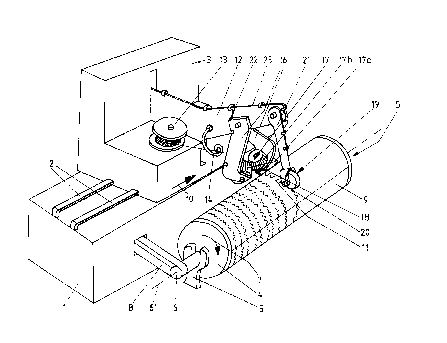
The apparatus illustrated includes a base block 1, set on a fixed
- 4 -
supporting structure, such as a floor, and provided with guides or the like
elements 2 on top of it for carrying a wire supply frame 3 during the
application of this method in the longitudinal direction of guides 2. The
apparatus further includes a cylindrical drum or a cylinder 4 which is
carried by support brackets 5 or the like elements upon axle stubs or the
like 6 projecting from the ends of the drum 4, said brackets being mounted
adjacent to 'base block 1 e.g, on a fixed supporting structure, such as a
floor. The drum has a circular cross-section and axle stubs 6 are located
centrally relative to the cross-section, said drum 4 rotating around the
centre axis 6' of axle stubs 6 extending in the direction of guides 2 and,
thus, in the travelling direction of supply frame 3 (arrow 7). In order to
rotate said drum 4, the base block 1 is provided e.g. with belt drive 8 or
a like driving mechanism to operate at the end of at least one of the axle
stubs 6.
The external surface of drum 4 is provided with a plastic film 9
e.g. by using suitable fastening arrangements, such as providing the drum
with a perforation for creating a vacuum effect to adhere plastic film 9 to
the external surface of drum 4. The vacuum system is not shown in the
drawing as it is obvious to a skilled man. Naturally, it is also possible
to use adhesive fastening.
In the illustrated embodiment, a supply frame 3 travels continuously
in the direction of an arrow 10 from left to right as seen in the drawing,
whereby a waveformed wire 11 coming from the supply frame is set in contact
with plastic film 9 on top of said drum 4.
In the illustrated embodiment, the supply frame 3 is provided with a
carrier arm 12 or a like, which is fitted with elements 17, 19 for giving
said wire 11 a waveform and for setting it in contact with plastic film 9.
The carrier arm 12 is preferably adapted to be movable in vertical
direction whereby, e.g. especially during 'the replacement of drum 4, it can
be turned out of the way and the drum already provided with wires 11 can be
picked up from its position on top of support brackets 5 and another drum 4
to be provided with wires 11 can be placed along with its plastic film 9 to
- 5 -
rest upon support brackets 5 and, if necessary, said supply frame 3 can be
carried to a starting position at either end of drum 4.
The supply frame 3 is provided with a wire spool 13 or a like wire
supply from which wire is passed by means of a guiding element 14 mounted
on carrier arm 12 to said elements 17 giving the wire a waveform. In the
drawing, said elements 17 for creating a waveform include a gear system
carried by an auxiliary frame lb fitted in connection with carrier arm 12,
said system comprising two mutually meshed gears, e.g, bevel gears, the
line of contact therebetween being substantially perpendicular to the
surface of drLUn 4, whereby the waveformed wire emerges from between the
gears in a manner that the waveform extend in the direction of the surface
of drum 4. Gears 17a, 17b receive their driving power e.g. from a driving
mechanism 18, which is common to both gears and mounted in contact with
auxiliary frame 16. A particularly preferred arrangement is that the gears
receive a driving power directly from the rotating motion of drum 4, the
toothing of at least one of the gears 17a, 17b being in a direct contact
with plastic film 9 on the external surface of drum 4. The element for
setting a wire in contact with plastic film 9 comprises a press roller or a
like 19 receiving its driving force from the rotating motion of drum 4,
said roller being located in alignment with the waveform wire whereby, upon
rotating around its axle 20, said roller presses waveformed wire 11 into
contact with plastic film 9. Press roller 19 is mounted on carrier arm 12
by means of an auxiliary link 21.
Furthermore, the drawing illustrates schematically an electrical
system for heating a resistance wire especially between gear assembly 17
and press roller 19, the setting of a resistance wire on a plastic film
being effected by the application of thermal effect and assisted by press
roller 19. Conductor wires 22 and 23 are connected on the one hand to the
gear assembly and on the other hand to the press roller, both elements
being made of an electrically conducting material. By way of carrier arm
12 said conductors are connected to a current source, e.g. a direct current
source included in supply frame 3, which creates a potential difference
between elements 17 and 19 to effect the heating of waveformed wire 11 as
- 6 -
it travels between said elements 17 and 19 whereby, immediately after
passing said zone, it will arrive within the range of action of press
roller 19 and at this time at least said wire adheres to plastic film 9.
In practice, e.g. one 17a of 'the gears can be made of a metal or a like
electrically conductive material and conductor wire 22 can be connected to
said gear 17a.
It is obvious that the invention is not limited to the above
embodiment but within the basic concept it can be subjected to major
modifications. Firstly, one and the same drum 4 can be simultaneously
provided with two or more wires. Thus, a plurality of carrier arms 12 can
be used in parallel or one carrier arm can be fitted with a plurality of
elements for supplying the wire, creating the waveform and securing the
wire to a plastic film. On the other hand, the base structure carrying
said plastic film 9 can be in the shape of an endless belt or a like web
structure supported by two or more cylinders (e.g. similar to drum 4)
adapted to be rotatable around an axle assembly comprising two or more
parallel axles. Thus, in the annexed claims, the element upon which a
plastic film 9 is laid has been defined as an endless surface. In
addition, the method and apparatus offer extensive possibilities for
variations in view of adjusting the wire density upon a plastic film 9. A
relative adjustment of the travelling speeds of endless belt 4 and supply ,
frame 3 makes it possible to have desired distances from a wire laid in
spiral form on endless surface 4 to the adjacent spirals in a direction
perpendicular to the travelling direction of endless surface 9. It is also
obvious 'that elements 17 arid 19 can be located in fixed positions relative
to base block 1 of the apparatus and to adapt said endless surface G
rnovable in the longitudinal direction of axle assembly 6 during the course
of setting a wire. The above alternatives can also be used simultaneously.
By reversing the travelling direction of endless surface 4 it is possible
to carry out a reciprocating setting of a wire. It is obvious that a wire
can also be set on endless surface in the longitudinal direction of an axle
assembly, said surface 4 being indexed forward in a manner that a new
section of a plastic film to be provided with a wire is located in
alignment with elements 17 and 19.
_ 7 _
When wire 11 has been laid on. an endless surface, a plastic film 9
is ready for use in a laminating operation after being removed. It is
obvious that the replacement of endless surface 4, particularly when using
a drum, can be automated in a simple manner to carry on the operation
continuously for the setting and removal of plastic film 9.