Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent: | (11) CA 2048991 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | FIBRE OPTICAL ICE DETECTOR |
| (54) French Title: | DETECTEUR DE GLACE SUR FIBRES OPTIQUES |
| Status: | Expired and beyond the Period of Reversal |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : | |
| (74) Agent: | |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | 1998-12-29 |
| (22) Filed Date: | 1991-08-12 |
| (41) Open to Public Inspection: | 1993-02-13 |
| Examination requested: | 1991-08-12 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | No |
|---|
| (30) Application Priority Data: | None |
|---|
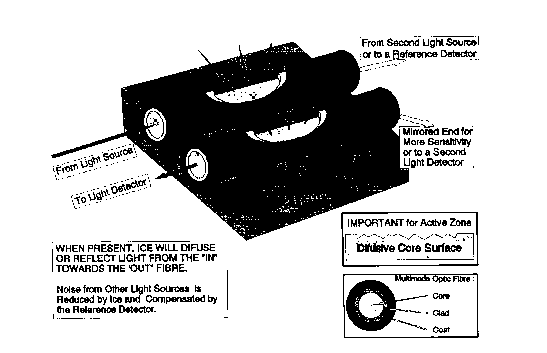
This invention called "Fiber Optical Ice Detector" (FOID)
remotely detects early formation of ice around dedicated optical
fibers on structure surfaces. The fibers may be glued to the
surface, embedded into it in case of composite materials, or
otherwise attached to it. The invention is based on the light
diffusion by ice and light reflection from ice boundaries, that
optically couple multimode optical fibres in specially built
sensitive zones. Such zones may be multiple in order to achieve
sensing distributed along the fibers (rather than at a single
location). Sensitive zones consist of specially profiled cross
sections that amplify the effects involved by allowing most of
the light to be modulated. Thus, the invention makes it possible
to achieve early detection of small quantities of ice at
multiple locations along the fibers. A most widespread use of
this invention is expected in the aircraft industry for remote
detection of ice formation around critical parts - wings.
Cette invention appelée «Détecteur de glace pour fibres optiques» (DGFI) détecte, à distance, la formation de glace autour de fibres optiques spécialisées sur les structures de surface. Les fibres peuvent être collées à la surface, y être enchâssées dans le cas des matériaux composés, ou y être fixées par un autre moyen quelconque. L'invention est fondée sur la diffusion de la lumière par la glace et la réflexion de la lumière à partir des bordures de la glace, qui couplent optiquement des fibres optiques multimodes dans des zones sensibles spécialement construites. Ces zones peuvent être multiples afin de permettre une détection le long des fibres (au lieu d'un endroit unique). Les zones sensibles consistent en des sections transversales spécialement profilées qui amplifient les effets en cause en permettant de moduler la majeure partie de la lumière. L'invention permet ainsi de détecter des petites quantités de glace à plusieurs endroits le long des fibres. On s'attend à ce que l'usage de cette invention devienne répandu dans l'industrie aéronautique pour fins de détection à distance de la présence de glace sur les parties critiques - ailes.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Time Limit for Reversal Expired | 2006-08-14 |
| Inactive: Adhoc Request Documented | 2006-05-15 |
| Letter Sent | 2005-08-12 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2004-03-30 |
| Grant by Issuance | 1998-12-29 |
| Inactive: Final fee received | 1998-08-04 |
| Pre-grant | 1998-08-04 |
| Letter Sent | 1998-06-30 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 1998-06-30 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 1998-06-30 |
| Inactive: Status info is complete as of Log entry date | 1998-06-25 |
| Inactive: Application prosecuted on TS as of Log entry date | 1998-06-25 |
| Inactive: Approved for allowance (AFA) | 1998-05-27 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 1993-02-13 |
| All Requirements for Examination Determined Compliant | 1991-08-12 |
| Request for Examination Requirements Determined Compliant | 1991-08-12 |
There is no abandonment history.
The last payment was received on 1998-07-07
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Please refer to the CIPO Patent Fees web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| MF (application, 6th anniv.) - small | 06 | 1997-08-12 | 1997-08-08 |
| MF (application, 7th anniv.) - small | 07 | 1998-08-12 | 1998-07-07 |
| Final fee - small | 1998-08-04 | ||
| MF (patent, 8th anniv.) - small | 1999-08-12 | 1999-08-09 | |
| MF (patent, 9th anniv.) - small | 2000-08-14 | 2000-08-01 | |
| MF (patent, 10th anniv.) - small | 2001-08-13 | 2001-06-28 | |
| MF (patent, 11th anniv.) - small | 2002-08-12 | 2002-08-02 | |
| MF (patent, 12th anniv.) - small | 2003-08-12 | 2003-07-11 | |
| MF (patent, 13th anniv.) - small | 2004-08-12 | 2004-07-23 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| ALEXANDAR DJORDJEVICH |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| None |