Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
'^~
~ 211~737
Condensed five-membered heterocyclic compounds
. .
This invention relates to novel condensed five-membered
heterocyclic compounds, their preparation,
pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their
use.
It has been found that certain novel condensed five- :
membered heterocyclic compounds have valuable
pharmacological properties, particularly aggregation-
inhibiting affects.
Thus viewed ~rom one aspect the present invention .
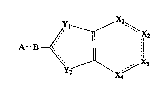
provides compounds of formula I
A~
(wherein
A denotes an aminoalkyl, amidino or guanidino group, at :
one of the nitrogen atoms whereof a hydrogen atom is
optionally replaced by a hydroxy, alkyl, alkoxycarbonyl
or phenylalkoxycarbonyl group, ~ .
or A denotes a piperidinyl group optionally substituted
in the carbon skeleton by one or two alkyl groups or at :~
the nitrogen atom by a group Ra ~ and wherein a >CH- unit .
în the 4-position is optionally replaced by a nitrogen ~: :
atom,
or A denotes an imidazolyl group
~, ` 21~737
- 2 -
or A denotes a pyridyl group which, if the heterocyclic
group attached to AB- is a benzoxazole group, is bound
to group B other than via the 2-position;
Ra denotes a hydrogen atom or an alkyl, phenylalkyl,
(C14-alkoxy)carbonyl or phenylalkoxycarbonyl group or
R1-CO-(R2CH)-o-CO- group (wherein R1 denotes an alkyl
group and R2 denotes a hydrogen atom or an alkyl or
phenyl group);
B denotes a straight-chain or branched C15-alkylene
group,
or an -alkylene-O-, -O-alkylene-, -alkylene-S-,
-S-alkylene-, -alkylene-NR3-, -NR3-alkylene-, -CO-NR3- or
-NR3-CO- group (wherein R3 denotes a hydrogen atom or an
alkyl or phenylalkyl group),
or a cyclohexylene.group,
or, if A denotes a piperidinyl group optionally
substituted in t~e carbon skeleton by one or two alkyl
groups or at the nitrogen atom by a group Ra~ optionally
with a >CH~ unit in the 4-position replaced by a
nitrogen atom,
or, if X1 denotes a carbonyl group (with the proviso
that, if -D-E-T denotes a 4-carboxybutyl or 4-
methoxycarbonyl-butyl group, X4 does not simultaneously
denote an N-methyl-imino group),
or, if -D-E-F denotes a 2-carboxyethylaminocarbonyl or
2-methoxycarbonylethylaminocarbonyl group and X4 does not
simultaneously denote a nitrogen atom,
then B may also denote a phenylene group optionally
mono- or disubstituted in the phenyl nucleus by
` 2115737
- 3 -
fluorine, chlorine or bromine atoms or by alkyl or
alkoxy groups, whilst the substituents may be identical
or different;
a first of the groups X1, X2, X3 and X4 denotes an
F-E-D-C< or F-E-D-N< group, (wherein
D denotes a straight-chain or branched C16-alkylene
group, a C26-alkenylene group, an oxygen or sulphur
atom, a -CO-, -SO-, -SO2-, -CO-NR3- or -NR3-CO- group, or
an -SO2NR3- group bound to group ~ via the nitrogen atom,
E denotes a bond or a straight-chain or branched C~ 5-
alkylene group, and
F denotes a carboxy, (C16-alkoxy)carbonyl,
phenylalkoxycarbonyl, (C37-cycloalkyl)oxycarbonyl, (C3 7-
cycloalkyl)alkoxycarbonyl, sulpho, phosphono, O alkyl-
phosphono, O,O-dialkyl-phosphono or tetrazol-5-yl
group);
a second of the g~oups X1 ~ X2 ~ X3 and X4 dênotes a
nitrogen atom or an Rb-C<, Rc-Nc or carbonyl group
(wherein
Rb denotes a hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine or bromine atom
or C16-alkyl, hydroxy, C16-alkoxy, phenylC16-alkoxy,
amino, C16-alkylamino or di(C16-alkyl)amino group, and - ~
denotes a hydrogen atom or a C16-alkyl group ~ :
optionally substituted by a hydroxy, alkoxy, amino, -
alkylamino, dialkylamino, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl,
pyrrolidino, piperidino, morpholino, piperazino or N- : :
alkyl-piperazino group,
or Rc denotes a phenylC15-alkyl group mono- or
-- ', '~
` ` 211S737
-- 4 --
disubstituted in the phenyl nucleus by fluorine,
chlorine or bromine atoms or by alkyl or alkoxy groups,
wherein the substituents may be identical or different);
and the remaining groups of groups X1, X2, X3 and X4 each
denote a nitrogen atom or an Rb-C< or carbonyl group,
while no more than two of the groups X1, X2, X3 and X4
denote carbonyl groups and at least one of the groups X1,
X2 t X3 and X4 denotes a carbonyl, FED-C< or Rb-C< group;
one of the groups Y1 and Y2 denotes a nitrogen atom or a
methine group and the other group Y1 or Y2 denotes an
oxygen atom or an Rd-N< group; and
Rd denotes a hydrogen atom or a C16-alkyl group
optionally substituted by a hydroxy, alkoxy, amino,
alkylamino, dialkylamino, pyrrolidino, piperidino,
morpholino, piperazino or N-alkyl-piperazino group,
or Rd denotes a phenyl(C15-alkyl) group optionally mono-
or disubstituted in the phenyl nucleus by fluorine,
chlorine or brom~ne atoms or by alkyl or ^alkoxy groups,
and the substituents may be identical or different, or Rd ~
denotes a C37-cycloalkyl group, or, if the groups RC-N<
and Rd-N< are bound to the same carbon atom, Rd together
with Rc may denote a straight-chain or branched C25-
alkylene group;
wherein unless otherwise specified each alkyl, alkylene
or alkoxy moiety contains l to 3 carbon atoms)
and the isomers (e.g. tautomers and stereoisomers),
isomer mixtures and salts thereof.
Preferred compounds according to the invention include
these of formula I wherein:
~ -
" ` 211~737
- 5 -
A denotes an amidino group optionally substituted by a
hydroxy or alkoxycarbonyl group,
or an aminoalkyl or benzyloxycarbonylaminoalkyl group,
or A denotes a piperidinyl group optionally alkyl-
substituted in the carbon skeleton and optionally
substituted by a group Ra at the nitrogen atom (wherein
Ra denotes a hydrogen atom or an alkyl, benzyl,
alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl or R1-CO-CH2~0-CO-
group (wherein R1 denotes an alkyl group)) and wherein a
>CH- unit in the 4-position may be replaced by a
nitrogen atom,
or A denotes an imidazolyl group,
or A denotes a pyridyl group which, if the heterocyclic
group attached to AB- is a benzoxazole group, is bound
to group B other than via the 2-position;
B denotes a straight-chain or branched C15-alkylene :~
group, :
.. . .
or an -alkylene-O-, -O-alkylene-, -alkylene-S~
-S-alkylene-, -alkylene-NR3-, -NR3-alkylene-, -CO-NR3- or ;~.
-NR3-CO--group t wherein R3 denotes a hydrogen atom or an
alkyl group~,
or a cyclohexylene group,
or, if A denotes a piperidinyl group optionally alkyl-
substituted in the carbon skeleton and optionally
substituted by a group Ra at the nitrogen atom, and with
a >CH- unit in the 4-position optionally replaced by a
nitrogen atom, :;~
or, if Xl denotes a carbonyl group (with the proviso
2115737
6 --
that, if -D-E-F denotes a 4-carboxybutyl or 4-
methoxycarbonylbutyl group, X4 does not simultaneously
denote an N-methyl-imino group),
or, if -D-E-F denotes a 2-carboxyethylaminocarbonyl or
2-methoxycarbonylethylaminocarbonyl group, and X4 does
not simultaneously represent a nitrogen atom,
B may also denote a phenylene group;
a first one of the groups X1, X2, X3 and X4 denotes an
F-E-D-C< or F-E-D-N< group (wherein
D denotes a straight-chain or branched C16-alkylene
group, a C24-alkenylene group, an oxygen or sulphur
atom, a -CO-, -SO-, -SO2-, -CO-NR3- or -NR3-CO- group or
an -SO2-NR3- group bound to group E via the N atom,
E denotes a bond or a straight-chain or branched C15-
alkylene group, and
F denotes a carb~y, (C15-alkoxy)carbonyl^or ~C57-
cycloalkoxy~carbonyl group); --
a second of the groups X1, X2, X3 and X4 denotes a
nitrogen atom or an Rb-C<, RC-N< or carbonyl group
(wherein
Rb denotes a hydrogen, chlorine or bromine atom or an
alkyl, hydroxy, alkoxy, amino, alkylamino or :~
dialkylamino group, and
-
Rc denotes a hydrogen atom, or a C15-alkyl group
optionally substituted by a hydroxy, alkoxy, amino,
alkylamino, dialkylamino, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl,
aminocarbonyl, pyrrolidino, piperidino, morpholino,
piperazino or N-alkyl-piperazino group, or Rc denotes a ~-
.
:`` 21~7~7
phenylC1s-alkyl group optionally mono- or disubstituted
by alkoxy groups in the phenyl nucleus, wherein the
substituents may be identical or different);
and the remaining groups of groups Xl, X2, X3 and X4 each
denote a nitrogen atom or an Rb-C< or carbonyl group
whilst no more than two of the groups Xl, X2, X3 and X4
denote carbonyl groups and at least one of the groups
X1 ~ X2~ X3 and X4 denotes a carbonyl, FED-C< or Rb-C<
group;
one of the groups Y1 or Y2 denotes a nitrogen atom and
the other group Y1 or Y2 denotes an oxygen atom or an
Rd-N< groupJ and ;
Rd denotes a hydrogen atom, or a C15-alkyl group
optionally substituted by a hydroxy, alkoxy, amino,
alkylamino, dialkylamino, pyrrolidino, piperidino,
morpholino, piperazino or N-alkyl-piperazino group,
or Rd denotes a phenylC1s-alkyl group optionally mono- or
disubstituted in the phenyl nucleus by alkoxy groups,
which substituen~ may be identical or different, or Rd
denotes a C36-cycloalkyl group, or, if the groups RC-N<
and Rd-N< are bound to the same carbon atom, Rd together
with Rc may denote a straight-chain or branched C24~
alkylene group; -
wherein unless otherwise specified each alkyl, alkylene
and alkoxy moiety contains l to 3 carbon atoms;
and the isomers (e.g. tautomers and stereoisomers)
thereof and the salts thereof.
Particularly preferred compounds according to the
invention includes those of formula I wherein:
A denotes an amidino group optionally substituted by a
,` 211~737
- 8 -
hydroxy or ~C13-alkoxy)carbonyl group
or A denotes an aminoalkyl or benzyloxycarbonyl-
aminoalkyl group,
or a piperidinyl group optionally methyl-substituted in
the carbon skeleton and optionally substituted by a
group Ra at the nitrogen atom (wherein Ra denotes a
hydrogen atom or a methyl, benzyl, methoxycarbonyl,
benzyloxycarbonyl or CH3-CO-CH2-O-CO- group), and wherein
a >CH- unit in the 4-position may be replaced by a
nitrogen atom,
or A denotes a 4-pyridyl or l-imidazolyl group;
B denotes a straight-chain or branched C14-alkylene
group,
or an -alkylene-O-, -O-alkylene-, -alkylene-S-,
-alkylene-NR3-, -NR3-alkylene- or -NR3-CO- group (wherein
each alkylene mo~èty contains 1 or 2 carbon atoms,
wherein the alkylene moiety of the -alkylene-S- group
and the nitrogen atom of the -NR3-CO- group are linked to :~-
the group A and wherein R3 denotes a hydrogen atom or a
methyl group), ~.
or a 1,4-cyclohexylene group,
or, if A denotes a piperidinyl group optionally
substituted by a methyl group in the carbon skeleton and
optionally substituted by a group Ra at the nitrogen atom
(wherein Ra is as hereinbefore defined) and wherein a
>CH- unit in the 4-position is optionally replaced by a
nitrogen atom, :
or, if X1 denotes a carbonyl group (with the proviso
`- 211~737
g
that, if -D-E-F denotes a 4-carboxybutyl or 4-
methoxycarbonylbutyl group, X4 does not simultaneously
denote an N-methyl-imino group),
or, i~ -D-E-F denotes a 2-carboxyethylaminocarbonyl or
2-methoxycarbonylethylaminocarbonyl group and X4 does not
simultaneously denote a nitrogen atom,
B may also denote a phenylene group;
a first of the groups Xl, X2, X3 and X4 denotes an
F-E-D-C< or F-E-D-N< group (wherein ~:
::
D denotes a straight-chain or branched C16-alkylene
group, a C24-alkenylene group, an oxygen or sulphur
atom, a -CO-, -SO-, -SO2-, -CO-NR3- or -NR3-CO- group or
an -SO2-NR3- group bound to group E via the nitrogen atom
(wherein R3 is as hereinbefore defined), . ~ :
denotes a bond or a straight-chain or branched C14-
alkylene group, and
F denotes a carboxy group, a (C1salkoxy)carbonyl or a ~:
cyclohexyloxycarbonyl group~
: .
a second of groups X1~ X2 ~ X3 and X4 denotes a nitrogen
atom or an RC-N~, RC-C< or carbonyl group, (wherein
Rb denotes a hydrogen or chlorine atom or a hydroxy,
methoxy, amino, methylamino or dimethylamino group, and
Rc denotes a hydrogen atom, or a C15-alkyl group
optionally substituted by a methoxy, carboxy, :.
methoxycarbanyl or aminocarbonyl group, or Rc denotes a
phenylC15-alkyl group);
and the remaining groups of groups Xl, X2, X3 and X4 each
2115737
-- 1 0 --
denote a nitrogen atom or an Rb-C< or carbonyl group
(wherein Rb is as hereinbefore defined) while no more
than two of the groups X1, X2, X3 and X4 denote carbonyl
groups and at least one of the groups X1, X2, X3 and X4
denotes a carbonyl, FED-C< or Rb-C< group;
one of the groups Y1 and Y2 denotes a nitrogen atom and
the other of the groups Y1 or Y2 denotes an oxygen atom
or an Rd-N< group (wherein
Rd denotes a hydrogen atom, or a C15-alkyl group
optionally substituted by a hydroxy, methoxy, amino,
methylamino, dimethylamino, morpholino, piperazino or N-
methyl-piperazino group, or Rd denotes a phenylC15-alkyl
group optionally mono- or disubstituted by methoxy
groups in the phenyl nucleus, or Rd denotes a C36-
cycloalkyl group, or~ if the groups RC-N< and Rd-N< are
bound to the same carbon atom, Rd together with Rc may
together denote a straight chain or branched chain C23-
alkylene group;
wherein unless o~erwise specified ~ach aikyl, alkylene
and alkoxy moiety contains l to 3 carbon atoms;
and the isomers (e.g. tautomers and stereoisomers)
thereof and the salts thereof.
. .
Especially preferred compounds according to the
invention include those of formula I wherein:
,
A denotes an amidino, aminoC12-alkyl or
benzyloxycarbonylaminoC12-alkyl group,
''
or a piperidin-4-yl group substituted by a group Ra at
the nitrogen atom (wherein Ra denotes a hydrogen atom or
a benzyl or benzyloxycarbonyl group);
~ 2115737
-- 1 1 --
B denotes a straight-chain or branched c14-alkylene
group,
or an -NH-CO- group the nitrogen atom whereof is linked
to group A,
or a 1,4-cyclohexylene group,
or, if A denotes a piperidin-4-yl group substituted at
the nitrogen atom by a group Ra (wherein Ra is as
hereinbefore defined),
or, if X1 denotes a carbonyl group ~with the proviso
that, if -D-E-F denotes a 4-carboxybutyl- or 4~
methoxycarbonylbutyl group, X4 does not simultaneously
denote an N-methyl-imino group),
or, if -D-E-F denotes a 2-carboxyethylaminocarbonyl or -
2-methoxycarbonylethylaminocarbonyl group and X4 does not
simultaneously denote a nitrogen atom, ~-
~ .
then B may also ~ènote a phenylene group;
a first o~ the groups Xl, X2, X3 and X4 denotes an
F-E-D-C< or F-E-D-N< group (wherein
:::
D denotes a straight-chain or branched C14-alkylene
group, a C23-alkenylene group, a CO- group or a CO-NH-
group the nitrogen atom whereof is linked to the group
E;
E denotes a bond or a straight-chain or branched C24-
alkylene group; and
F denotes a carboxy group or a (C14-alkoxy)carbonyl
group);
21~5737
- 12 -
a second of the groups X1, X~, X3 and X4 denotes an RC-N<
or Rb-C< group (wherein Rb denotes a hydrogen or chlorine
atom and Rc denotes a hydrogen atom or a methyl or ethyl
group);
and the remaining groups of groups Xl, X2, X3 and X4 each
denote a nitrogen atom or an H-C< or carbonyl group;
one of the groups Y1 and Y2 denotes a nitrogen atom and
the other group Y1 or Y2 denotes an Rd-N< group (wherein
Rd denotes a hydrogen atom or a C14-alkyl group or
Rd together with Rc denotes a straight-chain or branched
~23~alkylene group);
and the tautomers, stereoisomers and salts thereof.
Most especially preferred compounds according.to the
invention include those of formula I wherein:
A denotes an amidino- or piperidin~4-yl group,
B denotes an ethy~ene group,
or, if A denotes a piperidin-4-yl group,
or, if X1 denotes a carbonyl group (with the proviso
that, if -D-E-F denotes a 4-carboxybutyl or 4-
methoxycarbonylbutyl group, X4 does not simultaneously
denote an N-methyl-imino group),
or, if -D-E-F denotes a 2-carboxyethylaminocarbonyl or
2-methoxycarbonylethylaminocarbonyl group and X4 does not
simultaneously denote a nitrogen atom,
then B may also denote a phenylene group;
a first of the groups Xl, X2, X3 and X4 denotes an
` ` ~`~
~ ! 2 1 1 5 7 3 7
,, ~ .
F-E-D-C< or F-E-D-N< group ~wherein
D denotes a straight-chain or branched C24-alkylene
group, an ethenylene group, or a -CO- group or a -CO-NH-
group the nitrogen atom whereof is linked to the group
E;
E denotes a bond or an ethylene group; and
F denotes a carboxy group or a (C14-alkoxy~carbonyl
group~;
a second of the groups X1, X2, X3 and X4 denotes an RC-N<
or Rb-C< group, (wherein Rb denotes a hydrogen or
chlorine atom and Rc denotes a hydrogen atom or a methyl
group);
and the remaining groups of groups X1, X2, X3 and X4 each
denote a nitrogen atom or an H-C< or carbonyl group;
one of the groups Y1 and Y2 denotes a nitrogen atom and : .
the other group ~j or Y2 denotes an Rd-N< group (wherein
Rd denotes a methyl group or Rd together with Rc denotes
an n-propylene group);
and the tautomers, the stereoisomers and the salts
thereof.
Examples of particularly preferred compounds according
to the invention include:
(a) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-mPthyl-2-[2-
(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole,
(b) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-2-[(4-
piperidinyl)-aminocarbonyl]-benzimidazole,
`~ 2:1 15737
- 14 -
(c) 5-(4-carboxy-l-oxo-butyl)-l-methyl-2-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazoler
(d) l-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3-methyl-8-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)ethyl]-xanthine,
(e) l-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3,9-dimethyl-8-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine,
(f) 2-(4-amidino-phenyl)-9-(4-carboxy-butyl)-8,lO-
dioxo-5,6-dihydro-4H,9H-pyrimido[l,2,3-cd]purine,
(g) 5-[~2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-
methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
and the salts thereof.
Viewed from another aspect, the invention also provides
a process for preparing the compounds of the invention,
said process comprising at least one of the ~ollowing
steps:
a) (to prepare c~mpounds of formula I, wherein F denotes
a carboxy group)
cleaving a protecting group from a compound of formula
(wherein :-~
A, B, X1, X2, X3, X4, Y1 and Y2 are as hereinbefore - ~:
defined, with the proviso that F denotes a
(C16-alkoxy)carbonyl, phenyl(C13-alkoxy)carbonyl,
.: '
; . '~
' 211~737
- 15 -
(C37-cycloalkyl)oxycarbonyl or (c3-7-cycloalkyl)(c1 3-
alkyloxy)carbonyl group or a carboxyl group protected by
a cleavable group such as a trimethylsilyloxycarbonyl, ~:
methoxybenzyloxycarbonyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzyloxycarbonyl
or tetrahydropyranyloxycarbonyl group), by hydrolysis,
hydrogenolysis or thermolysis;
b) (to prepare compounds of formula I, wherein Ra denotes
a hydrogen atom)
cleaving a protecting group from a compound of formula
III
A~
(wherein
A, B, Xl, X2, X3, X4, Y1 and Y2 are as hereinbe~ore
defined, with th~ proviso that Ra denotes a
(C14-alkoxy)carbonyl, phenyl(C13-alkoxy)carbonyl, or
R1-CO-(R2CH)-O-CO- group (wherein R1 and R2 are as
hereinbefore defined), or a cleavable imino group
protecting group such as an acetyl, trifluoroacetyl,
benzoyl, benzyl, methoxybenzyl or 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl
group) by hydrolysis, hydrogenolysis or thermolysis;
c) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein one of the
groups Y1 and Y2 denotes a nitrogen atom and the other
group Y1 or Y2 denotes an Rd-N< group or, if the groups :
RC-N< and Rd-N< are bound to the same carbon atom, Rc and
Rd together may also denote a C25-n-alkylene group)
cyclising a compound of formula IV -:~
.
`
. ~
" 2115737
-- 16 --
~1~ .
ZQ~ \ ~3
....
(wherein X1, X2, X3, X4 are as hereinbefore defined,
one of the groups Z1 and Z2 denotes an A~B-CO-NRd1- group
and the other group Z1 or Z2 denotes an HNRd2- group,
wherein A and B are as hereinbefore defined, one of the. `
groups Rd1 and Rd2 denotes a hydrogen atom and the other
group Rd1 or Rd2 has the meanings given for Rd
hereinbe~oxe) optionally formed in the reaction mixture,
with optional subsequent cleaving of any protecting
group used;
:~,
d) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein B denotes
an -NR3-CO-~group~
: reacting a compound of formuIa V
Yl~ `~X2
;: (wherein
j X1, X2, X3, X4, Y1 and Y2 are as hereinbefore defined and -`:
Hal denotes a chlorine, bromine or iodine atom), with a
compound of formula VI ~:~:::
A ' -- HNR3 (VI ) : ~ `
2115737
- 17 -
(wherein
R3 is as hereinbefore defined and A' denotes a
piperidinyl group optionally substituted in the carbon
skeleton by one or two alkyl groups and optionally
substituted at the nitrogen atom by a group Ra (wherein
Ra is as hereinhefore defined with the exception of the
hydrogen atom) or denotes a cleavable imino group
protecting group such as an acetyl, trifluoroacetyl,
benzoyl, benzyl, methoxybenzyl or 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl
group), optionally with subsequent cleaving of any .
protecting group used;
e) (to prepare compounds of general formula I,
wherein F denotes a (C16-alkoxy)carbonyl,
phenyl(C13-alkoxy)carbonyl, (C37-cycloalkyl)oxycarbonyl
or (C37-cycloalkyl)(C13-alkoxy)carbonyl group)
reacting a compound of formula VII
~ xxl~
x1~X3
(wherein :
A~ B~ X1, X2~ X3, X4, Y1 and Y2 are as hereinbefore ~ -
defined, with the proviso that F denotes a carboxy group
or, if Z3 denotes a hydroxy group, F may also denote an
esterified carboxy group, e.g. (C14-alkoxy)carbonyl or ~:
phenyl(C~3-alkoxy)carbonyl group) with a compound of ~
formula VIII --
Z3 - R4 (VIII)
(wherein R4 denotes a C16-alkyl group, a phenyl(C
alkyl) group, a C37-cycloalkyl or (C37-cycloalkyl)C
j
2 11 5 7 3
- 18 -
alkyl group, and Z3 denotes a hydroxy group or, if F
denotes a carboxy group, Z3 may also denote a
nucleophili.c leaving group such as a halogen atom or a
sulphonyloxy group, e.g. a chlorine, bromine or iodine
atom, or a methanesulphonyloxy or p-toluenesulphonyloxy
group);
f) (to prepare compounds of formula I, wherein A denotes
an amidino group optionally substituted at a nitrogen
atom by a C13-alkyl group)
reacting a compound of formula IX
A-B
(wherein
A, B, Xl, X2, X3, X4, Y1 and Y2 are as ~lereinbefore
de~ined, with tha~`proviso that A denotes a Z4-C(=NH~-
group wherein Z4 denotes an amino group, an alkoxy or
aralkoxy group (such as a methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, :~:
isopropoxy ~r benzyloxy group) or an alkylthio or ~:
aralkylthio group such as a methylthio, ethylthio,
n-propylthio or benzylthio group) optionally formed in :~-
the reaction mixture, with an amine of formula X :~
: .
: Rs - NH2 (X)
(wherein
R5 denotes a hydrogen atom or a C~3-alkyl group) or an ~-
acid addition salt thereof;
g) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein ~ denotes
an amidino or guanidino group substituted at one of the
` 21~737
-- 19 --
nitrogen atoms by a C13-alkyl or (C13-alkoxy)carbonyl
groupl or A denotes a piperidinyl group optionally
substituted in the carbon skeleton by one or two alkyl
groups and, at the nitrogen atom, by a group R~ (wherein
R~ has the meanings given hereinbefore, with the
exreption of the hydrogen atom~ and in which a >CH- unit
in the 4-position may additionally be replaced by a
nitrogen atom)
reacting a compound of formula XI
~ ~ lX2 (Xl~
~wherein
A~ B~ X1~ X2, X3, X4, Y1 and Y2 are as hereinbefore
defined, with the proviso that A denotes an amidino or
guanidino group, or a piperidinyl group optionally
substituted by o*e or two alkyl groups in the carbon
skeleton and unsubstituted at the nitrogen atom and in .
which a >CH- unit in the 4-position is optionally
replaced by a nitrogen atom) with a compound of formula
XII -~
Zs ~ R6 (XII)
-
(wherein :-
R6 denotes an (C14-alkoxy)carbonyl, C13-alkyl,
phenyl(C13-alkyl) or phenyl(C13-alkoxy)carbonyl group or
an R1-CO-(R2CH)-O-CO- group, (wherein R1 and R2 are as ~.
hereinbefore defined), and Z5 denotes a nucleophilic ::
leaving group such as a halogen atom, an aryloxy,
arylthio, alkoxycarbonyloxy, aralkoxycarbonyloxy or N-
imidazolyl group, e.g. a chlorine, bromine or iodine ~ -
.~
211~737
- 20 -
atom or a 4-nitro-phenoxy group, or, if R6 denotes an
alkyl or phenylalkyl group, then Z5 together with a
hydrogen atom of the adjacent methylene group of the
group R6, may also denota an oxygen atom);
h) (to prepare compounds of formula I wherein D
represents a sulphinyl or sulphonyl group)
oxidising a compound of fo~mula XIII
y Xl
~ ~X2
A--B~
3 :
(wherein :
A~ B~ X1, X2, X3, X4, Y1 and Y2 are as hereinbefore
defined, with the proviso that D denotes a sulphur atom ~ ~:
or a sulphinyl group);
i) (to prepare c3~pounds of formula I, wXerein one of :~
the groups X1, X2, X3, and X4 denotes an F-E-D-N< group -
(wherein D denotes a straight-chain or branched C16~
alkyl group or a C26-alkenyl group)~ ~:
reacting a compound of formula XIV -
/~ ~~/ ~X2
A--~< ll .1 (XIV)
~ /~ ~X3
(wherein :~
A, B, Y1, Y2, X1, X2, X3 and X4 are as hereinbefore defined :~
with the proviso that on~ of the groups Xl, X2, X3 and X4
` 21i~737
- 21 -
denotes an H-N< group) with a compound of formula XV
Z6 ~ D' - E - F (XV)
(wherein
E and F are as hereinbefore defined, D' denotes a
straight-chain or branched C16-alkyl group or a Cz6-
alkenyl group, and Z6 denotes a leaving group, e.g. a
chlorine, bromine or iodine atom, or a hydroxy, methoxy,
ethoxy or benzyloxy group, or, if D' contains a carbon-
carbon double bond bound directly to group F, Z6 may also
denote a hydrogen atom).
j) (to prepare compounds of formula I, wherein D denotes
a C26-alkylene group)
hydrogenating a compound of formula XVI ~ -
(wherein ::-
A~ B~ Y1~ Y2~ X1~ X2~ X3, and X4 are as hereinbefore
defined, with the proviso that D denotes a C26-
alkenylene group);
k~ (to prepare compound of formula I, wherein A denotes ~ ~
an amidino group substituted by a hydroxyl group) ~:
reacting a compound of formula XVII
-
-`` 211573r~
- 22 -
~c ~
~X3
Y2 X~
~wherein
B, Y1, Y2 and X1, X2, X3, X4 are as hereinbefore defined),
with hydroxylamine or a salt thereof in the presence of ::
a base;
to prepare compounds of formula I, wherein at least ~
one of the group X1, X2, X3, and X4 represents a methine -~:
group)
dehalogenating a compound of formula XVIII ~:~
A ~ ~ ~ ~
~X3 ~ ~:
wherein
A~ B~ Y1, Y2, X1, X2, X3, and X4 are as hereinbefore
defined, with the proviso that at least one of the
groups~X1, X2, X3, and X4 denotes a methine group
substituted by a chlorine, bromine or iodine atom);
(m) ~to prepare a compound of formula I wherein at ~-~
least one of the groups X1, X2, X3, and X4 denotes a ~ -
methine group substituted by a chlorine, bromine or
iodine atom~;
halogenating a compound of formula I wherein at least
one of the groups X1, X2, X3, and X4 denotes a carbonyl
`.! ' '~ ` , ., ' ~. . ,'. ' ' `, ' ' ~
~ ' 21~5737
- 23 -
group;
(n~ performing the process of any one of steps (a) to
(m) on a reagent having a protecting group and
subsequently removing the protecting group used;
(o) converting a compound of formula I into a salt
thereof; and
(p) resolving a compound of formula I into its isomers.
The hydrolysis of step (a) is appropriately carried out
either in the presence of an acid such as hydrochloric
acid, hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid,
acetic acid, acetic acid/hydrochloric acid,
trichloroacetic acid or trifluoroacetic acid or in the
presence of a base such as lithium hydroxide, sodium -
hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, in a suitable solvent
such as water, methanol, water/methanol, ethanol,
water/ethanol, water/isopropanol, water/tetrahydrofuran
or water/dioxane, at temperatures between -10 and
120C, e.g. at t~mperatures between ambient temperature
and the boiling temperature of the reaction mixture.
During acid hydrolysis, depending on the conditions ~ --
used, other hydrolytically cleavable groups which may be
present in a compound of formula II, such as acetyl,
trifluoroacetyl, benzoyl, tert.~utyloxycarbonyl or
benzyloxycarbonyl groups, may be simultaneously cleaved.
If F denotes, for example, a tert.butyloxycarbonyl
group, the tert.butyl group may also be cleaved by
treating with an acid such as trifluoroacetic acid,
hydrochloric acid, formic acid, p-toluenesulphonic acid,
sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid or polyphosphoric acid,
optionally in an inert solvent such as methylene
chloride, chloroform, benzene, toluene, tetrahydrofuran
- 24 -
or dioxane, preferably at temperatures between -10C and
120C, e.g. at temperatures between 0 and 60C, or
cleaved thermally, optionally in an inert solvent such
as methylene chloride, chloroform, benzene, toluene,
tetrahydrofuran or dioxane and optionally in the
presence of a catalytic amount of an acid such as p-
toluenesulphonic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid
or polyphosphoric acid, preferably at the boiling
temperature of the solvent used, e.g. at temperatures
between 40C and 100C.
If F denotes, for example, a benzyloxycarbonyl group,
the benzyl group may also be hydrogenolytically cleaved
in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst such as
palladium/charcoal, in a suitable solvent such as
methanol, ethanol, ethanol/water, glacial acetic acid,
ethyl acetate, dioxane or dimethylformamide, preferably
at temperatures between 0 and 50C, e.g. at ambient
temperature, under a hydrogen pressure of l to 10 bar.
During hydrogenolysis, other groups may also be
simultaneously reduced, e.g. a nitro group may be -
reduced to an amino group, or a benzyloxy group to a
hydroxy group, or a benzylamino or ~ -
benzyloxycarbonylamino group into an amidino group. - -~
Furthermore, C=C double bonds may simultaneously be
hydrogenated form single bonds.
. - '
The hydrolysis of step (b) is appropriately carried out
either in the presence of an acid such as hydrochloric
acid, hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid,
acetic acid, acetic acid/hydrochloric acid,
trichloroacetic acid or trifluoroacetic acid, or in the ~-
presence of a base such as lithium hydroxide, sodium
hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, in a suitable solvent
such as water, methanol, water/methanol, ethanol,
water/ethanol, water/isopropanol, water/tetrahydrofuran,
ether/dioxane or water/dioxane at temperatures between
-'~ 211~737
- 25 -
-10 and 120~, e.g. at temperatures batween ambient
temperature and the boiling temperature of the reaction
mixture.
During the acid hydrolysis, depending on the conditions
used, other hydrolytically cleavable groups which may be
present in a compound of formula III, such as
alkoxycarbonyl or phenylalkoxycarbonyl groups, may be
cleaved simultaneously. -
If, for example, Ra denotes a tert.butyloxycarbonyl
group, the tert.butyloxycarbonyl group may also be
cleaved by treating with an acid such as trifluoroacetic
acid, hydrochloric acid, formic acid, p-toluenesulphonic
acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid or polyphosphoric
acid, optionally in an inert solvent such as methanol,
methylene chloride, chloroform, benzene, toluene,
tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, ether/dioxane or --
ether/dioxane/methanol, preferably at temperatures
between -10C and 120C, e.g. at temperatures between 0
and 60C, or cleaved thermally, optionally in an inert
solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, benzene, -
toluene; tetrahydrofuran or dioxane and optionally in
the presence of a catalytic amount of an acid such as p-
toluenesulphonic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid
or polyphosphoric acid~ preferably at the boiling
temperature of the solvent used, e.g. at temperatures
between 40C and 100C.
If, for example, Ra denotes a benzyl or benzyloxycarbonyl
group, the benzyl or benzyloxycarbonyl group may be
cleaved hydrogenolytically in the presence of a
hydrogenation catalyst such as palladium/charcoal, in a
suitable solvent such as methanol, ethanol,
ethanoljwater, glacial acetic acid, ethyl acetate,
dioxane or dimethylformamide, preferably at temperatures
between 0 and 50C, e.g. at ambient temperature, under a
2~ 73~
- 26 -
hydrogen pressure of 1 to 10 bar. During
hydrogenolysis, other groups may also be simultaneously
reduced, e.g. a nitro group may be reduced to an amino
group or a benzyloxy group to a hydroxy group or a
benzylamino group to an amino group. Moreover, any C=C
double bonds present may simultaneously be hydrogenated
to form single bonds.
The cyclisation of step (c) is optionally carried out in
a solvent or mixture of solvents such as methanol,
ethanol, isopropanol, glacial acetic acid, benzene,
chlorobenzene, toluene, xylene, glycol, glycol
monomethylether, diethyleneglycol dimethylether,
sulpholane, dimethylformamide, diphenylether or
tetralin, or in an excess of the acylating agent used to
prepare the compound of formula IV, e.g. in the
corresponding acid or the corresponding nitrile,
anhydride, acid halide, ester or amide, e.g. at
temperatures between 0 and 250C, but preferably at
temperatures between 100 and 250C, but particularly
advantageously at the boiling temperature of the ~
reaction mixture,~`optionally in the presence of a ~ -
condensing agent such as phosphorus oxychloride,
thionylchloride, sulphurylchloride, sulphuric acid, p-
toluenesulphonic acid, methanesulphonic acid,
hydrochloric acid, phosphoric acid, polyphosphoric acid,
acetic anhydride or optionally in the presence of a base
such as sodium hydroxide, potassium ethoxide or
potassium tert.butoxide. However, the cyclisation may
also be carried out without a solvent and/or condensing
agent.
However, it is particularly advantageous to carry out
the reaction by preparing a compound of formula IV in
situ by acylating a corresponding diamino compound or by
reducing a corresponding o-nitro-acylamino compound.
When the reduction of the nitro group is ceased at the
`- 211573~/
hydroxylamine stage, subsequent cyclisation produces the
N-oxide of a compound of formula I. The N-oxide thus
obtained can subsequently be converted by reduction into
a corresponding compound of formula I.
The subsequent reduction of the resulting N-oxide of
formula I is preferably carried out in a solvent such as
water, wat~r/ethanol, methanol, glacial acetic acid,
ethyl acetate or dimethylformamide, with hydrogen in the
pr~sence of a hydrogenation catalyst such as Raney
nickel, platinum or palladium/charcoal, with metals such
as iron, tin or zinc, in the presence of an acid such as
acetic acid, hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid, with
salts such as iron(II)sulphate, tin(II)chloride or ~-~
sodium dithionite, with derivatives of trivalent
phosphorus such as triphenylphosphine, triethylphosphite -
or phosphorus trichloride, or with hydrazine in the
presence of Raney nickel at a temperature between 0 and
50C, but preferably at ambient temperature.
The optional subsequent cleaving of any protecting group
used is preferab~ carried out by hydrolysis in an
aqueous solvent, e.g. in water, isopropanol/water,
tetrahydrofuran/water or dioxane/water, in the presence
~of an acid such as trifluoroacetic acid, hydrochloric
acid or sulphuric acid, or in the presence of an alkali
metal base such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide
or potassium hydroxide, or by ether cleaving, e.g. in
the presence of iodotrimethylsilane, at temperatures
between 0 and 100C, preferably at temperatures between
10 and 50C.
The reaction of step (d) is conveniently carried out in
a solvent such as methanol/water, ethanol/water,
isopropanol/water or water, optionally in the presence
of a base such as sodium hydrogen carbonate, at
temperatures between 80 and loaoc~ but preferably at the
211~737
- 28 -
boiling temperature o~ the solvent used.
The optional subsequent cleaving of any protecting group
used is preferably carried out hydrolytically in an
aqueous solvent, e.g. in water, isopropanol/water,
tetrahydrofuran/water or dioxane/water, in the presence
of an acid such as trifluoroacetic acid, hydrochloric
acid or sulphuric acid, or in the presence of an alkali
metal base such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide
or potassium hydroxide, or by ether cleaving, e.g. in
the presence of iodotrimethylsilane, at temperatures -~-
between 0 and 100C, preferably at temperatures between
10 and 50C.
The reaction of step (e) is expediently carried out in a
suitable solvent, e.g. in a corresponding alcohol such
as methanol, ethanol or isopropanol, methylene chloride,
tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, pyridine, toluene or
dimethylsulphoxide in the presence of an acid activating
and/or dehydrating agent such as hydrogen chloride,
conc. sulphuric acid, thionylchloride,
ethylchloroforma~e, carbonyldiimidazole or N,N'-
dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide or the isourea esters thereof,
optionally in the presence of a reaction accelerator
such as copper chloride, or by transesterification, e.g
with a corresponding carbonic acid diester, or by
reacting with a corresponding halide, preferably in the
presence of a base such as potassium carbonate, and
optionally in the presence of a reaction accelerator
such as potassium iodide at temperatures between 0 and
100C, but preferably at temperatures between 20C and
the boiling temperature of the chosen solvent. ;
If Z3 denotes a nucleophilic leaving group, the reaction
is preferably carried out with an alkali metal salt of a
compound of formula VII.
':
~" 2 ~ 7 3 7
29
The reaction of step (f) is expediently carried out in a
solvent such as methanol, ethanol, n-propanol, water,
methanol/water, tetrahydrofuran or dioxane, at
temperatures between 0 and 150C, pre~erably at
temperatures between 20 and 120C, with a corresponding
free amine or with a corresponding acid addition salt
such as, for example, ammonium carbonate or ammonium
acetate.
A compound of formula IX may be obtained, for example,
by reacting a corresponding -nitrile with a suitable
alcohol such as methanol, ethanol, n-propanol,
isopropanol or benzyl alcohol, in the presence of an
acid such as hydrochloric acid or in the presence of a
corresponding alkoxide such as sodium methoxide or
ethoxide, or by reacting a corresponding amide with a
trialkyloxonium salt such as triethyloxonium-
tetra~luoroborate, in a solvent such as methylene
chloride, tetrahydrofuran or dioxane, at temperatures
between -10 and 50C, but preferably between 0 and 20C,
or a corresponding nitrile with hydrogen sulphide,
appropriately in$~ solvent such as pyridine or
dimethylformamide and in the presence of a base such as
triethylamine and subsequent alkylation of the resulting
thioamide with a corresponding alkyl or aralkyl halide.
The acylation of step (g) is appropriately carried out
in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, methylene
chloride, chloroform, dimethylformamide, water or
mixtures of these solvents, optionally in the presence
of a base such as sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate
or sodium hydroxide solution or in the presence of a
tertiary organic base such as triethylamine, N-ethyl-
diisopropylamine, N-methyl-morpholine, pyridine or 4-
dimethylamino-pyridine, which may simultaneously serve
as solvent, at temperatures between -30 and 100C, but
preferably at temperatures between -10 and 60C.
211~737
- 30 -
The alkylation with a compound of formula XII wherein Z5
denotes a nucleophilic leaving group, is conveniently
carried ou~ in a solven~ such as methylene chloride,
tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, dimethylsulphoxide or
dimethylformamide, optionally in the presence of a base
such as sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate or sodium
hydroxide solution or in the presence of a tertiary
organic base such as N-ethyl-diisopropylamine or N-
methyl-morpholine, which may simultaneously serve as
solvent, at temperatures between -30 and 100C, but
preferably at temparatures between -lO and 80OC.
The reductive alkylation with a carbonyl compound of
formula XII is carried out in the presence of a complex
metal hydride such as sodium borohydride, lithium
borohydride or sodium cyanoborohydride, expediently at a
pH from 6-7 and at ambient temperature, or in the
presence of a hydrogenation catalyst, e.g. with hydrogen
in the presence of palladium/charcoal under a hydrogen
pressure of l to 5 bar. However, the methylation is
preferably carried out in the presence of formic acid as
reducing agent a~elevated temperaturas, e.g. at
temperatures between 60 and 120C. ~ -
The oxidation of step (h) is preferably carried out in a
solvent or mixture o~ solvents, e.g. in water,
water/pyridine, acetone, methylene chloride, glacial
acetic acid, glacial acetic acid/acetic anhydride,
dilute sulphuric acid or trifluoroacetic acid,
conveniently at temperatures between -80 and 100C,
depending on the oxidising agent used.
To prepare a corresponding S-oxide compound of general
formula I, the oxidation is expediently carried out with
one equivalent of the oxidising agent, e.g. with
hydrogen peroxide in glacial acetic acid,
trifluoroacetic acid or formic acid at 0 to 20C or in
211~737
- 31 -
acetone at o to 600C, with a peracid such as performic
I acid in glacial acetic acid or trifluoroacetic acid at o
to 500C or with m-chloroperbenzoic acid in methylene
chloride or chloroform at -20 to 60C, with sodium
metaperiodate in aqueous methanol or ethanol at -15 to
25C, with bromine in glacial acetic acid or aqueous
acetic acid, optionally in the presence of a weak base
such as sodium acetate, with N-bromo-succinimide in
ethanol, with tert.butyl-hypochlorite in methanol at -80
to -30C, with iodobenzodichloride in aqueous pyridine
at 0 to 50C, with nitric acid in glacial acetic acid at
0 to 20C, with chromic acid in glacial acetic acid or
in acetone at 0 to 20C or with sulphurylchloride in
methylene chloride at -70C and the resulting thioether-
chlorine-complex is expediently hydrolysed with aqueous
ethanol.
To prepare an S,S-dioxide compound of formula I, the
oxidation is carried out, starting from a corresponding
alkylsulphinyl compound, expediently with one or more
equivalents of the oxidising agent, or starting from a
corresponding al~lsulphenyl compound expêdiently with
two or more equivalents of the oxidising agent, e.g.
with hydrogen peroxide in glacial acetic acid/acetic
anhydride, trifluoroacetic acid or in formic acid at 20
to 100C or in acetone at 0 to 60C, with a peracid such
as performic acid or m-chloroperbenzoic acid in glacial
acetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid, methylene chloride or
chloroform at temperatures between 0 and 60C, with
nitric acid in glacial acetic acid at 0 to 20C, or with
chromic acid or potassium permanganate in glacial acetic
acid, water/sulphuric acid or in acetone at 0 to 20C.
The reaction of step (i) is preferably carried out in a
suitable solvent, e.g. in a corresponding alcohol such
as methanol, ethanol or isopropanol, in methylene
chloride, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, pyridine, toluene or
, ' 211~737
- 32 -
dimethylsulphoxide, optionally in the presence of a base
such as potassium carbonate or sodium hydride, and
optionally in the presence of a reaction accelerator
such as potassium iodide at temperatures between 0 and
100C, but pxeferably at temperatures betweeen 20C and
the boiling temperature of the solvent in question.
If Z6 denotes a hydroxy group, the reaction is preferably
carried out in the presence of an activating agent such
as triphenylphosphine/diethyl azodicarboxylate.
The catalytic hydrogenation is of step (j) is
conveniently carried out in the presence of a
hydrogenation catalyst such as palladium/charcoal, in a
suitable solvent such as methanol, ethanol,
ethanol/water, glacial acetic acid, ethyl acetate,
dioxane or dimethylformamide at temperatures between 0
and 50C, e.g. at ambient temperature, under a hydrogen
pressure o~ 1 to 10 bar. During catalytic
hydrogenation, other groups may be reduced
simultaneously, e.g. a nitro group may be reduced to an
amino group, a b~nzyloxy group to a hydroxy group, or a 1
benzylamino or benzyloxycarbonylamino group to an amino
group. Moreover, other C=C double bonds may
simultaneously be hydrogenated into single bonds.
Th~ reaction of step (k) is preferably carried out in a
solvent such as methanol, water/methanol, ethanol,
ethanol/water or tetrahydrofuran/water, optionally in
the presence of a base such as sodium carbonate,
potassium carbonate or N,N-diisopropylethylamine, at
t~mperatures between 20 and 100C, but preferably at the
boiling temperature of the solvent used. ;~-
. . .: .
The dehalogenation of step (1) is conveniently carried
out in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst such as
I palladium/charcoal in a suitable solvent such as
~` 2:115737
- 33 -
methanol, ethanol, ethanol/water, glacial acetic acid,
ethyl acetate, dioxane or dimethylformamide, pre~erably
at temperatures between 0 and 50C, e.g. at ambient
temperature, under a hydrogen pressure of 1 to 10 bar.
Duxing catalytic hydrogenation, other groups may be
simultaneously reduced, e.g. a nitro group may be
reduced to an amino group, or a benzyloxy group to a
hydroxy group, or a benzylamino or
benzyloxycarbonylamino group to an amino group.
Moreover, other C=C double bonds may simultaneously be
hydrogenated into single bonds.
The halogenation of step (m) is preferably carried out
with a halogenating agent such as phosphorus
oxychloride, phosphorus oxybromide or phosphorus
pentachloride, in an inert solvent such as toluene, but
preferably the solvent used is an excess of the chosen
halogenating agent, such as phosphorus oxychloride, at
elevated tempteratures, e.g. at temperatures between 80
and 120C.
In the reactions~described hereinbe~ore, âny reactive
groups present, such as hydroxy, carboxy, phosphono,
amino, alkylamino or imino groups, may be protected
during the reaction by means of conventional protecting
groups which are cleavsd again after the reaction.
For example, the hydroxy group protecting group may be a
trimethylsilyl, acetyl, benzoyl, tert.butyl, trityl,
benzyl or tetrahydropyranyl group,
the carboxyl group protecting group may be a
trimethylsilyl, methyl, ethyl, tert.butyl, benzyl or
tetrahydropyranyl group, the phosphono group protecting
group may be a trimethylsilyl, methyl, ethyl or benzyl
group,
and the amino, alkylamino or imino group protecting
group may be an acetyl, trifluoroacetyl, benzoyl,
` ~ 7 3 7
ethoxycarbonyl, tert.-butoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl,
benzyl, methoxybenzyl or 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl group,
and for the amino group a phthalyl group may also be
considered.
The optional subsequent cleaving of a protecting group
may, for example, be carried out hydrolytically in an
aqueous solvent, e.g. in water, isopropanol/water,
tetrahydrofuran/water or dioxane/water, in the presence
of an acid such as trifluoroacetic acid, hydrochloric
acid, hydrobromic acid or sulphuric acid, or in ~he
presence of an alkali metal base such as lithium
hydroxide, sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, or
by ether cleaving, e.g. in the presence of
iodotrimethylsilane, at temperatures between 0 and -~
100C, preferably at temperatures between 10 and 50C.
However, a benzyl, methoxybenzyl or benzyloxycarbonyl
group may for example be cleaved hydrogenolytically, eg. ~ -
using hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst such as
palladium/charcoal in a solvent such as methanol,
ethanol, ethyl a~etate or glacial acetic acid,
optionally with the addition of an acid such as -~
hydrochloric acid at temperatures between 0 and 50~
but preferably at ambient temperature, under a hydrogen
pressure of 1 to 7 bar, preferably 3 to 5 bar.
~ ' ' ,:,
A methoxybenzyl group may also be cleaved in the-
presence of an oxidising agent such as cerium(IV)~
ammonium nitrate in a solvent such as methylene
chloride, acetonitrile or acetonitrile/water at
temperatures between 0 and 50C, but preferably at -~
ambient temperature.
The cleaving o~ only one alkyl group from an O,0'- -
dialkylphosphono group is carried out, for example, with
sodium iodide in a solvent such as acetone,
``` 2115737
- 35 -
ethylmethylketone, acetonitrile or dimethylformamide at
tamperatures between 40 and 150C, but preferably at
temperatures between 60 and 100C.
The cleaving of both alkyl groups from an 0,0'-
dialkylphosphono group is preferably carried out with
iodotrimethylsilane, bromotrimethylsilane or
chlorotrimethylsilane/sodium iodide in a solvent such as
methylene chloride, chloroform or acetonitrile at
temperatures between 0C and the boiling temperature of
the reaction mixture, but preferably at temperatures
between 20 and 60~. :
A tert.butyl or tert.butyloxycarbonyl group is
preferably cleaved by treating with an acid such as
trifluoroacetic acid or hydrochloric acid, optionally
using a solvent such as methylene chloride, diGxane or
ether. :
The cleaving of a phthalyl group is preferably carried
out in the presence of hydrazine or a primary amine such
as methylamine, ~hylamine or n-butylamin~e in a solvent
such as methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, toluene/water or
dioxane, at temperatures between 20 and 500C. ~:
Furthermore, the compounds of formula I obtained may be
resolved into their enantiomers and/or diastereomers as
mentioned hereinbefore. Thus, ~or example, cis/trans
mixtures may be resolved into their cis and trans :
isomers, and compounds having at least one optically
active carbon atom may be resolved into their
enantiomers. : :
Thus, for example, the cis/trans mixtures obtained may -
be resolved by chromatography into the cis and trans
isomers thereof and the compounds of formula I which
occur in racemate form may be separated by methods known
``~ 2115737
- 36 -
per se (cf. Allinger N. L. and Eliel E. L. in "Topics in
Stereochemistry", Vol. 6, Wiley Interscience, 1971) into
their optical antipodes and compounds of formula I
having at least 2 asymmetric carbon atoms may be
separated on the basis o* their physical-chemical
di~ferences usiny known methods, e.g. by chromatography
and/or fractional crystallisation, into the
diastereomers thereof which, if they occur in racemic
form, may subsequently be separated into the enantiomers
as mentioned above.
The separation of enantiomers is preferably effected by
column separation on chiral phases or by -
recrystallisation from an optically active solvent or by
reacting with an optically active substance (especially
an acid and an activated derivative thereof or an
alcohol) which forms salts or derivatives such as esters
or amides with the racemic compound, and separation of
the diastereomeric salt mixture or derivative thus
obtained, e.g. on the basis of their different
solubilities, whilst the free antipodes may be released
from the pure di~stereomeric salts by thê action of
suitable agents. Particularly common, optically active
acids include, for example, the D- and L-forms of -
tartaric acid and dibenzoyltartaric acid, di-o-tolyl
tartaric acid, malic acid, mandelic acid,
camphorsulphonic acid, glutamic acid, aspartic acid or
quinic acid. Examples of optically active alcohols
include for example (~)- or (-)-menthol and examples of
optically active acyl groups in amides include for
example (~)- or (-)-menthyloxycarbonyl.
Moreover, the compounds of formula I obtained may be
converted into the salts thereof, particularly for
pharmaceutical use into-the physiologically acceptable
salts thereof, with inorganic or organic acids.
Examples of suitable acids include hydrochloric acid,
` 21~737
hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid,
acPtic acid, fumaric acid, succinic acid, lactic acid,
citric acid, tartaric acid or maleic acid.
In addition, the new compounds of formula I thus
obtained, if they contain a carboxyl group, may
subsequently, i~ desired, be converted into the addition
salts thereof with inorganic or organic bases, more
particularly, for pharmaceutical use, into the
physiologically acceptable addition salts thereof.
Examples of suitable bases include sodium hydroxide,
potassium hydroxide, ammonia, cyclohexylamine,
ethanolamine, diethanolamine and triethanolamine.
The starting compounds used in the processes of the
invention are-known or may be obtained by conventional
methods (see Examples I to XV~.
As already mentioned, the compounds of the invention
have valuable properties. Thus, the compounds of formula -~
I wherein A denotes an amidino or guanidino group
optionally subst~-~uted at one of the nitrogen atoms by
an alkyl group or by a group which can be cleaved in ~;
vivo, or A denotes a piperidinyl group optionally
substituted in the carbon skeleton by one or two alkyl
groups and at the nitrogen by a group Ra which can
optionally be cleaved in vivo and in which a >CH- unit
in the 4-position may additionally be replaced by a
nitrogen atom, and F denotes a carboxy, sulpho,
phosphono, O-alkyl-phosphono or 5-tetrazolyl group or a
group which may be converted in vivo into a carboxy,
sulpho, phosphono or O-alkyl-phosphono group, have
valuable pharmacological properties, and in addition to
having an inhibitory effect on bone degradation, they
have in particular antithrombotic, antiaggregatory and
tumoùr- or metastasis-inhibiting effects.
` "-` 2115737
- 38 -
The compounds of formula I wherein F denotes an 0,0-
dialkyl-phosphono group, are valuable intermediate
products for preparing the compounds of general formula
I.
Viewed from a further aspect the invention provides a
pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of
formula I or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof
together with at least one physiologically acceptable
carrier or excipient.
~ '
Viewed from a still further aspect the invention also
provides tbe use of a compound of formula I or a
physiologically acceptable salt thereof for the
manufacture of a medicament for use in combatting bone
degradation, tumours, metastases, thrombosis or
aggregation-related conditions.
Viewed from a yet still further aspect the invention
provides a method of treatment of the human or non- ~
human, preferably mammalian, body to combat bone - -
degradation, tumours, metastases, thrombosis or
aggregation-related conditions, said method comprising
administering to said body a compound of formula I or a
physiologically acceptable salt thereof.
By way of example, the biological activity of the
compounds according to the invention were investigated
as follows:
,
~ 211~737
- 39 -
1. Inhibition of binding of 3H-BIBU 52 to human
thrombocytes~
A suspension of human thrombocytes in plasma is
incubated with 3H-BIBU 52 [3H-BIBU 52, which is disclosed
in DE-A-4214245, is (3S,5S)-5-[(4'-amidino-4-
biphenylyl)oxymethyl]-3-t(carboxyl)methyl]-2-
pyrrolidinone[3-3H-4-biphenylyl] and is used in place of
the conventional l25I fibrinogen ligand] and various
concentrations of the test substance. The free and
bound ligand are separated by centrifuging and
quantitatively determined by scintillation counting.
The inhibition of 3H~BIBU 52 binding by the test
substance is determined from the measurements obtained.
In order to do this, donor blood is taken from an
anticubital vein and anticoagulated with trisodium
citrate (final concentration 13 mM). The blood is
centrifugad for 10 minutes at 170 x g and the
supernatant platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is removed. The
remaining blood is vigorously centrifuged once more in
order to obtain ~asma. The P~P is diluted 1:10 with
autologous plasma. 750 ml are incubated with 50 ml of
physiological saline solution, 100 ml of test substance
solution, 50 ml of 14C-sucrose (3700 Bq) and 50 ml of
3H-BIBU 52 (final concentration: 5 nM) at ambient
temperature for 20 minutes. -In order to measure the
non-specific binding, 5 ml of BIBU 52 (final
concentration: 30 mM) arP used instead of the test --
substance. The samples are centrifuged for 20 seconds
at 10,000 x g and the supernatant is poured off. 100 ml
thereof are measured in order to determine the free
ligand. The pellet is dissolved in 500 ml of 0.2N NaOH,
450 ml are mixed with 2 ml of scintillator and 25 ml of
5N ~Cl and measured. The residual plasma remaining in
the pellet is determined from the l4C-content and the
bound ligand is determined from the 3H-measurement.
2115737
-- ~o --
After ths non-specific binding has been deducted, the
pellet activity is plotted against the concentration of
the test substance and the concentration for a 50%
inhibition of binding is determined.
2. Antithrombotic activity
Method
Thrombocyte aggregation is measured using the Born and
Cross method (J. Physiol. 170: 397 (1964)) in platelet~
rich plasma taken from healthy volunteers. To inhibit ~-
coagulation the blood is mixed with 3.14% sodium citrate
in a volume ratio of 1:10.
. ':
Collaqen-induced aqgreqation
The pattern of the decrease in optical density of the
platelet suspension is photometrically measured and
recorded after the addition of the aggregation-
triggering substance. The rate of aggregation is
determined from ~e angle of inclination of the density
curve. The point on the curve where there is maximum
light transmittance is used to calculate the optical
density.
The quantity of collagen used is as small as possible
but sufficient to produce an irreversible reaction
curve. Standard commercial collagen produced by
Hormonchemie of Munich is used.
Before the addition of the collagen the plasma is
incubated with the test substance for 10 minutes at
37~C.
From the measurements obtained an ECso is determined as
the concentration giving a 50% change in the optical
r~.FE3-l994 15: 0E3 FRRNI~ DEHI`I ~ CO 2 1 :L 5 7 3 7 ~71 z4a 1~776 p~ æ
. ~ denE~ity in ter~3 of thet inhibition c)f aygregation.
Th~ ~ollowing Ta:~lea shows t2~e r~sults wnich w~re
obt~in~d:
¦ 'r~8~ Sub~anç~rino~n bind~gInhibi~ion of
(EX~ No. l t~ latelet
t~aggr~g~tic,~,
ECso [ nM]
I ~
j 1 1~0 430 ~
! ~ oo ~loo~o
2 200 200~
1 tl5~ 4g0 12S0
l .1~48~ 2ao 2~0
:1 1(~,~3 270 lS0
! 1~61) lS0 110
(S3 ? 9~00 4400
~ 4) 50~00 300~0
!1 1(67) lloo 2300
Il 6~12) 24000 6~00
7(12) 1300 ~60
. ~ ''.,.
The co~p~und~ acGordl~n~ to the i~v~ntion are well
tolorated be~u~e a~te~r int~aY~anous ~d~ini st~:ation of
30 mgfkg o~ tha ao~pound o~ Example 1 t~ 3 ~ica in each
ca~e, rao ani~als di~d.
~n tha li~ht o~ ~heir inhibitory effect on call-cell or
cel~ atr~x interactions, the n~ condens~d f~e-
me~ber~d he'cerocycl~c cc~mpolmds Or ~ormula I and tl~Q
phys~o1Ogic~11y a~epta~ ~ addition isalts ~her~oE ar~
suitable for oo~bating or pre~enting dis~lBes in w~i~h ::
slDalle~ or gre~r cell aggregates ~ :
T'-TRL P . E12 `
.::
2 1 1 ~ 7 3 7
- ~2 -
occur or in which cell-matrix interactions play a part,
e.g. in treating or preventing venous and arterial
thrombosis, cerebrovascular diseases, lung embolism,
cardiac infarction, arteriosclerosis, osteoporosis and
the metastasis of tumours and the treatment of
genetically caused or ac~uired disorders of cell ~:
interactions with one another or with solid structures.
They are also suitable for parallel therapy in
thrombolysis with fibrinolytics or vascular
interventions such as transluminal angioplasty or in the
treatment of shock, psoriasis, diabetes and
inflammatian.
For treating or preventing the diseases mentioned above
the dosage is generally between O.1 mg and 30 mg/kg of
body weight, preferably l mg to 15 mg/kg of body weight,
given in up to 4 doses per day. For this purpose the
compounds according to the invention, optionally in
conjunction with other active substances such as
thromboxane receptor antagonists and thromboxane
synthesis inhibitors or combinations thereof, serotonin
antagonists, ~-r~eptor antagonists, alkylnitrates such
as glycerol trinitrate, phospho-diesterase inhibitors,
prostacyclin and the analogues thereof, fibrinolytics
such as tPA, prourokinase, urokinase, streptokinase, or
anticoagulants such as heparin, dermatan sulphate,
activated protein C, vitamin K antagonists, hirudine,
inhibitors of thrombin or other activated clotting
factors, may be incorporated together with one or more
inert conventional carriers and/or diluents, e.g. corn
starch, lactose, sucrose, microcrystalline cellulose,
magnesium stearate, polyvinylpyrrolidone, citric acid,
tartaric acid, water, water/ethanol, water/glycerol,
water/sorbitol, water/polyethyleneglycol, :
propyleneglycol, stearylalcohol, carboxymethylcellulose
or fatty substances such as hard fat or suitable
mixtures thereof, into conventional galenic preparations
such as plain or coated tablets, capsules, powders,
: -
211~737
- 43 -
suspensions, solutions, sprays or suppositories.
The following Examples are provided to illustrate the
invention in a non-limiting fashion. Percentages and
ratios are by weight (unless otherwise indicated) except
eluant ratios which are by volume: ::
;~ . `` .
21~737
- 44 -
Example I
3-(1-Benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)~propionylchloride
.
3.09 g of 3-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4i-piperidinyl)-
propionic acid, 50 ml of methylene chloride and 2.08 g
of phosphorus pentachloride are combined and left to
stand for 6 hours at ambient temperature. The mixture
is evaporated down in vacuo and evaporated once more
with toluene. The residue remaining is used without
further purification.
Yield: 3.1 g (100 % of theory).
Example II
3-(1-Benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-propionic acid
-
24.5 g of 3-(4-piperidinyl)-propionic acid are dissolved
in 170 ml of lN sodium hydroxide solution, cooled to 0C
and, using a Vibro mixer, 175 ml of lN sodium hydroxide
solution and 25 ml of benzyloxycarbonylchloride, are
added separately, dropwise, over a period~ of 30 minutes.
The resulting mixture is left to react for a further 60
minutes at 0C and then left to stand for 16 hours at
ambient temperature. Tha mixture is washed with 125 ml
of a 4:1 mixture of ether/petroleum ether, the aqueous
phase is acidified with 4N hydrochloric acid and
extracted with ether. The ether extracts are evaporated
down in vacuo. The oily residue is used further
directly.
Yield: 50 g (100 % of theory),
Rf value: 0.65 (silica gel; methylene chloride/
methanol/glacial acetic acid = 5.1:0.1)
The following compound is obtained analogously:
(1) trans-4-(Benzyloxycarbonylamino-methyl)-cyclohexane-
carboxylic acid
Melting point: 109-110C
2 1 1 ~ 7 3 7
Exam~le III
5-[(2-Methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-
trichloromethyl-benzimidaæole
,
lO g of 3-amino-4-methylamino-benzoic acid-[N-(2-
methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-amide] are dissolved in 35 ml of
glacial acetic acid and within 20 minutes a solution of
7.05 g of methyl trichloroacetimidate in 5 ml of glacial
acetic acid is added dropwise thereto. The mixture is
stirred for a further 16 hours at ambient temperature,
the glacial acetic acid is distilled o~f in vacuo and
the residue is used without further purification.
Yieldo 15 g (100 % of theory),
Rf value: 0.71 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 7:3)
Example IV
Isopropyl 5-(3-amino-4-methylamino-phenyl)-5-oxo-
valeriate
2.4 g of isopropyl 5-(4-methylamino-3-nitro-phenyl)-5-
oxo-valeriate are hydrogenated for 48 hours in 80 ml of
isopropanol in the presence of 0.1 g of 10%
palladium/charcoal (a further 0.1 g being added after 14
hours) using hydrogen at 4 bars at ambient temperature.
The catalyst is filtered off, the filtrate is evaporated
down in vacuo and the residue is purified over silica -~-
gel (eluant: ethyl acetate/petroleum ether = 8:2). -
Yield: 1.0 g (46 % of theory),
Rf value: 0.67 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 9:1)
: ::
Example V
~ ':
4-Amino-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-lH,3H-
pyrimidin-2,6-dione
Prepared from 4-amino-3-methyl-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione
analogously to Example 11(4) using solid sodium
211 ~73~
- 46 -
hydroxide as base.
Melting point: 110-112C
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 5-(4-cyano-benzoylamino)-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-
3-(4-methoxy-benzyl)-4-methylamino-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-
dione
Dimethylformamide with potassium tert.butoxide is used.
Rf value: 0.52 (silica gel; methylene chloride/
methanol/conc. ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
(2) ~-(4-cyano-benzoylamino)-7-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-
3,4-dihydro-2H,7H-pyrimido[1,6-a]pyrimidin~6,8-dione
Rf value: 0.55 (silica gel; methylene chloride/
methanol/glacial acetic acid = l9:1~0.1)
Exam~le VI
8-(4-Cyanophenyl)-3,9-dimethyl-xanthine
. :
2.1 g of 5-amino~-methyl-6-methylamino-lX,3H-pyrimidin-
2,4-dione are suspended in 150 ml of tetrahydrofuran and
9.1 g of 4-dimethylamino-pyridine are added with
stirring and refluxing. After 15 minutes, 2.2 g of 4-
cyano-benzoylchloride are added and the mixture is
re~luxed for a further 2 hours with stirring. The
reaction mixture is avaporated down and the residue is
heated to 200 to 205C for 45 minutes. After cooling,
the product is triturated with 15 ml of methanol,
filtered and washed with methanol and ether and further --
used in this form. ~ -
Yield: 2.0 g (58 % of theory),
Rf value: 0.79 (silica gel; methylene choride~
methanol/glacial acetic acid = --
9:1:0.1, after developing twice)
he following compounds are obtained analogously:
-
211573'~
- 47 -
(1) 8-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-3,9-
dimethyl-xanthine
a) 5-[~2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
carbonylamino]-l-methyl-6-methylamino-uracil
The mixture is refluxed for 5 hours and the residue
remaining after evaporation of the tetrahydrofuran is
digested with ethyl acetate/ethanol (3:1j
Rf value: 0.79 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/conc.
ammonia = 7:3:0.1)
b) 8-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-3,9-
dimethyl-xanthine
Heated to 250C for lo minutes
Rf value: 0.62 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/glacial acetic acid = ~ -
8:2:0.~)
(2) 2-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
8,10-dioxo-5,6-dihydro-4H,9H-pyrimido[1,2,3-cd]purine
a) 9-[[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
carbonylamino3-3,4-dihydro-2H,7H-pyrimido[1,6-a]- -~;
pyrimidin-6,8-dione -
3-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-propionic acid and
carbonyldiimidazole in dimethylformamide are used.
Rfvalue: 0.73 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol
= 8:2) -~
b) 2-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-8,10-
dioxo-5,6-dihydro-4H,9H-pyrimido[1,2,3-cd]purine
Heated to 240c for 1.5 hours
Rf value: 0.52 (silica gel; methylene chloride~methanol
= 9:1)
(3) 8-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-9-
isopropyl-xanthine
211~737
- 48 -
a) 5-C[2-(1 benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
carbonylamino]-4-isopropylamino-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-
dione
Procedure analogous to (2a).
Rf value: 0.59 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/glacial acetic acid =
19:1:0.1, after developing three times)
b) 8-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl~-9-
isopropyl-xanthine
Batches of not more than 2.5 g are used and the mixture
is heated to 250-275C for a maximum of 10 minutes.
Rf value: 0.69 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/glacial acetic acid =
19;1:0.1, after developing three times)
(4) 8-(4-cyano-phenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-xanthine
a) 4-amino-5-CN-(4-cyanobenzoyl)-N-methyl-amino]-3~
methyl-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione -
The work is done in tetrahydrofuran and sodium hydroxide
solution at ambien~t temperature. The sta~ting material
4-amino-3-methyl-5-methylamino-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione
is obtained from 4-amino-5-bromo-3-methyl-lH,3H-
pyrimidin-2,6-dione. ~ -
Melting point: >275C
Rf value: 0.29 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/glacial acetic acid =
9:1:0.1)
b) 8-(4-cyano-phenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-xanthine ;-~
Heated to 250C for lO minutes in the presence of 4-
dimethylaminopyridine
Melting point: >300C
Rf value: 0.30 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/glacial acetic acid =
9 : 1 : O . 1 )
21~737
- 49 -
(5) 8-[2~ benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-3,7-
dimethyl-xanthine
a) 4-amino-5-[[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4 piperidinyl)-
ethyl]carbonylamino]-3-methyl-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione
The procedure is analogous to (2a) but using 0-(lH-1-
benzotriazolyl)N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium-
tetrafluoroborate in the presence of triethylamine.
Melting point: 223~224C (sintering from 220C)
Rf value: 0.34 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/glacial acetic acid =
15:1O0.1, after developing twice)
.
b) 8-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-3,7-
dimethyl-xanthine.
Heating to 275C for 10 minutes
Melting point: 200-203C (sintering from 198C) ~-
Rf value: 0.88 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/glacial acetic acid =
15:1:0.1, after developing twice)
.
(6) 8-t4-(1-benz ~ oxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-phenyl]- ~ -
3,9-dimethyl-xanthine
a) 5-[4-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-
benzoylamino]-3-methyl-4-methylamino-lH,3H-pyrimidin-
2,6-dione
The procedure is analogous to (5a). -
Melting point: 262-265C (Decomp.)
Rf value: 0.35 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/conc. ammonia =
9:1:0.1, after developing twice)
.
b) 8-[4-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl~-phenyl]-3,9-
dimethyl-xanthine.
Heated dry to 259C, diphenylether is added with
stirring and the mixture is kept for a total of 3 hours
at this temperature.
211573~
- 50 -
Melting point: 260-263C.
Rf Yalue: O ~ 50 ~silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/glacial acetic acid =
9 : 1 : O . 1 )
(7) 5-~4-cyano-benzoylamino)-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-4-
methylamino-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione
The procedure is analogous to (la).
Melting point: 245-250C (Decomp.)
Rf value: 0.40 ~silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/conc. ammonia = :
9:1:0.1)
(8) 9-(4-cyano-benzoylamino)-3,4-dihydro-2H,7H-pyrimido-
[1,6-a]pyrimidin-6,8-dione :
Procedure analogous to (la). ::
Melting point: >290C
Rf value: 0.32 (silica gel; methylene - :
: chloride~methanol/glacial acetic acid =
: 9:1:0.1)
(9) Methyl 3-[4~ -tert.butyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-
: benzoylamino]-4-methylamino-cinnamate
The procedure is analogous to (5a)
: ~ Rf valueo 0.64 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/petroleum ~ :
ether = 7:3)
:~ Example VII
, Isopropyl 5-(4-methylamino-3-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo- -~
valeriate
, .
a) 5-(4-Methylamino-3-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-valeric acid
13.6 g of 5-~4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl~-5-oxo-valeric acid :--
(prepared by nitrogenating 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-oxo-
valeric acid with fuming nitric acid at -5C) are heated
with 250 ml of 40% aqueous methylamine solution in a
211~737
- 51 -
pressurised vessel to 50C for 8 hours. The reaction
solution is evaporated down in vacuo, the precipitate is
taken up in water and acidified with hydrochloric acid.
The product precipitated is used without further
purification.
R~ value: 0.35 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 9:1)
b) Isopropyl 5-(4-methylamino-3-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-
valeriate `
The crude 5-(4-methylamino-3-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-
valeric acid obtained is heated with 300 ml of ~-`,
isopropanolic hydrochloric acid over a steam bath for 6
hours. The mixture is evaporated down in vacuo and the
residue is purified by chromatographing twice on silica ~;
gel ~eluant: first ethyl acetate/ethanol = 100:1, then
ethyl acetate/petroleum ether = 1:1).
Yield: 2.4 g (15 % of theory),
Rf value: 0.80 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 9
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
',:'~
(1) methyl 3-amino-4-methylamino-cinnamate
The same procedure is used as in b).
Rf value: 0.65 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/petroleum ether
= 7 3)
:~
(2) 4-methylamino-3-nitro-cinnamic acid
Prepared analogously to a3. The starting material is
obtained by heating 4-chloro-3-nitro-benzaldehyde in ~`
acetic anhydride in the presence of sodium acetate. -~
Rf value: 0.83 (methylene chloride/methanol = 50:1)
Example IX
9-Amino-3,4-dihydro-2H,7H-pyrimido[1,6-a]pyrimidin-6,8-
dione
3.4 g of 9-nitroso-3,4-dihydro-2H,7H-
2115737
- 52 -
pyrimido[l,6-a]pyrimidin-6,8-dione are treated with
5 bars of hydrogen in the presence of 2.S g of Raney
nickel at ambient temperature for 16 hours in 250 ml of
methanol. 25 ml of water are added, the mixture is
heated over a steam bath and filtered hot. The filtrate
is evaporated down and the rPsidue is further processed
in its crude form.
Yield: 3 g (95% of theory),
Rf value: 0.13 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 7:3)
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 5-amino-4-isopropylamino-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione
Rf value: 0.52 (silica gel; methylenechloride/methanol/
glacial acetic acid = 8:2:0.1) ~ ~
(2) 4,5-diamino-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl- -
lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione
Rf value: 0.84 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/conc. ammonia =
9:1:0.1, after developing twice) ~,
(3) 5-amino-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-4-methylamino-lH,3H-
pyrimidin-2,6-dione
Rf value: 0.50 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol/conc.
ammonia = 8:2:0.1)
Example X
. .
3-Nitroso-3,4-dihydro-2H,7H-pyrimido[1,6-a]pyrimidin-
6,8-dione
3.35 g of 3,4-dihydro-2H,7H-pyrimido[1,6-a]pyrimidin-
6,8-dione are dissolved in 65 ml of water over a steam
bath and, after the addition of 1.63 g of sodium
nitrite, 2.75 ml of glacial acetic acid are added
dropwise over 30 minutes. The mixture is stirred for 30
minutes, evaporated down to half the volume, cooled with
211~737
- 53 -
ice water and the precipitate is filtered off.
Yield: 3.5 y (90% o~ theory)
Rf value: 0.02 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 7:3)
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 4-isopropylamino-5-nitroso-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione
Melting point: 224-226C (Decomp.)
(2) 4-amino-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-5-
nitroso-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione.
The work is done at ambient temperature. -~
Melting point: 182-183~C (Decomp.)
(3) 3-(4-methoxy-benzyl)-4-methylamino-5-nitroso-lH,3H-
pyrimidin-2,6-dione.
Melting point: 167C (Decomp.)
Example XI
~ ~ .
3,4-Dihydro-2H,7H-pyrimido[1,6-a]pyrimidin-6,8-dione
16 g of 6-[(3-toluenesulphonyloxy-propyl)-amino]-lH,3H-
pyrimidin-4,6-dione (prepared from 6-chlorouracil and 3- -
aminopropanol and subsequent reaction with --
toluoenesulphonylchloride) are heated to 90 in 100 ml ~
~; of lN sodium hydroxide solution for 2 hours. The ~ -
mixture is buffered with ammonium chloride and the
precipitate formed is digested with ethyl acetate.
Yield: 3.5 g (45% of theory),
Rf vaIue: 0.89 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
Example XII
5-(4-Cyano-benzoylamino)-1-~4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-4-
methylamino-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione
3.3 g of 5-(4-cyano-benzoylamino)-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-
- ~,
211~737
- 54 -
butyl)-3-~4-methoxy-benzyl)-4-methylamino-lH,3H-
pyrimidin-2,6-dione are stirred in 30 ml of
trifluoroace~ic acid for 4 days under nitrogen at 65C.
The mixture is evaporated down, the residue is
triturated with water and the solid product obtained is
filtered off.
Yield: 1.62 g (63% of theory),
Melting point: above 200C
Rf value: 0.33 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol
= 9:1)
Example XIII
3-(4-Methoxy-benzyl)-4-methylamino-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6- ~-
dione
68 g of 4-chloro-3-(4-methoxy-benzyl)-lH,3H-pyrimidin-
2,6-dione are heated to 120C for one hour with 150 ml -
of 40% aqueous methylamine solution in a bomb. 500 ml
of water are added, the solid product is filtered off
and decocted with ethanol.
Yield: 17 g (22~f theory),
Rf value: 0.55 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 8:2) -
Example XIV
4-Chloro-3-(4-methoxy-benzyl)-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione
.
A mixture of 45.1 g of 6-chloro-uracil, 30.9 g of
potassium hydrogen`carbonate and 300 ml of
dimethylsulphoxide is heated to 80C for 2 hours.
41.9 g of 4-methoxy-benzylchloride are added and the
mixture is heated to 80C for a further 4 hours. The
solvent is evaporated off in vacuo, the residue is
poured onto 2000 ml of water and the solid product
obtained is filtered off.
Yield: 68 g (96% of theory),
Melting point: 270-274C
Rf value: 0.90 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 7:3)
21~737
- 55 -
Example XV
3-Amino-4-methylamino-cinnamic acid
-
11 g of 4-methylamino 3-nitro-cinnamic acid are placed
in 190 ml of boiling 5% sodium hydroxide solution and
sodium dithionite is added until the red colour has ~ ~
disappeared (a total of 31 g). The product crystallises~:
on cooling.
Yield: 6 g (63% of theory),
Rf value: 0.31 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 7:3)
Example 1 ~ ~:
5-[(2-Carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-[2-(4~
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide :
_. _
0.4 g of 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1- ~-
methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole are
stirred for 18 hours at ambient temperature with 2 ml of ~:
48% hydrobromic acid. The mixture is evaporated to :~:
dryness in vacuo and driad over solid sodium hydroxide
at 90C in vacuo. ~: :
Yield: 0.5 g (90 % of theory), ~ -
Rf value: 0.71 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%:~
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
The following compounds are obtained analogously: -
(1) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-m~thyl-2-[(4-
piperidinyl)-aminocarbonyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
Rf value: 0.72 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodlum chloride solution = 6:4)
(2) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocar~onyl]-1-methyl-2-[2- -:
(l-methyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-
dihydrobromide
. .
(3) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-[1- -
- ~
21i~737
- 56 -
(4-piperidinyl)-2-propyl]-benzimidazole dihydrobromide
(4) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-[2-
(4-piperidinyl)-propyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(5) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9- ::
cyclohexyl-3-methyl-xanthine-dihydrobromide
(6) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-[(4-
piperidinyl)-aminomethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
:~
(7) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-[N- .
mathyl-N-(4-piperidinylmethyl)-amino]-benzimidazole-
dihydrobromide
(8) 5-C(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-2-[[N-
methyl-N-(4-piperidinyl)-amino]-methyl~-benzimidazole-
trihydrobromide
(9) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-[(4-
piperidinyl)-methylthio]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(lO) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2 [4-
(4-piperidinyl)-butyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(11) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-[3-
(4-piperidinyl)-propyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(12) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl~-aminocarbonyl~-1-methyl-2-~2-
piperazino-ethyl)-benzimidazole-trihydrobromide
(13) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-[2-
(2-methyl-piperazino)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-
trihydrobromide
(14) 5-(4-carboxy-butyl)-l-methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-
ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
211~737
- 57 -
(15) 5-(4-carboxy-1-oxo-butyl)-l-methyl-2-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
Rf value: 0.66 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
~16) 5-[(2-carboxy-propyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-2-[2-
(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(17) 5-[(3-carboxy-propyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-[2-
(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(18) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)~aminocarbonyl]-1-cyclohexyl-2-
[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(19) 5~(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-6-
methylamino-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-
dihydrobromide
(20j 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-6-
dimethylamino-l-methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(21) 5-[(2-(carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-6-hydroxy-1-
methyl-2-~2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole- ::~
dihydrobromide
(22) 6-amino-5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl~-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-t2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-
dihydrobromide
(23) 5(6)-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-2-~2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(24) 6-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-[2-
(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
::
(25) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-(4-phenyl-
butyl)-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-
' ":
`` 21~573~
- 58 -
dihydrobromide
(26) 6-(3-carboxy-propylsulfonyl)-1-methyl-2-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(27) 1 n-butyl-5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-2-[2-
(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(28) 5 t~2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-(3-
morpholino-propyl)-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-Pthyl]-
benzimidazole-trihydrobromide
(29) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-~3-(4-methyl-
piperazino)-propyl]-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
benzimidazole-trihydrobromide
(30) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl~-1-(3-
piperazino-propyl)-2-t2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
benzimidazole-trihydrobromide
(31) 1-(2-amino-ethyl)-5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-
aminocarbonyl]-2'f--[ 2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
benzimidazole-trihydrobromide
(32) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl~-2-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzoxazole-hydxobromide
(33) 6-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-3-methyl-2-[2-
(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-
dihydrobromide
(34) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbony~ -methyl-2-[2
(4-pyridyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(35) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-2-(3-
imidazolyl-propyl)-l-methyl-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(36) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-carbonylamino]-1-methyl-2-[2-
- 211~737
- 59 -
(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(37) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminosulphonyl]-1-methyl-2-[2-
(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(38) 6-(3-carboxy-propylthio)-1-methyl-2~[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl~-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
(39) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3-methyl-
9-(3-phenyl-propyl)-xanthine-dihydrobromide
(40) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-
isobutyl-3-methyl-xanthine-dihydrobromide
(41) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-~4-carboxy-butyl)-3-methyl-
9-(2-morpholino-ethyl)-xanthine-trihydrobromide
(42) 8-~4-amidino-phenyl)-3-benzyl-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-
9-methyl-xanthine-dihydrobromide
(43~ 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-methyl-
3-(3-phenyl-propyi)-xanthine-dihydrobromide
. .:
.
(44) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-3-n-butyl-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)- ~ ;~
9-methyl-xanthine-dihydrobromide
(45) 6-(3-carboxy-propyloxy)-1-methyl-2-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide ~:
(46) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-n-pentyl)-3,9- -~dimethyl-xanthine-dihydrobromide
(47) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-
isopropyl-xanthine-dihydrobromide
(48) 1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3-methyl-8-t2-(4-piperidinyl)-
ethyl]-xanthine-dihydrochloride - -~
The mixture is heated with 6N hydrochloric acid over a :
21~5737
- 60 -
steam bath for 1 hour.
Melting point: 211C (Decomp.)
Rf value: 0.61 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(49) 1-(4-carboxy-butyl)~3,9-dimethyl-~-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine-dihydrobromide
Rf value: 0.70 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(50) 1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-isopropyl-8-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine-dihydrobromide
The starting material used is 8-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-
4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-2-[(4-
ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-oxy]-9-isopropyl-lH-purin-6-one
Rf value: 0.59 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; Methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(51) 1-(3-~arboxy-propyl)-3,9-dimethyl-8-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine-dihydrobromide :
(52) 1-(5-carbox~pentyl)-3,9-dimet~yl-8-~2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine-dihydrobromide
: . ~
(53) 1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3-methyl-9-(2-morpholino-
ethyl)-8-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine-
trihydrobromide
(54) 8-(4-carboxy-butyl)-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]- ~
7,9-dioxo-4,5-dihydro-8H-imidazo[1,2,3-cd]purine- ~ :
dihydrobromide
(55) 1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3-methyl-8-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-
ethyl]-xanthine-dihydrobromide
(56) 3-n-butyl-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-methyl-8-[2-(4- ~ ~
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine-dihydrobromide ~-.
.
211~737
- 61 -
(57) 1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3-carboxymethyl-9-methyl-8-[2-
(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine-dihydrobromide
(58) 3-aminocarbonylmethyl-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-methyl-
8-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine-dihydrobromide
(59) 1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3-isopropyl-7-methyl-a-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine-dihydrobromide
(60~ 1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-methyl-8-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-
ethyl]-hypoxanthine-dihydrobromide
(61) 2-(4-amidino-phenyl)-9-(4-carboxy-butyl)-8,10-
dioxo-5,6-dihydro-4H,9H-pyrimido~1,2,3-cd]purine-
dihydrohromide
Melting point: sintering from 40C
Rf value: 0.68 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5~ :
sodium chloride solution -. 6:4) : :~
(62) 2-(4-amidino-phenyl)-8-(4-carboxy-butyl)-7,9-dioxo-
4,5-dihydro-~H-imidazorl,2,3-cd]purine-dihydrobromide ~:~
.
(63) s-(4-carboxy-butyl)-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
8,10-dioxo-5,6-dihydro-4H,9H-pyrimido[1,2,3-cd]purine-
dihydrobromide
Rf value: 0.72 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5% -~
; sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(64) 8-(trans-4-aminomethyl-cyclohexyl)-1-(4-carboxy~
~: butyl)-3-methyl-xanthine-dihydrochloride -:~
The starting matarial used is 8-[trans-4- ::~
~ .
(benzyloxycarbonylamino-methyl)cyclohexyl3-1-(4-
; ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-xanthine and the same : procedure is used as in (48~
~: Melting point: 248~C (Decomp.)
Rf value: 0.59 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5
: sodium chloride solution = 6:4~
2115737
- 62 -
(65) 1-(2-carboxy-ethyl)-3,9-dimethyl-8-[4-(4-
piperidinyl)phenyl]-xanthine-dihydrochloride
The same procedure is used as in (64).
Melting point: 122C (Decomp.)
Rf value: 0.61 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(66) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-methyl-
xanthine-dihydrobromide
Rf value: 0.48 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(67~ 5-(2-carboxy-ethenyl)-1 methyl-2-~4-(4-
piperidinyl)phenyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
Melting point: over 250C
Rf value: 0.67 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(68) 5-(2-carboxy-ethyl)-1-methyl-2-[4-(4-piperidinyl~-
phenyl]-benzimidazole-dihydrobromide
Melting point: 256C (Decomp.)
Rf value: 0.67 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(69) 5-(2-carboxy-ethyl)-1-methyl-2-(4-piperazino-
phenyl~benzimidazole-trihydrobromide
(70) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-2-chloro-
9-methyl-hypoxanthine-dihydrochloride ~ :
Concentrated hydrochloric acid is used and the work is
done at ambient temperature :~
f value: 0.54 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18: methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(71) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-methyl-
hypoxanthine-dihydrochloride
The same procedure is used as in (70)
211~737
- 63 -
Rf value: 0.71 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
Example 2
5~[(2-Methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-2-
~2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
1 g of 2-~2-~1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-
benzimidazole in 20 ml of methanol is treated with 4
bars of hydrogen for 6 hours at ambient temperature in
the presence of 0.1 g of 10% palladium/charcoal. After
the catalyst has been filtered off the mixture is
evaporated down in vacuo.
Yield: 0.7 g (97 % of theory),
Rf value: 0.68 (Reversed Pha~e Plate RP18, methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 5-[(2-methoxycarbQnyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-
methyl-2-[(4-piperidinyl)-aminocarbonyl]-benzimidazole - ~-
Obtained from 2-[(1-benzyl-4-piperidinyl)- ~- -
amino~arbonyl~-5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-
aminocarbonyl3-1-methyl-benzimidazole using 20% -~
palladium/charcoal and with the addition of methanolic
hydrochloric acid.
Rf value: 0.56 (Reversed Phase Plate RPI8, methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(2) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[l-(4-piperidinyl)-2-propyl]-benzimidazole
(3) 5-[(Z-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-
methyl-2-~2-(4-piperidinyl)-propyl]-benzimidazole
(4) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
2115737
- 64 -
methyl-2-[(4-piperidinyl)-oxymethyl]-benzimidazole
(5) 5-[~2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl~-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[(4-piperidinyl)-aminomethyl]-benzimidazole
(6) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[N-methyl-N-(4-piperidinylmethyl)-amino]-
benzimidazole
(7) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[[N-methyl-N-(4-piperidinyl)-amino]-methyl]-
benzimidazole
(8) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-
methyl-2-[(4-piperidinyl)-methylthio]-benzimidazole
(9) 5-~(2-meth~xycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[4-(4-piperidinyl)-butyl]-benzimidazole
(lO) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[3-(4-piperidinyl)-propyl]-benzimidazole -:
(11) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1- :~
methyl-2-(2-piperazino-ethyl)-benzimidazole :~
(12j :5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1- :
methyl-2-[2-(2-methyl-piperazino)-ethyl]-benzimidazole :~
(13) 5-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-1-methyl-2-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(14) 5-(4-isopropyloxycarbonyl-1-oxo-butyl)-1-methyl-2-
[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
Rf value: 0.31 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4~
(15) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-propyl~-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
~ '~` 211~737
- 65 -
(16) 5-[(3-methoxycarbonyl-propyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(17) 6 methoxy-5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-
aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
benzimidazole
(18) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1- :~ :
methyl~6-methylamino-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]
benzimidazole
(19) 6-dimethylamino-5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)- ~: :
aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
benzimidazole
~
(20) 6-hydroxy-5-E(2-methoxyaarbonyl-ethyl)-
aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
benzimidazole
: - :
(21) 6-amino-5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-
aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
benzimidazole
(22) 5(6)-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-2-
[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(23) 6-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(24) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-(4- :.
phenyl-butyl)-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(25) 1-[2-(3,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-5-[(2-
methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-2-[2-(4-
piperidinylj-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(26) 1-n-butyl-5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-
aminocarbonyl]-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
F.`~
2~1~737
- 66 -
(27) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-(3-
morpholino-propyl)-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl~-ethyl]-
benzimidazole
~28) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-[3-
(4-methyl-piperazino)-propyl]-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-
ethyl]-benzimidazole
(29) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-(3-
piperazino-propyl)-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
benzimidazole
(30) 1-(2--amino-ethyl)-5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-
aminocarbonyl]-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(31) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-2-[2-
(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-henzoxazole ~-
(32) 6-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-3-
methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl~-imidazo[4,5b]pyridine
(33) 5-[(2-methoxycarbanyl-ethyl)-carbonylamino]-1-
methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole ~:,,,:
(34) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminosulphonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
:
(35) 3,9-dimethyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-8-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine
Rf value: 0.41 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
.
(36) 3,7-dimethyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-8- L 2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine
Melting point: 206-208C (sintering from 205C)
Rf value: 0.34 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
--' 211~ ~ 3 J
- 67 -
(37~ 3,9-dimethyl~ 3-methoxycarbonyl-propyl)-8-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine
(38) 3,9-dimethyl-1-(5-methoxycarbonyl-pentyl)-8-t2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine
(39) 1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-9-(2-
morpholino-ethyl)-8,-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine
- ~:
(40) 1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-9-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-3~
methyl-8-t2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine -
(41) 1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-8-~2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine
(42) 3-n-butyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-9~methyl-8-
[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine
.:
(43) 1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-
methoxycarbonylmethyl-9-methyl-8-[2-(4-pip~ridinyl)-
ethyl]-xanthine
i,~- .
(44) 3-aminocarbonylmethyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-
9-methyl-8-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine :.
(45) 3-isopropyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-7-methyl-8-
[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine
(46) 1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-9-methyl-8-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-hypoxanthine
(47) 9-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-
ethyl]-8,10-dioxo-5,6-dihydro-4H,9H-pyrimido[1,2,3-cd]-
purine
Rf value: 0.03 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol - 7:3)
(48) 8-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-
ethyl]-7,9-dioxo-8H-imidazo[1~2,3-cd]purine
21~737
- 68 -
(49) 6-(3-methoxycarbonyl-propyloxy)-1-methyl-2-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(50) 6-(3-methoxycarbonyl-propylthio)-1-methyl-2-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(5}~ 6-(3-methoxycarbonyl-propylsulphonyl)-1-methyl-2-
[2-(4-piparidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(52) 1-cyclopropyl-5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-
aminocarbonyl]-2-[2-~4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
~53) 1-cyclohexyl-5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)~
aminocarbonyl]-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(54) 9-cyclopropyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-
8-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine
(55) 1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-8-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)ethyl]-xanthine-dihydrochloride
The work is done in ethanol.
Melting point: I8~5C (Decomp., starting at 155~C)
Rf value: 0.38 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/glacial acetic acid =
8:2:0.1)
: ~ :
Example 3
2-[2-(1-Benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-5-~(2-
methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-
benzimidazole
A mixture of 2.5 g of 3-amino-4-methylamino-benzoic
acid-CN-(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-amide] [Rf value: 0.28
(silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 50:2); prepared
from 4-chloro-3-nitro-benzoylchloride and B-alanine by
reaction in lN sodium hydroxide solution to obtain 4- --~
chloro-3-nitro-benzoic acid-[N-(2-carboxyethyl)-amide]
` ' 21:L~737
- 69 -
(melting point: 165-167C), reacting this product wi~h
40~ aqueous methylamine solution at 50C in a
pressurised ve~sel to obtain 4-methylamino-3-nitro-
benzoic acid-[N-(2-carboxy-ethyl)-amide] (melting point:
187-189C), esterification with methanol/ethereal
hydrochloric acid to obtain 4-methylamino-3-nitro-
benzoic acid-[N-(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-amide]
(melting point: 125-127C) and reduction with hydrogen
in the presence of 10% palladium/charcoal in methanol at
3 bars of pressure and at ambient temperature], 50 ml of
methylene chloride, 1.74 ml of N-ethyl-diisopropylamine
and 0.1 g of 4-dimethylamino-pyridine is combined with
3.1 g of 3-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-
propionylchloride and the mixture is stirred for 16
hours at ambient temperature. The mixture is evaporated
down in vacuo, taken up in ethyl acetate/dilute
hydrochloric acid and the aqueous phase is extracted
twice more with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate phases
are evaporated down, the residue is taken up in 30 ml of
glacial acetic acid and heated for 1.5 hours over a
steam bath. The mixture is evaporated down in vacuo,
water is added an~ the resulting mixture is neutralised
by the addition of sodium bicarbonate. It is extracted
with ethyl acetate, the organic phases are evaporated
down and the residue is purified by chromatography on
silica gel (eluant: ethyl acetate/ethanol = 100:1 to
6:4).
Yield: 1.2 g (24 % of theory),
Rf value: 0.63 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 8:2)
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-2-[2-(1-
methoxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl3-1-methyl-
benzimidazole
'~:
(2) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[2-(4-pyridyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
- ~ 211573~
- 70 -
(3) 2-[3-(1-imidazolyl)-propyl]-5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-
ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-benzimidazole
~4) 2-[(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-5-(4-
isopropyloxycarbonyl-l-oxo-butyl)-1-methyl-benzimidazole
Rf value: 0.62 (silica gal; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 9 1)
(5) 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-[2-(1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
benzimidazole
Example 4
2-[(1-Benzyl-4-piperidinyl)-aminocarbonyl]-5-[~2-
methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl- -
benzimidazole
.
A mixture of 3.78 g of 5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-
aminocarbonyl]-l-methyl-2-trichloromethyl-benzimida~ole,
1.9 g of 4-amino-1-benzyl-piperidine, 2.5 g of sodium
bicarbonate and 40 ml of water is heated over a steam
bath for 10 hour~ The solid product present is
filtered off, washed with water and recrystallised from
ethyl acetate.
Yield: 1.0 g (22 % of theory),
Melting point: 168-170C
Rf value: 0.32 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 7:3)
.
Example 5
8-(4-Amidino-phenyl)-3,9-dimethyl-1-(4-isopropyloxy- -~
carbonyl-butyl)-xanthine-dihydrochloride
0.1~ g of 8~(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3,9~
dimethyl-xanthine are suspended in 30 ml of isopropanol.
Hydrochloric acid gas is piped in for 60 minutes and the
mixture is stirred for a further two hours. It is then
evaporated to dryness and the residue is triturated with
ether, whereupon an amorphous solid product is obtained.
211~737
- 71 -
Yield: 0.14 g (72 % of theory),
Rf value: 0.38 (silica gel; n-butanol/glacial acetic
acid/water = 4:1:2)
Tha following compounds are obtained analogously:
(l) 5-[(2-isobutyloxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-~2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(2) 5-[(2-cyclohexyloxycar~onyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-
methyl-2-~2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-ben2imidazole
(3) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-cyclohexyloxycarbonyl- ~:
butyl)-3,9-dimethyl-xanthine : ~-.
(4) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-3,9-dimethyl-1-(4-ethoxy-
carbonyl-butyl)-xanthine
(5) 8-(trans-4-aminomethyl-cyclohexyl)-1-(4-
methoxycarbonylbutyl)-3-methyl-xanthine-dihydrochloride
The work is done in methanol with the addition of
ethereal: hydrochl~oric acid. ~:
Melting point: 264-266C (Decomp.)
Rf value: 0.49 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5~
sodium solution = 6:4) ; :
:(6) 3,9-dimethyl-1-(2-methoxy-carbonyl-ethyl)-8-[4-(4- :~
piperidinyl)-phenyl]-xanthine-dihydrochloride. ~ -
Melting point: 120C (Decomp.)
Rf value: 0.18 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5~
sodium chloride solution = 6:4) ~ :
Example 6
8-(4-Amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3,9-dimethyl-
xanthine
0.4 g of 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-3,9-dimethyl-(4-
211~737
- 72 -
methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-xanthine, 5 ml o~ water, 5 ml of
lN lithium hydroxide and 5 ml of tetrahydrofuran are
stirred for 60 minutes at ambient temperature. The
tetrahydrofuran is evaporated down in vacuo and 0.27 g
of ammonium chloride are added, after which the reaction
mixture is evaporated down in vacuo to half its volume.
The solid product precipitated is washed with a little
water and then with acetone and ether.
Yi~ld: 0.35 g (99 % of theory),
Melting point: 263-265C (Decomp.)
Rf value: 0.49 (silica gel; butanol/glacial acetic
acid/water = 4:1:1.5)
The following compounds-are obtained analogously:
(1) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-2-[(4-
piperidinyl)-oxymethyl]-benzimidazole
(2) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-6-methoxy-1-
methyl-2-[(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole -~
(3) 5-[(2-carbox~ ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-[2-(3,4-
dimethoxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
benzimidazole
(4) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-t2-(3,4
dimethoxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-3-methyl-xanthine
(5) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3-(3-
methoxy-propyl)-9-methyl-xanthine
(6) 1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-3-methyl-8-
-[2-(4-piperidinyl3-ethyl]-xanthine
(7) 6-(3-carboxy-propylsulphinyl)-1-methyl-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(8) 5-[(2-carboxy-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-cyclopropyl-2-
- 211 S 7 3 ~
- 73 -
[2-(4 piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole
(9) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-
cyclopropyl-3-methyl-xanthine
(10) 1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-9-cyclopropyl-3-methyl-8-[2-(4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine
(11) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3,7-
dimethyl-xanthine-dihydrobromide
Melting point: 290-292C (sintering from 288C)
Rf value: 0.68 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4, after
developing twice)
(12) 1-(4-carboxy-butyl)-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-(4-
piperidinyl~ethyl]-xanthine
Melting point: 278-280C (sintering from 270C)
Rf value: 0.57 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5~
sodium chloride solution = 6:4) -~--
Example 7
8-(4-Amidino-phenyl)-3,9-dimethyl-1-(4-methoxy~arbonyl-
butyl)-xanthine-hydrochloride-hydrog~n acetate
3.3 g of 8-(4-cyanophenyl)-3,9-dimethyl-1-(4-
ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-xanthine are suspended in 150 ml
of methanol and cooled to -30C. Hydrochloric acid gas
is piped in for 30 minutes whilst the temperature i5
maintained between -5 and -10C, and the mixture is left
to stand for 16 hours at ambient temperature. The
mixture is evaporated to dryness in vacuo and evaporated
down once more with methanol. The re~idue is dissolved
in 150 ml of methanol and ammonium carbonate is added in
batches thereto. The resulting mixture is stirred for a
further 16 hours at ambient temperature, acidified
slightly with ethereal hydrochloric acid and evaporated
`-~ 211~737
- ~4 -
to dryness in vacuo. It is triturated with methylene
chloride and the solid product obtained is purified by
chromatography on silica gel (eluant: methanol, then
methanol/2N acetic acid - 10:1).
Yield: 1.0 ~ (24 % of theory),
Melting point: 224-226C (Decomp.)
Rf value: 0.37 (silica gel; n-butanol/glacial acetic
acid/water = 4:1:2)
~he following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-9-[2-(3,4-dimethoxy-phenyl3-
ethyl]-l-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-xanthine
:
(2) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-
methyl-9-(3-phenyl-propyl)-xanthine :~
(3) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-9-isobutyl-1-(4-methoxy- ~ ~ :
carbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-xanthine
(4) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3- :
methyl-9-(2-morp~lino-ethyl)-xanthine ~::
(5) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-3-benzyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-
butyl)-9-methyl-xanthine
, .
(6) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-9-
methyl-3-(3-phenyl-propyl)-xanthine
(7) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-3-n-butyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-
butyl)-9-methyl- xanthine
' ..
(8) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl~-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3- ~ -:
(3-methoxy-propyl)-9-methyl-xanthine
(9) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-3,9-dimethyl-1-(4-methoxy-
carbonyl-pentyl)-xanthine
2115737
- 75 -
(10) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-9-isopropyl-1-(4-
methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-xanthine
(11) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-1-(4-
methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-xanthine
Melting point: 248-250C (Decomp.)
Rf value: 0.43 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol/conc. ammonia =
3:1:0.1, after developing twice)
(12) 2-(4-amidino-phenyl)-9-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-
8,10-dioxo-5,6-dihydro-4H,9H-pyrimido[1,2,3-cd]purine
Melting point: Decomposition from 105~C
Rf value: 0.38 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(13) 2-(4-amidino-phenyl)-8-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-
7,9-dioxo-4,5-dihydro-8H-imidazo~1,2,3-cd}purine
(14) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl~-9-cyclopropyl-1-(4-
methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-xanthine
(15) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-9-cyclohexyl-1-(4-
methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-xanthine
(16) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-9-
methylxanthine
Melting point: 225C (Decomp., sintering from 202C)
Rf value: 0.35 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
(17) 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)~2-chloro-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-
butyl)-9-methyl-hypoxanthine
Ethanolic hydrochloric acid is used.
Rf value: 0.30 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6: 4 )
211573 ~
- 76 -
Example 8
3,9-Dimethyl-8-~4-(N-methoxycarbonyl-amidino)-phenyl]-l-
(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-xanthine
Prepared ~rom 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-3,9-dimethyl-1-(4-
methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-xanthine and methylchloroformate
in methylene chloride with the addition of sodium
hydroxide solution and vigorous stirring.
Example 9
8-[2-(1-Acetoxymethoxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl~
3,9-dimethyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)-xanthine
Prepared from 3,9-dimethyl-1-(4-methoxycarbonyl-butyl)- ~-
8-~2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-xanthine and acetoxymethyl-
(4-nitro-phenyl)-carbonate in methylene chloride in the
presence of N-ethyl-diisopropylamine at ambient
temperature.
The following compound i~ obtained analogously:
~ 3` ' ~ :
2-[2-(1-acetoxymethyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]- -
5-[(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-aminocarbonyl]-1-methyl-
benzimidazole
:: .
Exam~le 10
6-(3-Methoxycarbonyl-propylsulphinyl)-l-methyl-2-t2-(4-
piperidinylj-ethyl]-benzimidazole
Prepared from 6-(3-methoxycarbonyl-propylthio)-1-methyl-
; 2-[2-(4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-benzimidazole with 30%
hydrogen peroxide in glacial acetic acid whilst cooling
with ice.
::
211~7~7
- 77 -
Example 11
8-(4-Cyanophenyl)-3,9-dimethyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-
butyl)-xanthine
4.5 g of 8-(4-cyanophenyl)-3,9-dimethyl-xanthine are
dissolved at 80C in dimethylsulphoxide, 2.3 g of
potassium carbonate are added and the mixture is stirred
for 2 hours at ~0C. It is left to cool, 2.6 ml of -~
ethyl 5-bromo-valeriate are added dropwise and the
resulting mixture is heated to 80C for 4 hours with
stirring. The solvent is evaporated off in vacuo and ~-
the residue is taken up in a mixture of 250 ml o~ ethyl
acetate and 150 ml of water. The aqueous phase is
separated off, extracted twice more with 100 ml of ethyl
acetate and the combined organic phases are evaporated
down. The residue is purified by column chromatography
on silica gel ~eluant: ethyl acetate).
Yield: 3.4 g (52 % of theory),
Melting point: 148-150C
Rf Yalue: 0.69 (silica gel; methylene chloride/
mathanol/glacial acetic acid = 19:1:0.1)
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 8-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-3,9-
dimethyl-l-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-xanthine
Potassium tert.butoxide is used and the reaction lasts
for 6 hours
Rf value: 0.24 (silica gel; methylene
chloride/methanol = 19:1)
(2) 2-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-9-
(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-8,10-dioxo-5,6-dihydro-4H,9H-
pyrimido~l,2,3-cd]purine
The same procedure is used as in (1).
Rf value: 0.84 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/ethanol = 7:3)
'~
211~737
- 78 -
(3) 8-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-1-
(~-ethoxy-carbonyl-butyl)-2-C(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-
oxy]-9-isopropyl-lH-purin-6-one.
Dimethyl~ormamide is used as solvent and initially
equimolar amounts of potassium-tert.butoxide, ethyl 5-
bromo-valeriate and 8-[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]-9-isopropyl-xanthine are used, the
resulting mixture is heated to 80C for 16 hours, one
equivalent af ethyl 5-bromo-valeriate and one equivalent
of potassium carbonate are added and the mixture is
stirred for a further 5 hours at 80C.
Rf value: 0.24 (silica gel: methylene chloride/methanol
= 19:1)
(4~ 8-(4-cyano-phenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-
butyl)xanthine
Dimethylformamide is used.
Melting point: 98-99C
Rf value: 0.83 (silica gel; methylene chloride/
methanol/glacial acetic acid = 19:1:0.1
(5) 8-[2-~1-benz~loxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-
3,7-dimethyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-xanthine
Potassium tert.butoxide in dimethylformamide is used.
Rf value: 0.36 (silica gel; methylene chloride/
methanol/conc. ammonia = 19:1:0.1)
(6) 8-[4-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-phenyl]-
3,9-dimethyl-1-(2-ethoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-xanthine
The work is done in dimethylformamide using
ethylacrylate
Melting point: 208-210C
Rf value: 0.75 (silica gel; methylene chloride/
methanol/glacial acetic acid = 19:1:0.1)
211~737
- 79 -
Example 12
8-~2-(1-Benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-1-t4-
ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-xanthine
a) 4-Amino-5-[[2-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-
ethyl]carbonylamino]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-
methyl-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione
A solution of 9.9 g of 1-benzyloxycarbonyl-4-(2-
ethoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-piperidine, 9.7 g of 4,5-diamino-
1-~4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-
dione and 4.8 ml of triethylamine in 250 ml o~
dimethylformamide is combined with 11 g of 0-(lH-l-
benzotriazolyl)-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium-
tetrafluoroborate and stirred for 2~5 hours at ambient
temperature. The mixture is evaporated down, the
residue is stirred with a mixture of 300 ml of water,
200 ml of tetrahydrofuran and 200 ml of ether and the
organic phase is evaporated down. It is triturated with
ether, the solid product formed is filtered off and
dissolved in war~acetone and precipitated with ether.
Yield: 12 g (62~ of theory),
Melting point: 114-115C
Rf value: 0.37 (silica gel; methylene chloride/
methanol/conc. ammonia = 9:1:0.1, after
developing twice)
(b) 8-[2~ benzyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-ethyl]-1-
(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl~-3-methyl-xanthine
10 q of 4-amino-5-~[2~ benzyloxycarbonyl-4-
piperidinyl)-ethyl]carbonylamino]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-
butyl)-3-methyI-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione are heated to
275C for 15 minutes. 0.1 g of 4-dimethylamino-pyridine
are added and the mixture is heated to 275C for a
further 10 minutes. The product is purified by
chromatography over silica gel (eluant: ethyl
211~737
- 80 -
acetate/ethanol = 9:1).
Yield: 6.4 g (66% of theory),
Melting point: 99-100C
Rf value: 0.68 (sili~a gel; methylene chloride/
methanol/conc. ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
The following compounds are obtained analogously:
(1) 8-[trans-4-(benzyloxycarbonylamino-methyl)-
cyclohexyl]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-xanthine
a) 4-amino-5-[[trans-4-(benzyloxycarbonylamino-methyl)-
cyclohexyl]-carbonylamino]-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-
methyl-lH,3H-pyrimidin-2,6-dione
Melting point: 152-154C ~sintering from 149C)
Rf value: 0.41 (silica gel; methylene chloride/
methanol/conc. ammonia = 9:1:0.1)
~ b) 8-[trans-4-(benzyloxycarbonylamino-methyl)-
;~ cyclohexyl] 1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-3-methyl-xanthine
Melting point: 155-56C
Rf value: 0.58 ~silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol
; = 19:1, after developing twice)
(2) 8-(4-cyano-phenyl)-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-9-
methyl-xanthine
The mixture is heated to 250C for 10 minutes in the -
presence of 4-dimethylamino-pyridine.
Melting point: over 250C
Rf value: 0.56 (silica gel; methylene chloride/methanol
~ = 9 ~
(3) 2-(4-cyano-phenyl)-9-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-8,10-
dioxo-5,6-dihydro-4H,9H-pyrimido[1,2,3-cd]purine
The mixture is heated for 15 minutes at 295-300C
Melting point: 140C
Rf value: 0.59 (silica gel; methylene chloride/
methanol/glacial acetic acid = 9:1:0.1)
21157 3 ~'
- 81 ~
Example 13
3,9-Dimethyl-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-8-[4-(N hydroxy-
amidino)-phenyl]-xanthine
20.5 g of 8-(4-cyano-phenyl)-3,9-dimethyl-1-(4-
ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-xanthine are suspended in 1000 ml
of methanol and combined with 10 g of hydroxylamine-
hydrochloride and 17.5 ml of N,N-diisopropyl-ethylamine.
The mixture is refluxed for 4 hours, evaporated down and
the residue is triturated with 300 ml of ice water. The
solid produGt is dried and then washed with 35 ml of
methanol and with ether
Yield: 19.7 g (89% of theory),
Melting point: 226-228C
Rf value: 0.39 (silica gel; methylene chloride/
methanol/conc. ammonia = 15:1:0.1, after
developing twice)
Exam~le ~14
5-~2-Methoxycarbonyl-ethenyl)-1-methyl-2-[4-(4-
piperidinyl)phenyl]-benzimidazole -
1.7 g of 2-[4-(1-tert.butyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-
phenyl]-5-(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethenyl~-1-methyl-
benzimidazole are dissolved in 10 ml of methylene
chloride, mixed with 10 ml of trifluoroacetic acid and
stirred for 1.5 hours at ambient temperature. The
mixture is evaporated down in vacuo, neutralised with
sodium bicarbonate solution and stirred for two hours at ~ -
ambient temperature. The solid product precipitated is
filtered off and dried at 100C in vacuo.
Yield: l.l g (82% of theory),
Melting point: sintering from 205C
Rf value: 0.52 ~Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
211~73'~
- 82 -
Exam~le 15
2-~4-(1 tert.Butyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidinyl)-phenyl~-5-
(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethenyl)-1-methyl-benzimidazole
4 g of methyl 3-~4-(1-tert.butyloxycarbonyl~4-
piperidinyl)-benzoylamino]-4-methylamino-cinnamate are
heated in 250 ml of glacial acetic acid ~or 2 hours over
a steam bath. The mixture is evaporated down, taken up
in ethyl acetate and washed with sodium bicarbonate
solution. The ethyl acetate phase is evaporated down
and the residue is purified by column chromatography
over silica gel (eluant: ethyl acetate/petroleum ether =
6:4).
Yield: 1.5 g (40% of theory),
Melting point: 177-179C
Rf value: 0.55 (silica gel; ethyl acetate/petroleum
ether = 7:3)
Exam~le 16
' -:
5-(2-Methoxycarh~.~nyl-ethyl)-1-methyl-2-[4-(4- ~ -
piperidinyl)phenyl]-benzimidazole
0.7 g of 5-(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethenyl)-1-methyl-2-[4-(4
piperidinyl)-phenyl]-benzimidazole in 15 ml of methanol
at ambient temperature in the presence of 0.2 g of 10% ~
palladium/charcoal are treated with 4 bars of hydrogen ::
for 3 hours . The catalyst is filtered of~ and the
filtrate is evaporated down.
Yield: 0.7 g (100% of theory),
Melting point: 138-140C ~:
Rf value: 0.56 (Reversed Phase Plate RP18: methanol/5%
sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
The following compound is obtained analogously:
(1) 5-(2-methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-1-methyl-2-(4-
piperazinophenyl)-benzimidazole
- 83 - 2 1~ 7 3 7
Exam~le 17
8-(4-Cyano-phenyl)-2-chloro-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-
9-methyl-hypoxanthine
.
4.5 g of 8-~4-cyano-phenyl)-1-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)~
9-m~thyl-xanthine are refluxed for 4 hours in 50 ml of
phosphorus oxychloride. The phosphorus oxychloride is
distilled off in vacuo and the residue is taken up in
20 ml of methylene chloride. It is poured on to water,
neutralised with sodium bicarbonate, extracted with
ethyl acetate and purified, after evaporation, by
chromatography on silica gel (eluant: methylene
chloride/ethanol = 100:1 to 100:3).
Yieldo 2.5 g (53% of theory),
Rf value: 0.52 (silica gel: ethyl acetate/ethanol = 9:1)
Example 18
.
8-(4-AmidinQ-phenyl)-1-(4-ethQxycarbonyl-butyl)-9-
methyl-hypoxanthine-hydrochloride
0.2 g of 8-(4-amidino-phenyl)-2-chloro-1-(4-
ethoxycarbonyl-butyl)-9-methyl-hypoxanthine in a mixture
of 10 ml of ethanol and 5 ml of tetrahydrofuran are
treated with 4 bars of hydrogen at 40C for 2 hours in
the-presence of 0.1 g of 10% palladium/charcoal. The
catalyst is filtered off, the filtrate is evaporated
down and the residue is triturated with petroleum ether.
Yield: 0.13 g (65% of theory),
Rf value: 0.44- (Reversed Phase Plate RP18; methanol/5%
~; sodium chloride solution = 6:4)
211~737
- 84 -
Example 19
Dry ampoule containing 2.5 mg of active substance per
1 ml
Composition:
Active ubstance 2.5 mg
Mannitol 50.0 mg
Water for injections ad1~0 ml
Preparation:
The active substance and mannitol are dissolved in
water. After transferring the solution to the ampoule,
it is freeze-dried.
At the point of use, the solution is made up with water
for injections. ~ ,
:: :
Example 20 ~ -
Dry ampoule containing 35 mg of active substance per
2 ml -
" ~:'
Composition:
:-;,
Active substance 35.0 mg
Mannitol 100.0 mg
Water for injections ad2.0 ml
Preparation:
The active substance and mannitol are dissolved in
water. After transferring the solution to the ampoule,
it is freeze-dried.
:: .
~, '
^~
21~7~7
- 85 -
At the point of use, the solution is made up with water
for injections.
Example 21
Tablet containing 50 mg o~ active substance
Composition: ^
(1) Active substance 50.0 mg
(2) Lactose 98.0 mg
t3) Corn starch 50.0 mg
(4~ Polyvinylpyrrolidone15.0 mg
(5) Magnesium stearate 2.0 mq
215.0 mg
Preparation~
Components (1), (2) and (3) are mixed together and
granulated with an aqueous solution of component (4).
Component (5) ispadded to the dried granules. From this ;~
mixture, compressed tablets are produced, biplanar, ~
facetted on both sides and notched on one side.
Diameter of tablets: 9 mm.
Exam~le 22
Tablet containing 350 mg of active substance
,
Composition:
..
(1) Active substance 350.0 mg
(2) Lactose 136.0 mg
(3) Corn starch 80.0 mg
(4) Polyvinylpyrrolidone30.0 mg
(5) Magnesium stearate 4.0 mq
600.0 mg
~--,
211573'~
- 86 -
Preparation:
Components (1), (2) and (3~ are mixed together and
granulated with an aqueous solution o~ component (4).
Component (5) is added to the dried granules. From this
mixture, compressed tablets are produced, biplanar,
facetted on both sides and notched on one side.
Diameter of tablets: 12 mm.
Exam~le 23
Capsules containing 50 mg of active substance ~;
Composition:
(1) Active substance 50.0 mg ~ ;
(2) Dried corn starch 58.0 mg
(3) Powdered lactose 50.0 mg
(4) Magnesium stearate ~.0 mq
160.0 mg
Preparation: ~
Component (1~ is triturated with component (3). This `
triturate is added to a mixture of components (2) and
(4), with thorough mixing.
: -:'-
This powdered mixture is packed into size 3 hard gelatin
oblong capsules in a capsule filling machine.
;~ . .
:
2115737
- 87 -
Example 24
Capsules containing 350 mg of active substance
_
Compositiono
(1) Active substance 350.0 mg :~
(2) Dried corn starch 46.0 mg
(3) Powdered lactose 30.0 mg
(4) Magnesium stearate 4.0 mq
430.0 mg
Preparation~
Component (1) is triturated with component (3). This :~-
triturate is added to a mixture of components (23 and
~4), with thorough mixing. :~
This powdered mixture is packed into size O hard gelatin
~ oblong capsules in a capsule filling machine.
:: ::; -. ''
~ ~ - : , .
: .