Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
21~73~3
918-042-1
A RECOVERABI,E TUB~SHAl'ED DEVICE
Ar~ MEI~OD FQR PRODIJCIN~ SAME
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention generally relates to a recoverable, tube-shaped
device, and, in particular, relates to one such recoverable tube-shaped device
S having an expanded tube and a coil of thermoplastic material disposed over the
outer surface of the expanded tube.
DESCRIPrION OF T~E PRIOR ART
Cold shrinking products are known for covering objects, such as cable
splices, cable ends, or the like and are preferred where heat or an open flame are
undesirable.
One such cold shrinking article is known from U.S. Patent No.
3,515,798. The article contemplated therein includes a rubber tube that is kept in
an expanded condition by a wire coil disposed inside the rubber tube. When the
wire coil is withdrawn, the rubber tube shrinks over the object to be covered.
lS A tube having an interlaced elastomer insulation material is known from
DE-OS 26 47 12~. In this arrangement, the tube is maintained in an expanded
condition by a tensioning agent located on the outer surface of the tube. The
tensioning agent is securely attached to the outer surface of the expanded tube.The tensioning agent can be separated, or removed, from the surface of the tube
2Q for the purpose of allowing the shrinWng of the tube. To that end, the connection
between the tube and the tensioning agent can be detached by a solvent that
dissolves an adhesive, or alternatively, the tensioning agent can be removed from
the outer surface of the tube by fracturing it and/or peeling it off in strips. In the
21~7383
918-WZ-1
latter case) a layer of thermoplastic material is extruded over the tube in the ~orm
of a unitary tube-like sheath. In ~he case where the sheath is removed by
fracturing, the sheath consists of a hard plas~ic and may include predetermined
helical breaking points on the surface to assist in peeling off the strips.
The use of hard brittle plastic tensioning agents greatly limits the
application where such tensioning agentg are useable, particularly in instances
where the object to be protected is not flexible. In addition, there is the danger of
unwanted destruction of the tensioning agent from impact stress. Such unwanted
destruction could render the object to be protected unusable.
Further, the subsequent addition of the predetermined breaking points is
an additional labor step, making the sheath more expensive.
Consequently, it is highly desirable to provide a recovera~le device that
substantially overcomes the above recited difficulties of the prior art.
SUMMAR~ C)F THE INVENTION
Accordingly, it is one object of the present invention to provide a
recoverable tube-shaped device that overcomes these diMculties.
This object is accomplished, at least in part, by a tube-shaped device that
can be reset to its size, for covering substrates, particularly for covering cable
splices, cable ends, etc., includes a tube made of a rubbery elastic material that is
expanded in the radial direction. The tube is maintained in the expanded condition
by a tensioning agent connected to the outer surface of the tube. The tensioningagent can be removed from the surface of the tube to allow the tube to recover ashrunken, or unexpanded, shape. In one embodiment, the tensioning agent is a
profile made of a thermoplastic material, which is coiled about the outer surface of
the expanded tube.
210738~ 918-042-1
The presellt invention contemplates the provision of a devi&e that can
recover its size and wherein the connection between an expanded tube and the
tensioning agent is not destroyed by unwanted impact stress, and which further can
be procluced in a cost-effective manner.
This task is preferably fulfilled in that the tensioning agent is a
thermoplastic matenal profile that is coiled about the outer surface of the expanded
tube. Such a device can be produced without any large equipment. Another
significant advantage is that the tensioning agent can be successively peeled, or
uncoiled, from the outer surface of the expanded tube. During removal of the
tensioning agent, the expanded tube shrinks about the substrate to be covered.
To maintain the expanded condition of the tube over an extended period
of time, it has proven advantageoug to coat the outer surface of the tube, and/or
the inner surface of the tensioning agent facing the tube, with an adhesive.
Typically, such as adhesive should be selected so that the shear stress that is
needed to peel off the tensioning agent, unfastens the connection between the tube
and the tension agent without damaging the tube. It is advantageous if the
adhesive is a hot-melt adhesive, however, a contact adhesive can also be used. As
more fully discussed herein, the selection of the adhesive is primarily determined
by the manufacturing process of the device.
In applications where the device is to be used as the so-called sealed end
for medium or high voltage cables, it has been found to be advantageous ~or the
device to have a slightly electrically conductive coating on the inner surface
thereof.
It is particularly useful if the tensioning agent is formed with a nearly
square cross section. Such a cross-section is stable, and can absorb the forces
oAginated by the expanded tube, furthermore the tensioning agent should cover a
2~ ~7383 918-042-1
large area of the h~be. In fact, the tensioning agent preferably covers substantially
off of the outer surface of the expanded tube.
Another aspect of the present invention concerns a proc~ss for producing
a recoveIable tube-shaped device that can recover its unexpanded size, wherein aS tube is expanded radially and the tensioning agent is installed on the outer surface
of the expanded tube. In this process, the tensioning agent is applied to the outer
surface of the radially expanded tube like a coilj and the expansion means is
removed after the connection between tube and tensioning agent has been
established.
If the tensioning agent is a strand of thermoplastic material that is wound
over the expanded tube, it is useful to wind the strand with a slight tension. If a
hot-melt adhesive is used in the winding operation after the winding is complete,
the device is heated to a temperature at which a hot-melt adhesive, which has been
applied to the outer surface of the tube and/or to the inner surface of the strand
facing the tube, melts. The hot-melt adhesive is then allowed to cool and thereby
establishes the connection between the expanded tube and the strand. Subsequent
heating can be omitted if the layer of hot-melt adhesive liquifies during the
winding operation by the heating the surface of the expanded tube created by thewinding process.
Alternatively, if a contact adhesive is used, the connection between the
tube and the strand can be improved by applying pressure, such as, for example,
by applying tension to the tensioning agent or the strand during the application of
the tensioning agent or strand to the expanded tube.
In one particularly advantageous method, a strand of thermoplastic
material is extruded over nearly the entire outer surface of the expanded tube. In
this particular method, the tube is rotated around its longitudinal axis and moved
21~73g3
918-042-l
alcially. As before, tlle means of expanding the tube is removed after the strand
has hardened.
It has been found that the connection between the tube and the strand is
improved if a layer of hot-melt adhesive is applied to the outer surface of the
S expanded tube before the strand is extruded.
It is advantageous for many applications if the strand includes a
therrnoplastic hot-melt adhesive. However, care must be t~cen during the
application, so that adjacent windings of the strand are not glued to each other.
Other objects auld advantages will become apparent to those skilled in the
art from the following detailed description of the invention read in conjunctionwith the appended claims and the drawings attached hereto.
ESRIEF DESCRIPI ~ON OF 1~ DRAWlNGS
The drawings, not drawn to scale, include:
Figure 1 which is a cross-sectional view of a device embodying the
principles of the present invention; and
Figure 2 is a schematic of a method for producing a clevice embodying
the principles of the present invention.
DE~AILED DESCRIPIION OF l~HE INVE~TION
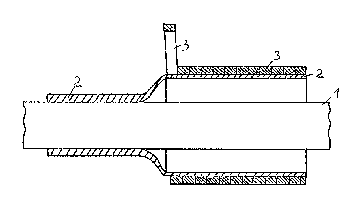
A device, generally indicated at 10 in the Figures and embodying the
principles of the present invention, includes a radially expanded tube 2 the
expanded condition of which is maintained by a tensioning agent 3 that is coiledover the outer surface 12 of the tube 2. In the preferred embodiment, the outer
surface 12 of the tube 2 is glued to the inner surface 14 of the tensioning agent 3.
2 1 ~ 7 ~ 3
918-042-l
In one particular embodimentl the tensioning agent 3 has a nearly square
cross section and substantially completely covers the outer surface 12 of the
expanded tube 2. 'I`he use of such a cross sectional shape has been determined to
be stable and capable of absorbing forces originated by the expanded tube 2.
Naturally, other cross sectional shapes can also be implemented and are
contemplated herein.
During use, as shown at the left side of Figure l, when the tensioning
agent 3 is unwound from the tube 2, the tube 2 springs back elastically to coverthe substrate 1. Typically, almost any elastically ductile, i.e. expandable material,
is suitable for the tube 2, such as, fsr example, l~PDM, neoprene, etc.
A thermoplastic material, such as polyethylene, is a suitable material for
the tensioning agent 3. The interface connection between the outer surface 12 ofthe tube 2 and the inner surface 14 of the tensioning agent 3 must be strong
enough to prevent the tube 2 from recovering its unexpanded shape as long as thetensioning agent 3 remains affixed thereto. In some embodiments, it is
advantageous if the interface connection is produced by using a coating of hot-melt
adhesive or by use of a contact adhesive between the outer sur~ace 12 of the tube
X and the inner surface 14 of the tensioning agent 3. Such an adhesive is
preferred in those embodiments where the tensioning agent 3 is wound abol!t the
outer surface 12 of the tube 2. Alternatively, if the tensioning agent 3 is directly
extruded over the outer surface 12 of the expanded tube 2, an adhesive coating
may be omitted with the right combination of materials.
One particularly advantageous manufacturing process is schematically
depicted in Figure 2.
As depicted therein, the expandable tube 2 is initially placed over a
mandrel 4 and maintained in the expanded condition thereon. The tensioning
agent 3 is then extruded over the outer surface 12 of the expanded tube 2 by an
21~7383 gl8-0~2-l
extruder 5. In the embodiment depicted, the mandrel 4 is caused to rotate aroundits longitudinal axis 18 in cooperation with the speed of the extrusion and
simultan~usly is translated longitudinally in the axiai direction. In the preferred
embodiment, the extruder 5 remains in a fixed position while the mandrel 4
S translates along its axis and rotates thereabout. This manufacturing method has
been found to achieve a good connection between the outer surface 12 of the tube2 and the inner surface 14 (not shown in Figure 2) of the tensioning agent 3.
The invention is not restricted to the depicted configuration examples. It
is, of course, quite possible to install the tensioning agent 3 on an almost endless
tube 2 by means of a continuous operation process. In that case the v~inding is
achieved with a rotating winder.
In use, the device 10 is disposed over the substrate 1 to be covered, such
as a cable splice, cable end or the like. Once in position, the tensioning agent 3 is
peeled, or uncoiled, away from the tube 2. Upon release, i.e. as the tensioning
lS agent is removed, the elasticity of the tube 2 allows the tube 2 to shrink about the
substrate 1. When the tensioning agent 3 is completely removed, the tube 2 has
fully contracted about the substrate 1 to thereby cover and protect the substrate 1.
Although the present invention has been described herein with respect to
one or more embodiments, it will be understood that other arrangements and
configuration can also be used that do not depart from the spirit and scope hereof.
Hence, the present invention is deemed limited only by the appended claims and
the reasonable interpretation thereof.