Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
716
The invention relates to a new process for the
preparation of new heterocyclically substituted
carbamates, which are important intermediates for the
synthesis of pharmaceutical active substances, in
particular for the synthesis of biologically active
peptide~ and peptide mimetics.
The invention also relates to new heterocyclically
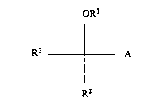
substituted carbamates of the general formula (I)
oR3
Rl A (1).
R2
in which
0 R2 represents a 3- to 8-membered, saturated or
unsaturated heterocycle having up to 2 heteroatoms
from the series comprising S and 0 or having a group
of the formula -NR', -SiR5RsR7 or -SnR5R6R7,
in which
R' denote~ hydrogen, straight-chain or branched
alkyl having up to 8 carbon atoms, phenyl or
Le A 28 841 - 1 -
,
, .
.,..... . ,~
,
' , ,.
, . - . .
`` ~ 7~;
benzyl,
Rs, R6 and R' are identical or different and denote
straight-chain or branched alkyl having up to
8 carbon atoms or phenyl,
S where these substitutents can optionally be sub-
stituted up to 3 times b~ identical or different
straight-chain or branched alkyl or alkoxy each
having up to 8 carbon atoms, hydroxyl, phenoxy or
benzyl or by a 5- to 7-membered, saturated or unsat-
urated heterocycle having up to 3 heteroatoms from
the series comprising S, N and O, by aryl having 6
to 10 carbon atoms or by a group of the formula
-NR8R9
in which
R8 and R9 are identical or different and have the
abovementioned meaning of R4,
R1 represents hydrogen or the group -SiRsR6R7,
in which
Rs, R6 and R7 have the abovementioned meaning,
R3 represents a group of the formula -CO-NRl0R1l,
in which
Le A 28 841 - 2 -
.
Rl and R1l, together with the nitrogen atom, form a
heterocyclic radical of the formula
R~<RI3
N O
Rl, ¦ I Rl4
Rl6 Rls
in which
Rl2 Rl3 R14, Rl5, Rl0 and Rl7 are identical or dif-
S ferent and denote hydrogen, staight-chain or
branched alkyl having up to 8 carbon atoms,
phenyl or cycloalkyl having 3 to 6 carbon atoms
or in each case R12 and Rl3, Rl4 and Rls and/or Rl6
and Rl7 together form a 3- to 6-membered,
saturated carbocycle,
A represents straight-chain or branched alkyl or
alkenyl each having up to 8 carbon atoms, each of
which is optionally sub6tituted up to 3 times by
identical or different substituents from the series
comprising hydroxyl, phenyl and cycloalkyl having 3
to 7 carbon atoms or by a group of the formula
-NRl0Rl9 -HN-CO-OR20, -SiR2lR22R23 or -SnR2lR22R23
in which
Rl8 and Rl9 have the abovementioned meaning of R4 and
are identical to or different from this
Le A 28 841 - 3 -
..-
` ~ : -
:
~c~
and
R20 denotes straight-chain or branched alkyl having
up to 6 carbon atoms, which is optionally
substituted by phenyl,
R21, R22 and R23 have the abovementioned meaning of Rs,
R6 and R7 and are identical to or different
from this,
or
represents straight-chain or branched acyl Xaving up
to 8 carbon atoms,
represents cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl having 3 to 7
carbon atoms, which is optionally substituted by
hydroxyl, or
represents carboxyl, alkoxycarbonyl having up to 4
carbon atoms or a group of the formula -SiRZ1R22R23,
-SnR21R22R23 or R24-co
in which
R21, R22 and R23 have the abovementioned meaning
and
R2~ denotes hydrogen or straight-chain or branched
alkyl or alkenyl each having up to 8 carbon
atoms, each of which i8 optionally substituted
up to 3 times by phenyl or by the group of the
Le A 28 841 - 4 -
' .
2~
formula -NH-CO-OR20,
in which
R20 has the abovementioned meaning.
In the sub-substitution, heterocycle in general
S represents a 5- to 7-membered, preferably 5- to 6-
membered, saturated or unsaturated ring which as
heteroatoms can contain up to 2 oxygen, sulphur and/or
nitrogen stoms. Preferred S- and 6-membered rings are
those having an oxygen, sulphur and/or up to 2 nitrogen
atoms. The following are mentioned as being particularly
preferred: pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl, pyridyl, pyrimidyl,
pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl, thiazolyl, oxazolyl, imidazolyl,
isoxazolyl, pyrrolidinyl, piperidinyl, piperazinyl,
tetrazolyl or morpholinyl.
A 3- to 8-membered, saturated heterocycle is in general
represented by pyrrolidine, piperidine, pyrazolidine,
imidazolidine or oxazolan. Pyrrolidine and oxazolan are
preferred.
Preferred compounds of the general formula (I) are those
in which
R2 represents a heterocyclic radical of the formula
Le A 28 841 - 5 -
........ ...... ..
,: - ~ . . . . . . . :
. , . . . - ::
;.
.: . - : .
. - .. ~ . ..
\
R~ H3C
or O y N-R~
H3C CH3
in which
R~ denotes hydrogen, straight-chain or branched
alkyl having up to 6 carbon atoms, phenyl or
benzyl,
Rl represents hydrogen,
R3 represents a group of the formula -CO-NRlRll,
in which
R10 and Rll, together with the nitrogen atom, form a
heterocyclic radical of the formula
Rl2 R~3
O
¦ ¦ Rl4
Rl6 Rl5
in which
Rl2 Rl3 R1~, Rls, R16 and R17 are identical or dif-
ferent and denote hydrogen, straight-
Le A 28 841 - 6 -
chain or branched alkyl having up to 6
carbon atoms, cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl or
cyclohexyl, or in each case Rl2 and Rl3, Rl~
and Rls or Rl6 and Rl7 together form a
cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl
ring,
A represents straight-chain or branched alkyl or
alkenyl each having up to 6 carbon atoms, each of
which is optionally substituted up to 2 times by
identical or different substituents from the group
comprising hydroxyl, phenyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl
and cyclohexyl or by a group of the formula -NR1~R19,
_NH_co-OR20, -SiR2lR22R23 or -SnR2lR22R23
in which
R19 and Rl9 have the abovementioned meaning of R~
and are identical to or different from this,
R20 denotes straight-chain or branched alkyl having
up to 4 carbon atoms, which is optionally sub-
stituted by phenyl,
R21, R22 and R23 are identical or different and
denote straight-chain or branched alkyl having
up to 4 carbon atoms or phenyl,
or
Le A 28 841 - 7 -
'
. .
., ~ .
',
...
~s~l6
represents straight-chain or branched acyl having up
to 6 carbon atoms,
represents cyclobutyl or cyclohexyl, each of which
is optionally substituted by hydroxyl, or
represents carboxyl, alkoxycarbonyl having up to 3
carbon atoms or a group of the formula -SiRZlR22R23,
-SnR2lR22R23 or R24-co
in which
R21, R22 and R23 have the abovementioned meaning
and
RZ4 denotes hydrogen or straight-chain or branched
alkyl or alkenyl each having up to 6 carbon
atoms, each of which is optionally substituted
by phenyl or by the group of the formula
-N~-CO-ORZ,
in which
RZ has the abovementioned meaning.
Particularly preferred compounds of the general formula
(I) are those
in which
Le A 28 841 - 8 -
~, .. ' :
~ ¢~ 5 ~ 6
R2 represents a heterocyclic radical of the formula
N-R4 H3C ~
or N-R4
H3C CH3
in which
R4 denotes hydrogen, straight-chain or branched
alkyl having up to 4 carbon atoms, phenyl or
benzyl,
Rl represents hydrogen,
R3 represents a group of the formula -CO-NRl0R1l,
in which
Rl and Rll, together with the nitrogen atom, form
a heterocyclic ring of the formula
R12 R13
\NXO
R" ~ R~4
R~6 R15
in which
R12 R'3 Rl~, Rls, Rls and Rl7 are identical or dif-
ferent and denote hydrogen, straight-
chain or branched alkyl having up to 4
Le A 28 841 - 9 -
. ~
.. - - ~ ~ - - . ~ ............... :
. ; - .
carbon atoms, cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl or
cyclohexyl, or in each case Rl2 and R1~, Rl4
and Rls or Rl6 and Rl7 together form a
cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl
ring,
A represents straight-chain or branched alkyl or
alkenyl each having up to 4 carbon atoms, each of
which is optionally substituted by hydroxyl, phenyl,
cyclobutyl or cyclohexyl or by a group of the
formula -NR~8R~9 -NH-CO-OR20, -SiR2~R22~23 or
-SnR2lR22R23
in which
Rl3 and R19 are identical or different and have the
abovementioned meaning of R4 and are identical
to or different from this,
R20 denotes methyl or ethyl, each of which is
optionally substituted by phenyl,
R2l, R22 and R23 denote straight-chain or branched
alkyl having up to 4 carbon atoms,
or
represents straight-chain or branched acyl having up
to 4 carbon atoms,
represents cyclobutyl or cyclohexyl, each of which
is optionally substituted by hydxoxyl,
Le A 28 841 - 10 -
~?.G~57~fi)
represents carboxyl, alkoxycarbonyl having up to 3
carbon atoms or a group of the formula -SiR21R22R23,
-SnR2~R22R23 or R24-co_,
in which
R2l, R22 and R23 have the abovementioned meaning
and
R2~ denotes hydrogen or straight-chain or branched
alkyl or alkenyl each having up to 4 carbon
atoms, each of which is optionally substituted
by phenyl or by the group of the formula
-NH-CO-OR20,
in which
R20 has the abovementioned meaning.
Additionally, a new process for the preparation of the
compounds of the general formula (I) according to the
invention has been found, characterised in that
carbamates of the general formula (II)
Le A 28 841 - 11 -
~,
, .
~¢~5~
Rl Rl
CH 0 C
in which
Rl, R2, Rl and Rll have the abovemen~ioned meaning,
are first enantio electively deprotonated in inert
solvents, in the presence of a selective base, preferably
S sec-butyllithium, and of a chelate-forming di~mine (in
the following designated by D) to give the carbanion
complex compounds of the general formula (III)
Rlo
~ N`
~ B ~0
in which
Rl, R2, R10 and Rll have the abovementioned meaning,
0 B represents a lithium, magnesium, titanium, zirconium
or potassium atom, preferably lithium,
and
Le ~ 28 841 - 12 -
16
D represents a chelate-forming diamine such as, for
example, tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA) or (-)-
sparteine, preferably TNEDA,
and then reacted with electrophiles of the general
formulae (IV) and (V)
o
A-M (rV) T ~ T'
in which
A has the abovementioned meaning,
M represents halogen, C,-C,-alkoxy or another typical
leaving group, preferably chlorine,
and
T and T' are identical or different and represent hydrogen or a chemi- cally useful radical shown under the substituent A,
or with CO2.
The process according to the invention can be illustrated
by way of example by the following reaction scheme:
Le A 28 841 - 13 -
. ~ ' ''' :
-
U ~ ~EDA
CH2 u~ auU / TMEDA ~ o CH
s ~ 2 O-C~ C~ H,C,~ ~CH,
CHJ HaC
S u r -- HCC~'H~C Cl 1, 0 C- H,
prisin
gly,
the proce~s according to the invention gives the desired
compounds of the general formula ~I) in high yields.
The process is distinguished by ~everal advantages: in
contrast to the prior art, stoichiometric amounts of
bases, preferably sec-butyllithium, are adequate for
deprotonation. Additionally, the process according to the
invention enables both control of the diastereo-
selectivity by the choice of the electrophilic sub-
stituents and the influencing of asymmetric induction in
the case of prochiral carbamates in the presence of
chiral complex-forming diamines.
By the use of enantiomerically pure diamine compounds
such a~, for example, TMEDA, deprotonation of the
compounds of the formula (II) takes place
enantioselectlvely and in very good yields to give the
Le A 28 841 - 14 -
-
35~
corresponding chiral compounds, preferably to give the
(S)-lithium compounds of the formula (III), which can
preferably be converted into the R-configuration by
further reaction with electrophiles.
It is additionally surprising with knowledge of the prior
art that the metallated compounds of the general formula
(III) undergo no decomposition and a deprotonation in the
benzyl radical. In particular, a high diastereo-
selectivity and stereochemical control in the attack of
the electrophile due to the induction of the stereocentre
already present is of great advantage.
In addition to chlorine, bromine and iodine, the radicals
tosylate, meaylate or -OS02-CF3 are also covered under the
definition leaving group. Chlorine is preferred.
Suitable solvents for the deprotonation are preferably
inert organic solvents such a6 hydrocarbons such as
hexane, pentane, ligroin or toluene, and ethers, for
example tetrahydrofuran, diethyl ether, dioxane,
dimethoxyethane, diglyme, triglyme or tert-butyl methyl
ether. Tetrahydrofuran and diethyl ether are particularly
preferred.
Deprotonation is carried out in a temperature range from
-lOO-C to room temperature, preferably at about -78-C to
O-C .
Deprotonation can be carried out either at normal
Le A 28 841 - 15 -
-' .- ~ ~ . .
.
;7~6
pressure or at elevated or reduced pressure (for example
0.5 to 2 bar)l preferably at normal pressure.
Suitable selective bases are alkyllithium compounds
having up to 6 C atoms in the alkyl group, preferably n-
butyllithium or sec-butyllithium.
The base is employed in an amount from 0.5 to 5 mol,
preferably in stoichiometric amounts, relative to 1 mol
of the compounds of the general formula (II).
Electrophilic substitution likewise takes place in the
abovementioned solvents, preferably in tetrahydrofuran at
normal pressure.
Electrophilic substitution is carried out in a tempera-
ture range from about -100-C to +40-C, preferably in the
range from -78-C to room temperature.
The compounds of the general formula (II) are also new
and can be prepared by a process in which
compounds of the general formula (VI)
Rl
~C-OH (Vl),
I
R2
in which
Le A 28 841 - 16 -
: . . .: . .
: . ~
-. ...
,: ' , :-: '.:. ~
. .: ; . . .:
.. . . ::,
- ~:
7~Lfi
R' and R2 have the abovementioned meaning
are reacted with compounds of the general formula (VII)
O
Il
Z - C NRlR~l (VII),
in which
R10 and R11 have the abovementioned meaning
and
Z represents halogen, preferably chlorine,
in one of the abovementioned solvents, preferably ether,
in the presence of a base, preferably sodium hydride.
The compounds of the general formulae (VI) and (VII) are
known or can be prepared by a customary method [cf., for
example, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans l, 1074, 1101].
The compound of the general formula (III) are new and
can be prepared by the process indicated above.
The compounds of the general formulae (IV) and (V) are
known or can be prepared by customary methods.
The compounds according to the invention are also
Le A 28 841 - 17 -
' : ' ,. ~ .
5~ 3L6
distinguished by the fact that, after the enantio-
selective introduction of the electrophile, the pro-
tective group -CO-NR10Rl1 can be very easily removed with
the formation of the free hydroxyl group.
Removal of the protective groups (carbamic acid esters)
i8 carried out by a customary method, for example by
sequential treatment with acids and bases, preferably in
methanol.
Suitable acids are strong inorganic acids and organic
sulphonic or carboxylic acids such as, for example,
methanesulphonic acid, ethanesulphonic acid, benzene-
sulphonic acid, toluenesulphonic acid, acetic acid or
propionic acid.
Suitable bases are alkali metal and alkaline earth metal
hydroxides such as, for example, sodium hydroxide,
potassium hydroxide or barium hydroxide. Barium hydroxide
is preferred.
The acids and bases are employed in an amount from 0.01
to 10 mol, preferably l mol, relative to 1 mol of the
compounds of the general formula (I).
Removal of the protective groups is carried out at normal
pressure in a temperature range from 0C to +130-C,
preferably from +20-C to +lOO-C.
Le A 28 841 - 18 -
,
,~ -.
...
35~3~fi
Removal can al80 be carried out with lithium aluminium
hydride in one of the abovementioned solvents, preferably
tetrahydrofuran.
The compounds according to the invention are thus useful
S intermediates for the preparation of hydroxy-substituted
heterocycles, some of which are known and some of which
are new, in particular proline derivatives, which are of
great importance for the synthesis of biologically active
peptidec or peptide mimetics.
The abbreviations a and b used in the following have the
following meaning:
0~
-C-N ~ 0
0~
Il /
b= -C-N~x~O
/\
Le A 28 841 - 19 -
;, ., . '
; -. ' ~ . ~ ` '
.
:
~,2~q~6
,startinq Compounds
Example I
(S)-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-l-benzyl-pyrrolidine
~CH2C~s
C~H
3.79 g (37.5 mmol) of (S)-prolinol and 5.5 ml (47.4 mmol)
of benzyl chloride are heated under reflux for~48 h with
3.7 g of potassium carbonate in 100 ml of ~toluene.
Contrary to the literature procedure;, the mixture is
fractionated in vacuo. 5.52 g (77%, Lit.s66%) of the
title compound are obtained a~ a colourless oil. The
~pectro~copic~data correspond to those given in the
literature.
~U
(S)-(-)-(l-Benzylpyrrolidinyl)-methyl 2,2,4,4_
eetramethy~ 3-oxazolidine-3-carboxylate
CH2-C,H,
~ ~O-b
402 mg (14 mmol) of sodium hydride (80% strength in
mineral oi}) are initially introduced into 10 ml of ether
at room temperature. 1.91 g (10 mmol) of the compound
from ~xample I are added dropwi~e to thi~ mixture. It 1
Le A 28 841 - 20 -
= ...... . . . .
- : - ~, . . - : .
.. ...
5~:~L6
stirred for 1 h for complete deprotonation and then
treated with 2.30 g (12 mmol) of the carbamoyl chloride,
dissolved in 5 ml of ether. The reaction mixture is
stirred for 5 days at room tempersture. Hydrolysi~ i8
then carried out with 5 ml of water. The aqueous pha~e is
extracted three times with 5 ml of ether each time, and
the combined organic phases are dried over magnesium
sulphate and concentrated in vacuo. After separation by
column chromatography on silica gel (ether~pentane = 1:2,
silica gel 0.2-0.06), 2.84 g (82%) of the title compound
are obtained as a colourless oil.
R~ = 0.37 (silica gel, ether/pentane = 1:1)
la]20 = -60.2 (c = 2.1, CHC13).
Preparation Examples
Example 1
(lR,2'S)-(-)-(l-Benzylpyrrolidinyl)ethyl 2,2,4,4-tetra-
methyl-1,3-oxazolidine-3-carboxylate
a) Precursor CH2-C~
N
C~b
U x T~ED~
Le A 28 841 - 21 -
Zj,~
CH2-C,H~
b) N/
r ~ O~b
CH~
346 mg (1.0 mmol) of the compound from Example II and
446 ~1 of tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA, 3.0 mmol)
are dissolved in 8 ml of ether. This solution is treated
at -78C with 2.17 ml (3.0 mmol) of sec-butyllithium
(1.4M in cyclohexane/isopentane); in this process the
solution changes colour to orange-yellow (a). The mixture
is stirred at this temperature for 3 h and 187 ~1
(3.0 mmol) of iodomethane are then in~ected. The mixture
is additionally stirred at this temperature for a further
1 h and the cooling bath is then removed. After thawing
at room temperature, the solution is hydrolysed with 2 ml
of water. After separation of the phases, the aqueous
phase is extracted a further three times with 5 ml of
ether cach time. The combined organic phases are dried
over magnesium sulphate and concentrated in vacuo. After
separation by column chromatography on alumina (activity
stage II), 259 mg (72~) of the title compound are
isolated as colourless crystals.
M.p.: 52-C ~from the melt)
R~ = 0.67 (a~umina, ether/pentane = 1:1)
[a]20 = -51.0 (c = 0.5, CHCl3).
Le A 28 841 - 22 -
- -- - , ': . . -
,..-
.
-
~5~
Example 2
(IR,2'S)~ (l-Benzylpyrrolidinyl)-trimethylsilyl-methyl
2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-oxazolidine-3-carboxylate
~ H2-C,Hs
N
r ~. Ob
By the method described above, in the case of the
reaction of 346 mg (1.0 mmol) of the compound from
Example II with 2.17 ml (3.0 mmol) of sec-butyllithium,
446 ~1 (3.0 mmol) of TMEDA and 378 ~1 of trimethylsilyl
chloride, 140 mg (33%) of the title compound are obtained
as a waxy ~olid. M.p.: 45C (from the melt)
Rf = 0.55 (alumina, ether/pentane = 1:1)
t]20 = -54.8 (c = 1.5, CHCl3).
Example 3
(IR,2'S)-(-)-(l-Benzylpyrrolidinyl)tributylstannyl-methyl
2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-oxazolidine-3-carboxylate
Le A 28 841 - 23 -
:
' '~
. . .
:
' ~ :
7~Ç~
CH2 C6Hs
r s Ob
Sn(C~H~
Analogously, from 346 mg (1.O mmol) of the compound from
Example II and 865 ~1 (3.0 mmol) of tributylstannyl
chloride, 451 mg (71~) of the title compound are obtained
as a colourless oil.
R~ = O.66 (alumina, ether/pentane = 1:1)
t~]20 = -69.6 (c = 1.0, CHCl3).
Example 4
Methyl (2S,2'S)-(-)-2-[1-benzylpyrrolidinyl-(2,2,4,4-
tetramethyl-1,3-oxazolidin-3-yl-carbonyl)oxy]ethanoate
CH2 C,~s
r S. 0~
COOCH,
346 mg ll.0 mmol) of the compound from Example II are
metallated for 3 h by the method described above. Carbon
dioxide is then introduced at -78C for 1 h and the
mixture is warmed to room temperature under a carbon
dioxide atmosphere. The reaction solution is hydrolysed
with 10 ml of 2N hydrochloric acid. The aqueous pha~e is
Le A 28 841 - 24 -
.
' , , .
.. . ... ..
~C~357~6
extracted a further three times with 10 ml of ether each
time. The combined ethereal phases are dried over
magnesium sulphate and concentrated in vacuo. The residue
is dissolved in 10 ml of ether and treated with
diazomethane (0.6M in ether) until a yellow coloration
remains; excess diazomethane is destroyed using ~ilica
gel. The solution is freed of solvent in vacuo and
purified by column chromatography on silica gel
(ether/pentane = 1:4). 162 mg (40%) of the title compound
are obtained as a colourless oil.
Rf = 0.46 (silica gel, ether/pentane = 1:1)
ta]20 = -19.2 (c = 1.0, CHC13).
Example 5
(lS;2'S)-(-)-l-(l-Benzylpyrrolidinyl)-2-hydroxymethyl-
propyl 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-oxazolidine-3-carboxylate
CH2-C,H5
~O b
~--OH
H3C
In the metallation 346 mg (1.0 mmol) of the compound from
Example II with 446 ~1 (3.0 mmol) of TNEDA and 2.1~ ml
(3.0 mmol) of sec-butyllithium and subsequent reaction
with 220 ~1 (3.0 mmol) of acetone, 135 mg (35%) of the
title compound result as colourless crystals.
N.p.: 102-C (ether/pentane)
Le A 28 841 - 25 -
~C~71fi
Rf = 0.20 (silica gel, ether/pentane = 1:1)
[a]236S = -17.4 (c = 1.0, CHC13).
Example 6
(lS,2RS, 2'S)-(-)-1-(1-Benzylpyrrolidinyl)-2-hydroxy-3-
methylbutyl 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-oxazolidine-3-
carboxylate
CH2-C,Hs
~'
H3C ~ OH
H3C
Two dia~tereomers are obtained from the reaction of
346 mg (1.O mmol) of the compound from Example II with
273 ~l (3.0 mmol) of isobutyraldehyde. One diastereomer
is isolated as colourless crystals in 23% (95 mg) yield.
M.p.: 64C
Rr = O.52 (alumina, ether/pentane = 1:1)
ta]D = -8.1; [a]2355 = -13.7 (c = 1.2; CHC13).
The second diastereomer is obtained as 8 colourless oil
in 62% (260 mg) yield.
Rf = O . 43 (alumina, ether/pentane = 1:1)
[a]20 = -1.3; [a]235S = -15.8 (c = 1.2; CHCl3).
By Examples A and B, it is intended to illustrate by way
of example how the compounds of the general formula (I)
according to the invention can be converted into the
Le A 28 841 - 26 -
5716
corresponding hydroxy compound~.
Example A
(IR, 2'Sj-(-)-(1-Benzylpyrrolidinyl)-ethanol
~ 1'12 C~Hs
r s 0
~ ',~
CH,
1.41 g (3.9 mmol) of the compound from Example 1 are
heated under reflux for 16 h with 74Q ~1 (11.4 mmol) of
mathanesulphonic acid in 15 ml of methanol. After addi-
tion of 5 g of barium hydroxide, the mixt ~-e is then
heated under reflux for a further 4 h. After cooling to
room temperature, the inorganic residue is filtered off
on a short silica gel column. The filtrate i8 concen-
trated in vacuo, the residue is taken up with ether and
the solution is dried over magnesium sulphate. After
removal of the solvent in vacuo, the residual oil is
purified on alumina (activity stage III, ether/pentane
= 1:2). 532 mg (66~) of the title compound are obtained
as a colourless, slightly unstable oil.
Rr = 0.56 (alumina, ether/pentane = 1:1)
t]20 = -85.0 (c = 0.7, CHCl3).
Example B
(2S, 3S)-(-)-2-(Hydroxyethyl)-pyrrolidine
Le A 28 841 - 27 -
.- -
,
,
2~35716
~OH
CH,
For the removal of the benzyl group, 481 mg (2.3 mmol) of
the compound from Example A are hydrogenated for 8 h
under a slight hydrogen overpressure using 488 mg
(0.46 mmol) of palladium (10% strength on carbon) in
lS ml of methanol and 0.5 ml of formic acid. After
completion of the reaction, the palladium is filtered off
through a thin silica gel layer. The filtrate is concen-
trated in vacuo and taken up with 5 ml of SN hydrochloric
acid. The hydrochloric acid solution is extracted three
times with 5 ml of ether each time and the extracts are
discarded. After careful neutralisation with 30% strength
sodium hydroxide solution, the aqueous phase is extracted
three times with 10 ml of ethyl acetate each time. The
combined organic ethyl acetate phases are dried over
magnesium sulphate and freed of solvents in vacuo. The
residue is recrystallised from ethyl acetate/pentane.
112 mg (42%) of the title compound are thus obtained as
slightly unstable, colourless crystals.
M.p.: 86C
[a]20 = -36.4 (c = 1.0, CH30H).
Le A 28 841 - 28 -
- ' ' . ' ''' ~ ~ ','
.
: ~ . .