Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
WC~D TYPE GOLF C~UB~ 2 0 7 ~ 7 0 6
~ Ou~ OF THE lhv1n.lON
FIELD OF THE lNvhn,lON
This invention relates generally to golf clubs and, in
particular, to a type of golf club commonly referred to as
~woods~ which have an enlarged head attached to one end of an
elongated sha~t.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PRIOR ART
A full set of golf cIubs generally consists of a
correlated set of wood type clubs and a correlated set of iron
type clubs. A conventional wood type golf club is disclosed in
U. S. Patent No. 3,625,518 while conventional iron type golf
clubs are disclosed in U. S. Patent No. 3,655,188. Wood type
golf club~ have heads constructed of materials such as wood,
metal and plastlc. Iron type golf clubs have heads usually
made of metal.
Referring to Figs. 1 - 3, a wood type golf club according
to the prior art has an enlarged head 10 including a specially
shaped body 12 preferably formed of wood with a hosel 14 which
receives and is attached to one end of an elongated shaft 16. A
grip (not shown) i5 mounted on the other end of the shaft 16 so
that head 10 may be swung in an arc to contact a golf ball
resting on a tee or on the ground. An insert 18 preferably
formed of a resin material is centrally mounted in a face
portion 12a of the body 12, and a metallic sole plate 20 is
attached to a bottom portion 12b of the body 12 by a plurality
of screws 22 and/or epoxy. The sole plate 20 has an arcuate
notch 24 at one end and a straight edge 26 at the other end.
When the sole plate is attached to the body 12, the notch 24
and the edge 26 are engaged with an arcuate shoulder 28 and a
straight shoulder 30, respectively, formed on the body 12. The
sole plate 20 also has a curved side 32 and a relatively
straight side 34. Shoulder 30 is located in a heel 10a of the
head 10 while shoulder 28 is located in a toe lOb of the head
2072706
When making a wood type golf club that is designated a~ a
driver or a No. 1 wood, a hole 36 shown in Fig. 1 is bored in
the bottom of the driver body 12 to remove weight therefrom so
that the finished golf club will have a desired swingweight.
Swingweight i8 generally defined as a measurement of a golf
club's weight distribution about a point which is at a
specified distance from the grip end of the golf club. Hole
36 is neces~Ary because the body 12 in a driver is larger
and heavier than in other golf clubs in a correlated set. When
making other wood type golf clubs with relatively smaller heads
(e.g., those designated as Nos. 3, 5 and 7 woods), holes 38, 40
6hown in Fig. 2 are bored in the body 12 and then filled with
weighted in~erts 39, 41 made of lead or brass in order to
provide finished golf clubs of desired swingweights. In a
correlated set of wood type golf clubs according to the prior
art including for example Nos. 1, 3, 5 and 7 woods, the sole
plates 20 on the Nos. 3, 5 and 7 have been made of a
heavyweight material such as brass whereas the sole plate 20 on
the No. 1 wood has been made of a lightweight material such as
aluminum. This helps to reduce, but not eliminate, the
additional weight that mu~t be added to the body 12 in the
Nos. 3, 5 and 7 woods by using the weighted inserts 39, 41.
The golf club shown in Figs. 1 - 3 has the face portion
12a of the body 12 arranged for contacting a golf ball.
Located on the face portion 12a is a center point 11 known as a
~sweet spot~ which is in general alignment with the center of
gravity of the head 10. If the head 10 impacts a golf ball at
precisely the sweet spot 11 during a golf swing, maximum energy
will be transferred from the head 10 and the golf ball will
travel along its intended path. If the club head 10 impacts a
golf ball at off-center point~ lla, llb which are also located
on the face portion 12a but in the heel and toe lOa, lOb of the
head 10, twisting -ve -~t~ of the head 10 will occur resulting
2072706
68319-29
ln less than maxlmum energy belng transferred from the head 10
and devlatlon of the golf ball from lts lntended path of
travel. Such devlatlon of the golf ball ls generally referred
to as a "sllce" or a "fade" when lmpactlng the head 10 at polnt
lla and as a ~'hook" or a "draw" when lmpactlng the head 10 at
polnt llb.
SUMMARY OF TH~ INVFNTION
The present lnventlon provldes a wood type golf club
comprlslng: a shaft; a head attached to one end of sald shaft,
sald head lncludlng a heel, a toe, and a body havlng a face
portlon arranged for lmpactlng a golf ball; a sole plate
attached to a bottom portlon of sald body, sald sole plate
havlng a welght and a substantlally clrcular cavlty formed ln a
center sectlon thereof whlch decreases the sole plate welght ln
sald center sectlon whlle lncreaslng the sole plate welght ln
perlmeter sectlons thereof, sald cavlty havlng an outer edge
extendlng ln a generally clrcular path, sald sole plate also
havlng a ledge clrcumscrlblng sald cavlty and contactlng sald
bottom portlon of sald body, sald outer edge of sald cavlty
deflnlng an lnner extremlty of sald ledge wlth sald ledge
extendlng outwardly ln all dlrectlons from sald outer edge of
sald cavlty and havlng an upper surface whlch ls elevated above
a ~ottom surface of sald cavlty; and sald perlmeter sectlons of
sald sole plate lncludlng a heel perlmeter sectlon located
ad~acer~t sald heel of sald head, a toe perlmeter sectlon
located ad~acent sald toe of sald head, a forward central
perlrneter sectlon located forwardly of sald cavlty between sald
heel and toe sectlons, and a rearward perlmeter central sectlon
located rearwardly of sald cavlty between sald heel and toe
sectlons, sald ledge extendlng through all of said sole plate
perlmeter sectlons.
h_~
2 0 7 2 7 0 ~
68319-29
A flrst proportlon of the sole plate welght ls
preferably concentrated ln a heel of the head, and a second
proportlon of the sole plate welght ls concentrated ln a toe of
the head. These flrst and second welght proportlons together
constltute more than 50 percent of the sole plate welght that
ls concentrated ln the perlmeter of the sole plate.
BRIEF D~S~ ON OF THE DRAWINGS
Flg. 1 ls an exploded perspectlve vlew of a golf club head
accordlng to the prlor art;
Flg. 2 ls an exploded perspectlve vlew of another golf
club head accordlng to the prlor art;
Flg. 3 ls a bottom perspectlve vlew of the prlor art golf
club heads ~hown ln Flgs. l and 2 taken when they are
assembled;
Fig. 4 18 an exploded perspective view of a golf club
~ad according to the preferred embodiment of the present
invention; 20~27~6
Fig. S is a bottom perspective view of the golf club
head shown in Fig. 4 taken when it is fully assembled;
Fig. 6 is a vertical cross-sectional view of the golf
club head shown in Fig. 5; and
Fig. 7 is a top plan view of a sole plate used in the
golf club head of Figs. 4 - 6.
D~DTPTION OF TRE PREFERRED EMBODI~ENT
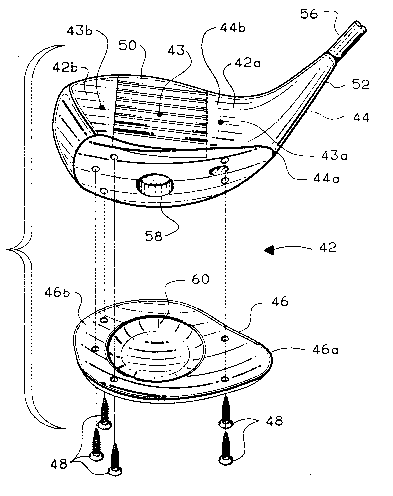
Referring to Fig. 4, a wood type golf club according to
the preferred embodiment of the present invention includes an
enlarged head 42 having a specially shaped body 44 and a sole
plate 46 which is attached to a bottom portion 44a of the body
44 by conventional means such as a plurality of screws 48
and/or epoxy. The body bottom portion 44a has a bottom surface
of compound curvature. An insert 50 preferably formed of a
resin material is mounted in a face portion 44b of the body 44.
The face portion 44b is arranged for impacting a golf ball.
The body 44 includes a neck or hosel 52 with a bore 54 (Fig. 6)
therethrough for receiving and attachment to one end of an
elongated shaft 56. Mounted on the other end of the shaft 56
is a grip (not shown). In the preferred embodiment of the
head 42, body 44 is formed of wood and sole plate 46 iB made of
metal. Alternatively, body 44 could be made of other suitable
materials such as plastic or metal.
If the head 42 is manufactured for use on a wood type golf
club designated a8 a driver (i.e. No. 1 wood) with the body 44
made of wood, a hole 58 is bored in the bottom of the body 44
to remove weight therefrom 80 that when the sole plate 46 is
attached, the head 42 will have a desired total head weight
which i~ used in calculating a swingweight for the golf club.
As previously stated swingweight is generally defined as a
mea~uL~ -nt of a golf club's weight distribution about a point
which ls at a specified distance from the grip end of th2eO~o~f
lub. If the head 42 is manufactured for use on a wood type
golf club ~uch as those designated as a No. 3, 5 or 7 wood with
the body 44 made of wood, no weiqht is removed from the body
44 before attachment of the sole plate 46. Therefore, in all
woods except the driver such as the Nos. 3, 5 and 7 woods, the
boring of hole 58 is not required.
The swingweight for the golf club shown in Figs. 4 - 7 is
determined by taking into account the total head weight of the
head 42 and other factors such as the welght and length of the
shaft 56. The body 44 and the sole plate 46 each have an
individual weight which is less than the total head weight of
the head 42. When making the head 42, the body 44 is weighed
to insure that its weight is within a preselected range, and
then the sole plate 46 is selected from a plurality of sole
plates which are formed of identical material (e.g., aluminum)
but have different weights so that the weight of the selected
sole plate 46 is equal to the total head weight less the weight
of the body 44. Instead of using additional weights (e.g.,
weighted inserts 39, 41) in the body 44 to comr~ncate for
deficiencies in the total head weight of the head 42 as in
prior art golf clubs, the weight of the sole plate 46 iB
increased by merely selecting a heavier sole plate.
As seen in Figs. 4, 6, and 7, the sole plate 46 has a
substantially circular cavity 60 formed in its interior surface
and located generally intermediate a heel 42a and a toe 42b of
the club head 42. The cavity 60 has inclined side walls and
a relatively flat bottom wall. The inclined side walls of
the cavity 60 form an acute angle with the bottom surface of
the body 44 which is adjacent the hole 58 as best shown in Fig.
6. Alternatively, the cavity 60 could be of a different shape
such as an oval. The purpose of cavity 60 is to concentrate a
majority of the weight of the sole plate 46 in perimeter
sections 46a, 46b, 46c and 46d (Fig. 7) of the sole plate 46
by reducing the weight of the sole plate 46 in its center
sectlon 46e. Thus, the cavity 60 in the sole plate 46 ~ 6
~ perimeter weighting of the club head 42. An advantage of
this perimeter weighting is i~n~oved weight distribution in
the heel and toe 42a, 42b of the club head 42 which causes
the club head 42 to resist twisting movements in direction~
indicated by arrow 62 in Fig. 5 when impacting a golf ball at
off-center points 43a, 43b located on the body face portion
44b in the heel and toe 42a, 42b of the head 42. No such
twisting r-v~ ts of the club head 42 occur when impacting a
golf ball at a center point or ~sweet spot~ 43 which is also
located on the body face portion 44b.
The sole plate 46 has an extended heel section 46a and an
extended toe section 46b. The extended heel section 46a
concentrates a first proportion of the perimeter weight of the
sole plate 46 in the heel 42a of the club head 42 while the
extended toe section 46b concentrates a ~econd proportion of
the sole plat perimeter weight in the club head toe 42b. When
combined, these first and second perimeter weight proportions
constitute more than 50 percent of the perimeter weight of the
sole plate 46.
It should be noted that the sole plate 46 does not have a
notch such as notch 24 in sole plate 20 or a straight edge such
as straight edge 26 on sole plate 20. Therefore, the sole
plate 46 is significantly heavier at its ends than the sole
plate 20 thereby resulting in the club head 42 having increased
heel and toe weighting when compared with the club head 10.
Due to the cavity 60, sole plate 46 has significantly less
weight at its center than the sole plate 20. This also
contributes to the improved heel and toe weighting of the club
head 42.
It will be understood that when the club head 42 is
constructed for use on a golf club designated a~ a No. 1 wood,
the sole plate 46 will weigh less than when the club head 42 is
constructed for use on a golf club designated as a No. 3, S
or 7 wood. This is because in a No. 1 wood, the body 44 weighs
more than in the other wcods. In all of the ~o~odrs~ the
~ombined weights of the body 4~ and the sole plate 46 must be
within a preselected range in order to provide a desired
swingweight.
In a correlated 6et of golf clubs, the diameter and the
depth of the cavity 60 may be changed in order to increase or
decrease the weight of the sole plate 46. For example in a No.
5 wood, the cavity 60 has a smaller diameter and iB shallower
than in a No. 3 wood which results in the sole plate weight
being sreater in the No. 5 wood.