Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
- ~ 2095272
Mid-sole or Sole of Shoes
This invention relates to a mid-sole or a sole of shoes,
which seeks to provide shock absorption during walking and
also a massage effect owing to excitation of the sole of
foot, while providing for comfortable wear. Of course, the
invention also is applicable to and covers sandals and the
like.
In the prior art, it is well known that absorption of
shocks and massaging of the sole of the foot during walking
are effective for maint~;ning health. The applicant has
earlier proposed a sole (or a mid-sole) for shoes, which
comprises a base plate with a recess and a plurality of
slanted blades formed therein. A flexible cover with the
outer periphery thereof fused to the outer periphery of the
top of the base plates has water sealed in the recess (as
disclosed in United States patent specification 5,189,816).
When a person wearing shoes with such soles walks, the sealed
water moves in the recess to absorb shocks during the walking
while providing a stable and comfortable sense of wearing.
In addition, with adequate rigidity of the blades and action
of water to alleviate the rigidity, the sole of the foot can
be excited continuously with adequate strength while not
providing any pain even when the shoes are worn for a long
time.
However, shoes using the above sole are subject to
leakage of the sealed-in water. From examination, water
leaks from a specific portion, i.e., a front end portion
adjacent to, for instance, the little to middle toes of the
-- 1 --
.~
2095272
foot. Investigation found the following. Since the cover is
formed with a recess having a shape corresponding to the sole
of the foot, the base plate portion corresponding to the
recess is naturally reduced in thickness, and a portion
corresponding to the little to middle toes, particularly to
the third toe, is usually strongly pushed down and deformed
when the shoe is about to be lifted from the ground. With
this force, together with the urging force of the water, the
fused portion in the neighborhood of the portion contacted by
the little to middle toes, is weakened, which results in the
leakage of water.
An object of the invention is to provide a mid-sole or
sole for shoes, which can prevent the leakage of sealed water
and improve the sense of wearing of shoes.
A feature of the present invention is that the cover has
an increased thickness portion formed around its recess
portion, thus to reduce the deformation of the marginal
portion of the cover around the recess portion thereof caused
by concentrated urging force from the toes. This maintains
the effect of fusion of the marginal portion and prevents
leakage of sealed water reliably and for long time. In
addition, another aspect of the invention is that the feeling
of contact between the sole of the foot and the cover can be
alleviated by the increased thickness portion, thus improving
the sense of wearing the shoes. Further, another feature of
the present invention resides in that blades formed on a
cover portion subject to urging by the toes and enlarged toe
-- 2
~,
2095272
roots, has an effect of damp~ning the movement of fluid thus
assisting in prevention of leakage of the sealed fluid more
completely, more reliably and for longer period of time.
The invention provides, in a mid-sole or sole of shoes,
a base plate with a plurality of integral blades, a cover
fused to a marginal portion of the base plate, and a fluid
sealed in the space defined between the base plate and cover.
The top surface of the base plate is formed with a recess
having an area corresponding to the sole of the foot, the
blades being slanted toward the recess of the base plate, the
cover having an increased thickness portion with a
predetermined width formed around the recess of the shape
corresponding to the sole of the foot. The base plate and
cover have their marginal portions fusedly bonded to each
other.
Another aspect of the invention resides in that at least
a portion of the cover in the recess thereof, which is
pressed by the toes and swollen toe roots, has slanted fluid
shock buffer blades exten~ing in a direction perpendicular to
the longitudinal direction of the cover.
More particularly, the invention provides a half, mid or
full sole for a shoe comprising a base plate of a shape
corresponding to a sole of a shoe, having an upper surface
provided with a border area and with a recessed area, which
recessed area corresponds substantially in shape to the sole
of a shoe. A plurality of blades are arranged in the
recessed area of the base plate so as to lie substantially
parallel to each other and substantially perpendicular to an
-- 3 --
20~5272
axis running from the heel to the toe of the shoe, the blades
extending in a slanted direction outwardly from the recessed
area of the base plate. A cover is provided, with a recessed
area corresponding substantially in shape to the sole of a
shoe and with a border area which is bonded to the border
area of the base plate. A fluid is sealed in the space
between the base plate and the cover formed by the recessed
area of the base plate and the recessed area of the cover.
An intermediate area is formed around at least a part of the
recessed area of the cover so as to be positioned between the
recessed area of the cover and the border area of the cover,
which intermediate area is of a predetermined width and
increases in thickness in a direction ext~n~;ng from the
recessed area of the cover to the border area of the cover.
The border area of the base plate has the same shape as the
border area of the cover, and the blades are higher than the
border area of the base plate. The recessed area of the base
plate is formed in only the upper surface of the base plate,
each blade has uniformly spaced-apart grooves and the
opposite ends of each blade are coupled to the border area of
the base plate via webs, the webs being lower than the blades
and the border area of the base plate, and the base plate is
also provided with an intermediate area formed around at
least a part of the recessed area of the base plate so as to
be positioned between the recessed area of the base plate and
the border area of the base plate, which intermediate area is
of a predetermined width and increases in thickness in a
-- 4 --
2095272
direction ex~n~;ng from the recessed area of the base plate
to the border area of the base plate.
Now, specific embodiments of the invention will be
described, with reference to the accompanying drawings, in
which:
Fig. 1 is a front view showing a base plate of a sole of the
invention;
Fig. 2 is a front view showing a cover;
Fig. 3 is a developed view taken along line a-a in Fig. l;
Fig. 4 is a front view showing another cover of a sole of the
invention;
Fig. 5 is a developed view showing a base plate and cover;
and
Fig. 6 is a fragmentary enlarged-scale sectional view showing
a base plate and cover in a fused state thereof.
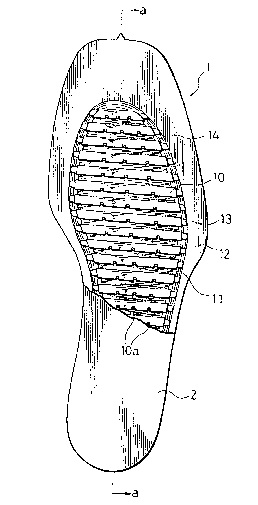
The construction according to the invention roughly
comprises a base plate 1, as shown in Fig. 1, with a
plurality of integral blades 10, a cover 2, as shown in Fig.
2, overlapped over the base plate and welded to the outer
periphery thereof, and water sealed between the base plate 1
and cover 2.
The base plate 1 is formed as one-piece molding of an
elastic thermoplastic resin, i.e., polyvinyl chloride. It
has an outer shape of the sole of shoes as shown in Fig. 1.
The upper surface of the base plate is a recessed area having
a shape corresponding to the sole of a foot as shown in Fig.
1. The recessed area 11 is surrounded by a border area 12
for welding. The border area 12 has an upper portion which
_ 5 _
2095272
is wider than the rest of it. The wider portion may be cut
to suit the size of shoes, and thus it serves as a portion
for providing variation to the sole.
The blades 10 are formed in the recessed area 11 of the
base plate 1 such that it is integral therewith. They extend
in a direction perpendicular to the longitll~;n~l direction of
the sole of shoes (i.e., in the transverse direction in Fig.
1). As shown in Fig. 3, they are slanted downward, i.e.,
toward the heel. They have a height greater than the height
of the border area 12. In the completed state of the mid-
sole or sole of shoes according to the invention, the blades
are urged and curved by a recessed area 21 of the cover 2,
thus enhancing the state of close contact between the base
plate and cover, while the sealed water can move through webs
13 and grooves lOa. For adjusting the rigidity of the
blades, the opposite ends of each blade 10 are coupled to the
border area 12 via webs 13, as shown in Fig. 1. The webs
have a smaller height than the blades so that water can be
moved gently. Each blade 10 has three uniformly spaced-apart
grooves lOa. These grooves have such dimensions as to permit
gentle movement of the sealed water.
The cover 2 is molded from polyvinyl chloride, the same
material as for the base plate 1. It has a recessed area 21
having a shape corresponding to the sole of shoes. It also
has a border area 22 surrounding the recessed area 21 and
having a predetermined width. The border area 22 has an
increased thickness and has the same shape as and is to be
bonded by fusing to the border area 12 of the base plate 1.
- 6 -
2095272
Like the base plate 1, the border area 22 has a wider upper
portion to be cut to the size of shoes. The cover 2 has an
increasing thickness intermediate area 23 surrounding the
recessed area 21. The intermediate area 23 is formed
slantedly with increasing thickness toward the increased
thickness border area 22. The intermediate area 23 has to be
formed in a portion, to which concentrated urging force is
applied, for instance, at least a portion contacted by the
toes of a foot. Particularly, a portion contacted by the
middle to little toes is important. This portion varies
depending on the habit of the person wearing the shoes, and
thus the intermediate area 23 is desirably formed over the
entire portion contacted by the toes as noted above.
Further, since it is possible that the corners of the
boundary between the border area 22 and the recessed area 21
of the cover 2 strikes the sole of a foot to produce a
condition commonly termed corns, the intermediate area 23 is
desirably formed around the entire edge of the recessed area
21.
The base plate 1 also has an increasing thickness
intermediate area 14 around the recessed area 11. This
intermediate area 14 is formed such that it is slanted with
increasing thickness toward the increased thickness border
area 12. This is made so because the lower side walls of a
shoe are upwardly flaring, and the side surfaces of the cut
such as to provide an upward flaring when finally assembling
the sole inside the shoe. It is thus necessary to make the
inner side surface of the border area 12 around the recessed
- 7 -
- 2095272
area 11 of the base plate 1 also upwardly flaring by
providing the intermediate area 14 slanted with increasing
thickness toward the increased thickness border area 12.
The border area 22 of the cover 2 is bonded to the
border area 12 of the bottom plate 1, the bonding surfaces
being fused together by high frequency welding. Then, water
is injected into the space defined between the recessed areas
11 and 21 and also between the intermediate areas 14 and 23
through a port (not shown) formed in the border area 12 of
10 the base plate 1 and the border area 22 of the cover 2, and
then the port is sealed.
Since the intermediate area 23 is formed with a
predetermined width around the recessed area 21 of the cover
2, the cover is less deformed when it is partly
concentratedly urged by the toes. Thus, there is no
possibility for the sealed water to reduce the sealing force
of the bonded surfaces of the border areas 12 and 22.
When the shoes using the sole having the above
construction are worn, water gently reciprocates along the
20 spaces between adjacent blades in the transverse direction,
i.e., in the longit~ n~l direction of the blades and also
gently reciprocates back and forth via the grooves lOa and
webs 13, thus absorbing the shocks produced when walking
while providing a stable and comfortable sense of wearing.
Further, as the blades 10 are urged, the sole of foot is
excited by adequate rigidity provided by the slanted form of
the blades. Further, the gentle movement of water noted
2095272
above has an effect of alleviating the excitement caused by
the rigidity of the blades. It is thus possible to massage
the sole of a foot continuously without producing any pain
even when the shoes are worn for long time.
A different embodiment of the invention will be
described with reference to Figs. 4 to 6.
This embodiment has a feature in the structure of the
cover. As shown in Fig. 4, in the recessed area 31 of the
cover 3 a plurality of (i.e., four in the Figure) blades 30
10 are formed on at least a portion, which is urged by the toes
and swelling toe roots. These blades extend in a direction
perpendicular to the longit~ in;~l direction of the cover, and
they are slanted as shown in Fig. 5.
As shown in Fig. 6, the border area 32 of the cover 3 is
bonded to the border area 12 of the base plate 1, with the
bonding surfaces fused together by high frequency welding.
Water is injected into the space defined by the recessed
areas 11 and 31 and also between the increasing thickness
intermediate areas 14 and 33 through an injection port (not
20 shown) provided in the border area 12 of the base plate 1 and
the border area 32 of the cover 3, and then the port is
sealed.
With the blades 30 formed in the recessed area 31 of the
cover 3 and the intermediate area 33 with a predetermined
width formed around the recess, the cover is less deformed
when it is partly urged concentratedly by the toes. Thus,
there is no possibility for the sealed water to reduce the
sealing force of the fused surfaces of the border areas 12
_ g _
- 2095272
and 32. Further, when a portion of the cover corresponding
to the toes and swelling toe roots is to be urged
concentratedly by the blades 30, the movement of water is
alleviated by the blades to further alleviate the impact
force applied to the fused surfaces of the border areas 12
and 32. The force of sealing the sealed water thus is not
reduced. In this way, the blades 30 have an effect of
alleviating the impact of water moved as the user wearing the
shoes walks step by step.
-- 10 --