Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
93/2070~ 2 i 1 7 9 ~ PCr/GB92/00697
RO~E~SS AND A~PARA~US FOR M~NUFACTURING S~.~PED
CONFECTIONERY PRODUCTS
The present invention relates to a process for
manufacturing confectionery and similar products shaped,
at least on the external surface, according to a
preselected design. The ir.vention also relates to a
m~chine for carrying out said process and ~o the shaped
final products.
Confectionery products such as chewing gum and bu~ble gum
products, soft candies, toffees etcetera, are mass-
produced with very high outputs per hour. Methods to
produce them in symmetrical shapesf such
as spherical ~ cylindrical or ellipsoidal shapes, are }cnown
in the art. On the contrary it is not ~ssible to obtaln
them with shapes reproducing fancy obj~c~s, nor is it
possible to obtain such products with their surface shaped
according to a selected design, i,e. with a pl~rality o~
shaped lines and ar~as formed in high- or bas~relief.
The aim of the p~esent invention is to solve the above
mentioned problem by providing a way of industri~ 71y
producing sh~p2d: confectionery products with a hig~ output
per hour iR a simple and ec:onomical way.
P.nother aim of the present inYention is to provide an
apparatus for carrying out the above referred to
irdu~trial process.
W093/2~70~
21 ~ 7 ~, 3 9 PCT/GB9~/00697 ;~
According to a first aspect of the present
in~ention, there is provided a process for
manufacturing confectionery products, comprising the
steps of: producing an intermediate product which is
plastically deformable and has a smaller size than a
desired final product; positioning said intermediate
product in a mold having a preselected shape;
connecting an interior portion of said intermediate
product to a source of pressurized fluid; feeding said
pressurized fluid into said intermediate product
interior portion to conform said intermediate product
to said preselected shape of said mold to produce said
final product; disconnecting said final product from
said fluid source; and extracting said final product
from~said mold.
According to a~ second aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a confectionery product
mo:lded to a preselected shape and having a plurality
o~:molded areas and lines on its outer surface.
:According to a third aspect of the present
invention, there is provided apparatus for producing
haped:~confectionery products, comprising: a plurality
of~upper and lower mold parts; positioning means for
positioning intermediate products in said mold parts;
fluid ~eeding means for feeding pressurized fluid into
a~ innex portion of each intermediate product to
produce said shaped products; and extractor means ~or
removing said shaped products from said mold parts~
Preferred features and e~bodiments of the present
invention ar2 describ~d below with reference to the
accompanying drawings, in which:
:~:
..
W093/2~705 2~ PCr/G~9~97
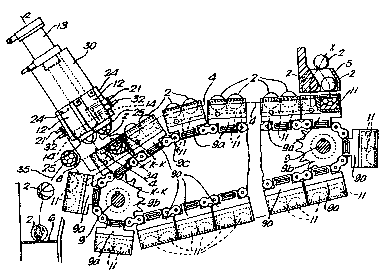
- figure 1 is a side view, partially sec~ioned, of
a preferred embodiment of an apparatus according to
the invention;
- figure 2 is a front view, partial'~,r sectioned, of
the apparatus of figure 1;
- figures 3 to 5 are enlarged side views, in
partial section, of the apparatus of figure 1 and show
sequential st ps of the in~ention process;
- figures 6 to 11 are side and top enl~rged views,
in partial section, of details of the apparatus
according to the inYention; and
- figures 12 and 1~ are partially sectioned side
and front views, respectively, of a further embodiment
o~ an appara~us according to the inventi.on.
With reference to the accompanying drawings,
~;` reference 1
:
~: :
, ~ :
,, :
WO 93/~705
PCr~G:B92J006~7 '
21~L79~9 4 ``
generally ref~rs to an apparatus for the production of
shaped candy products 2 reproducing a predetermined
design.
Apparatus 1 comprises a plurality of lower half molds 11
and upper half mo7ds 1~, feeding means 5 for feedi~g
intermedi~t products 2, i . e . the ~ dW co~fectionery
~roducts to be shaped, to thP lower half molds, and means
12 for temporarily closing together upper and lower molds
11 and 14. Moreover, apparatus 1 comprises fluid feeding
means 16, 21 that are connectable to the interior portion
of the intermediate products ? and to a source of
pressurizPd fluid (not shownJ, and extractor means for
extracting the shaped product ~rom the molds 11 or 14.
In the pr ferred embodiment disclosed in the drawings, the
upper molds 14 are ~fixed~ i.e. they are reciproca~able
: :
along~ their vertical axis z-z but they cannot undergo any
lateral ~ traYerse. The lower half molds 1~ are movable from
: ~ ~ a first : position corresponding to feeding means 5 to a
s~cond position where molds 14 are located, and viceversa,
along~ a closed loop path ~.
According to the prefe~red embodiment disclosed in figures
5~ ~he lower molds ll are housed within a plurality of
:~1'" i supp~rti~lg ~ars 9a parallel to each other and mounted on a
chain conveyor 9, 9c, 9b that forms the closed path
4 . ~s also discl osed in figure 2, the chain conveyor
3 v~
WO 93/2~705 P~/GB92/00697
comprises a couple of shafts 9 rotatably mounted on a
frame 3. The shafts 9 are coupled to sprocket wheels 9b,
~y means of which chains 9c are moved, together with bars
9a that are secured to the chain iinks. Frame 3 is also
proYided with low ~riction elements F ~fig. 2)
supporting bars ga at least at the
shaping posi tion .
E~ch bar ga houses a plurality of half molds 11 offset to
each other (figure 1.) in order to have a pitch P
corresponding to the ln~ermediate product sorting pit~h
in the machqnes (not shown) producing products 2. These
machines are known in the art and are not central ~o the
present invention.
rame 3 also rigidly supports element 30 wnich
~ .
houses . a plurality of reciprocata.ble saddles 1~ or
simllar: means carrying the upper half molds 14. Molds 14
are offset in the same way 2S lower molds 11, with the
same~ :~ pitch :P (see figure ~),and are movable from a
:closing position, in which they cooperate with lower half
molds ~11 to form~a~ closed mold, to ~n upper stop
position.
The sadd7es 12 are supp~ ed so as to be slidable in
direction z-z, and are reciprocated by the action of motor
means such as a pneumatiF cylinder 73. In order that the
W O 93~20705 2 ~ ~ 7 9 ~ ~ P ~ /GB92/00697
saddle 12 is moved axially in direction z-z without
rotating about the axis æ-z, both an
operating shaft 38 and an "idlel' shaft 38a are
provided. ~owever it is also possible to use a pneumatic
cylinder with a non-rsta~ing shaft.
Each lower half-mold ll and upper hal f-mold 14 ~ s
internally shaped in a way that its inner sur.ace
reproduces the corresponding half of the obje-t,
~: so that, wh n juxtaposed, the elosed ;nold 8
reproduces the shape of ~he whole object witr.
high- and bas-relief areas and lines.
In the preferxed embo~iment herein disclosed, upper molds
14 are mounted onto saddles 12 together with the
f1uid feeding means 16, holding means for
temporarily retaining the shaped prducts 2 in the moids 14 9
and extractor means f or extracting ~he shaped
products fro~ the upper molds.
di~sclosed in detail in figures 6-9, the pressuriæed
luid fe ding means comprises a hollow needle ~ 7 fixed
to the upper half-mold 14 and having axis b-b coinciding
with ~ axis k-~ of ;the saddle 12 (figure 9) 0 ~e
n~edle 17 has a free end 18 with a tip 19, preferably
oblique, which'projects into the upper half-mola l4. lhe intermediate
roduct 2 is preferably hollow: ~n this case
~ .
- WO ~3/20705
PCI`./GB92/006g7
the length of the projecting portion of the needle is
greater than the thickness of the wal G.` ~h~ Droauct
and 9).
An opposite end 20 of the bored needle 17 is connected to
duct 21 which is in turn connectable to a source of
pressurized fluid, known per se and not shown, suitable for
delivering a fluid at a preset pressure. The pressuri~ed
fl:~id can be air or an edible filler, ~cn as G
sugar syrup or the like.
~: Adjacent the needle 17 is provided a collar 18 havlng
a sharp edge facing into the half-rnoid 14
and projecting ~herein for a predetermined dls~ance.
~ ,
The ~ purpos2 of collar l~ is to seal the hole ~ade by ~he
needle 17.
The holding means 22 comprises two opposed arms 24, hin~ed
to: saddl e 12, and having free pointed f:ront ends 25 and
rear ends 26.
he~ : arms 24 are biased by elast c ~eans, such as
:springs 27, which towards a cl~sed
posi:~on in which ~heir free e~ds 25 ~roject nto
the~ closed: mold 8 :at the interface 15 be~ween the hal~-moids 1
: (figure 8). The free ends 25 project through notches l~a and 14a
provided in thP lower half-mold ll and in the upper half-
mold 1 4, respectiv~ly.
The r~ar ends 26 of arms 24 are provided with projecting
W O 93/2fl705
PCT/GB92~00697
2~ 1 7 ~ ~ ~ 8
portions 29 in order~ upon heir engag~ment by the fixed
element 30 once the saddle 12 reaches its back s~op
position, to have the arms 24 open against l,he ac,,.on of
spring means 27 and thus release the shaped product.
Extractor means comprises a plurality of blowing nozzles
31, located in the internal surface of t,~2 upper half-mold
14. I~he axes c-c of ducts 23 of the nozzles are parallel
t~ the axis b-b of needle 17 and the nozzles are
symmetrically positioned around the needie. ~his
provides optimal extraction of the shaped product
The noz~les 31 are connectable through ducts 21 and 32
~;
to a source of ~ressurized air fnot shown~.
In figure 7 is s~wn the preferred configalration of
reciprocatable saddles 12. According to this embodiment,
e~h s~ddle 12 carries two upper molds 14 offset ~rom each
o ther by the required pitch P. ~ch saddle has a
transverse: . section that is substantially rectangular~
with~ two~opposit~ co~er portions missing~
i ~ :
~; It:~is thus possible to position two adjacent saddles 12
very ~ close together (see figure 7) and to maintain
~: the required pitch P between molds mounted on adjacent saddles.
1'ne duc~s 21 and 32 for each half-mold 14 are positioned above
each other and the ducts for the two molds 4 of each saddle 12 are
positioned on
,
.~ W O 93t20705 2 r ~ 3 ~
P ~ /GB92/00697
opposite side of the saddle
Figtlres 10 and 11 show a preferred em~odiment for ste-pwise
movement of the bars 2a along the chain conveyer. In this c^~se,
instead of known motors acting on one shaft 9, bars 9a are
moved by means of a pneumatic piston directly acting on
the bars 9a. More specifically each bar ~a is provided
each side adjacent to frame 3 ~ith a hole 1~. ~n tne outsid~
o f frame 3 is provided
piston U~2 pneuma ically insertable and ~etrac~able into
and from the hole 10.
Piston U~2 is mounted on slider H and is rec:iprocatable
between two positions, along guiding ways M, ~y means of
nother pneumatic piston U/1.
::::: :
;With reference also to figure 1, piston U/2 and slider H
are: ~movable from position 9a/1 (i.e. the bar position
immediately upstream of the molding position) to
posltion ga/2 (i.e. the molding position itself)-
: ~:: During ~operation, ~ piston U/2 is first inserted into hole
10 of bàr ~a located at position 9a/1. ~ hen piston U/l is
. , ,
actu~ted and th~ bar is moYed from position 9a/1 to
position 9a/2; the pitch R of this traverse can thus be
perfectly controlled in order to obtain a correc~
lignment of lower half molds 11 and upper half molds 14
at position ga/2.
;`
WO 93/20705 PCI`/&B92/006g7
21~ 7~9 lo
Once molds 11 and 14 are aligned and Joined ~o for~
mold 8, piston U/2 is retracted and moYed b~ck to position
9a/1 to which a new bar 9a has been traversed upon
movemen~ of the original bar to position 9a/2. The cycle i s the:
repea~ed.
It should also be no~ed that, thanks to this emhodiment,
bars sa and therefore the molding step can be operated at
the same pace at which is operated the equipment producing
~ he intermediate raw product.
:~ The proc~ss according to the invention will now be
described with xeference to figures l to 5.
: rhe intermediate raw products 2 are produced in a know~
machine,~:upstream to the . apparatus 1 of the present invention.
By intermediate ( raw ) products are meant confectionery
products ;that ccording to prior art a_e either suitable
to : be packed as inished products or have to undergo only
some~ fini~shing steps, such as coating. In the following
description reference will be made to spherical and hollow
bu~l~e-~ums, hut, as ~ previously mentioned, the p~ocess
appl i 5 ~lso to non-spherical and non-hollow bubble-gums
and~other products such as toffees etc~
From this known machine fnot shown~ the products 2 are fed
to ifeeding means havin~2 an inter-product pitcn the sa~.e as t~,~t
of the oUtDUt row of the known machine. This mear;, ~hat
~`::
:
~ W O 93/20705 2 ~ ~ 7 3 ;3 ~ P ~ /GB92/00697
11 !
if the known machine produces a row of, e. 5., _ ' raw
products a~ 32 different output positicr;s, ~ e bars 9a wi i have '2
offset molds 11 with the same pitch as t:le out?u., ?ositio~.s
and products.
Feeding means 5 is a hopper having offset du~ts 7 through
which products 2 are fed to correspondingly offset lower
molds 11 on bar 9a mounted on ~hain conveyor 9.
The bar is then moved, by known mea~s or by the d e~i ce
above disclosed with reference to figures 10 and 11, to
position ~a/2 (figure 3~. Upper molds 14 are then lowered
by saddles 12 onto lowe~ half molds 14 (figure 4), thus
fo~ming a whole shaping mold 8, and ~dle 17 pierces
product 2. At the same time, collar 1S sli~htly compresses the
D~er surface of product 2, providing a fluid-tigh~
: se~ 1 around needle l7.
Air,~ sugar syrup or another suitable pressurized f l uid is
then ::fed through needle 17 to the hollow interior of
produ~t 2 . This expands the product and urges it against the
inner surface of molds 11 and 14 and confc~rms its shape
to :: the mold design. Durin~ this swelling step,
product :2 is also urged against collar 1~ and ~ree pointed
ends 25 of ~rms 24 (see . igure 9).
In or~er to be expanded and molded,
intermediate products 2 are in a plastically deforma~le
condition. In the case of bubble gums, this condition is
.
::
W O 93t20705 PCT/~B92/00697
12
achieved by ensuring that the intermediate ?roaucts 2 are hot
enough when they exit ~ om the upstream
producing machine to be su~ficien~l~ deformable.
However, heating or cooling means may be
provided upstxeam of feeding means 5 LO optimize produa~ 2
temperature.
At the end of this step, shaped product 2 is therefore
secured b~f arms 24 to the upper half mold 14 and to
s~ddle 12.
The fluid pressure required depends on the nature and
kind of product ~bubb 7 e gum, toffee e~cetera). For ~the
a~erage bu~ble-gum product having a wall thickness within
he range of 2 mm to 6 mm arld an initial diameter of 23-
24 mm and a final diameter of about 26 mm, the air
;~ ~pr~ssure va7ue is about 3,5-4,0 atm. The skilled man will
a-~ily ~detsrmine the suitable pressure for each product
after~:a few tests.
After~ ~the shaping s~ep the pressurized fluid source is
disconnected from needle 17, and saddles 12 are brought to
their raised stop position (figure ~). Shaped products 2
are retain~d by arms 4 and follow path 34 (figures 1 and
23 until saddl~ 12 reaches its upper stc~. Then projecting
portions 29 are pressed and arms 24 open to îree the
products 2.
Compressed air is then fed througn aucts 32, 21 to nozzle- _'
~ - ~ W~ ~3/2070~ 7 ~ a 9 PCr/G~9~/0~6g7
13
and shaped products 2 are extracted (eiectedl fxom uppPr
half molds 14 to fall onto conveyor 6 that brings them
after cooling to wrapping and packaging equipment (not
sho~n) or to coating apparatus (not shownJ. Where
products 2 are bubble-gums, they preferably undergo a
su~sequent sugar coating step in a way known per se, still
retaining their shaped appearance notwithstanding this
coatlng step.
It should be noted that molds ll plus ~ars 9a in positions
9aJ1 and 9a/2, and molds 14 plus saddles 12, while having
rele~ant axes perpendicular to each oth r, are incllned
with respect to the plane of the first portion of path 4.
Bec~use of this incliRation~ after the molding and shaping
;step,~when shaped products are released ~nd extracted from
upper; molds 11, the rel evant bar 9a will have moved from
position 9a/2 to the position shown with do~ted lines in
:figure~ the released And ejected products will fall
first ~on ~: the thus~moved bar and fro~ it to conveyor 6
al:ong ~ path 35 .
:Dimensions; of products 2 depend on dimensions of
~aw~;~ produc~s and can vary within, e.g., 10 to 40 mm if the
produc~s are spherical, and withiI~, e.g., 1 to 12 cm if
thé I products are roughly cylindrical or elli~tical . I The
: : : : ::
sh~pes of the products may vary accordingly: football,
basket, ba5e~all or soccer balls, ca, toon char~ct~rs,
WO 93/20~05
P~/GB92~00697
2 ~ 1 7 9 9 9 1 4
corn, vegetables, fruits, etcetera.
In fig~res 12 and 1~ is show~ another possible embodiment
according to t~le present invention.
In these figures the same references of previous figures
1-11 are used for the same elements.
In this embodiment the basic principle is the same as
before, but instead of chain conveyor g bars 9a are
mounted on a rotating cylinder 28.
Besides this, the other main difference from previous
embodiment resides in the means for feeding intermedlate
products to lo~er half molds 11. In this case (figure 12)
raw products 2 are fed from the known producing machine
(not shown) to a feeder 36 comprising a plurality of
offset ducts 37, each aligned with the stop position of
relevant mold 11. Feeder 36 further comprises two
retaining arms 39, e~h cooperating with a plurality of
the~ o~fset ducts 7 in order to ret~ 7 n raw pro~ucts 2 ~..hile
cylinder 28 is rotat~d from onP position to the next one.
h the preferred~e~mbodiment, arms 39 are
hinged and pneumatically operated by pistons 40 at a
preset rate to alternately block and unblock the
ducts 7. An even Sett~r feeding of raw intermedlates 7
is obtained'by using a belt conveyor ~not shown~ upstream
of feeder 36 to ca~ry products 2 from the known
producing madine. Th~ belt con~eyor will be m~vable
W093/20705 ~ 3 ~ 9 PCT/GB92/00697
- 15 -
in steps substantially equal to the diameter of
product 2: products 2 will thus be ~ed to molds 11 by
the combined action of gravity and movement of the
belt conveyor.
From the above em~odiments it is evident that the
present invention provides- several further
advantageous features. In fact, by working at the
same rate as the machine producing the intermediate
products, it is possible to have a very high rate that
results in a very high output, usually above 500
pieces per minute. Moxeover, by using the same
: inter-product pitch as the output of the machine
producing the intermediate products, space is saved.;
A further advantageous feature is that the
apparatus can be located at the end of a known n.achine
producing the intermediate products without
expensively modifying the known machine.
. :Ano~her advantage is that molds 11, 14 and/or
bars 9~a can be easily removed from chain conveyor ~-9c
:or~:cylinder 28 in order to be repl~ced with different
molds for differently shaped products.
A still further adYantage is that bigger final
products can be obtained, with the same weight as the
: intermediate products.
Last but not least, the final s~sar ooating step~
: if: done, does not conceal the molded lines and areas
on :~the product 2, but instead enhances them,
~:::especiall~ if the co~ting colour is different from the
product colour. In this case a coating process
producing a thin coat will be used so as to coat only
the high-relief areas.
`~ ~In order to obtain this result the coating syrup
:is spread on the walls of the coating pans, and is not
W0~3/20705 PCTJGB92~00697 ~ ~
2 ~ 9
- lS -
applied directly to the shaped products. Filling in
of bas-relief lines and areas is thus avoided.
However, even if a thick coating is used, i.e.
the bas-relief areas are coated in the same colour as
the rest of the surface, the high- and bas-relief
areas are still discernable and the shaped appearance
is maintained. In fact, a greater amount of coating
syrup will be deposited in bas-relief lines, thus
giving a more intense colour to those lines compared
with the high-relief areas.
:~,
: :
~ '
-
~,