Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
W093/02052 PCT/US92/0497~
21 1 3.~ fi 8
52-(4-HYDROXYPIPERIDINO)-l-ALKANOL
DERIVATIVES AS ANTIISCHEMIC AGENTS
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is directed to neuroprotective
(antiischemic excitatory amino acid receptor blocking) 2-
(4-hydroxypiperidino)-1-alkanol derivatives defined by
formula (I) below; pharmaceutically acceptable salts
thereof; a method of using these compounds in the treat-
ment of stroke, traumatic injury to the brain and spinal
cord, and neuronal degenerative diseases including (but ,
not limited to) senile dementias such as Alzheimer's
disease, Huntington's disease and Parkinson's disease in
mammals, especially humans; and to certain intermediates
therefor.
Ifenprodil (A) is a racemic, so-called dl-erythro -~
compound having the relative stereochemical formula
,...: . -
''.~:''- .
OH o~CI~
HO 3
: -
which is marketed as a hypotensive agent, a utility shared
by a number of close analogs. Carron et al., U.S. Patent ~-~
3,509,164; Carron et al., Drug Res., v. 21, pp. 1992-1999
(1971). More recently, ifenprodil has been shown to
possess antiischemic and excitatory amino acid receptor
blocking activity. Gotti et al., J. Pharm. Exp. Therap., --
v. 247, pp. 1211-21 (1988); Carter et al., loc. cit., pp.
1222-32 (1988).
See also French Patent 2546166 and EP0 publication
EP-Al-351282, published January 17, 1990. A goal,
substantially met by the present invention, has been to
W093/02052 PCT/US92/0497~
21 l 3~68 -2-
find compounds possessing neuroprotective activity in good
measure, while at the same time having lowered or no
significant hypotensive effect.
Certain l-phenyl-3-(4-aryl-4-acyloxy-piperidino)-1-
propanols have also been reported to be useful asanalgesics, U.S. Patent 3,294,804; 1-[4-(amino-and
hydroxy-alkyl)phenyl]-2-(4-hydroxy-4-tolylpiperazino)~
alkanols and alkanones have been reported to possess
analgesic, antihypertensive, psycho- tropic or
antiinfla~matory activity, Japanese Kokai 53-02,474 (CA
89:43498y; Derwent Abs. 14858A) and 53-59,675 (CA
89:146938w; Derwent Abs. 48671A); and 2-piperidino-1-
alkanol derivatives have been reported to be active as
antiischemics, EP 398,578-A and Der 90-350,327/47.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
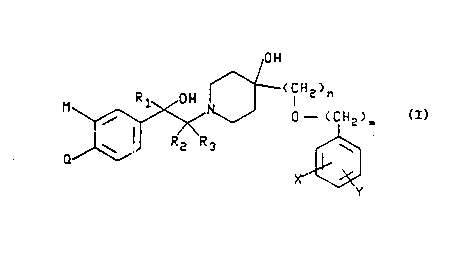
The present invention is directed to compounds of the
formula
~ ~ (CU~n
(I)
wherein R~, ~ and R3 are each selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, alkyl having 1 to 6 carbons,
phenyl and substituted phenyl, wherein the substituent on
W093/02052 PCT/US92/~973
211~Sfi8
--3--
said substituted phenyl is selected from the group --
consisting of hydroxy, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbons,
chloro, bromo, fluoro, trifluoromethyl, amino, nitro and
alkoxy having 1 to 4 carbons; :
5 or Rl and ~ when taken together form a methylene, :
ethylene, propylene or butylene group; .--:
m is O to 2; -
n is l or 2;
X and Y are each selected from the group consisting of .-
lO hydrogen, chloro, bromo, fluoro, trifluoromethyl, alkoxy .~:-
having 1 to 4 carbons, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbons, :
hydroxy, amino, nitro and substituted phenoxy, wherein -~ :
the substituent on said substituted phenoxy is selected
from the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, alkyl --~
having 1 to 4 carbons, chloro, bromo, fluoro,
trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino and alkoxy having 1 to 4 .;
carbons; ~-
M and Q are each selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen, hydroxy, amino, chloro, bromo, fluoro, :::
20 trifluoromethyl, nitro, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbons, ~ -
alkoxy having 1 to 4 carbons, N,N-dialkylamino having 1 to -~-~
4 carbons in each of said alkyls, N-alkylamino having 1 to -:~
4 carbons, NHCO~, NHCOOR5 and NHSO2~;
wherein ~ is selected from the group consisting of -~
25 hydrogen, alkyl having 1 to 6 carbons, phenyl and -
substituted phenyl, wherein the substituent on said
substituted phenyl is selected from the group consisting ~-
of hydroxy, chloro, bromo, fluoro, trifluoromethyl, amino,
nitro, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbons and alkoxy
having 1 to 4 carbons;
and wherein R5 and ~ are each selected from the group -~
consisting of alkyl having 1 to 6 carbons, phenyl and
substituted phenyl, wherein the substituent on said
substituted phenyl is selected from the group consisting
of hydroxy, chloro, bromo, fluoro, trifluoromethyl, amino,
W093/02052 PCT/US92/~973
2113~G8
nitro, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbons and alkoxy having 1 to
4 carbons;
or M and Q when taken together form a divalent radical Z,
wherein Z is selected from the group consisting of
R7
H ' ~ '
~N-- N~N--
H ' H
N N~
olN/ e~nd H2NJ~N~
wherein R7 and R8 are each selected from the group ~-
consisting of hydrogen and methyl;
and the pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts of
these compounds.
The expression "pharmaceutically acceptable acid
addition salts" is intended to include but is not limited
to such salts as the hydrochloride, hydrobromide, hydro-
iodide, nitrate, hydrogen sulfate, dihydrogen phosphate,
mesylate, maleate, and succinate. Such salts are
conventionally prepared by reacting the free base form of
W093/02052 PCT/US92/04973 ~
-5- 5 6 8
the compound (I) with an appropriate acid, usually one ~-
molar equivalent, and in a solvent. Those salts which do
not precipitate directly are generally isolated by
evaporation of the solvent and/or addition of a non-
5 solvent followed by filtration. -
A preferred group of compounds of the present
invention are those in which M and Q form a radical Z, -~
~ ,,.,~, .
wherein Z is ~ , R~ and R2 are hydrogen and R3 is methyl -
H ~-
and the compounds possess lr*, 2s* or erythro relative
10 stereochemistry at the 1- and 2-positions of the propanol -~
chain, i.e., --~
OH
15 ~
C H3
A second preferred group of compounds of this invention
are those in which M and Q form a radical Z, wherein Z
H ~:
N
is ¦ , Rl and R2 are hydrogen and R3 is methyl and
~ H .: . :
" ~,:
the compounds possess ls*, 2s* or threo relative -
stereochemistry at the 1- and 2- positions of the propanol
chain, i.e.,
OH
~ 2
1 ~ ''.'
CH3
W O 93/02052 PC~r/US92/0497
~ 1 1 3 ~i 6 ~ -6-
The present invention is also directed to pharma-
ceutical compositions containing a compound of the
invention of formula I, and to methods of treating a
mammal, particularly human subject, suffering from a
central nervous disorder, which comprises administering to
said mammal a neuroprotective effective amount of a
compound of the formula (I). Said compositions and
methods are particularly valuable in the treatment of
traumatic injury to the brain and spinal cord, stroke,
Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington~s
disease and related disorders of the central nervous
system.
The present invention is further directed to
intermediate compounds of the formula
OH
M ~ ~ (CH
.
(IV)
wherein
R2 and R3 are each selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen, alkyl having 1 to 6 carbons, phenyl and
substituted phenyl, wherein the substituent on said : -
substituted phenyl is selected from the group consisting
of hydroxy, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbons, chloro, bromo,
W093/02052 PCT/US92/04973 ~
2113~68 :
-7-
fluoro, trifluoromethyl, amino, nitro and alkoxy having 1
to 4 carbons; ~ -
m is 0 to 2;
n is 1 or 2;
X and Y are each selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen, chloro, bromo, fluoro, trifluoromethyl, alkoxy
having 1 to 4 carbons, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbons,
hydroxy, amino, nitro and substituted phenoxy, wherein the
substitu2nt on said substituted phenoxy is selected from
lo the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, alkyl having 1 :
to 4 carbons, chloro, bromo, fluoro, trifluoromethyl, ~:
nitro, amino and alkoxy having 1 to 4 carbons; ~
M and Q are each selected from the group consisting of . -
hydrogen, hydroxy, amino, chloro, bromo, fluoro,
15 trifluoromethyl, nitro, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbons, :~
alkoxy having 1 to 4 carbons, N,N-dialkylamino having 1 to ~:
4 carbons in each of said alkyls, N-alkylamino having 1 to ~ :
4 carbons, NHCO~, NHCOO~ and NHSO2R~;
wherein ~ is each selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen, alkyl having 1 to 6 carbons, phenyl and
substituted phenyl, wherein the substituent on said :
substituted phenyl is selected from the group consisting ..
of hydroxy, chloro, bromo, fluoro, trifluoromethyl, amino, -: -
nitro, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbons and alkoxy having 1 to :~
4 carbons;
and wherein ~ and ~ are each selected from the group --:
consisting of alkyl having 1 to 6 carbons, phenyl and .:.
substituted phenyl, wherein the substituent on said
substituted phenyl is selected from the group consisting
of hydroxy, chloro, bromo, fluoro, trifluoromethyl, amino,
nitro, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbons and alkoxy having 1 to
4 carbons; :~:
W093/02052 PCT/US92~0497~
2113~6~ `
-8-
or M and Q when taken together form a divalent
radical Z, wherein Z is selected from the group
consisting of
R7
O ~ 0~
~ N~N :
H
N ~\
~ N / and H2N ~ N
H
~- :
and wherein R~ and R8 are each selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen and methyl.
Depending on the precise values of R~, R2 and R3, the --
10 compounds of formula (I) can have one or two asymmetric ~ -
centers, and can therefore exist in various isomeric
forms. All such isomers are within the scope of this
invention. The individual isomers can be separated by ;
classical methods well-known to those skilled in the art.
DETAILED DE5CRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The compounds of the present invention, having the
formula (I) defined above, are readily and generally
W093/02052 PCT/US92/04973
9 ~1135fi8 ~-.
prepared by reaction of chloro compound (II) with piper-
idine (III), followed by reduction of the resulting ketone
(IV) to an alcohol as detailed below.
The precursor ketones are generally initially
prepared with -OH and -NH2 substituent groups in protected
form, i.e., as -OAI, or -NHA2 groups in the compounds of
formula (IV). A~ and ~ are defined below. Such protected -~
ketones are generally formed by reacting an appropriately
substituted 2-halo-1-alkanone (II) with an appropriately
substituted piperidino derivative (III), e.g.,
o
n~C~ ~ ~<cu~
15(tl) ~y
clll) ':
OH
~ R2~-
~-
~IV>
Reaction of compound (II) with compound (III) is -
carried out under conditions typical of nucleophilic
displacements in general. Where the two reactants are
W093/020~2 PCT/US92/0497~
5 ~ o-
about equivalent in availability, close to substantially
molar equivalents may be used; although when one is more
readily available, it is usually preferred to use that one -
in excess, in order to force this bimolecular reaction to
completion in a shorter period of time. The reaction is
generally carried out in the presence of at least 1 molar
equivalent of a base, the piperidine derivative itself, if
it is readily available, but more usually a tertiary amine -
which is at least comparable in base strength to the
nucleophilic piperidine; and in a reaction inert solvent
such as ethanol. If desired, the reaction is catalyzed by
the addition of up to one molar equivalent or more of an
iodide salt (e.g., NaI, RI). Temperature is not critical,
but will generally be somewhat elevated in order to force
15 the reaction to completion within a shorter time period, ~-
but not 80 high as to lead to undue decomposition. A
temperature in the range of 50-120C is generally
satisfactory. Conveniently, the temperature is the reflux ~-
temperature of the reaction mixture. ~-
As used in the preceding paragraph, and elsewhere
herein, the expression "reaction inert solvent" refers to ~
any solvent which does not interact with starting -;
materials, reagents, intermediates or products in a manner
which adversely affects the yield of the desired product. ;;
If desired, those ketone intermediates (IV) having OH
or NH2 groups in protected form (OAI or NHA2), can be
deprotected at this stage by conventional methods.
For example when A~ is triisopropylsilyl or tert-
butyldimethylsilyl, the protecting group is conveniently
3C removed by reaction with tetrabutylammonium fluoride
(generally, substantially 2 molar equivalents) in a
reaction inert solvent such as tetrahydrofuran. When A~ is
benzyl or A2 is benzyloxycarbonyl, the protecting group
will generally be removed by conventional hydrogenolysis
over a noble metal catalyst in a reaction inert solvent,
WO 93102052 PCI'/US92/04973
2113~68 ~ ~
e.g., using 10% Pd/C as catalyst, preferable at low
pressures (e.g., ~-10 atmospheres) and temperatures ~e.g., -
20-75OC) and generally in a reaction inert solvent such as ;
methanol.
Generally, the ketone intermediates (~v) are -
conveniently converted to corresponding alcohols by one of -
two conventional reduction methods, to selectively produce - -
either the threo compounds or the erythro compounds of
formula (I).
As used in the precading paragraph, and elsewhere
herein, the term "threo" or lE*, 2s~ refers to the
relative stereochemistry at the 1- and 2- positions of the
propanol chain, i.e.,
O H
C H 3
~
and the term "erythro" or lr*, 2s* refers to the relative ---
stereochemistry at the 1- and 2-positions of the propanol
chain, i.e.,
OH
2s ~
CH3 ~ :
To obtain the desired erythro compounds of formula
(I) the corresponding ketone intermediates (I~) are
conveniently reduced with potassium borohydride, usually
in excess (e.g. greater than 5 mole equivalents), in the
3s presence of glacial acetic acid in a protic solvent such
as ethanol, generally at a temperature range of 15-25C.
W093/02052 PCT/US92/04973
5 ~ 8
-12-
,
To obtain the desired threo compounds of formula (I~
the corresponding ketone intermediates (IV) are
conveniently reduced with sodium borohydride, usually in
excess (e.g. greater than 5 mole equivalents), in a protic ~-
solvent such as ethanol, generally at a temperature range
of 15-25C. The resulting reaction mixture is
chromatographed on a silica gel column to obtain the said
threo compounds of formula (I). ~-
Any protecting groups which are still in place after
lO ketone reduction are then removed according to standard ~-
methods described above.
The starting materials and reagents required for the
synthesis of the compounds of the present invention are ~ -
readily available, either commercially, according to ~
15 literature methods, or by methods exemplified in ~-
Preparations below.
The present compounds of the formula (I) possess
selective neuroprotective activity, based upon their
antiischemic activity and ability to block excitatory
amino acid receptors, while at the same time having
lowered or no significant hypotensive activity. The
antiischemic activity of the present compounds is
determined according to one or more of the methods which
have been detailed previously by Gotti et al. and Carter
et al. cited above, or by similar methods.
The ability of the compounds of the present invention
to block excitatory amino acid receptors is demonstrated
by the drugs ability to rescue fetal rat neurons in
~culture which have been exposed to the excitotoxic amino
acid glutamate. The following is a typical procedure.
Part I: Cell Isolation:
Embryos at 17 days gestation are removed from rats
and placed into Tyrode's solution. The brains are then
removed and placed into fresh Tyrode's solution. Using
fine iris knives, the hindbrain and thalamus are removed.
W093to20s2 PCT/US92/04973
2113~8
-13- ~-~
The forebrain is then separated into two hemispheres.
Next, the meninges are removed gently. The hippocampus
appears as a darkened folded area on the inner side of the
cortex edge. The hippocampus is carefully cut away from -
5 the rest of the tissue and placed in a ceparate corner of -
the dish. When all of the dissection is completed, the ;~
hippocampal tissue reserved in the corner is minced into 1
mm pieces. These pieces are removed, using a Pasteur ~-
pipette and placed into a sterile tube. The Tyrode's ~-
solution is aspirated off gently and Calcium-Magnesium
Free Tyrode's solution is added. The tissue is washed 3
times with Calcium-Magnesium Free Tyrode's solution. This
final wash is incubated 15 minutes at 37 degrees
Centigrade. The buffer is again removed and replaced with
15 1 ml fresh Calcium-Magnesium Free Tyrode's solution. -
Trypsin is now added at 0.1% (100 ~l of a 10 mg/ml stock
sterile solution). The tube is incubated for 1 hour at 37 -
degrees Centigrade. After trypsin incubation the tissue
is washed with serum containing medium in order to stop
the action of the trypsin. The tissue is resuspended in 1
ml of fresh medium and triturated with a fine bore Pasteur
pipette.
Cells are then counted using a hemocytometer. Cells are
then seeded onto a 96-well Falcon Primeria tissue culture
plates at 75000 cells per well in complete medium.
Complete medium is composed of Minimal Essential Medium
(MEM) with Earle's salts, 10% Fetal Calf Serum (Hyclone),
10% Equine Serum, L-glutamine (2mM), Penicillin-
Streptomycin (lOOU per ml) and Glucose (to make the final
concentration 21 mM a lOOx stock containing 27.8 g per 100
ml is prepared). The plates are fed on day 3 with fresh
medium. Then on day 6 cytosine arabinoside at 10 ~m is ;
added to the cultures with fresh medium. Then two days
later the cytosine arabinoside is removed and replaced
with Maintenance medium, which is complete medium minus
the Fetal Calf Serum. The plates are then fed twice a
WO 93/020~;2 PCr/US92/04973
~l3~fi8 l4
week. Three weeks from the time of dissection the plates
are used in the glutamate toxicity experiments, in order
to insure proper development of the neurons in culture.
Part 2: Glutamate Treatment and Post-Glutamate Drug
Addition:
After three weeks in culture, the medium is removed
from the cells and the cells are washed three times in
chloride free controlled salt solution (CSS-Cl). CSS-Cl
contains 69 mM Na2SO4, 2.67 mM K2SO4, 0.33 mM NaHPO4, 0.44
mM KH2PO4, 1 mM NaHCO3, 1 mM MgS0~, 10 mM HEPES (N-2-
hydroxyethylpiperazine-N~-2-ethanesulfonic acid), 22.2 mM
glucose, and 71 mM sucrose at pH 7.4. After washing,
glutamate is added at 1 to 3 mM in CSS-Cl buffer with
appropriate control wells containing buffer without
glutamate. The plates are incubated at 37 degrees celsius
for 15 to 20 minutes. Following glutamate incubation, the
plates are washed with serum free medium twice. The test
drugs are prepared at the appropriate concentrations in
serum free medium and added to the corresponding wells of
the microtiter plate (100 ~1 per well). Negative control
wells receive serum free medium with no drug. Several
glutamate treated wells are also given serum free medium - -
with no drug to serve as positive controls. The plate is
25 incubated overnight at 37 degrees celsius and the -
following day viability is assessed using the LDH ~lactate
dehydrogenase) and MTT (methyl thiotetrazolinium) assays. `-
Part 3: Assessment of Cell Viability:
The 100 ~1 of medium from each plate is removed and -
transferred to a clean plate to be assayed for the amount -
of LDH released. Then 100 ~1 per well of MTT solution is
added. This MTT solution is prepared by adding 10 ~il of
MTT stock (5 mg/ml in PBS, phosphate buffered saline) for
every 100 ~1 serum free medium. Plates are incubated at
37 degrees for 4 to 6 hours. Then 100 ~1 of acid-alcohol
. ,, ~- '
;
W093/02052 PCT/VS92/04973 ~
2113 3 6 8
-15-
solution (0.08 N HCl in isopropanol) is added to each well ~ -
and the wells were mixed vigorously in order to dissolve -
the purple crystals. Control wells should contain medium
with MTT and acid-alcohol, but no cells. The plates are
then read on a microplate reader, using a dual wavelength
setting test filter at 570 nm and reference filter at 630
nm. The plates must be read within 1 hour.
The medium which is removed is then assayed for ~DH.
Equal volumes of the samples removed are added to LDH
reaction mixture. In this case appropriate wells are
pooled to make 500 ~1 samples. For each sample, reaction
mixture is prepared by mixing 480 ~1 of 0.1 M sodium
phosphate buffer, pH 7.5, 10 ~1 of sodium pyruvate (66 mM)
and 10 ~1 NADH reduced (each vial of NADH containing 5 mg
is reconstituted in 440 ~1 0.1 N NaOH and 10 ~1 of this is
used per sample). The sample is quickly added to the
reaction mixture in cuvettes and the disappearance of
absorbance at 340 nm is measured on a Beckman DU-8
spectrophotometer.
Undesired hypotensive activity is also determined by
known methods, for example, according to the methods of
Carron et al, also cited above.
Such selective neuroprotective antiischemic and ~-
excitatory amino acid blocking activities make the
compounds of the present invention useful in the treatment
of tra~matic injury to the brain and spinal cord,
degenerative CNS (central nervous system) disorders such
as stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and
Huntington's disease, without significant potential for
concurrent undue drop in blood pressure. In the systemic
treatment of such diseases in a human subject with a
neuroprotective amount of compounds of the formula (I),
the dosage is typically from about 0.02 to 10 mg/kg/ day
(1-500 mg/day in a typical human weighing 50 kg) in single
or divided doses, regardless of the route of
administration. Of course, depending upon the exact
W093/02052 PCT/US92/04973
~11 3 ~ 6 ~
-16-
compound and the exact nature of the individual illness,
doses outside this range may be prescribed by the
attending physician. The oral route of administration is
generally preferred. However, if the patient is unable to
swallow, or oral absorption is otherwise impaired, the
preferred route of administration will be parenteral
(i.m., i.v.) or topical.
The compounds of the present invention are generally
administered in the form of pharmaceutical compositions
comprising at least one of the compounds of the formula
(I), together with a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle
or diluent in a ratio of 1:20 to 20:1 respectively. Such
compositions are generally formulated in a conventional
manner utilizing solid or liquid vehicles or diluents as
appropriate to the mode of desired administration: for
oral administration, in the form of tablets, hard or soft
gelatin capsules, suspensions, granules, powders and the
like; for parenteral administration, in the form of --- -
injectable solutions or suspensions, and the like, and for
topical administration, in the form of solutions, lotions~
ointments, salves and the like.
The present invention is illustrated by the following ~
examples, but is not limited to the details thereof. ~ --
All non-aqueous reactions were run under dry, oxygen
free nitrogen for convenience and generally to maximize
yields. All solvents/diluents were dried according to -
standard published procedures or purchased in a predried ~
form. All reactions were stirred either magnetically or ~--
mechanically. NMR spectra are recorded at 300 MHz and are
30 reported in ppm downfield from trimethylsilane. The NMR -
solvent was CDCl3 unless otherwise specified. IR spectra
are reported in micrometers, generally specifying only
strong signals.
''~,.
. .
W093/020s2 PCT/US92/~973
~113~68 ~
-17-
Example 1
(~)-3,4-Dihydro-6-(1-hydroxy-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenoxy-
methyl)piperidinyl)ethyl)quinol ine-2-(lH)-one
A mixture of 300 mg (1. 23 mmol) of 4-hydroxy-4-(phenoxy-
methyl)piperidine hydrochloride, 409 mg (1.84 mmol) of 6-
(2-chloroacetyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(lH)-one and O.514
mL (O.373 g, 3.7 mmol) of triethylamine in 25 mL of
acetonitrile was heated at 60C overnight. The solven~
was then removed in vacuo and the residues partitioned
between water and ethyl acetate and the organic layer was
washed again with water and with brine. The ethyl acetate -~
layer was dried with brine and magnesium sulfate and the
solvent was evaporated to give 3,4-dihydro-6- -
(l-oxo-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenoxymethyl)piperidinyl)ethyl) -
quinoline-2-(lH)-one as a brown solid which was used in
the subsequent reduction step without further
purification.
The above ketone was dissolved in 25 mL of absolute `
ethanol and SOO mg (13.1 mmol) of NaBH4 was added portion-
wise over 20 min. The reaction mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 4 hrs. and then the solvent was ~-
removed and the residues were partitioned between water
and ethyl acetate. After drying, the ethyl acetate was
removed in vacuo and the residue was chromatographed on
silica gel to give the product, 73 mg (15%), m.p. 186-
188C. NMR (CD30D) ~ 1.70-2.10 (4H, m), 2.52-3.07 (lOH,
m), 3.33 (2H, s), 3.83 (2H, s), 6.82-7.38 (8H, m).
Example 2
(+)-5-(1-Hydroxy-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenoxymethyl)-
piperidinyl)ethyl)benzimidazolin-2-one
Following the procedure of Example 1, the present title
compound was obtained from 4-hydroxy-4-(phenoxy-
methyl)piperidine hydrochloride (1.23 mmol), 5-(2-
chloroacetyl)-2-hydroxybenzimidazole (1.84 mmol) and tri-
ethylamine (3.7 mmol) in 25 ml of acetonitrile. The
resulting ketone was stirred with sodium borohydride (13.1
W0~3/02052 PCT/US92/04973
21~ 33 6 8 -18-
mmol~ in absolute ethanol to yield the desired compound
after chromatography on silica gel. Yield 35%, m.p. 232-
235C. Anal. Calcd. for C2~H~N304 H20: C, 62.81; H, 6.77; N,
10.46. Found: C, 62.9~; H, 6.54; N, 10.32. -
Example 3
(+)-5-(1-Hydroxy-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenoxymethyl)- -`
piperidinvl)ethyl~-2-oxindole
Following the procedure of Example 1, the present title
compound was obtained from 4-hydroxy-4-
(phenoxymethyl)piperidine hydrochloride (1.23 mmol), 5-(2- -
chloroacetyl)oxindole (1.84 mmol) and triethylamine (3.7 ~
mmol) in 25 ml of acetonitrile. The resulting ketone was `~ -
stirred with sodium borohydride (13.1 mmol) in absolute --
ethanol to yield the desired compound after chromatography
on silica gel. Yield 40%, m.p. 171-174C.
Example 4 `-;
(+)-~rythro-5-(1-hydroxy-2-~1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenoxymethyl) `~
piperidinyl)propyl)benzimidazolin-2-one --``
A solution of 933 mg (2.36 mmol) of (+)-1-(5-(2- ~- ~
hydroxybenzimidazolyl))-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenoxymethyl) ` ~-
piperidinyl)propan-l-one in 10 mL of glacial acetic acid -~
and 50 mL of absolute ethanol was treated portionwise with ` -
.
944 mg (17~48 mmol) of potassium borohydride between 15-
20C and the resulting solution was stirred overnight at ~-~
room temperature. The reaction mixture was then ` ~`
evaporated to dryness and the residues taken up in minimal
~ water. The pH of this solution was adjusted to 7-8 with
30 solid NaHC03, precipitating a solid. This material was -~
insoluble in chloroform and relatively insoluble in ethyl -~
acetate. The whole was again evaporated to dryness and
the residues, which had crystallized, were taken up in
ethanol and filtered to remove salts. The ethanol was `
evaporated and the residue taken up in isopropanol and
treated with HCl gas in ether to precipitate a non-
W093~020~2 PCT/US92/04973
-19- 21~.3~6$
crystalline salt which was separated by filtration and
dried in a stream of dry nitrogen. This material was
dissolved in hot ethyl acetate with methanol and clarified
with decolorizing charcoal and then the methanol was ;~
boiled off. Cooling gave a colorless crystalline product,
410 mg (40%), m.p. 254-255~C. IR (RBr) 5.90 ~m; NMR
(CD30D) ~ 1.22 (3H, d, J=7), 1.95-2.09 (2H, m), 2.15-2.30
(2H, m), 3.42-3.76 (4H, m), 3.91 (2H, s), 5.47 (lH, s),
6.92-7.35 (8H, m).
Example 5
(+)-Threo-5-(1-hydroxy-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenoxymethyl)-
piperidinyl)propyl)benzimidazolin-2-one:
A total of 700 mg (18.4 mmol) of sodium borohydride
was added portionwise to a suspension of 325 mg (0.82
mmol) of (+)-l-(S-(2-hydroxybenzimidazolyl)-2-(1-(4-
hydroxy-4-phenoxymethyl)piperidinyl)propan-1-one in 20 mL
of absolute ethanol and the reaction mixture was stirred
overnight at room temp. The solvent was then evaporated
and the residual foam was taken up between ethyl acetate
and water and the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl
acetate. The combined ethyl acetate extracts were dried
and evaporated and the residual foam was chromatographed
on silica gel using 1:1 ethanol/ethyl acetate to give the
product as a white solid, m.p.>250C. NMR (Acetone-d6) ~
0.79 (3H, d, J=7), 1.71-1.88 (2H, m), 11.90-2.08 (2H, m),
2.48-2.88 (4H, m), 3.01 (lH, t, J=7), 3.88 (2H, s), 4.26
(lH, d, J=7), 6.86-7.32 (8H, m); Anal. Calcd for
C~H~N304.1.5 H~O:C, 62.24; H, 7.12; N, 9.89. Found: C,
61.72; H, 6.73; N, 9.03.
Example 6
(l)-Erythro-3,4-dihydro-6-(1-hydroxy-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-
phenoxYmethyl)pi~eridinyl!propyl)quinolin-~LlH)one:~__
A solution of 7.13 g (17.5 mmol) of (+)-1-t6-(1,2,3,4-
tetrahydro-2-oxoquinolinyl))-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-
W093/02052 PCT/US92/0497~
211~568 -20-
phenoxymethyl)piperidinyl)propan-l-one in 135 mL of
absolute ethanol and 70 mL of glacial acetic acid was
treated portionwise with 6.22 g (115 mmol) of KBH4 at 15-
20C and was th~n allowed to warm to room temperature for
5 30 min. The reaction mixture was evaporated to dryness -
and the residue was taken up in ice and cold water and
this was basified with solid NaHCO3. The solid which -
precipitated was separated by filtration, washed with ;
water and air dried to give 3.66 g of crystalline free
basej m.p. 192-196C. The filtrate was extracted with
ethyl acetate and the combined extracts were dried with
brine and with MgS04 and evaporated to give an additional
786 mg of product (total yield 62%). A SlQ mg sample of -
this material was dissolved in ethyl acetate and treated
15 with a solution of HCl gas in ether to give 475 mg of the --~
crystalline hydrochloride salt, m.p. 214-216C (dec). IR
(KBr) ~m; NMR (CD30D) ~ 1.15 (3H, d, J=7), 1.86-2.04 (2H, -
m), 3.52-3.66 (2H, m), 3.69-3.80 (lH, m), 3.86 (2H, s), -
5.34 (lH, s), ~.81-6.96 (4H, m), 7.17-7.28 (4H, m).
Example 7
(+)-Threo-3,4-dihydro-6-(1-hydroxy-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4
phenoxymethyl ? piperidinyl~propyl)~uinolin-2rlH)one:
A total of l.S0 g (39.5 mmol) of NaBH4 was added
portionwise to a suspension of 700 mg (1.71 mmol) of (+)-
1-(5-(2-hydroxybenzimidazolyl))-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-
phenoxymethyl)piperidinyl)propan-l-one in 20 mL of
absolute ethanol and the reaction mixture was stirred -
overnight at room temperature. The solvent was then -~
evaporated and the residual foam was taXen up between
ethyl acetate and water and the aqueous layer was
extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined extracts were
dried and evaporated and the residual foam was
chromatographed on silica gel using 1:1 ethanol/ethyl ~ -
acetate to give the product as a white solid, m.p. 192-
196C. A small amount of the erythro compound was formed
in this reduction and could be separated from the column.
W093/02052 PCT~US92/~97~
2113S~8
-21-
NMR (CD30D) ~ 9.82 (3H, d, J=7), 1.72-2.06 (4H, m), 2.50-
2.82 (6H, m), 2.88-3.02 (2H, t, J=7), 3.02 (lH, t, J=7),
3.84 (2H, s), 4.28 (lH, d, J=7), 6.80-7.34 (8 H, m); Anal. -~
Calcd for C~H~N304.1.5 H20:C, 65.88; H, 7.60; N, 6.40. ~ ;
Found: C, 65.74; H, 7.09; N, 6.31.
Example 8
(+)-Erythro-5-(1-hydroxy-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenoxymethyl)
piperidinvl)propyl)oxindole
~ mixture of 0.5 g (2.05 mmol) of 4-hydroxy-4-
phenoxymethyl)piperidine hydrochloride, 0.5 g (2.25 mmol)
of 5-(2-chloropropionyl)oxindole and 1 ml (0.725 g, 7.18
mmol) triethylamine in 20 mL of acetonitrile was refluxed
for 24 h. The solvent was then removed in vacuo and the
residues were partitioned between ethyl acetate and water.
The ethyl acetate layer was washed with water and brine
and was dried over MgSO4 and concentrated to yield the
- ketone as a tan foam which was used for the following
reaction without further purification, 537 mg (66%).
A solution of 500 m~ (1.26 mmol) of the ketone in 20
mL of ethanol was treated portionwise with 1.0 g t26.3
mmol) of NaBH4 and the resulting mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 24 h. The solvent was removed in
vacuo and the residues were partitioned between ethyl
25 acetate ~nd water. The ethyl acetate layer was washed and --
dried with brine and MgS04 and then evaporated to dryness.
The residues were chromatographed on silica gel using
ethyl acetate and gradually increasing concentrations of
~ ethanol to gi~e the threo product in pure fractions, 121
mg (24%), m.p. 204-207C. NMR (DMSO-d6) ~ 0.70 (3H, d,
J=7), 1.58-1.92 (4H, m), 2.40-2.65 (4H, m), 2.86 (lH, m), -
3.32-3.40 (2H, m), 3.79 (2H, s), 4.20 (lH, d, J=7), 6.70- --
7.35 (8H, m), 10.34 (lH, s).
W0 93/020s2 PCI/US92/0497
2113ra68 22
Example 9
(+)-1-(6-(1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-2-oxoquinolinyl))-2-(1-(4-
hydroxy-4-phenoxymethyl)piperidinyl)propan-1-one
A suspension of 8.30 g (34.06 mmol) of 4-hydroxy-4-
phenoxymethylpiperidine hydrochloride and 8.09 g (34.06mmol) of 6-(2-chloro-1-propionyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquin-
olin-2(lH)-one in 100 mL of acetonitrile was treated with
16.61 mL (12.04 g, 0.12 mol) of triethylamine and the
mixture was heated at reflux for 3 h and then stirred
overnight at room temperature.
The reaction mixture was poured into water and
extracted 3 times with ethyl acetate and the combined
extracts were dried with brine solution and magnesium
sulfate and evaporated to give a foam. This foam was
dissolved in hot methanol and ethyl acetate and cooled to
give a tan solid which was found to be starting
chloroketone and discarded. The filtrates were evaporated
and dissolved in ethyl acetate and ether was added to
facilitate crystallization. The product was filtered and
washed with ether to give 8.84 g (63.6~) of the product as
a cream-colored solid, m.p. 137-139C. The analytical -~
sample was crystallized from hot ethyl acetate. NMR
(CD30D) ~ 1.28 (3H, d, J=7), 1.60-1.92 (4H, m), 2.52-2.84 ~--
(6H, m), 3.00 (2H, t, J=7), 3.75 (2H, s~, 4.22 (lH, q,
J=7), 6.82-7.00 (4H, m), 7.16 (2H, m), 7.82-7.98 (2H, m); -~
Anal. Calcd for ~4H28N204:C, 70.56; H, 6.91; N, 6.86. Found: ~ ~-
C, 70.16; H, 6.78; N, 6.76.
Example 10
(+)-1-(5-(2-Hydroxybenzimidazolyl))-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-
phenoxymethyl~piperidinyl)propan-l-one _ ;
A suspension of 2.43 g (10.0 mmol) of 4-hydroxy-4-
phenoxymethylpiperidine hydrochloride and 2.25 g (10.0
mmol) of 5-(2-chloro-1-propionyl)-2-hydroxybenzimidazole
in 40 mL of acetonitrile was treated with 4.88 mL (3.53 g,
35.0 mmol) of triethylamine and the reaction mixture was
wo93/o2os2 PCT/US92/0497~
~ 2113~8
-23-
heated at reflux for so min and then let sit ov~r a
weekend at room temperature.
The reaction mixture was then poured into a mixture
of water and ethyl acetate and the resulting suspended
solid was separated by filtration and found to be pure
product, 1.15 g after drying. The filtrate was adjusted
to pH=7.0 and extracted with ethyl acetate several times
to give, after drying with brine solution and MgSO4, a
colorless solid which was recrystallized from hot ethyl
acetate/methanol to give an additional 560 mg of product
(total yield, 43%), m.p. 230-235C (dec.). NMR
(CD3OD/DMSO-d6) ~ 1.29 (2H, d, J=7), 1.60-1.92 (4H, m),
2.54-2.84 (4H, m), 3.77 (2H, s), 4.26 (lH, q, J=7), 6.86-
7.10 (6H, m), 7.75-7.92 (2H, m).
Example 11
(+)-1-(5-(Oxindolyl))-2-(1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenoxymethyl)
_ piperidinyl)propan-l-one
Following the procedure of preparation 10, the present
title compound was obtained from 4-hydroxy-4-
phenoxymethylpiperidine hydrochloride ~10.0 mmol), 5-(2-
chloropropionyl)oxindole (10 mmol) and triethylamine (35 ~-
mmol) in 50 ml of acetonitrile. The title compound was
isolated by crystallization from hot ethyl acetate/
methanol to give an amorphous foam. Yield 66.4%.
NMR (CDCl3) ~ 1.28 (3H, d, J=7), 1.58-1.78 (4H, m), 2.40-
2.84 (4H, m), 3.54 (2H, s), 3.76 (2H, s), 4.09 (lH, q,
J=7), 6.78-6.96 (3H, m), 7.14-7.26 (2H, m), 7.84-8.05 (3H,
m), 9.52 (lH, broad s), 9.64 (lH, broad s).
w093/02052 PCT/US92/04973 -~
21135~8 -24- ~
PreDaration 1
3 4 DihydrogLui_o~ 2-(lH~-one --
A slurry of 50.0 g (0.259 mol) of o-nitrocinnamic
acid in 500 mL of ethanol was treated with S teaspoons of
Raney Ni and hydrogenated on a Parr shaker overnight at an
initial pressure of 50 psi. In the morning, the pressure ~
was increased again to 50 psi and the reaction was ~ -
continued for an additional 5 h. The reaction mixture was
filtered to remove the catalyst and then washed through a
bed of silica gel with a mixture of ethyl acetate and
ethanol to remove traces of nickel salts. Evaporation of
the filtrate gave the desired product in 57% yield. NMR
(DMSO-d6) ~ 2.45 (2H, t, J=7), 2.87 (2H, t, J=7), 6.87 (2H, ~ -
d of d, J=7, 7), 7.12 (2H, d of d, J=7, 10), 10.08 (lH,
s). m.p. 165-166C.
Preparation 2
6-t2-Chloropropionyl)-3.4-dihydroguinolin-2-(lH~-one
A suspension of 72.5 g (0.544 mol) of AlCl3 in 800 mL
of CS2 was stirred under dry N2 while 14.1 mL (20.0 g,
0.177 mol) of 2-chloropropionyl chloride was added
followed by 20.0 g (0.136 mol) of 3,4-dihydroquinolin-
2(lH)-one. The reaction mixture was refluxed for 4 h at
which time a separation of phases was noted. The reaction -~
was quenched by pouring onto ice with vigorous stirring.
The pale yellow precipitate which formed was separated by
filtration, washed with water and dried overnight over P2O
to give 27.7 g (91%) of the desired product, m.p. 236.5-
238C.
Preparation 3 -
5-(2-Chloropro~ionvl)-2-hydroxvbenzimidazole
Following the procedure of Preparation 2, the present
title compound was obtained from 2-hydroxybenzi-
midazole (0.136 mol), aluminum chloride (0.544 mol) and 2-
-chloropropionyl chloride (0.177 mol) in 800 ml CS2. The
~`''' '
WOg3/02052 PCT/US92~97~
-25- ~113 ~ 6 8
title compound was isolated by filtration. Yield 92%,
m.p. 245 dec. Anal. Calcd for Ci~ClN202: C, 53.47; H,
4.04; N, 12.47. Found C, 54.41; H, 4.07; N, 13.25.
Preparatio~ 4
5-(2-Chloropropionyl~oxindole
Following the procedure of Preparation 2, the present
title compound was obtained from oxindole (0.136 mol),
aluminum chloride (0.544 mol~ and 2-chloropropionyl
chloride (0.177 mol) in 800 ml CS2. The title compound was
isolated by filtration. Yield 91%, m.p. 157-158C.
Preparation 5
6-(2-ChlsroacetYl~-3.4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one
Following the procedure of Preparation 2, the present
title compound was obtained from 3,4-dihydroquinolin-2-
(lH)-one (0.136 mol), aluminum chloride (0.544 mol) and 2-
chloroacetyl chloride (0.177 mol) in B00 ml CS2. The title -~
compound was isolated by filtration. Yield 50~, m.p. 215-
216C.
PreDaration 6
5-r2-Chloroacetyl)-2-hydrox,ybenzimidazole ''~
Following the procedure of Preparation 2, the present
25 title compound was obtained from 2-hydroxybenzimidazole ~`~
(0.136 mol), aluminum chloride (0.544 mol) and 2- ~ `
chloroacetyl chloride (0.177 mol) in 800 ml C~. The title
compound was isolated by filtration. Quantitative yield,
m.p. 273-275C (dec). -
Preparation 7 ;
5-l2-Chloroacetyl)-oxindole
Following the procedure of Preparation 2, the present ~ -~
title compound was obtained from oxindole (0.136 mol),
aluminum chloride (0.544 mol) and 2-chloroacetyl chloride
W093/020~2 PcT/uss2/~97~
2~13~68 -26-
(0~177 mol) in 800 ml CS2. The title compound was isolated
by filtration. Yield 90%, m.p. 236.5-239OC.
Preparation 8
4-Hvdroxy-4-phenoxymethylpiperidine hvdrochloride
Oil free sodium hydride (2.16 g, o.os M) was added to
dry dimethyl sulfoxide (250 mL) under nitrogen gas and the
mixture was heated to 60-65C until a uniform black
solution was formed, about 1 h. Then 19.83 g (0.09 M) of
trimethylsulfoxonium iodide was added (slight exothsrm)
and the mixture was stirred until a brown solution
occurred, about 30 min. Then a solution of 13.40 g
(S7.3mM) of N-t-butyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidone in 50 mL of
dimethyl sulfoxide was stirred at room temperature for 1
h. The reaction mixture was then poured into 1 L of cold
water and the whole was extracted 4X with 100 mL portions
of hexane. The combined hexane extracts was back-washed
with 50 mL of water and with brine solution and was dried - ~
with magnesium sulfate, filtered and evaporated to give - -
11.75 g of white crystalline product, 6-t-butyloxycar- -
bonyl-1-oxa-6-azaspiro~2.5]octane, (78% yield). -~
- Further extraction of the aqueous layers with 3X 50 -~
mL of hexane gave a further 650 mg of product for a total ~ -
yield of 82.5%. ~ ~
m.p. 57.5-59.5C; IR(KBr) 5.90 ~m; NMR ~ 1.32-1.48 ---- ~`
(2H, m), 1.42 (gH, s), 1.74-1.80 (2H, m), 2.65 (2H, s),
3.31-3.43 (2H, m), 3.61-3.72 (2H, m); Anal. Calcd for -- -
Cl~H~O3: C, 61.94; H, 8.98; N, 6.57. Found: C, 62.05; H,
9.09; N, 6.58. -~-
A solution of 10.37 g (0.11 M) of phenol in 100 mL of ~-
dry dimethyl sulfoxide treated portionwise with 1.99 g
(82.8 mmol) of oil-free sodium hydride keeping the
temperature between 20-25C with a cold water bath. The
reaction mixture was then stirred at room temperature for
45 min to give a grey suspension. The 11.75 g (55.2 mmol)
of 6-t-butyloxycarbonyl-1-oxa-6-azaspiro[2.5~octane
dissolved in 65 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide was added
W O 93/02052 PC~r/US92/04973
~113~68
-27-
dropwise after which the reaction mixture was heated to
ss-600c for 7 h and was then sti_red at room temperature
overnight.
The reaction mixture was then poured into 1 L of cold
water and extracted ~X with ether. The combined ~ther
extracts was backwashe~ with 10% NaOH and with brine and
was dried with magnesium sulfate evaporated to give the
desired product, N-t-butyloxycarbonyl-4-hydroxy-
4-phenoxymethylpiperidine, as an oil weighing 17.01 g
(100%).
IR (Film) 5.91, 2.95 ~M; NMR (CDCl3) ~ 1.46 (9H, s);
1.53-1.80 (4H, m), 3.13-3.30 (2H, m), 3.80 (2H, s), 3.80-
3.98 (2H, m), 6.84-6.99 (2H, m), 7.22-7.44 (3H, m); Anal.
Calcd for C~7H25NO4: C, 66.42; H, 8.20; N, 4.56. Found: C,
65.72; H, 8.21; N, 4.77. -
A solution of 17.0 g (0.055 M) of N-t- ~-
Butyloxycarbonyl-4-hydroxy-4-phenoxymethylpiperidine in
150 mL of methanol was saturated with HCl gas. After the
mixture had cooled, it was again treated with HCl gas and
this procedure was again repeated. After crystals had
formed, the reaction mixture was treated with 500 mL of ~--
anhydrous ether and let stir at room temperature
overnight. --~-~
The product was filtered and washed with dry ether
and dried under a stream of dry N2 to give 10.85 g (80.6%) -~
of crystalline material, m.p. 202-204C. IR (KBr) 3.06,
3.14, 3.44, 3.57, 3.56, 6.33, 8.06 ~m; NMR tD2O) ~ 2.00 (4
H, broad s), 3.34 (4H, broad s), 4.00 (2H, s), 6.98-7.09 - -
(3H, m), 7.30-7.43 (2H, m). Anal. Calcd for Cl2HI~NO2.HCl:
C, 59.13; H, 7.44; N, 5.75. Found: C, 58.98; H, 7.11; N,
5.65.