Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2 o r~
-- 1 --
MACHINE WITH MOBILE GRID FOR THE ELIMINATION FROM CHANN_LS
AND SIMILAR OF SOLID PRODUCTS TRANSPORTED BY A LIQUID FLOW
DESCRIPTION
This invention concerns a macnine with a mocile grid
5 for the eiimination of solid products, transported by a
liquid flow, from channels and similar,
More particularly this invention refers to a machine o;
the abovementioned type formed so as to realise, by means of
a mobile grid combined with a fixed grid, a transport system
adapted to withdraw the solid product from the flow of liquid
carrying it and discharge it at a higher level from where the
said product is removed.
One such lifting and transPort system has been known
for some time, but the arrangements which realise it give
rise to various difficulties.
One of the difficulties of these known arrangements is
the poor rigidity of the supporting structure due essentially
to the fact that the restraining walls are mobile, Since the
mobile walls must be sufficiently light and unencumbering so
as not to hinder the motion, these are not able to contribute
sufficiently to the achievement of a good structural
rigidness, being, furthermore, subject to hydrodynamic thrust
.
2~55~.~6
-- 2 --
and viDrations wnich restrike the mobile group wai,s anb the
said connected walls. One sucn difficulty is particularly
notab e in heavy uses of the machines depending generally on
the high cc tent of solid products in the flow, on the
product type, on the pipe configurltion and on other factors
well known to an expert in the art.
Another difficulty met in the known technology is tne
difficulty of realising reliable machines with a hign
discharge height this being due to the abovementionec
difficulty regarding the poor rigidity of the supporting
structure.
A further difficulty, also due to the poor rigidity of
the supporting structure, consists of the width limitation
and therefore the limitation of the machine's use.
Furthermore this the use limitation of conventional
machines is due to the fact that conventional machines are
equipped with driving means of the mobile group, that is
electric motors which cannot be immersed in liquid and
therefore such m.achines cannot be used in channels or
similar, in which the level of the liquid is subject to
considerable changes in level.
In the conventional machines it is, furthermore,
necessary to provide a means of sealing with the supporting
structure, such means is subject to rapid wear and tear, the
2S possibility of clogging and leaking and therefore reduction
2 ~ 6
3 _
in the machine's performance.
The object of this invent;on is to produce a macnine of
the abovementioned type which substantially eliminates the
difficulties encountered with conventional machines.
This and other objects, characteristics and advantages
are evident to a person skilled in the art from the following
detailed description and from the appended claims.
The mobile grid machine for the elimination of solid
products transported by a liauid flow from channels and
similar according to the presC invention is characterised
by the features indicated in the characterising par ~f claim
1, further characteristics are indicated in the dependent
claims from 2 to 12.
A preferred form of embodiment of the machine is
illustrated - only exemplifying but not limiting - in the
figures of the attached sheets of drawings, where:
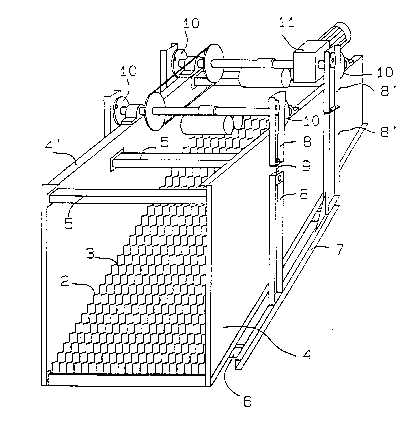
- Figure 1 is a perspective view of the machine as a whole;
- Figure 2 is a perspective view of the fixed group only;
- Figure 3 is a perspective view of the mobile group only
with parts removed for greater clarity;
- Figure 4 is a perspective view of an element of the mobile
group;
- Figure 5 is another simplified perspective view of the
machine as a whole;
- Figure 6 is a perspective view, with parts removed for
2 ~ 6
- 4 -
greater clarity, of an element or the mobile group an~ of tne
driving means; and
- Figure 7 illustrates the various positions of the mobile
group during a movement cycle.
With reference to the above figures, the machine
indicated generally in l as a whole - is of the type
comprising conventionally a first mobile group 2 and a second
fixed group 3 of elements formed as steps so as to permit, as
a consequence of the movement of the mobile group, the
raising and transport from one step to the next in the sieved
material.
hachine 1, as is known, is destined to be positioned in
any duct and to remove the solid material transported by the
liquid flowing in the duct from said liquid.
The elements of the fixed group are joined to a
supporting structure essentially composed of two lateral
plates 4,4' joined by upper crossbeams S and lower crossbeams
S'. The said lateral plates 4,4' have a profile which is
variab1e as a function of the desired inclination and
dimension of the machine.
Elements 2 of the mobile group are joined together by
crossbeams 6 which are in turn fixed to longitudinal members
7, 7' to which the motion is transferred by arms 8,8' on the
exterior of the plates 4,4'. As shown by the figure, the
arms 8 are made up of two elements joined together by an
s
oscillating joint 9. while the ar~s 8' are also const,tuteri
by two elements which are~bolted together.
The arms 8.8' are joined to cams 10. which receive the
motion from a driving unit 11.
The particular two-element form of the arms 8,8' allows
easy removal of the mobile group and relative elements 2 from
the body of the machine 1 maintaining the position of the
whole driving mechanism unchanged. The advantage of not
having to interfere with the driving mechanism togethe wi,h
the use of reference keys, conventional in itself, on all the
particulars of the motion transmission avoids problems of
phase displacement between the two groups and greatly reduces
the servicing times for repairs and/or maintenance.
With reference to Fig. 6, the movement of the mobile
group 2 is obtained by means of pairs of pistons lo and 19,
situated substantially vertically and horizontally or
slightly inclined, respectively, hinged on inferior
crossbeams 5' and of which the piston rods 18' and 19' are
hinged to longitudinal members 7,7'. For a reguiar movement
of the mobile group there are (as in the illustrated example)
two pair of pistons 18 and 19 positioned next to the lateral
plate 4 and two pairs positioned next to lateral plate 4'.
The pistons 18 and 19 are of hermetically sealed type
and so these, controlled by a suitable control box 20, can
operate even when immersed in liquid thus machine 1,
2 .~ r3
-- 6 --
according to the invention, can be used in channels, or
similar, in which the level of liquid varies considerably.
The movement of the mobile group 2 is outlined in Fig.
7:
- In the position 0(4) - the mobile group 2 and the fixed
group 3 are perfectly aligned, in phase - the piston rods 18
are in and the piston rods 19' are out (with respect to the
relative pistons);
- In position 1 - mobile group 2 raised, the piston rods 18'
are moved out and the piston rods 19' remain out;
- In position 2 - mobile group 2 moved forward, the piston
rods 18' are out and the piston rods 19' remain out;
- In position 3 - mobile group 2 lowered, the piston rods 18'
are moved in and the piston rods 19' remain out;
- In position 4 (0) - mobile group 2 moved backwards, the
piston rods 18' remain in and the piston rods are moved out;
- after this, the cycle repeats itself as described above.
As shown i`n detail in Fig. 4, each element 2 has the
points 12 of the steps curved alternatively in opposite
directions with respect to the plane of the said element,
said curved parts having the function of breaking up any
lumps and/or filaments of sieved material.
The mobile elements 2 and fixed elements 3 have the
upper part at least from the last step equipped with a boss
13 destined to prevent the sieved material from falling down
_ 7 _ 2~5~ ~ 5 6
again.
As results from the above, tne structure of tne machine
1 gets round all the difficulties encountered in the Known
technology.
The use of fixed lateral plates 4,4' allows the
realisation rf machines which are robust and thus insensitive
to hydrodynamic thrust and vibra~ions, of increaser neig,ht
and width according to necessity and without reauirinS tne
use of sealing means.
The hermetically sealed piston system, as alreaay said,
can operate even when immersed allowing the machine to be
used in any type of channel, or similar, and finally allows a
remar~able energetic saving with respect to existing s~stems.