Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2082350
MODULAR MOLD
Backqround of the Invention
The present invention concerns modular
molds for making containers, and more particularly
to modular molds for making a hot-fill bottle which
allows height and volume adjustments without
requiring metal modifications of the mold sections.
A container, such as a biaxially-oriented
PET beverage bottle, may be adapted to receive a
hot-fill product with a minimum of thermal shrinkage
and distortion. However, the bottle making and
filling processes include many parameters which
affect the product volume in the finished
container. Thus, the final fill volume can be a
function of: the metal dimensions of the blow mold,
the mold process time, the mold operating
temperature, the preform/bottle material
distribution, the bottle age and storage conditions
prior to filling (e.g., time, temperature, etc.),
the filling line speed, the product fill
temperature, the product fill pressure, and the time
spent between the filler, capper and spray cooler.
Changing any one of these parameters may have a
significant effect on the final product volume,
which is strictly controlled on the minimum side in
order to comply with government labeling
requirements and on the maximum side to avoid the
undue expense of overfilling with excess product.
20g235~
It would be desirable, everytime a bottle
making or filling process parameter is changed, to
avoid machining new mold pieces in order to achieve
the desired fill volume. In addition, it would be
desirable to make custom bottles for different
product lines without having to completely redesign
the mold.
It is known to split a bottle-making mold
above and below the vacuum panel section for making
a bottle of the type described in U.S. Patent No.
4,863,046 entitled "Hot Fill Container," which
issued September 5, 1989 to Collette et al. In the
known mold, a removable shoulder section provides
custom flexibility above the label panel, and a shim
is provided for varying the height (and thus the
volume of the bottle) of the lower glue land -- a
cylindrical section located below the vacuum panels
and above the base and to which adhesive is applied
for attaching the label. However, this creates a
glue land imbalance (since the upper glue land is
not similarly extended) which may hinder a smooth
attachment of the label, and the allowable height of
the shim is severely limited by this glue land
imbalance as well as by the required height of the
vacuum panels. Increasing the bottle height without
a similar increase to the height of the vacuum panel
results in excess bottle vacuum as the product cools
-~ - 3 - 2~2350
(and contracts) and the risk of vacuum collapse. Thus,
the volume and height adjustability with this known
modular mold is quite limited.
Summary of the Invention
It is an object of this invention to provide
an improved modular mold which solves the foregoing
problems.
A modular mold in accordance with the
present invention comprises a mold assembly for forming
a customized container of the type having shoulder,
panel and base portions, the assembly comprising a
central mold section having an inner molding surface
for forming an upper panel portion of the container,
the central mold section having upper and lower
cavities for receiving upper and lower mold sections
respectively; a plurality of upper mold sections each
having a different inner molding surface for forming a
different shoulder portion of the container, the upper
mold section being positionable within the upper cavity
of the central mold section; a lower mold section
having an inner molding surface for forming a lower
panel portion and a base portion of the container, the
lower mold section being positionable within the lower
cavity of the central mold section; and a plurality of
shims each having an inner molding surface for forming
a middle panel portion of the container, one or more of
the shims being positionable within the lower cavity of
the central mold section and above the lower mold
section in order to vary the panel height of the
container.
More specifically, the improved modular mold
of this invention provides volume and height
adjustability in the molded container and is
particularly useful for making bottles for a hot-fill
product. The mold is constructed of three mold
members, with mirror-image right and left upper mold
members and a unitary base member. Each of the two
2082350
_ - 3a -
upper mold members includes a central connecting member
to which the removable mold sections are attachable.
The central connecting member receives a neck finish
plate and customized shoulder section from above, and
one or more shims, lower panel section and base
receiving sections from below.
The one or more shims are thus positioned
between the upper and lower panel sections and define
part of the vacuum panels. By adjusting the number or
height of the shims, the manufacturer can easily and
incrementally adjust the height and final volume of the
bottle. Changing shims is a simple
_ 208235~
matter of loosening the lower bolts which hold the
lower panel and base receiving sections to the
central connecting member, replacing the shims,
reinserting the lower mold sections and tightening
the bolts. No machining of new parts is required.
Furthermore, because of the relatively
large height of the vacuum panel area and because
there is no loss of symmetry by the addition of more
shims, the height/volume adjustability is
extensive. For a 64 ounce PET beverage bottle,
having a total bottle height of about 270mm and a
vacuum panel height of about lOOmm, a shim height
range of up to 20mm or more is possible while still
maintaining a rigid and high-strength mold.
Generally, the filling machines can accommodate this
height change in the bottles. The mold strength is
preserved by maintaining an extensive upper panel
section as part of the central connecting member to
which the other mold pieces are bolted; preferably
the upper panel section is at least half of the
vacuum panel height (about 50mm or more in the
previous example). In contrast, the prior art mold
having a shim in the lower glue land was generally
limited to a maximum 5mm height adjustment and
created an imbalance between the upper and lower
glue lands. Even the addition of a second shim in
the upper glue land, to correct the imbalance, would
~, 2082350
increase the height adjustment only a limited amount
and be impractical because the multiple mold
sections required would be expensive and greatly
reduce the mold strength.
The height/volume adjustability is
particularly useful any time there is a modification
in the bottle making or filling processes which
would affect the dimensions of the hot-fill bottle.
Also, the height/volume adjustability enables the
manufacturer to provide customized shoulder and/or
base sections to make different size or shape
bottles, without having to design a new mold. Thus,
a 64 ounce bottle can be changed to a 2 liter bottle
simply by changing the shim height from say 8mm to
16mm in the previous example. Also, providing
different stylized shoulder and/or base sections,
which changes may substantially alter the volume of
the bottle, can be compensated for by changing the
height of the vacuum panel section with shims, thus
enabling the manufacturer to produce differently
shaped bottles for two different customers, but
having the same volume (e.g., each 64 ounce), while
using the same basic mold set.
Another advantage of providing the shim in
the center of the vacuum panel region is that as the
bottle size increases the manufacturer can increase
the vacuum panel region in order to offset the
additional vacuum contraction (during cooling) of
the product in the larger bottle.
- 6 - 2 082 350
Brief Description of the Drawings
Fig. 1 is a schematic view, partially in
section, of a formed bottle and the three separated
mold members, with both the parison and closed mold
members shown in phantom.
Fig. 2 is an exploded cross-sectional view
of the upper mold members, with two different shoulder
and base shapes in the left and right halves and the
corresponding bottle halves shown in the center.
Fig. 3 is an upper plan view, partially in
section, taken along the section lines 3-3 of Fig. 4.
Fig. 4 is a side plan view in cross-section
showing the three mold members of Fig. 1 closed to form
a complete mold set.
Detailed Description
The preferred mold apparatus described
herein is adapted for making a hot-fill PET
(polyethylene terephthalate) beverage bottle of the
type described in U. S. Patent No. 4,863,046 entitled
"Hot Fill Container", which issued 9/5/89 to Collette
et al.
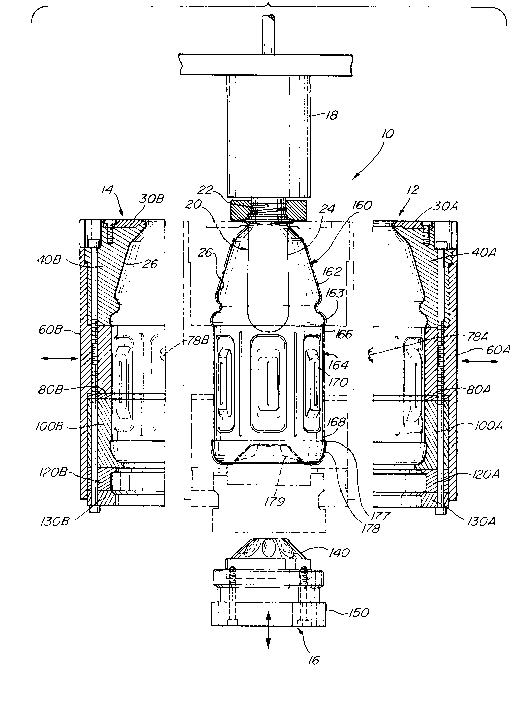
The bottle, as shown in Fig. 1 (bottle 160)
and described in the Collette patent, is made from a
preform 20 having a thread finish 22, attached to
2082350
carrier 18, and a lower tube portion 24 which is
blown into a bottle shape in a mold 10. During
blowing, the preform assumes the shape of the
interior molding surface 26 of the mold, to form: a)
an upper shoulder portion 162; b) a middle label
panel portion 164, which includes an upper glue land
166, vacuum panel region 170, and lower glue land
168; and c) a base 178. The upper shoulder 162
flares radially outwardly from the relatively narrow
diameter neck of the thread finish 22 to the label
panel 164, and includes a bumper 163 of greater
diameter than the label panel 164 in order to
protect the attached label 174 during shipment and
storage. The base 178 also includes an enlarged
diameter bumper 177 to protect the label and a
recessed closed bottom 179. The vacuum panels 170
may take different forms, as shown in Fig. 1 herein
or the Collette patent, but generally include a
plurality of vertically elongated recesses and
reinforcing ribs. The upper and lower glue lands
are cylindrical bands which, along with portions of
the vacuum panels, form the label area on which the
label rests.
The modular mold of this invention, as
shown in Fig. 1, has three movable mold members 12,
14, 16 which come together as indicated by the
arrows to form the closed mold shown in phantom
20g2~50
- 8 -
around preform 20. The upper right and left half
members 12, 14 respectively are mirror images and
move horizontally to close, with right retaining
member 78A engaging left retaining member 78B. For
ease of understanding, the mirror image components
of the right and left members have been labeled A and
B respectively. The third mold member is a unitary
base member 16 which moves vertically to fit within
a base receiving portion of the members 12, 14.
As shown in Fig. 1, the mold members 12, 14
each include a central fixed connecting member 60A,
60B which forms an outer rectangular housing of the
mold set (see Fig. 3), and to which the other mold
sections are attached with bolts. The members 60A,
60B each have an inner molding surface 62 which
together define the upper panel section of the
bottle. The members 60A, 60B each have an upper
cavity which receives a combined shoulder section
40A, 40B and neck plate 30A, 30B. The members 60A,
60B each have a lower cavity which receives a shim
80, lower panel section 100, base locator section
120, and bottom plate 130. The base member 16
includes an upper base plug 140 bolted to a base
pedestal 150.
Fig. 2 shows an exploded view of the left
and right members to show how these mold members are
assembled. Fig. 2 also shows two different mold
208~35D
halves on the left and right to illustrate how the
insertion of different shoulder and lower panel
sections and shims enables the production of two
different bottles, the different bottle halves being
disposed on opposite sides of the centerline in
Fig. 2. The left half is the same as that shown in
Fig. 1, while the right half is the same as Fig. 1,
except for a different customized shoulder 240, shim
280, and lower panel 300.
With regard to assembly of the mold, Fig. 2
shows that neck plate 30 fits within a cavity 44
(244) in the top of shoulder 40 (240), and a bolt 38
passes through aligned bores 34, 48 (248) in the
neck plate and shoulder to secure the same. The
combined neck plate and shoulder fit within an upper
cavity in upper panel section 60 defined by first
step 64 which receives that portion of the shoulder
above outer notch 41 (241) and a second step 66
which receives that portion of the shoulder below
the notch. A bolt 58 passes through aligned
apertures 46 (246) in the shoulder 40 (240) and
apertures 68 in the central section 60 to secure the
same. Similarly, the central section 60 has a lower
cavity defined by a third step 70 which receives, in
order from top to bottom, shim 80 (280), lower panel
section 100 (300), base locator section 120, and
bottom plate 130. A bolt 138 passes through aligned
apertures 68, 88 (288), 106 (306), 124, and 134 in
these sections respectively to secure the same to
central member 60.
~ 208~350
- 10 -
With regard to customizing the mold
sections, neck plate 30 is the same on the left and
right and has an inner surface 32 adapted to receive
the lower neck flange of the parison 20. Shoulders
40 and 240 on the left and right respectively have
differently shaped inner molding surfaces 42 and
242. The customized shoulder 162 of the left bottle
160 is straighter than shoulder 362 of the right
bottle 360, as determined by the different molding
surfaces 42 and 242 respectively. The upper panel
molding surfaces 62 are the same, but because of
differences in shoulder shape 42 (242) (and/or also
in base shape 103 (303) as described hereinafter),
different height or thickness shims 80 (280) are
provided to vary the overall height or length of the
label panel. Bottle 160 has a label panel of height
Ll covered by label 174, while bottle 360 has a
greater label panel height L2 covered by label
374. Left shim 80 has a height Tl, between top
and bottom surfaces 82, 83, which is less than the
height T2 of right shim 280 between top and bottom
surfaces 282, 283. The respective label panels are
defined by the combined molding surfaces 62, 81
(281), and 102 (302) of the upper panel, shim and
lower panel sections. The customized base 178 of
the left bottle is less rounded than base 378 of the
right bottle, as determined by the different molding
surfaces 103 and 303 respectively. The bottles 160
~ 2082~5~
- 11 -
(360) each receive a cap 176 (376) over the thread
finish and have designated thereon for illustrative
purposes the desired fill lines F for the hot-fill
product.
Figs. 3 and 4 show top and side sectional
views of the assembled mold of Fig. 1, wherein there
are shown feed tubes 180 which supply a liquid
cooling medium (e.g., water) to passages 182 in the
upper mold halves 12, 14. O-rings are provided
where the cooling passages pass from one mold
section to another, and include a set 56 in the
bottom of shoulder 40, a set 98 in the top of shim
80, a set 116 in the top of lower panel section 100,
and a set 118 in the bottom of lower panel section
100. Also, Fig. 4 shows how unitary base member 16
fits between the upper mold halves 12, 14. Base 16
includes upper base plug 140 and lower pedestal 150,
connected by bolt 158 which passes through aligned
apertures 152, 148 in the pedestal and plug
respectively. Liquid cooling passages 184 are
provided, which include a spiral configuration
between the plug and pedestal, and a set of O-rings
146 are likewise provided. Pedestal 150 has an
upper enlarged diameter registration or retaining
ring 156 which fits within a cylindrical cavity 128
in base locator section 120. Fig. 3 shows a top
sectional view of shim half 80A, with bolts 138A
-
2~82~5D
- 12 -
passing therethrough for connection to the central
member 60, cooling passages 182, and the inner
molding surface 81A which defines a section of the
vacuum panels.
While a preferred embodiment of the
invention has hereinbefore been described, it will
be appreciated that variations and equivalents
thereof will be perceived by those skilled in the
art, which are nevertheless within the scope of the
invention as defined by the claims appended hereto.