Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~3,ln~347~7
--1--
TOPSHEET FOR USE IN DISPOSABLE
BODY FLUID ABSORPTIVE GOODS
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to liquid-permeable
topsheets for use in disposable body fluid absorptive goods
such as sanitary napkin, disposable diaper and training
pants.
Concerning liquid-permeable topsheets used for body
fluid absorptive goods, a technique is well known to make a
topsheet from plastic film or nonwoven fabric, to provide the
topsheet with liquid passages each extending therethrough
from top to bottom thereof, an upper surface of the sheet
being adapted to be in contact with the wearer's skin, and to
arrange lower openings of the respective liquid passages so
as to be in contact with an absorbent core so that a capillary
action occurring within each liquid passage may be utilized
to transfer excreted body fluids toward the absorbent core.
For example, Japanese Patent Publication No. 1982-17081
discloses a technique according to which a topsheet made of
polyethylene film is provided with conically tapered liquid
passages and the lower ends of the respective passages are
arranged so as to be closely in contact with an absorbent
~1~3~7~
core.
According to a technique disclosed by Japanese patent
application Disclosure Gazette No. 1985-259261, a topsheet
made of plastic film is provided with cylindrical liquid
passages with their lower ends extending into an absorbent
core, on one side, and a fibrous layer is bonded to the lower
surface of the topsheet with fibres of said fibrous layer
extending into the liquid passages, on the other side. Such
cylindrical liquid passages are more stable and therefore
less deformable than the conical liquid passages under a
same large load. Additionally, the cylindrical liquid
passages are preferred to the conical liquid passages in that
the fibres extendingintothe liquidpassagesalso contribute
to accelerate body fluids to be transferred toward the
absorbent core under the capillary action.
According to a technique disclosed by Japanese patent
application Disclosure Gazette No. 1992-152945, there is
provided a high density area or rib continuously surrounding
loweropeningsofrespective liquidpassages. Thistechnique
certainly stabilizes the opening of each liquid passage
against deformation as well as collapse and allows body
fluids to be effectively transferred toward an absorbent
core.
--3--
Soft touch is essential to a topsheet, and therefore
such conventional topsheets as disclosed by the above-
mentioned Patent Publication and Disclosure Gazettes are also
made from thin and soft materials. With a negative
consequence, however, such conical liquid passages disclosed
by said Japanese Patent Publication No. 1982-17081 as well as
such cylindrical liquid passages as disclosed by said Japanese
patent application Disclosure Gazette No. 1985-259261 are
disadvantageous in that the lower openings, i.e., free ends of
those liquid passages are liable to be deformed, so the liquid
passages can readily collapse, for example, under a body
weight of a wearer and body fluids are often prevented thereby
from being smoothly transferred toward an absorbent core.
While a stability of each liquid passage against a compressive
force axially exerted on this liquid passage can be more or
less improved, such a liquid passage is still ready to be
collapsed under a force transversely exerted on it since it
comprises soft material after all. While the technique
disclosed by the above-mentioned Japanese patent application
Disclosure Gazette No. 1992-152945 may theoretically alleviate
a problem that a liquid passage is apt to be collapsed, both a
thickness of the topsheet and a diameter of the liquid passage
are unfeasibly fine so it would not be easy to provide the
previously mentioned high density area or rib continuously
surrounding the lower openings of the respective liquid
7 ~
--4--
passages although this is one of the most important features
of the disclosed technique.
In view of these problems left behind by the prior art
unsolved, it is a principal object of the invention to provide
a topsheet comprising a first sheet and a second sheet
underlying said first sheet wherein said first sheet is
provided with liquid passages and said second sheet is welded
to said first sheet around the lower openings of the
respective liquid passages so as to restrict possibly
occurring deformation of the liquid passages and thereby to
solve the problems encountered by the conventional topsheets.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The object set forth above is achieved, according to a
broad aspect of the present invention, by topsheet for use in
body fluid absorptive goods and wherein the topsheet comprises
a first sheet including at least one of a thermoplastic film
and nonwoven fabric of thermoplastic fibres welded to each
other. A second sheet is also provided and includes a
nonwoven fabric of thermoplastic fibres welded to each other.
The first sheet is formed with a plurality of liquid passages
each having a sidewall and extending through the first sheet
from an upper opening to a lower opening thereof and a skin-
contacting area continuously formed around the upper openings.
The second sheet underlies the first sheet and is welded to
the first sheet. The second sheet is also spaced from the
.
.~
* .~.
--5--
first sheet except around the lower openings to thereby define
cavities between the first and second sheets. The second
sheet also extends upward from adjacent the lower openings
into substantially each of the liquid passages along the
associated sidewall without filling up the liquid passages.
Preferably, the second sheet is hydrophilic in
comparison with the first sheet.
Such topsheet is obtained, for example, by blowing melt
fibres from an extruder against the underside of the first
sheet provided with the liquid passages and thereby forming
melt-blown nonwoven fabric so that said melt-blown fibres can
be welded to the first sheet around the lower openings of the
respective liquid passages and contribute to protect these
passages from being deformed in the proximity of their lower
openings. The first sheet and the second sheet are continuous
with each other around the upper and lower openings of the
respective liquid passages, so the liquid passages are
substantially stabilized against deformation and collapse
under an axial force as well as a transverse force exerted
thereon.
Liquid excretions flow into the liquid passages, and
reach the respective lower openings, whereupon the liquid
excretions are absorbed by the absorbent core at spots of the
core being in contact with the respective lower openings, then
spread over the second sheet and are absorbed by the absorbent
core also over an area being in contact with the second sheet.
~ ~ Q ~
--6--
However, the second sheet thus wetted as a result of said
spreading gives no significant wet touch to a wearer, since
the second sheet is welded to the first sheet around the
respective lower openings but well spaced from the first sheet
in the remaining zone.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The invention will be described by way of example in
reference with the accompanying drawings, in which:
Fig. 1 is a perspective view showing, as partially
broken away, a sanitary napkin;
Fig. 2 is a sectional view partially showing a topsheet
~r, ,~
~1~3~7~
--7--
in an enlarged scale; and
Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram illustrating a topsheet
manufacturing process.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
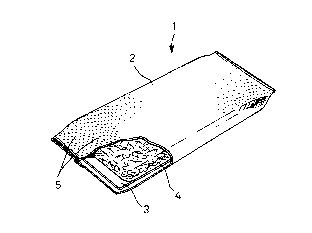
Referring to Fig. 1, a sanitary napkin 1 is shown in a
perspective view as partially broken away. As shown, the
~napkin 1 comprises a liquid-permeable topsheet 2, a liquid-
impermeable backsheet 3 and an absorbent core 4 sandwiched
between these two sheets 2, 3, wherein the topsheet 2
entirely envelops the absorbent core 4 with the opposite side
portions thereof being overlapped and sealed together on the
backside of the napkin 1 and end portions extending along
opposite ends of the absorbent core 4 being also sealed
together. The backsheet 3 is interposed between the topsheet
2 lying on the backside of the napkin 1 and the absorbent core
4.
Referring to Fig. 2, the topsheet 2 is schematically
illustrated in a partial section cut in the direction of its
thickness. As illustrated, the absorbent core 4 is contacted
to the underside of the topsheet 2. The topsheet 2 comprises
an upper sheet 7 which comprises, in turn, a laminate of a
first layer 7a and a second layer 7b both made of melt-blown
--8--
fibres, and a lower sheet 8 underlying said upper sheet 7 and
made of melt-blown fibres. The upper sheet 7 includes a
plurality of liquid passages 13 each extending through the
sheet 7 from an upper opening 11 to a lower opening 12 and a
skin-contacting area 14 which is formed as a continuous planar
zone extending around the respective upper openings 11. The
lower sheet 8 includes a planar area 15 which is formed as a
continuous planar zone around the respective lower openings 12
and rising areas 16 extending from said planar area 15
upwardly into the respective liquid passages 13. The melt-
blown fibres constituting the lower sheet 8 are welded to the
upper sheet 7 around the respective lower openings 12 and
thereby the lower sheet 8 is integrated with the upper sheet
7. However, these sheets 7, 8 define therebetween cavities
20, since the skin-contacting area 14 and the planar area 15
are spaced from each other.
Referring to Fig. 3, a process of manufacturing the
topsheet 2 is schematically illustrated. The process
comprises a first forming step 28 utilizing a forming drum 30
and first and second melt-blowing extruders 31, 32 provided
around said forming drum 30 and a second forming step 29
utilizing an endless belt 33 and a third melt-blowing extruder
34 provided above said endless belt 33. The forming
.
~r~
2103~1~ 7
g
drum 30 is provided around its outer peripheral surface with
protrusions 35 and indents 36 which are alternately arranged
and serve as forming dies so that melt-blown fibres 40 are
blown from the first extruder 31 against said forming dies
under effect of suction41 to form a nonwoven fabric layer 40a
destined to be the first layer 7a of the first sheet 7.
Similarly, melt-blown fibres 42 are blown from the second
'extruder 32 against the nonwoven fabric layer 40a to form a
nonwoven fabric layer 42a destined to be the second layer 7b
of the first sheet 7. A laminate of these nonwoven fabric
layers 40a, 42a is then formed by the drum 30 into a
continuity of the first sheet 7 having the skin-contacting
area 14 of the first sheet 7 formed by the protrusions 35 and
the liquid passages 13 formed by the indents 36. It should be
understood thatvarious factorssuch as respective amountsof
the fibres 40, 42 to be blown, intensity of respective
suction 41 and depth of each indent 36 may be adjusted during
the first forming step 28 to obtain a continuity of the first
sheet 7 containing the fibres 40, 42 extending upward along
side walls of the respective indents 36 so as to form the
liquid passages 13 and openings formed by bottoms of the
respective indents 36 destined to be the lower openings 12 of
the first sheet 7. The continuity of the first sheet 7 is
~.~..1034~7
--10--
separated from the peripheral surface of the forming drum 30
as it is transferred from the first forming step 28 to the
second forming step 29, and laid on the endless belt 33 with
its surface which has contacted the peripheral surface of the
forming drum 30 facing upward. Under effect of a suction 43,
melt-blown fibres 44 are blown against said surface facing
upward to form a nonwoven fabric layer 44a destined to be the
~second sheet 8. Amount of the fibres 44a to be blown and
intensity of the suction 43 may be adjusted to assure that the
fibres 44 are loosened around the openings 37 without
formation of an apparent nonwoven fabric layer and extend
upward into the liquid passages 13 along their inner walls
but never fill up the openings 37 destined to be the lower
opening 12. The roll of sheet 50 comprising these nonwoven
fabric layers 40a, 42a, 44a obtained in the manner as has been
described above can be unrolled and cut into sheets of
desired dimensions so as to be used as the individual
topsheets 2.
In each topsheet 2 cut from the roll of sheet 50, the
melt-blown fibres 40, 42 forming the first or upper sheet 7
are fluffed around the lower openings 12 in the direction of
the suction 41. The melt-blown fibres 44 blown from the third
extruder 34 against this upper sheet 7 are welded and/or
~1~347~
clung to the other melt-blown fibres 40, 42 and thereby
integrate the second or lower sheet 8 with the upper sheet 7.
By forming the upper sheet 7 in two-layered structure
comprising the melt-blown nonwoven fabric layers 40a, 42a as
in the illustrated embodiment wherein the lower layer 40a of
melt-blown nonwoven fabric having a higher density is first
formed in order to make the topsheet 2 firm and then the upper
layer 42a of melt-blown nonwoven fabric having a lower
density is formed, it will be easily achieved to provide the
goods utilizing such topsheet 2 which can give its wearer a
cloth-like soft touch. It should be understood that the
upper sheet 7 may be also formed by any one of the nonwoven
fabric layers 40a, 42a.
The melt-blown fibres 40, 42, 44 may be of suitable
thermoplastic resin such as polyethylene. It is also
possible within the scope of the invention to replace the
melt-blown nonwoven fabric of the upper sheet 7 by perforated
plastic film. Preferably, the upper sheet 7 is made from
suitable hydrophobic material so that a dry touch may be
maintained even after excretion of body fluids, on one hand,
and the lower sheet 8 is made hydrophilic in comparison with
the upper sheet 7 so that the body fluids may be transferred
toward the absorbent core and extensively spread over the
~03~7~
lower sheet 8 as rapidly as possible, on the other hand. Such
lower sheet 8 may be obtained, for example, by using
polyethylene previously mixed with hydrophilic agent.
In the topsheet constructed according to the invention,
the liquid passages are effectively shape-stabilized and
difficult to be blocked, since the lower sheet is welded to
the upper sheet around the lower openings of the respective
liquid passages.
The body fluids excreted over the topsheet flow into the
liquid passages and reach the lower openings of the
respective liquid passages, whereupon the body fluids are
absorbed by the portions of the absorbent core being in
contact with these lower openings and simultaneously spread
over the lower sheet, so the body fluids are absorbed also by
the portion being in contact with said lower sheet. In this
manner, the topsheet of the invention allows the absorption
rate to be improved over the topsheet of prior art.
The lower sheet of the topsheet gives no wet touch to the
wearer even after the lower sheet has been wetted with the
body flulds spreadingthereover, sincethere are thecavities
defined between the upper sheet and the lower sheet.
An excellent shape-stability of the liquid passages
improves acushioning effect andtherefore comfortofwearing
~1~3~7~
--13--
the absorptive goods.