Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
" n f' ; f' '1, ?s.;; "?
r'~.as :, .. is .~,:-
SPECIFICATION
Telescopic Support Arm
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
t. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a talescopic support
arm used in windows, inspection ports, doors of various
devices and others.
2. Prior Art
Various telescopic support arms have been hitherto
invented. For example, a support arm is designed in a
telescopic structure by moving a piston rod reciprocally
within a cylinder. Such a telescopic support arm is used
by attaching its one end to a door and the other end to a
door support frame.
In such a conventional telescopic support arm, however,
when a door is opened forcefully until the telescopic
support arm is fully expanded, impact then acts directly on
the ,junction of the cylinder and the piston rod, and
therefore the durability of the arm can not be sufficient,
but rather poor. Or when such telescopic support arms are
used at both sides of a door, if the door is attached to
the support frame in a distorted state or if a gap is formed
in mounting of the door on the support frame, either one or
both of the telescopic support arms may not be fully
1
~,~':~..,~ f-,T:T
v~ 5 h,
...s '..! ~.J.~~
expanded, and the door cannot be opened or closed smoothly.
Still more, in such a conventional telescopic support
arm, the door cannot be stopped and hold at an arbitrary
position, but is stopped only at the fully opened position
or at a position of a preset opening width of the door.
Therefore, if it is desired to stop the door at a slightly
opened position or to vary the opening width of the door
frequently, this type of telescopic support arm can not
suffice these requirements.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Tt is hence a primary object of the invention to solve
the problems of the conventional telescopic support arms.
In the present invention, a telescopic support arm
includes an outside arm 1 and an inside arm 2 which are
designed to slide freely each other, the outside arm 1
having a slot 3 and an abutting piece 8 inside thereof, and
the inside arm 2 having a slot 7 and a rotatable stopping
piece 4 inside thereof. The stopping piece 4 engages with
the end portions of the slots 3 and 7 and the abutting
piec a d respectively and rotates so as to project out of or
sink into the slots 3 and 7, and by its rotation the outside
arm and the inside arm 2 are free to slide each other in
both the extending and contracting directions. The stopping
piece 4 is provided with a buffer mechanism 14 which
comprises a holding piece 10 of the stopping piece ~, a
2
g s~., ~yJ~ ;r-~'i"?'
'~a.. '.! ,.J..
spring 13 for pulling the holding piece 10 in the
contracting direction of the telescopic support arm, and a
slot 12 for slidably supporting a support shaft 11 of the
stopping piece
In the present invention, moreover, a rack 5 with a
tooth part 5a is disposed in the outside arrn 1 along its
longitudinal direction, while a locking piece 6 with a pawl
part 6a is provided in the inside arm 2. While the support
arm expands, the pawl part 6a engages with each tooth of
the tooth part 5 one by one, so that the length of the
support arm may be ajdusted by arresting the pawl part 6a
on a tooth at a desired position.
Moreover holes 1'7 which align and penetrate through
both the outside and inside arms at a certain position may
be provided.
The telescopic support arm of the invention, provided
with such means as mentioned above, obtains the following
actions.
2n the telescopic support arm having the slots 3, 7,
the abutting piece 8 and the stopping piece 4, the abutting
piece 8 and the stopping piece ~4 are engaged with each
other, and then the stopping piece 4 is engaged with the end
portion of the slot 3 in the outside arm 1, so that the
support arm may be supported securely at the extended
position. Risks such as unexpected closing of a door while
working thereunder is avoided. Furthermore, a 180 degree
rotation of the stopping piece 4 causes the once extended
telescopic support arm to contract easily. If the door is
opened forcefully, the stopping piece being pulled in the
contracting direction by the spring 13 slides within the
range of the length of the slot 12 of the buffer mechanism
1~, and therefore direct damage on the abutting piece $ or
the stopping piece ~ is not induced, so that a durable
support arm may be provided.
In the telescopic support arm having the rack 5 and
the locking piece 6, when the telescopic support arm expands,
the pawl part 6a of the locking piece 6 moves intermittently
in small strokes on the tooth part 5a of the rack 5. In
this expanding state, to the contrary, when pushing force in
the contracting direction is applied on the support arm,
the pawl part 6a of the locking piece 6 engages with a
certain tooth of the tooth part 5a of the rack 5 and is
arrested there, so that the movement in the contracting
direction is deterred. Since the pawl part 6a moves with
engaging with each tooth of the tooth part 5a, it is
possible to provide a telescopic support arm capable of
being set at a desired length.
BRTEF DESCRIPTTON OF THE DRAWINGS
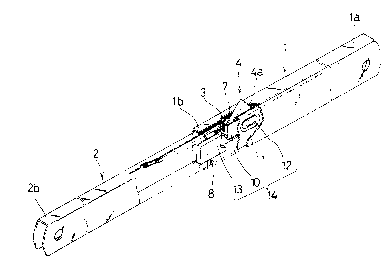
Fig. 1 is a partially cutaway perspective view of a
telescopic support arm of the invention;
Fig. 2 is a partially c~.~taway perspective view of an
4
~; ~~ .T?, ~,'
v, J '..,/ 'L.
outside arm of the invention;
Fig. 3 is a partially cutaway perspective view of an
inside arm of the invention;
Fig. ~d is a perspective view showing a state of use in
mounting the telescopic support arm of the invention;
Fig. 5 is an explanatory diagram showing a state of a
tooth part of a rack and a pawl part of a locking piece
while the telescopic support arm extends;
Fig. 6 is an explanatory diagram showing a state of
the tooth part of the rack and the pawl part of the locking
piece while the telescopic support arm contracts;
Fig. ~ is an explanatory diagram showing a state where
a stopping piece of the inside arm abuts against an
abutting piece of the outside arm (a state just before the
stopping piece slightly projects from the slot of the arm);
Fig. 8 is an explanatory diagram showing a state where
the stopping piece of the inside arm slightly projects from
the slot of the outside arm;
Fig. 9 is an explanatory diagram showing a state where
the stopping piece of the inside arm stops in the end
portion of the slot of the outside arm;
Fig. 10 is an explanatory diagram showing a state
where the stopping piece rotates and disengages from the
front-end-side (right) end portion of the slot of the
outside arm and then engages with the rear-end-side (left)
end portion;
5~ .,/ '._9 ~.~.,
Fig. 11 is an explanatory diagram showing a state
where after the state in Fig. 10 the stopping piece of the
inside arm rotates further to sink again into the outside
and inside arms while the telescopic support arm contracts;
Fig. 12 is an explanatory diagram showing a state
where in the state in Fig. 8 the telescopic support arm
further extends under a buffer action when further force is
added in the extending direction;
Fig. i~ is a perspective view showing a configuration
of the stopping piece, the abutting piece, and the slot of
the outside arm in the state in Fig, 10; and
Fig. 14 is a perspective view of the outside and
inside arms which have holes designed to align and form a
penetrating hole through both the arms.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
The constitution of a telescopic support arm relating
to the invention is described below while referring to an
embodiment in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
As shown in Fig. 1 which is a perspective veiw of the
telescopic support arm of the invention, an outside arm 1
and an inside arm 2 are free to slide. As specifically
described below, in this diagram, the telescopic support arm
is extended, and a stopping piece 4 of the inside arm 2 is
stopped at the front end side end portion of a slot 3 of the
outside arm 1.
6
a
N ~'.e ~a' v.i..
Tn the specification herein, the right side in each
drawing except Fig. ~ is referred to as the front end side,
and the left side is referred to as the rear end side.
As shown in Fig. 2, the outside arm 1 is formed in a
quadrangular tube by joining face to face two metal plates
folded in an approximately pi-section, and a rack 5 is
disposed inside along the longitudinal direction. A slot 3
is disposed at the rear end side 1b of the outside arm, and
an abutting piece 8 is provided inside this rear end side
1 b.
The inside arm 2 is made of a metal plate folded in an
approximately pi--section as shown in Fig. ~. At the front
end side 2a of this inside arm 2, there is a locking piece 6
having a pawl part 6a to engage with the tooth part 5a of
the rack 5 of the outside arm 1. This locking piece 6 is
rotatably mounted on the inside arm 2 as shown in Fig. 3,
and is linked with a spring 9 disposed at the front end
side 2a of the inside arm 2. At the front end side 2a of
the inside arm 2, a slot ~ and a rotatable stopping piece ~1
is disposed, and the stopping piece ~ is designed to
project out of the slots 3 and '7 in contact with the
abutting piece 8 of the outside arm 1. The stopping piece
4 includes a stopping part 4a designed to project out of the
slots 3 and 7, and a stopping part 4b configured as shown
in the drawings and designed to securely engage with and
stop at the end part of the slot 3. This stopping piece a
7
~., ,~. .r, ~;.,'~.;r
. ._i ~i:
is provided with a buffer mechanism 1~t comprising a holding
piece 10 of the stopping piece ~, a spring 13 for pulling
this holding piece 10 in the contracting direction of the
telescopic support arm, arid a slot 12 for slidably
supporting a support shaft 11 of the stopping piece u.
The state of action of the telescopic support arm
relating to thus composed invention is described below.
A telescopic support arm of the invention is used for
example as shown in Fig. 4. One end of a telescopic support
arm is attached to one side of the door and the other end
of the supprt arm is attached to the same side of a support
frame 16 of the door 15. And another support arm is
likewise attached to the other side of the door and its
. support frame. In this diagram, in the fully opened
position of the door 15, the stopping piece 4 of the inside
arm is stopped by the front-end-side end portion of the
slot 3 of the outside arm 1.
When the telescopic support arm extends from the
contracted state, as indicated by virtual line in Fig. 5,
the pawl part 6a of the locking piece 6 moves
intermittently at small strokes along the tooth part 5a of
the rack 5. That is, the pawl part 6a of the locking piece
6 moves further while sequentially engaging with each tooth
of the tooth part 5a of the rack 5. At this time, to the
contrary, when force in the contracting direction is applied
to the telescopic support arm, the pawl part 6a of the
8
~ ~..d t_r.~:.
locking piece 6 engages with the tooth part 5a of the rack 5
and is arrested, thereby no longer contracting. By thus
adjusting the engaging position, the telescopic support arm
is adjusted to a desired length, and therefore the door 15
may be stopped at a specified position.
When the telescopic support arm extends, as shown by
solid line in Fig. 6, the pawl part 6a of the locking piece
6 rides over the tooth part 5a of the rack 5, and the
engagement between the pawl part 6a and the tooth part 5a
is cleared, and the locking piece 6 is returned to the
position approximately vertical to the longitudinal
direction by the spring 9.
Since the lcoking piece 6 returns to the position
approximately vertical to the longitudinal direction after
riding over the rack 5, the pawl part 6a and the tooth part
5a are securely engaged with each other in the extending
direction, and are securely disengaged in 'the contracting
direction.
Fig. ? shows the state in which the telescopic support
arm is extended, and the stopping piece ~ of the inside arm
2 is abutting against the abutting piece 8 of the outside
arm i, that is, the state just before the stopping piece a
is projecting out of the slots 3 and 7. Here, when the
telescopic support arm is further extended, the stopping
piece ~ of the inside arm 2 is rotated as being pushed by
the abutting piece 8 of the outside arm t, thereby slightly
9
a w~,~' !1.'C'~~;t
.a 'J uJ.,
projecting out of the slot 3 (see Fig. 8).
At this time, when the telescopic support arm is
contracted, the stopping piece ~ moves away from the
abutting. piece 8, and the stopping part 4a of the stopping
piece contacts with the front-end-side end portion of the
slot 3 of the outside arm 1. When pushed further in the
contrating direction, the stopping piece 4 slightly rotates,
and is securely stopped in the f rout-end-side end portion
of the slot 3 by the stopping piece a-lb (see Fig. 9).
From this state, when the telescopic support arm is
extended, as shown in Fig. 70, the engagement of the
stopping piece 4 of the inside arm 2 and the front-end-side
end portion of the slot 3 of the outside arm 1 is cleared,
and the stopping piece 1~ abuts against the abutting piece 8
again. At this time, since the stoping piece has turned
further, the abutting piece 8 contacts with the side free
from the stopping part ~b of the stopping part ~l. When
extended furthermore, the abutting piece 8 pushes to rotate
the side free from the stopping part 4b of the stopping
piece 4, and the stopping piece 4 stops with the side free
from the stopping part ~.b abutting against the rear-end-side
end portion of the slot 3 of the outside arm. Here, when
the telescopic support arm is contracted, the other side
free from the stopping part ~b of the stopping piece ~. abuts
against the front-end-side end portion of the slot 3.
However, since this side has no stopping part 4b, the
1 0
~J ~_J .
4~~1~ ~...r ~~~ ~~
stopping piece ~4 rotates and sinks into the inside arm. At
this time, the stopping piece 4 is rotated by 180 degrees
from the original position. This state is clearly
illustrated in Fig. 11.
As clear from the drawings above, the shaft 11 of the
stopping piece 4 is disposed slidably in the slot 12, and is
provided with a spring 13 for pulling the telescopic
support arm in the contracting direction. Therefore, if the
door 15 is opened forcefully, or otherwise further force is
applied in the extending direction to the telescopic
;,
support arm which is already in~fully extended state in
ordinary condition, the support arm is extended more by the
range of 'the length of the slot 12 (see Fig. 12), and is
returned to the ordinary maximum length by the spring 13,
by the buffer action. In the state shown in Fig. 10, too,
the telescopic support arm can be extended more than the
ordinary maximum length by the Length of the slot 12, by
means of the buffer mechanism 14. Therefore, the members of
the support arm does not suffer direct damage, and
furthermore, even if the door i5 is mounted distortedly on
the support frame 16 or there is a gap in mounting of the
door 15 on the support frame 16, such a distortion or a gap
on the telescopic support arms at both sides of the door
may be adjusted by the buffer mechanism 14.
In Fig. 1~, holes 17 are provided in both the outside
arm 1 and the inside arm 2. The holes 1~ are designed to
~ 1
'i ~ :...' V.,.
align at a certain position to form a penetration hole
through both the arms 1, 2. By passing iron bars or the
like into and through the holes 1~ of the outside and inside
arms 1, 2, the risk of sudden contraction of the telescopic
support arm may be further reduced. In this embodiment,
the holes 1~ are disposed at one position of the ordinary
maximum length of the telescopic support arm, but it is not
limitative, and it may be located at any position or at
plural positions. It is also possible that the door can be
locked by inserting a locking key or the like through the
holes 17.
The telescopic support arm of the invention possesses
the above constitution and hence brings about the following
benefits.
By the constitution comprising the slots, the abutting
piece and the stopping piece, the support arm can be
securely maintained at a position of an extended length, and
by rotation of the stopping piece, the telescopic support
arm once extended may be easily contracted. Furthermore,
by the constitution of the buffer mechanism, if the door is
opened forcefully, or if the telescopic support arms are
mounted distortedly on both sides of the door, direct damage
is not induced on the abutting piece or the stopping piece,
so that the durability is improved.
The engagement of the tooth part of the rack and the
pawl part of the locking piece enables the telescopic
12
s~pf~l~~;f~16.~ .T
~..
?Ga ,,. ~. -.,r _~..
support arm to be set to a desired length. Therefore, the
telescopic support arm of the present invention may be used
so much conveniently in various doors, and in a desired
length.
Holes penetrating through both the inside and outside
arms enhance the safety of the support arm in use and
enables the support arm to be locked with a key.
13