Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~ ~4 ~ ~ ~
RACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a gas-filled
discharge tube, and more particularly to a gas-filled
discharge tube for operation as a series gap of an ignition
system of an automotive spark-ignition engine or the like.
nescriptio~ of the Prior ~rt
There has been proposed a conventional gas-filled
discharge tube for operation as a series gap of an ignition
system of an automotive spark-ignition engine or the like, a
case in point being the one disclosed by the same applicant as
the present specification; a Japanese Utility Model Laid-open
No. 182245.
In a conventional gas-filled electric discharge tube
as disclosed above, at the opposite open ends of a tubular
body formed of an electrically insulating material such as
ceramic, there are formed a pair of electrode bases airtightly
A4~
4 2~
adhered to the respective open ends for installing electrodes
as discharge electrodes which are formed by pressing a porous
metal sheet on the respective electrode bases, and to this
structure,-a gas-filled tube is airtightly mounted on one
electrode base, and a connecting portion (which is explained
later on) is protrudingly formed on the other electrode base.
With this construction, a gas-filled discharge tube is formed
such that a high-pressurized inert gas is injected into the
tubular body from the gas-filled tube, and after the
completion of the gas injection, the tube is sealed by a gas
sealing member, and thereafter a cylindrical shaped protection
terminal is provided to cover the external side of the tube,
and further, an electrically conducting adhesive member is
filled between the protection terminal and the tube.
The gas-filled discharge tube as constructed above
is incorporated into a plug gap which is to be engaged with a
terminal of the spark plug, whereby a pair of intermediate
connecting terminals which are formed respectively at one end
of the connecting terminal to be connected to the spark plug
and at one end of a cable terminal connected to an end portion
of a high-voltage cable, are engageably fixed respectively
with a first protection terminal of one of the electrode base
and a second connecting portion of the other of the electrode
base of the gas-filled discharge tube 4, so that a so-called
series gap is connected in series to the spark plug.
However, in the conventional gas-filled discharge
tube of the above construction, since the gas-filled tube for
c ~
f~
-
injecting the gas into the tubular body and the first
protection terminal are largely protruding from the electrode
base, the whole length of the discharge tube becomes
4 ~ ~ ~
incorporating the discharge tube therein is forced to
become a big si7e, so that a minimization of the size of
the above ignition system with a series gap becomes
difficult, and consequently ;f an automobi]e has not a
large capacity for mounting engine auxi.liary devices or the
like, it will become d;fficult to adopt such an ignition
system therein.
SUMMA~Y 0~ THE INVENTION
The present invention has been made to elimi.nate such
problems as described above, and it is an object of the
- present invention to provide a dischar~e tube which is
capable of making the discharge tube itself smaller to
minimize a plug cap that incorporates the discharge tube
therein, thereby to realize a minimi~ation of the si~e of
the whole ignition system having a series gap.
In order to achieve the above object, the gas-~il.led
discharge tube according to the present i.nvention is
constructed such that it comprises a tubular body formed of
an electrically in.sulating material and having a notch
portion at least one of the opposite open ends thereof, and
a notch or projecting porti.on at the other open end
thereof; a pair of electrode bases, at least one of which
is formed of ~n electrica]ly conducti.ng thin metal sheet,
airtigiltly adhered to the respective open ends; and a pair
of discharge electrodes having f]ange portions to be
engageably fixed with the notch and/or projecting portions
2064942
and sandwiched between the tubular body and the respective
electrode bases, and with this construction, the electrode
base is first formed with a gas filling bore by a laser
beam for filling an inert gas, which bore being welded also
by the laser beam after the inert gas is filled in the
tubular body so as to enclose the gas therein.
By the present invention, since it is constructed such
that at least one of the electrode bases which are
supporting discharge electrodes and airtightly adhered to
the electrically insulating tubular body is formed of an
electrically conducting thin sheet, and this electrode base
is formed with a bore which is made by a laser beam for
filling an inert gas and welded also by the laser beam
after the inert gas filling operation is completed to
enclose the filled gas, it is no longer necessary to use a
gas-enclosed tube to inject a gas to the tubular body
because of the above gas filling bore, so that the above
conventionally adopted gas-enclosed tube that largely
protrudes from the electrode base can be obviated, thereby
a reduction of the whole length of the gas-filled discharge
tube can be made possible.
Other objects and features of the invention will be
more fully understood from the following detailed
description and appended claims when taken in conjunction
with the accompanying drawings.
2064942
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
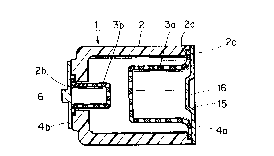
Fig. 1 is a sectional view of the gas-filled discharge
tube according to one embodiment of the present invention;
Fig. 2 is a sectional view showing the state that the
gas-filled discharge tube of Fig. 1 is incorporated into a
plug cap;
Fig. 3 is an illustration showing one embodiment of a
welding device to be used for assembling the gas-filled
discharge tube of Fig. 1;
Figs. 4A and 4B are illustrations respectively showing
the state that an bore is formed and that the bore is
welded to be sealed both by a laser beam;
Fig. 5 is a sectional view of the gas-filled discharge
tube according to another embodiment of the present
invention;
Fig. 6 is a sectional view of a conventional gas-filled
discharge tube; and,
Fig. 7 is a sectional view showing the state that the
conventional gas-filled discharge tube is incorporated into
a plug cap.
In the drawings, reference numeral 1 denotes a gas-
filled discharge tube, numeral 2 denotes a tubular body, 3a
and 3b respectively denote electrodes, 4a and 4b
respectively denote electrode bases, 5 a gas-enclosed tube
6 a connecting portion, 8 a protection terminal, 10 a plug
cap, 14 an intermediate connecting terminal, 16 a gas
4 ?
..
filling bore, 17 an electrically conducting spring, 18 a
carrier belt, 19 a welding device, 20 a laser beam and
reference numeral 21 denotes an installing projection.
D~T~TT-Fn D~SCRIPTION OF T~ p~F~RR~n ~MRODIM~TS
Fig. 6 shows a conventional gas-filled electric
discharge tube 1 as disclosed above, wherein at the opposite
open ends of a tubular body 2 formed of an electrically
insulating material such as ceramic, there are formed a pair
of electrode bases 4a and 4b airtightly adhered to the
respective open ends for installing electrodes 3a and 3b as
discharge electrodes which are formed by pressing a porous
metal sheet on the respective electrode bases 4a and 4b, and
to this structure, a gas-filled tube 5 is airtightly mounted
on one electrode base 4a, and a connecting portion 6 (which is
explained later on) is protrudingly formed on the other
electrode base 4b. With this construction, a gas-filled
discharge tube 1 is formed such that a high-pressurized inert
gas is injected into the tubular body 2 from the gas-filled
tube 5, and after the completion of the gas injection, the
tube 5 is sealed by a gas sealing member 7, and thereafter a
cylindrical shaped protection terminal 8 is provided to cover
the external side of the tube 5, and further, an electrically
conducting adhesive member 9 is filled between the protection
terminal 8 and the tube 5.
The gas-filled discharge tube 1 as constructed above
is, as shown in Fig. 7, incorporated into a plug gap 10 which
is to be engaged with a terminal of the spark plug, whereby a
pair of intermediate connecting terminals 14, 14, which are
formed respectively at one end of the connecting terminal 11
to be connected to the spark plug and at one end of a cable
7 g)
terminal 13 connected to an end portion of a high-voltage
cable 12, are engageably fixed respectively with the
protection terminal 8 of the electrode base 4a and the
connecting portion 6 of the electrode base 4b of the gas-
filled discharge tube 1, so that a so-called series gap is
connected in series to the spark plug.
However, in the conventional gas-filled discharge
tube 1 of the above construction, since the gas-filled tube 5
for injecting the gas into the tubular body 2 and the
protection terminal 8 are largely protruding from the
electrode base 4a, the whole length of the discharge becomes
substantially long, and thereby the plug cap 10 for
incorporating the discharge tube 1 therein is forced to become
a big size, so that a minimization of the size of the above
ignition system with a series gap becomes difficult, and
consequently if an automobile has not a large capacity for
mounting engine auxiliary devices or the like, it will become
difficult to adopt such an ignition system therein.
In the following, one embodiment of the present
invention is described with reference to the Figs. 1 to 5.
Fig. 1 is an illustration showing one embodiment of a
gas-filled discharge tube 1 according to the present
invention, in which the discharge tube comprises a tubular
body 2 formed of an electrically insulating material such
as ceramic, one end of which is formed with an aperture 2a
of a large diameter, while the other end thereof is formed
with the other aperture 2b of a small diameter, and
further, notch portions 2c, 2c are provided at the
respective apertures 2a and 2b. With this construct1on,
7a
A
4 ~ ~ ~
discharge electrodes 3a and 3b, which are respectively
formed by pressing a porous metal sheet so as to fit with
each of these apertures, are engageably fixed with these
notch portions 2c, 2c of the respective apertures 2a and 2b
of the tubular body 2, and these electrodes 3a and 3b are
supported by electrode bases 4a and 4b respectively, which
are airtightly adhered to the end surfaces of the
respective apertures of the tubular body 2 through
soldering or the like.
Here, the electrode base 4a of a large diameter for
supporting the electrode 3a of a large diameter is formed
7b
~"
20649~2
of a thin metal sheet whose thickness is below 1.00 mm, and
this electrode base 4a is further formed with a dented
portion 15 at the center portion thereof to be contacted
with an electrically conducting spring 17 (explained later)
and the dented portion 15 is further formed with a tiny gas
filling bore 16 which is, as explained later on, welded to
close after the gas filling operation is completed so as to
enclose the gas in the tubular body. On the other hand,
the other electrode base 4b of a small diameter for
supporting the electrode 3b of a small diameter is formed
of a lid-like metal sheet, at the center portion of which a
connecting portion 6 is protrudingly formed just like the
above-explained conventional device.
Thereafter, a gas-filled discharge tube 1 enclosing an
inert gas is, as shown in Fig. 2, incorporated into a plug
cap 10 which is to be engageably fixed to a terminal of the
spark plug, wherein a spring 17 is suppressedly provided
between a connecting terminal 11 to be connected to the
spark plug and the electrode base 4a of the discharge tube
1, and a connecting portion 6 of the other electrode base
4b is engageably fixed to an intermediate connecting
terminal 14 provided to a cable terminal 13 which is
connected to one end of the high-voltage cable 12, thereby
forming a so-called series gap connected in series to the
spark plug.
In the following, an assembling process for the above
206~942
gas-filled discharge tube 1 is explained.
~ irst, the electrodes 3a and 3b are engageably fixed to
the notch portions 2c, 2c of the respective apertures 2a
and 2b of the above tubular body 2, and the electrode bases
4a and 4b are airtightly adhered through soldering or the
like to the respective end surfaces of the tubular body 2,
whereby the discharge tube 1 without inert gas enclosed
therein is first assembled. Then, as shown in Fig. 3, put
the discharge tube 1 with the electrode base 4a side facing
upward using a jig or the like on a carrier belt 18. Here,
the carrier belt 18 is extended to the inner side of a
chamber (not shown) having a pressure-proof character, and
above the carrier belt 18 within the chamber a welding
device 19 such as a YAG laser is movably mounted in
respective vertical directions.
In the above state, the carrier belt 18 is moved in a
step-by-step form, and when the discharge tube 1 comes just
below the welding device 19, the welding device 19 is
activated to irradiate a laser beam 20 onto the center
portion of the electrode base 4a of the discharge tube 1
for 1 to 10 shots to form a gas filling bore 16 having a
diameter 0.3 to 1.00 mm on the electrode base 4a.
Thereafter, the chamber in which the discharge tube 1 is
located is put in a vacuum state, and high-pressurized
Argon or Xenon gas and a mixed gas with a rare gas N2 are
injected into the chamber so as to fill the chamber with
2064942
the inert gas. By this operation, the high-pressurized
inert gas is filled into the discharge tube 1 by way of the
above gas filling bore 16.
After the above operation, the welding device 19 held
at the location where the gas filling bore 16 is formed is
slightly moved upward and downward so as to shift the focal
point of the laser beam 20 and irradiate the laser beam 20
again onto the center portion of the electrode base 4a of
the discharge tube 1. By this operation, as shown in Fig.
4B, the gas filling bore 16 formed on the above discharge
tube 1 is welded and sealed, and a gas-filled discharge
tube having a high-pressurized inert gas enclosed therein
is thereby formed.
Subsequently, since in the present embodiment an
electrode base 4a of a large diameter airtightly adhered to
the tubular body 2 for supporting the electrode 3a of a
large diameter is formed of a thin metal sheet, and is also
formed with a gas filling bore 16 by a laser beam 20 which
bore is welded to be closed also by the laser beam 20 after
the inert gas filling operation is completed, the gas can
be filled into the tubular body 2 by way of the gas filling
bore 16 obviating the use of a conventionally adopted gas-
enclosed tube, and the gas-enclosed tube largely protruding
from the electrode base 4 can also be unneeded, thereby
enabling to shorten the whole length of the gas-filled
discharge tube 1. Further, by minimizing the size of the
20649~2
gas-filled discharge tube 1 as above, the plug cap 10 of an
ignition system having a so-called series gap for
incorporating this discharge tube 1 therein can also be
minimized, so that the whole ignition system having a
series gap can be minimized, and due to this fact, an
engine room adopting such ignition system can have more
space for other functions.
Furthermore, since its assembling procedure is such
that a discharge tube 1 without any inert gas enclosed
therein is first formed, and carried into a chamber where
the laser beam 20 is irradiated onto an electrode base 4a
thereof formed of a thin metal sheet to form a gas filling
bore 16, and also after the completion of the gas filling
operation by way of this gas filling bore 16, the laser
beam 20 is again irradiated to the focal point slightly
shifted from the above made bore so as to weld and seal
this gas filling bore 16, a mechanical assembling procedure
of the discharge tube 1 which should conventionally be done
in a chamber with full of high-pressurized gas can be
avoided, the device for manufacturing the gas-filled
discharge tube 1 can be prevented from becoming large and
complicated, so that its manufacturing cost can be greatly
reduced in due course.
Still further, since the gas filling bore 16 which has
been formed by a laser beam 20 can be easily welded only by
shifting the focal point of the laser beam 20, a laser beam
2064942
treating operation itself can be largely facilitated, and
thereby the productivity thereof can be enormously
improved.
By the way, both of the electrode bases 4a and 4b
airtightly adhered to the opposite end portions of the
tubular body 2 can be respectively formed of thin metal
sheets, and the electrodes 3a and 3b to be engageably fixed
to the tubular body 2 can be formed of a same diameter.
Fig. 5 is an illustration showing a gas-filled
discharge tube according to another embodiment of the
present invention. In this embodiment, the inner
peripheral wall 2d of the tubular body 2 is formed as thin
as possible to the extent that it can endure the high-
pressure of the inert gas filled into the tubular body 2,
and in addition, an installing projection 21 is formed at
the aperture 2a of a large diameter of the tubular body 2,
whereby a flange portion 3a' of a the large diameter
electrode 3a is engageably fixed to the aperture 2a. In
the state that the electrode 3a is engageably fixed to the
installing proiection 21 of the tubular body 2, an
electrode base 4a of a large diameter is further airtightly
adhered to the end surface 21a of the installing projection
21.
This above construction is same as that of the first
embodiment in that the electrode base 4a is formed of a
thin metal sheet, and that the gas filling bore 16 formed
20649d2
in the electrode base 4a is welded to seal the bore after
the inert gas is filled therein.
In this embodiment also, the gas can be filled into the
tubular body 2 by way of the gas filling bore 16 without
using a conventionally adopted gas-enclosed tube, so that
the gas-enclosed tube largely protruding from the electrode
base 4 can also be unneeded, thereby the whole length of
the gas-filled discharge tube 1 can be shortened. Further,
by minimizing the size of the gas-filled discharge tube 1
as above, the whole ignition system having a series gap can
be minimized.
Furthermore, with the above construction, by forming
the inner peripheral wall 2d of the tubular body 2 as thin
as possible, the weight of the whole gas-filled electric
discharge tube 1 can be reduced, and by minimizing the
quantity of an electrically insulating material such as
ceramic forming the tubular body 2, the manufacturing cost
for the whole discharge tube 1 can be also reduced, so that
the total weight of the whole ignition system having a
series gap to incorporate this discharge tube 1 therein,
and the total cost for its production can also be greatly
reduced.
[Effect of the Invention]
As mentioned heretofore, a gas-filled discharge tube
according to the present invention is constructed such that
it comprises a tubular body formed of an electrically
20649~2
insulating material, and electrode bases to be airtightly
adhered thereto, at least one of which electrode bases
being formed of an electrically conducting thin sheet,
wherein the electrode base is formed with a gas filling
bore 16 by a laser beam so as to first fill the gas, and
then welded to close the bore by the laser beam after the
inert gas filling operation is completed, whereby the inert
gas can be filled into the tubular body 2 by way of the gas
filling bore without using a conventionally adopted gas-
enclosed tube, so that the conventional gas-enclosed tube
largely protruding from the electrode base 4 can also be
unneeded, and thereby the whole length of the gas-filled
electric discharge tube 1 can be shortened, and
consequently, the size of the whole ignition system having
a series gap for incorporating the discharge tube therein
can be minimized.
Although the invention has been described with a
certain degree of particularity, obviously many changes and
variations are possible therein. It is therefore to be
understood that the invention may be practiced otherwise
than specifically described herein without departing from
the scope and spirit thereof.
14