Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~~~~.~~4
1
A c~.s~art~ rtACxaNx
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates to a cabling machine for laying
optofibres, cables or the like in an oscillating wavy path around
a smooth pull-reliever, or down into grooves of oscillating
waveshape that have been extruded around a pull-reliever, so-
called S/Z°cabling, said machine comprising a pull-reliever
reeling-off device, a braking capstan, a fibre/fibres unreeling
device, a S/Z-bench for laying the fibrejfibres around the pull-
reliever, a yarn spinner for fixating the fibre/fibres on the
pull-reliever, and a wheel capstan and a taking-up device for
pulling the pull-reliever through the machine and taking-up the
finished cable, wherein the S/Z-bench includes fibre-laying-on
tube which is provided with a fibre-laying-on head, and wherein
the fibre/fibres passes/pass over the laying-on tube up to and
through holes provided in the laying-on head, where said fibre ox
fibres is or are laid on the pull-reliever and fixated with yarn
taken from the yarn spinner located immediately downstream of the
laying-on heads
BACKGROL7ND ART
Cabling machines for laying optofibres or the like in an oscilla-
ting, wavy path around a smooth pull-reliever are known to the
art. These cabling machines include an S/Z-bench which includes a
laying-on tube or discs which are oscillated backwards and
forwards for the purpose of laying the fibres on the pull-relie-
ver. The fibres, which pass along the laying--on tube to a laying-
on head located on the forward end of said tube, become wound to
a greater or lesser extent around the laying-on tube during
operation of the machine, which causes the fibres to be subjected
to friction forces. These frictional forces will vary in accor-
dance with the rotational movement of the laying-on tube at that
particular moment in time, and when the fibres are wound to a great
extent on the tubs, the frictional forces can be so high as to
damage the fibres.
CA 02051934 2002-06-27
2
Also known to the art are cabling machines which are
intended to lay optofibres or the l_ke in grooves of
oscillating waveform extruded around a pull-reliever.
These machines also include an S/Z-bench provided with a
laying-on tube or discs over which the fibres pass to a
laying-on head. The pull-reliever is pulled rectilinearly
through the laying-on tube and, because of the oscillating
form of the grooves, the tube tends to rotate forwards and
backwards as a result of the fibres being guided down into
the grooves. This rotational movement or twisting of the
laying-on tube will also cause fibres to be wound around
the tube and subjected to frictional forces that are liable
to damage the fibres, similar to the former case.
Thus, the known cabling machines have the disadvantage of
subjecting fibres to large frictional forces with
subsequent risk of damage to the fibres. Furthermore, the
known machines are intended for laying fibres in an
oscillating waveform, so-called S/Z-cabling, solely on one
2o type of pull-reliever, namely either on a smooth pull-
reliever or on a pull-reliever on which grooves have been
pre-extruded.
DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION
An object of the present invention is to provide a cabling
machine which will not subject the fibres to harmful
frictional forces and which can also be readily switched
between modes in which fibres can be laid on both smooth
3o and grooved pull-relievers.
CA 02051934 2002-06-27
2a
More specifically, the present invention provides a cabling
machine for laying a fiber in an oscillating waveform
' around a smooth pull-reliever which i.s travelling i:n a
travelling direction, the machine comprising a pull
s reliever reeling-off device for reeling off a pull
reliever, a braking capstan located downstream from the
pull-reliever reeling-off device with respect to the
travelling direction, a fiber reeling-off device for
reeling off a fiber which is to be laid on the pull-
IO reliever, an S/Z-bench located downstream of the braking
capstan with respect to the travelling direction for laying
the fiber on the pull-reliever, a yarn .spinner for fixating
the fiber on the pull-reliever, and a wheel capstan and a
taking-up device located downstream of the S/Z-bench with
IS respect to the travelling direction for forwardly pulling
and taking-up the finished cable, respectively. The S/Z-
bench includes a laying-on tube provided with a laying-on
head, wherein the fiber passes along the laying-on tube up
to and through a hole in the laying-on head, where the
20 fiber is laid on the pull-reliever and fixated with yarn
supplied from the yarn spinner. The S/Z-bench also
includes an aligning mechanism which grips and guides the
pull-reliever, and a motor and transmission for driving the
aligning mechanism in an oscillatory, rotational movement,
25 the laying-on tube being connected to the transmission such
that an oscillatory, rotational movement is imparted to the
laying-on tube by the transmission in a direction opposite
to the rotational movement of the aligning mechanism, the
fiber reeling-off device being separate from the laying-on
30 tube so that oscillatory rotational movement of the laying-
on tube occurs independent of the fiber reeling-off device,
and a sensor connected to the transmission for controlling
CA 02051934 2002-06-27
2b
operation of the motor and therewith the rotational
movement of the laying-on tube and the aligning mechanism
' so that rotational movement of the laying-on tube is
limited such that winding of the fiber with respect to the
laying-on tube and frictional forces acting on the fiber
are minimized.
The transmission can include two mutually coaxial first
toothed wheels through which the pull-reliever passes, two
l0 mutually parallel second toothed wheels spaced from and
perpendicular to the first toothed wheels, and a toothed
belt which extends in a continuous loop around the first
and second toothed wheels, wherein the aligning mechanism
is connectable to one of the first toothed wheels and the
laying-on tube is connectable to the other of the first
toothed wheels.
The sensor can be an absolute sensor and can be connected
to the transmission via gearing. The motor can be a
reversible stepping motor. The alicJning mechanism can
include a plurality of rollers which engage the pull-
reliever on diametrically opposite .sides thereof. A
banding machine can be positioned up~~tream of the wheel
capstan with respect to the travelling direction. The yarn
spinner can be a double yarn spinner which lays two yarns
in mutually opposite directions. A free length of the
pull-reliever between the bra~.ing capstan and the wheel
capstan can be of sufficient length to enable the pull-
reliever to rotate about its longitudinal axis.
In another embodiment, the present invention provides a
cabling machine for laying a fiber in an oscillating
CA 02051934 2002-06-27
2c
waveform on a pull-reliever which it; travelling in a
travelling direction, the machine comprising a pull-
' reliever reeling-off device for reeling off a pull
reliever, a braking capstan located downstream from the
pull-reliever reeling-off device with respect to the
travelling direction, a fiber reeling-off device for
reeling off a fiber that is to be laid on the pull-
reliever, an S/Z-bench located downstream of the braking
capstan with respect to the travelling direction for laying
l0 the fiber on the pull-reliever, a yarn spinner for fixating
the fiber on the pull-reliever, and a wheel capstan and
taking-up device located downstream of the S/Z-bench with
respect to the travelling direction for forwardly pulling
and taking-up the finished cable. The S/Z-bench includes a
laying-on tube provided with a laying-on head so that the
fiber passes along the laying-on tube up to and through
holes in the laying-on head where the fiber is laid on the
pull-reliever and fixated with yarn from the yarn spinner.
The S/Z-bench also includes a transmission, an aligning
mechanism connected to the transmission so that operation
of the motor effects rotational movement of the aligning
mechanism, and a sensor connected to the transmission for
controlling rotational movement of the aligning mechanism
such that frictional forces acting on the fiber are
minimized, the pull-reliever reeling-off device and the
braking capstan being stationary, the transmission
including two coaxially aligned first toothed wheels
through which the pull-reliever passes, two parallel second
toothed wheels that are spaced from and perpendicular to
3o the two first toothed wheels, and a continuous toothed belt
that extends around the two first toothed wheels and the
two second toothed wheels, the aligning mechanism being
CA 02051934 2002-06-27
2d
connected to one of the first toothed wheels and the
laying-on tube being connected to the other of the first
toothed wheels.
The laying-on tube can be fixed and can be connected to the
transmission to effect oscillatory and rotational movement
of the laying-on tube in a direction opposite to the
rotational movement of the aligning mechanism, the sensor
controlling operation of the motor t.o thereby control
rotational movement of the laying-on tube and the aligning
mechanism to limit the extent to which the fiber is wound
on the laying-on tube. The aligning mechanism can include
two rows of opposing rollers that engage the pull-reliever
on diametrically opposite sides.
In another embodiment, the present invention provides a
cabling machine for laying optofibers,, cables or other
elongate elements into oscillating, waveshape grooves
extruded around a pull-reliever to produce a finished
article, the machine comprising a pull-reliever reeling-off
device for reeling-off a pull-reliever in a first
direction, a braking capstan located downstream of the
pull-reliever reeling-off device in the first direction, a
fiber reeling-off device located downstream of the braking
capstan in the first direction for reeling-off fibers, an
S/Z-bench located downstream of the fiber reeling-off
device in the first direction for laying the fibers around
the pull-reliever, a yarn spinner located downstream of the
S/2 bench in the first direction for fix<~ting the fibers on
the pull-reliever, and a wheel capstan and a taking-up
device located downstream of the spinner in the first
direction for forwardly pulling and taking-up the finished
CA 02051934 2002-06-27
2e
article respectively. The S/Z-bench includes a laying-on
tube provided with a laying-on head so that the fibers pass
over the laying-on tube up to and through holes in the
laying-on head, where the fibers are laid on the pull-
s reliever and fixated with yarn taken from the yarn spinner
located immediately downstream of the laying-on head, the
pull-reliever reeling-off device and t:he braking capstan
being rotatably mounted, the laying-on tube being freely
rotatable and being guided by way of the fibers being laid
into the grooves in the pull-reliever, the laying-on tube
being connected to a transmission, and a sensor connected
to the transmission for detecting rotation of the laying-on
tube caused by the oscillating, waveshape of the grooves in
the pull-reliever and for causing the reeling-off device
and the braking capstan to rotate and perform a correcting
function which counteracts excessive rotation or twisting
of the laying-on tube such that the grooves in the pull-
reliever in a vicinity of the laying-on head will extend
substantially rectilinearly and such th<~t the fibers will
extend substantially parallel with the laying-on tube in
the absence of friction thereagainst.
The inventive cabling machine has the advantage of being
usable for both types of pull-reliever and also of
minimizing the risk of damage to the fibres, since the
fibres pass over the laying-on tube in a frictionless
fashion. This enables the fibres to ~>e laid at a high
production rate.
Further objects of the inventive cabling machine and further
advantages afforded thereby will be evident from the following,
detailed description, in which the invention is described in more
detail with reference to a preferred exemplifying embodiment
thereof and also with reference to the accompanying drawings.
BRIEF DISCLOSURE OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 illustrates schematically the construction of an
inventive cabling machine.
Figure 2 illustrates an S/Z-bench included in the
cabling machine.
Figure 3 illustrates a part of the S/Z-bench.
BEST MODE OF CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
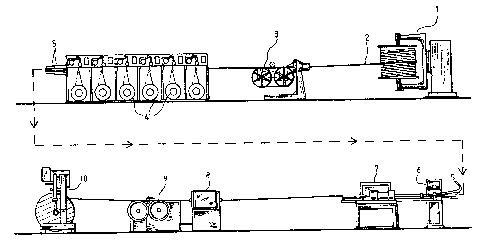
Figure I illustrates schematically the general construction of a
cabling machine. The illustrated machine includes a reeling-off
device 1 for reeling-off a pull-°reliever 2, a braking capstan 3,
unreeling devices 4 far reeling-off fibres 5 which are to be laid
around the pull-reliever 2, an S/Z-bench 6, a yarn spinner 7 which
is located immediately downstream of the S/Z-bench and which
functions to fix the fibres on the pull-reliever, optionally a
banding machine 8 for banding the fibre-laid cable to a finished
cable, a wheel capstan 9 for drawing the cable forwards, and a
coiling device 10 for coiling-up the finished cable. The reeling-
off device 1 is provided with a basic braking arrangement, and the
braking capstan 3 is provided with sensors far determining and
setting the tension in the pull-reliever 2, this being necessary
so as to obtain a sufficient fibre surplus which will enable the
temperature-cycling requirement to be fulfilled. Both the reeling
off device 1 and the braking capstan 3 are ratatably mounted, for
reasons made apparent herebelow. The fibre reeling-off devices 4
are arranged in a common station and include, in a known manner,
basic braking arrangements, forwardly pulling devices and sensors
for measuring and adjusting the tension in the fibres.
The S/Z-bench 6 will now be described in more detail with refe-
rence to Figure 2. The S/Z-bench can be said to be the hub ~f the
cabling machine and of the invention, and includes z~ fibre-laying-
4
on tube 11 over which the fibres 5 pass from the reeling-off
devices 4. The fibres 5 are guided to the S/Z-bench so as to be
conducted concentrically over the laying-on tube 11 and up to a
laying-on head 12 mounted on the outer end of the tube, where the
fibres are guided and conducted down onto the pull-reliever 2
drawn through the laying-on tube. The laying-on head may be of any
conventional kind and is only shown schematically in the Figure
and will not be described in detail. The S/Z-bench 6 also includes
an aligning mechanism 13, a transmission 14 capable of being
driven by a reversable stepping motor 15, and an absolute sensor
17 connected to the transmission over gearing 16.
The transmission 14 is illustrated in more detail in Figure 3. The
transmission includes two toothed wheels l8 which are in mutual
axial alignment and through which the pull-reliever 2 can pass.
The aligning mechanism l3 can be non-rotatably connected to one
toothed wheel by means of a key-joint or the like, and the laying-
on tube 1l can be non-rotatably connected to the ether toothed
wheel. Two further toothed wheels 19 and 20 are mounted perpen-
dicularly to and at different distances from the toothed wheels
18, of which further toothed wheels the tooth wheel 19 is connec-
ted to the motor 15 and the toothed wheel 20 is connected to the
absolute sensor 17, via the gearing 16. An endless toothed belt 21
runs in a continuous loop over the toothed wheels 18, 19 and 20,
the arrangement being such that when one toothed wheel 18 rotates
in one direction, the other toothed wheel 18 will rotate in the
opposite direction.
Tn the illustrated embodiment, the gearing 16 comprises a smaller
toothed wheel which is connected to the toothed wheel 20 and which
drives a large taothed wheel connected to the sensor 17 via a
toothed belt, although it will be understood that other types of
gearing can be used. The gearing is intended to prevent the
absolute sensor 17 from rotating mare than one revolution.
When cabling smooth pull-relievers 2, the reeling-off device 1 and
'the braking capstan 3 are both stationary, i.e. not rotatable. '.Che
aligning mechanism 13, which comprises a number of gripping wheels
:~~.~
which grip around the pull-reliever 2 and guide the same through
the aligning mechanism, is connected to the transmission 14. The
stepping motor 15 is also connected to the transmission 14 and
drives the transmission, and consequently also the aligning
mechanism 13 and the pull-reliever 2, in an oscillating reciproca-
ting rotary movement. This movement is regulated by the absolute
sensor 17 via a regulating and controlling device, The fibres 5
will therefare be laid on the pull-reliever 2 in an oscillating
waveform and are fixated with the aid of yarn taken from the yarn
spinner 7 immediately downstream of the laying-on head 12. The
yarn spinner 7 is prefexabl~r a double-yarn spinner with which the
two yarns are laid in mutually opposite directions, thus in both
an S-direction and a Z-direction. Because the laying-on tube 11
does not rotate when in operation, the fibres 5 will pass parallel
through the tube, and hence the frictional forces acting on the
fibres will be minimal.
In accordance with an alternative embodiment, for cabling a smooth
pull--reliever 2, the laying-on tube 11 may also be connected to
the transmission 14. Because of the configuration of the trans--
mission, both the aligning mechanism 13 and the laying-on tube 11
will, in this case, be imparted an oscillating, reciprocating
rotary movement, although in different directions. Rotation is
regulated by the absolute sensor 17 also in this case. Because of
these counterdirectional rotary movements, the total rotation of
the aligning mechanism 13 may be smaller than in the former case,
while still laying the fibres in an oscillating waveform on the
pull-reliever. Total rotation of the laying-on tube 11 is equal to
the total rotation of the aligning mechanism 13, therewith
limiting the extent to which fibres 5 become wound around the
laying-on tube 11 and thus also limiting the frictional forces on
the fibres.
Cabling of grooved pull-relievers 2 will now be described. In this
case, the aligning mechanism 13 is removed, the stepping motor 15
is disconnected, and the laying-an tube 11 is connected to the
transmission 14. In this case, the reeling-off device 1 and the
braking capstan 3 can be rotated to effect a correcting function.
When the fibres 5 are laid into the oscillating, wave grooves in
the pull-reliever 2, the laying-on tube 11 will tend to rotate.
This rotation is detected by the absolute sensor 1? connected to
the transmission 14, which now causes the reeling-off device 1 and
the braking capstan 3 to rotate in a remedial or correcting
fashion in response to the set turning-limits of the laying-on
tube 1.1. such that the grooves in the pull-reliever 2 will extend
substantially rectilinearly past the laying-on head 22. The
laying-on tube 11 will thus only rotate or twist to a limited
extent and consequently fibres 5 will not be wound onto the tube
or subjected to frictional forces to any appreciable extent.
In all of the aforedescribed alternative embodiments, it must be
ensured that the free length of the pull-reliever 2, i.e. the
distance between the braking capstan 3 and the wheel capstan 9, is
sufficiently great to enable the pull-reliever to rotate about its
longitudinal axis.
It will be understood that the invention is not restricted to the
aforedescribed and illustrated embodiment, and that modifications
can be made within the scope of the accompanying Claims.