Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~ ~ ~ o ~ ~ ~
BAG-TIE FOL~ING APPARATUS A~ METHO~
FIELD OF THE lNv~NllON
The present invention pertains to tie bags used most
commonly for the storage and disposal of debris and other
ubiquitous waste materials and, more particularly, to the
manufacture and packaging of bags having ties that are
folded "on-the-fly" within the body of the webbing (which
has a discontinuous fold line), as the web of the bag is
being continuously advanced and conveyed during the stacking
and packaging operations.
BACKGROUND OF THE Ihv~NllON
The manufacture and use of polyethylene storage and
disposal bags is well known in the art. One of the
bothersome problems with the use of plain storage bags is
the inconvenience involved in trying to tie the bag.
Several brands use separate metal wire ties which are
packaged along with the bags. As a separate item, these
metal wire ties can be unwieldy to use and often become
lost.
A convenient user feature of the polyethylene bags of
this invention is its ties, which are integral with the body
of the bag. These integral ties comprise a curved, cut-out
~-15633
- ~ 2120901
.. ..
......
portion of the bag web. Built in, the ties can be grasped
and knotted to seal the bag; hence, they are referred to in
the trade as ~tie bagsn. The tie bags of this invention are
illustrated in United States ~atent No. 4,890,736, issued to
Greyvenstein on January 2, 1990.
In the manufacture and packaging of tie bags, it has
been determined that folding the ties within the webbing of
the bag provides everal advantages. One advantage is that
a neat and compact packaging can be accomplished. Another
advantage is that the user of the bag can more easily open
the bag when the two ties have been tucked inside the body
thereof.
Although it has already been determined that several
advantages are achieved by folding the ties within the bag
body, nevertheless, heretofore it has been difficult or
impossible to accomplish the packaging of the tie bags with
the desired configuration. This is particularly true under
high-speed conditions.
The invention incorporates a system for folding the
ties within the body of the bag webbing while the web is
being conveyed. In other words, the ties are folded while
moving on-the-fly.
When presented with the task of folding the ties within
the body of the moving web, expert~ in the art have
previously stated that it could not be achieved. The reason
for their belief was based on three ma~or stumbling blocks
that needed to be overcome:
D-15633 2
2:~20~
.. .. .
. ~ ~
a) The folding on-the-fly at high speed of both
flexible ties within the U-shaped flexible ~heet
is a formidable task, in part due to the possible
entrapment of air between the sheet~.
b) Folding has to be achieved with a discontinuous
fold line, so that each tie requires individual
folding.
The second major breakthrough in resolving the problem
was the folding of the tie itself as the webbing i8 rapidly
moving. Although difficult to accomplish, the present
inventive apparatus holds the ties in an aligned position
while it passes the webbing of the bag through a web-
separating device. The two halves of the webbing are then
separated, and each half is passed over a guide member. The
guide members force the tie of each web half to fold under,
rejoining the web halves. The webbing is under tension so
that the ties are maintained in a smootb, folded-in
configuration until the webbing is sized, cut and finally
packaged. It is important to note that the two halves of
the U-shaped web are opened only momentarily as they pass
over the guide members. This ensures that, at worst, only a
minimum amount of air can be entrapped within.
DISCUSSIO~t OF RELATED ART
In United States Patent No. 4,906,228, i~sued on ~arch
6, 1990, to Reifenhauser et al, entitled MEIHOD AND
APPARATUS FOR THE MANUFACTURE OF PLASTIC BAGS IN PAIRS WITH
SIDE SEAMS, an apparatus for folding the ties of the bags is
illustrated. The wave crests and wave troughs that are
D-15633 3
212~901
~ . .... .
characteristic of the tie patterns of this invention are cut
through the center of the sheet body, thus forming two
oppositely facing bags. The ties are then folded down, in
whole or in part, along a continuous fold line. The fold
can be toward either the inside or the outside of the bag.
The ties are then welded to the bag body. Thereafter, holes
are punched in the folded and welded portions to form a
handle.
The aforementioned bag manufacturing method differs
from the current invention in that the registration of the
bags is achieved by scanning the inner or outer edges of the
wave crests and wave troughs to convey them synchronously.
Although not clearly described in the reference, this
scanning is, nonetheless, a process step which is completely
alien to the invention. The method described for the
current invention needs no complicated scanning or
electronics to achieve registration. Rather, the invention
uses a flow of air to align each wave crest to its fully
extended position. The present invention provides ties that
are substantially devoid of wrinkles, which may or may not
be the case with the prior patented apparatus. It is not
evident from the Reifenhauser description as to what the
folding device comprises. However, since the crests are
subsequently welded, there i8, most probably, no concern
about wrin~ling. Furthermore, there i8 probably a similar
lack of concern as to whether the folds are inside or
outside of the bag, since the weld will be accomplished in
either case. This is a concern with the present invention,
however, as the ties must be tucked only within the bag. In
addition, since Reifenhauser tucks the ties toward the
D-15633 4
outside and even welds them, the concern for air entrapment
when the halves are separated is never raised. This
concern, highly relevant to the present invention, is one
which is neither contemplated nor addressed by Reifenhauser.
Finally, the folding in Reifenhauser is intermittently
accomplished along a continuous fold line, vis-a-vis the
present invention, in which the folding of individual ties
is continuously accomplished along a discontinuous fold
line.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In accordance with the present invention, there are
provided an apparatus and a method for both ext~n~;ng and
folding the ties of a-tie bag into the body of the bag.
The apparatus and the method of this invention fold the ties
while the webbing of the bag is rapidly moving. In other
words, the invention first extends the ties; this invention
individually folds each tie within the continuously moving
web. The folding apparatus facilitates the folding on-the-
fly by passing the U-shaped webbing of the bag through a
web-separating device. The two halves of the U-shaped
webbing are then separated, and each half is passed over a
guide member. Each guide member forces the tie of each
respective web half to fold under. Thereafter, two
additional guide members rejoin the two web halves, with the
tie folded in. While the webbing is under tension, the ties
are maintained in a smooth, folded-in configuration.
Likewise, the positions are maintained during the sizing,
D-15633 5
" - ~
2120901
,,_
cutting and final packaging into a stack of individually
folded bags.
It is an object of the present invention to provide a
system and method for folding the ties of a tie bag into the
body of the bag, while the webbing of the bag is being
continuously conveyed through the manufacturing system.
It is another ob;ect of the invention to provide an
improved method and apparatus for folding the ties of a tie
bag while the webbing of the bag is moving on-the-fly.
It is a further ob~ect of the invention to provide the
folding of ties within the respective pocket of a plurality
of flexible plastic bags created from a web having a
discontinuous fold line, with the web being continuously
conveyed past a folding apparatus.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
A complete understanding of the present invention may
be obtained by reference to the accompanying drawings, when
considered in conjunction with the subsequent detailed
description, in which:
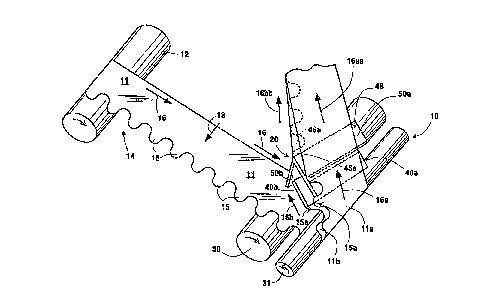
FIGURE 1 illustrates a perspective, schematic view of
the web ~eparating and folding ~ystem of this invention; and
FIGURE 2 depicts ~n enlarged, top view of the web
separating and folding guide members of the folding
apparatus of the invention depicted in FIGURE 1, with the
plastic bag webbing continuously traveling therethrough.
D-15633 6
- ~ 2120901
For the purposes of clarity and brevity, like elements
and components will bear the same designation throughout the
figures.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODI~F~T
Generally speaking, the invention features ~ system and
a method for achieving packaging of a plastic bag having its
ties internally folded within the body of the bag. The bag
is made by a continuous process in which the bags are
manufactured as a continuous double web of polyethylene.
The end of the web is cut in a serpentine pattern to provide
tie-shaped surfaces. The ties are extended as they move
along the conveyor and then folded by the apparatus and
method of this invention. Thereafter, in subsequent
operations, the continuous webbing is sized, cut into
individual bag units, stacked and packaged.
Now referring to FIGURE 1, the folding system 10 of
this invention is shown. The system 10 illustrates a
continuous, double-layered web 11 of polyethylene that is
being fed over a feed roller 12 on the left-hand side of the
FIGURE. The double-layered web 11 is cut on one end thereof
in a serpentine pattern, as shown by arrow 14. The web 11
will be subsequently ~ized and cut in later processes in
order to provide individual bag units. Each unit, or bag of
the web 11, has two back-to-back ties 15 that extend from
the U-shaped webbing, so as to provide two extended,
contiguous ties. The webbing 11 is fed along a feed path,
generally depicted by the arrows 16.
D-15633 7
_ 212~q~
" -
The ties 15 are free to roll, wrinkle, ripple and fold
as they exit from the feed roller 12, due to the flexibility
and thinness of the web 11.
The web 11 with extended ties 15 is fed to a pair of
nib rollers 30 and 31, respectively. The nip rollers 30 and
31 feed the web 11 to a folding apparatus, shown generally
by arrow 20. Other feeding mec~Anisms can also be used.
The folding apparatus 20 featuring the second invention
of system 10 comprises a double pair of guide plates 40a,
40b, and 50a, 50b, respectively. The first pair of guide
plates 40a, 40b are divergently positioned according to the
upward direction of travel of web 11, so that the webbing 11
is caused to separate into its two respective layers lla and
llb, as shown by arrows 16a and 16b. It i~ necessary to
open the webbing 11, 80 that each tie 15 passing through the
folding apparatus 20 can be tucked, or folded into, the
interior portion of the double-layered web.
It should be understood that, as the web feed is
continuous, the inventive system 10 requires that the two
respective layers lla and llb of the webbing 11 must each be
divergently threaded through the folding apparatus 20 prior
to the activation of the feeding rollers 12, 30 and 31.
This threading is usually accomplished manually, since it
must be done only once per production run.
As the layers lla and llb diverge, they are
respectively fed to guide plates 50a and 50b, which converge
toward each other. These converging plates 50a and 50b have
D-15633 8
'~ 2120~0 1
a dual purpose: they fold in the respective ties 15a and
15b into the webbing 11, and a1BO close the layers lla and
llb of the webbing 11 after the folding has been
accomplished, as shown by arrows 16aa and 16bb.
Each plate 50a and 50b, respectively, is provided with
respective folding plates 46a and 46b (not shown), each of
which has a cam-like surface, 45a and 45b (not shown)
respectively. The cam-like surfaces respectively engage the
diverging web layers lla and llb. In order to describe the
folding operation in sufficient detail without causing
confusion, and since upper and lower guide plates function
in like manner, reference will be made only to the upper
guide plate 50a and its corresponding folding plate 46a, as
illustrated in FIGURE 2.
Referring to FIGURE 2, the ties 15a of the upper web
half lla is fed seriatim under cam-like guide member 45 that
is part of folding plate 46a, as shown. As the upper web
lla exits over the top surface of plate 50a, the ties 15a
fold under the web lla.
As will be seen from FIGURE 2, the travelling web half
lla comprises serpentine tie units 15a, having convex
prominences that are additionally defined by concave wells
47a disposed therebetween. The wells 47a travel into
contact registration with the cam-like well surface 45a of
folding plate 46a. As the web lla is caused to move over
the top of plate SOa, each of the convex prominences lSa is
discretely caused to be folded ~eriatim under the web lla
on-the-fly, as the respective concave wells 47a are cammed
D-15633 9
~ 1 2 ~
-
(folded under) by surface 45a of folding plate 46a.
After being folded under the web lla, the convergent
shape of plate 50a guides the web lla back into contact with
the similarly converging web llb. ~oth web portions lla and
llb are more clearly shown in their converging relationship
with reference to arrows 16aa and 16bb, as illustrated in
FIGURE 1.
The folded-in ties 15 become permanently folded within
the web 11 as the web is fed under tension to the subsequent
sizing and cutting sections of the manufacture, not shown
here. The web 11 may also be rolled upon a storage drum
(not shown), when the manufacturing operation is performed
on a partitioned or modular basis.
Since other modifications and changes varied to fit
particular operating requirements and environments will be
apparent to those skilled in the art, the invention is not
considered limited to the example chosen for purposes of
disclosure, and covers all changes and modifications which
do not constitute departures from the true spirit and scope
of this invention.
Having thus described the invention, what is desired to
be protected by Letters Patent is presented in the
subsequently appended claims.
D-15633 10