Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2B~3~6
In-the-ear hearing aid with sound compensating channel
The invention relates to an in-thé-ear hearing aid for
persons with impaired or defective hearing with an ear
mold which ccntains a microphone, amplifier, earphone,
battery compartment with battery and a compensating
channel leading from the inside to the outside and which
is covered by a cover plate.
Such hearing aids are already known. Such compensating
channels are required for all in-the-ear hearing aids in
order to establish sound and pressure compensation
between the inside of the auditory canal and the
surroundings, otherwise the person with impaired hearing
may have the impression when talking that the ear is
"closed".
These compensating channels simultaneously serve as a
kind of low-pass filter, i.e. feedback of low
frequencies, whereby gain is reduced for low frequencies.
This is often desired, because hearing losses are mostly
restricted to high frequency ranges.
A person's own voice usually contains a high proportion
of low frequencies. Transmission of sound from the head
to the hearing aid must therefore be avoided if possible.
Such compensating channels have often been produced up to
now by an additional hole next to the sound channel in
the hearing aid. Production of these holes is extremely
difficult and time-consuming.
A solution to this problem is described in
FR-Al 2.596 644.
Holes are located in the tip of the ear mold in addition
to the sound outlet channel, which utilizes the cavity
between the earphone and ear mold wall in order to
20~3~
produce a link with the outside world via capillary
tubes. Such capillary tubes are also called vents.
The nature of these capillary tubes means that they are
difficult to produce, whether by drilling or when casting
the ear mold.
The task of the invention is to create a hearing aid of
the type mentioned at the start where the sound and
pressure compensating channel can be produced much more
easil~ and thus with reduced work or costs. In addition,
it should be ensured that it is also possible to provide
a compensating channel, i.e. a vent with at least certain
dimensions, in cases where the hearing aid can be
inserted in the auditory canal.
This is achieved by the invention due to the fact that
the compensating channel partially or completely encloses
at least part of the sound outlet channel from the
earphone.
Refer to the other claims for further characteristics of
the invention.
The invention will now be described in more detail on the
basis of the enclosed drawings.
The drawings show the following:
Fig. 1
A schematic sectional view of an in-the-ear hearing aid
in accordance with the invention;
Fig. 2
A schematic perspective view of the in-the-ear hearing
aid;
.
.. ~ . .. . . .
- ' ' ' : -'. ' '. - .
. . , , : . . . .- : .. - . , -
; . . :: ... . .. . . . - . .. - - ,, -. ~. . ., .. -, . .
.... . . . .
~Q~38~b
Figs. 3, 4 and 5
Various configurations of sound outlet channel and
compensating channel;
Fig. 6
A sectional view along the section line in Fig. 1;
Fig. 7
A further sectional view along the section line in Fig.
l;
Figs. 8~ and 8B
A unit in which the invention is realized;
Fig. 9
A partial section of the sound outlet of the hearing aid
and
Fig. 10
A view of the sound outlet channel and compensating
channel from below. ~ -
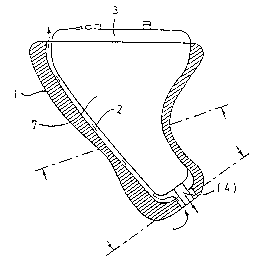
Fig. 1 shows a purely schematic sectional view of an in-
the-ear hearing aid 1 in accordance with the invention
with a compensating channel 2 and a cover plate 3 on
which various components are mounted (not shown). The
sound outlet channel 4 is located at the bottom end of
the hearing aid.
Whereas previously sound outlet channels and compensating
channels have been realized separately, it is now
suggested in accordance with the invention to combine
these two channels at the outlet.
This is shown particularly clearly by Fig. 2, where the
sound outlet channel 4 is enclosed at least partially by
an initial section of the compensating channel 2A. In
addition, it is possible to schematically recognize the
-: . ' . : - : .
.: . . ~ . -
- .' - ~
-. . : .: : - -
- - -
.. . .
.' ' . - ' . . . ~ :: .
.
20~3~
earphone 5, around which at least one but preferably two
sections of the compensating channel 2B are routed.
Figures 3, 4 and 5 show various configurations of the
sound outlet channel 4A and various inlets 2A for the
compensating channel.
In Fig. 3, the sound outlet channel 4A is located in the
center and the compensating channel 2A possesses four
inlets located around the sound outlet channel, for
example.
In Fig. 4, the sound outlet channel 4A is arranged
asymmetrically and is not completely surrounded by 3
inlets of the compensating channel 2A, for example.
In Fig. 5, the compensating channel 2A and sound outlet
channel 4A are located next to each other and possess an
approximately semi-circular cross-section.
As a result of these configurations, the sound outlet
channel and compensating channel are clearly fixed with
respect to the ear mold.
If we consider a section along the section line for
Figures 6 and 7 in Fig. 1, we can see that the
compensating channel (above the earphone) can be produced
on the one hand by a continuous recess in the inner
housing, designated here by 2C. Equally, however, the
compensating channel 2D can be molded in the otoplastic
mold. In this case, however, the bottom section 2A of the
compensating channel is located below the earphone in the
way shown in Figs. 1 and 2.
A particularly elegant solution for a combination of
sound outlet channel and compensating channel is shown by
unit 6 in Figs. 8A and 8B. This unit contains the
earphone 5 and it is possible to see on the right side of
,
. ...................... ... . . .
. .
.
~ 2063~
the figure the sound outlet channel 4 and the
compensating channel 2A, which continues inside the unit
6 as compensating channel 2B. This is in principle also
intimated in Fig. 2.
Fig. 8B shows a sectional view along the section line in
Fig. 8A. The earphone 5 is surrounded and held by the
unit 6, preferably in the form shown. A compensating
channel section 2B is molded in this unit. This section
is shown with a rectangular cross-section, but may also
possess an approximately semi-circular cross-section.
The bottom end of the in-the-ear hearing aid is shown in
the sectional view in Fig. 9. It is again possi~le to see
the sound outlet channel 4 and the compensating channel
2. A cerumen trap 8 is inserted in the bottom end of the
hearing aid which can be closed off by a cap 9.
Fig. 10 shows the bottom end of the hearing aid from
below, without the cover cap. It is again possible to see
the sound outlet channel 4A, the compensating channel 2A
and the cerumen trap 8.
This new arrangement of the compensating channel in
conjunction with the sound outlet channel eliminates the
need for additional production steps in order to produce
holes or channels for the compensating channel.
on the one hand, it is possible to produce one part of
the compensating channel in a very simple way with the
unit in accordance with Figs. 8A and 8B and the
arrangement in accordance with Fig. 9i on the other hand,
the remaining part of the compensating channel in
- ~ . . .. - ~ . .
. ', ~ ' ' ' ' . " '' '
' ': ''"' ''`- ' ' : :
- . . - .
'~ ~ ~ - ' . '" ' - ' -
6 2~3~6
accordance with Fig. 6 or Fig. 7 can be produced very
simply, either in the otoplastic mold or in the actual
device housing itself.
This considerably simplifies the whole production
procedure for a compensating channel.
. .
:: -
.