Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2122~96
A Quick--and--slow Sp~ed Screw 13riYe Mech~nism
.
The invention rdates to a novel screw drlve mechanism, especial~ suitable
for use in f~ed drive system between kinematic pair of manual bench vice,
rnachine vioe, screw jack, tail~tack and sl.:ding table of machine toc~l, and
every apparatus using screw drive mechar~sm but in need of quickly passing
over an idle strokc.
I ne appllcant disclosed a novel screw drive mechanism in his patent
application document in China (~o. Cn~1201540. 3, titled by " An
automatically open--and--clGsed no~rel screw drive mochalli~n with rlut in
up--and--down movement" ~ . Sa~d mechanism use~ the up--and--down
rnovement of a half nut relative to a screw to realize quick engagement and
disenga~ement between the nut and screw, and aetain the object for quickly
pas~ing o ~er an idle stroke, sp~edily adjusting a distanoe and improving work
efficiency. In said application document, an up--and--down sleeve is
adopte~ as the mechanism for up--and--down movement. 'l~e curved
surface of a cam on the inner side of left end of said sleeve is in mesh wlth
the cam meshing points on th~ outer circwnference of ~aid half nut to
comp~e a cam pair for controlling the up--and--dowr~ movement d ~aid
hal~ nut, wherein the profile of cam acting as the dslving member is located
on the inner side of up--and--down sleev~ and ehe sharp Tneshing points
actinEç as the driven member are loeated on the b~ttom end of outer
circumference of half nut. This design has the drawb~cks of high proce~ing
c~st and complex structure. F~rthermore, the locking device as mentioned in
said application documen~ also has the problem~ of comple~ i~tructure and ba~
relabity etc.
-- 1--
21220~6
The present invention makes improvements to the afore--mentioned
drawbacks and hlis the ob~ect to provl~le a quick and--alow speed screw
drive mechanism with simple structu~e and easy processing.
According to the lnvention, the afore--mentioned problems are solved asfo11ows. A quick--and--slow speed screw drive mechanism i~ compc~sed of
supporting seat, half nut, up--and ~down sleeve, screw, locking device,
spring and pawl ~ wherein ~upportlng æat has supporting holes on its left and
right ends, as well as two side plates on its two side~ forming a frame
structure, half nut has in its inner hole Inner screw threads not more than
half turn, up--and -down sleeve has pawl device whlch comprises spring
and pawl in its inner hole at right end, and at its left end an up--and --
dow~ plate whieh interacts with the casn profile on the outer ¢ircumf~rence of
half nut. Il~e half nut and the up--and--down slee~e are mounted in an
supporting seat, wh~le thc screw passes through the supporting holes and the
holes Or half nut and up--and--down sleeve within the seat, integrating
them as a whole. ~e invention i9 characterised in that, on the outer surface
of half nut, ~esides therc are guide surface sued for guiding on the lateral
surfaces, from one guide surface to the bottom and to the top of half nut
there are further rise portions of cam profile respectively, while the inner
acting surface of up--and--down plate which interacts with th~ rise and drop
portions of cam pro~ïle on the outer surface of half nut i~ a flat plane or an
inwardly cutved plane.
When the mechar~sm of the invention is on operation, at first, the screw
totates clockwise (or anticlockwise), through the action of the keyway of the
screw with the pawl device, the up--and--down plate of the up--and--
down sleeve is brought into rotation, further through the action of irse
portion of cam profile on the out surface of half nut, the half nut itself is
forced to make upward (or downward) movement, thereby automatically
2122096 C`
~eali~ing ~uick engagement and disengagement between the inner thread of
half nut and the outer t~read of the screw.
The inventlon i9 ~ngenious and c~npact in con3~uction, in addition, the half
nu~ and the up--and--down sleeve are easy to proce~s, thereby the object of
the invention is achieved.
The present invention will be explained in the following by tak~ng bench vice
and screw jacks etc. as embodiment respectively in referenee to the
accompanying drawings. In which,
Fig. 1 illustrating an embodi~ent of bench vice employing the quick--and--
slow speed screw ~irive mechanism ac¢~rding to the invention is a main
sectional view showing the half nut 2 at a rise position, who~e inner thread ls
in mesh with the outer thread of the screw.
Fig. 2 is a sectional view taken fsorn A--A llne in Flg. 1, showing the work
state when the screw 4 rotates clockuise, the up--and--down plate 3. 1
rotates to its lowest position, th~ half nut 2 arises, the inner and outer screwthreads are just in mesh.
Fig. 3 is a sectionsl view also taken from A--A l;ne in Fig. 1, showing the
work state when the screw 4 rotates anticlockwise, the up--and~down plate
3. 1 rotates to the uppermost position, the hal~ nut 2 descend~, the inner and
outer screw threads are in æperation from e~ch other, ~nd the screw can be
pushed or drawn axlally relative to the half nut at wiU.
Fig. 4 is a perspective view of the supportin~ seat 1 in F~g. 1.
Fig. 5 is a perspeceive view of ~he up--and--down sleeve 3 in Fig. 1.
21220~6
c
~g. 6 is a pers~ective ~riew o the half nut 2 in Fig. l.
Fig. 7 is a seel;lonal view taken from B--B line in F~g. 1 showinB the work
state that the inner and outer threads of the up~ d--down sleeve 3 and the
half nut 2 are in mesh as shown i~ Fig. 2, while the eccentric handle 5. 5 is
operated so that the tip of pin 5.1.1. ig ~nserted in the locking hole 3. 4 of
the up--and--down sle~ve 3f in th~s case, in spite of the direction of
rotation of the screw 4, the inner and outèr ærew thread9 always remain in
me~h, the screw 4 has to move with 910w speed.
Fig. 8--1 is a schematic drawing illust~ating the principle of a scissor type
scrcvv jacl~. On~ portion "K" of which is shown in Fi8. ~--II as an assembly
of components of the hlnged shaft 0~
Fi~. 8--II is a main sectional view of an embodiment when the invention is
applied to a scissor type screw jack with quick--and--slow speed l~fting
function. In the ~igure, the inner and outer threads of the half nut 2 and the
screw 4 are just in mesh.
Fig. 9 is a sectional view taken from A--A line in Fig. 8--II showing the
work state when the screw 4 rotates clockwise, the up~and--down plate 3.
1 rotates to the upperma6t position, the inner and outer screw threads are just
in mesh.
Flg. 10 is a sectional view also taken from A--A line in Fig. 8--II showing
the work state when the screw ~ rotates anticlockwise, the up--and--down
plate 3. 1 rotates to the lowest position, thc inneT and outer screw threads arewholly disengagcd, and ~he screw 4 can be pushed or drawn axii ~Iy relative
to the half nut 2 at will.
---- 4
.
2 ~ 2 ~
~ . .
Fig. 11 is a perspective vlew of ~he haLf nut 2' with -~e hin~ed shaft 0~ in
Fig. 8.
Fig. 12 is a drawin8 showing the work state when the pawl 7 in Fig. 10 is
changed from that with bilateral conic surface~ to a one--way pawl 7' in
which one face is set at right angle ar~d the another face is tapered.
Fig. 13 is a main sectional view showing the state when the ~upporting seat 1
is eliminated and a stop pin 12 is used in up--and--down sleeve 3 to prevent
axial sh~ft.
Fig. 14--I is a main sectional view showing the state when a frame 13 with
three holes is used to up- and--down sleeve 3 to prev~nt axial shift.
~ig. 14--II is a perspective view of the frame 13 wlth three holes.
Fig. 1~--III is a sectional view taken from K~K line in Fig. 14
Fig. 15~ a main sectional view of one cm~odiment A of quick--and~
slow speed screw drivc ~nechanigm wlth multi--segmental half nut. By the
latter, the radial forces within the up--and--down sleeve 3A are u~holly
bal~nced.
Fig. i5--TI is a sec~ional view taken from E--E; line m Fig. 15--1, wherein
the inncr and outer scrcw threads are in mesh.
Fig. 15--III is a sectional view also taken from E~E line in Fig. 15--I,
wherein the inner and outer screw thre ds are disengaged. Fig. 16--I is a
perspective view of the supporting seat lA in Fig. 15--I.
2~22~
Flg. 16--II Is a pe~Ye VieW of the up--and--down sleeve 3A ln Flg. 15
--I.
Fig. 16--In ig a ~the view of the half nut 2A in Flg. 15
~ig. 17--I is a main sect~onal view o~ another embodiment }3 of quick--and ,
--slow speed screw drive mechanism with multisegmental hal~ nut.
Fig. 17--II ls a sec~lonal view taken from G--G l}ne ~n F'ig. 17--1, wherein
the inner and outer ærew threads are in mesh. ,
Fig, 17~ s a sectlonal view al~o tak~n f~<~m G--G line.in Fig. 17--1, , ;
wherein the inner and outer screw threads are in seperatian from each other. ; -
Fig. 18--I is a perspective view of the supporting seat 1B in Fig. 17--I.
Fig. 18--II is a perspective view of one segment of half nut 2B' in Flg. 17--
1.
Fig. 18--111 is a perspective view of another segment of half nut 2B in ~'ig.
17--I.
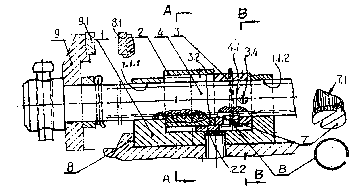
Fig. 1 shows the firs,t embodlment of a bench vi~ employing the screw drive
nnechanism according to the present in~ention which is compo~ed of a
supporting seat 1, a half QUt 2, an up--and--down sleeve 3, a screw 4, a
locking device 5, a spring 6, and a pawl 7, wherein th~ supporting seat 1 has
supporting holes 1. 1. 1 and 1.1. 2 on i~s left and right ends, as well as two
side plates 1. 2 and 1. 3 on its two sides forn~ing a frarne structure, the halfnut 2 has in its inner hole inner screw U~re2ds not more than half turn, the
2 ~ 2 2 ~
up and--down sleeve 3 has pawel device which cornpri~es sprin~ 6 and
pawl 7 in its inner hole ut right end, and at its left end an up--and--down
plate 3. 1 which Interacts with the cam profile on the outer circumference of
half nut 2 9 the half nut 2 and the up--and--down sleeve 3 are mounted on
the supporting seat 1, while the screw 4 pa~es through the supporting holes
1.1.1 and 1. 1. 2 of supporting seat 1 and the holes of h~lf nut 2 and up--
and--down sleeve 3 wi~in the seat, integrating them as a whole. On the
outer surface of half nut 2, besides there are guide surfaces 2. 1 and 2. 4 usedfor guiding on the lateral surfaces, from one guide surface 2. 4 to the bottom
and to the top of half nut 2 ~ there are further r~e portions of cam profile 2.
2 and 2. 3 respectively, while the inner acting surface 3. 2 of up--and--
down plate 3. 1 interacting ~ith the risc and down portions of cam profile on
the outer surface of half nut 2 is a flat plane or an inwardly curved planc.
As shown in Fig. 1, the screw 4 is connected to the movable body 9 of abench vice . the supporting scat i9 fastened on the stationary vice body 8 by.
screw bolts. When the screw 4 rotates clockwise, its keyway 4. 1 hits on the
slope 7. 1 of pawl 7 (see Fig. 7 and Fig. 2), under the action of a ring spring
6, the pawl 7 can stand with a certain amount of torque and brings the up--
and--down--plate 3. 1 of the up--and--down slceve 3 to rotate clockwise,
until it is under the half nut 2 and is hindered by strilcing on the limiting
surface 1. 4 of supporting seat 1. In the meantirne, the screw 4 still rotates
clockwise. the pawl 7 tends to overcome the pres~ure.of ring spring 6, run
out from the keyway 4. i of the screw 4, and continue rotating clockwise.
At the same time, the half nut 2 makes an arising movement under the action
of rise portion of cam proffle 2 2 itself, until th~ lower cam sharp point 2.
2. 1 of the half nut 2 comes into contact with the engagin~ s lrace 3. 2 of thecam on the up--and--down plate 3. 1 of the up--and--down sleeve 3. At
that 1irne, the inner thread of the half nut 2 ~s just in mesh with the outer
thread of the screw 4. So the screw 4 will not only rotate clo~kwise but also
-- 7--
2~22~
~ .
bring the "movable body" 9 of bench vice forward until the work is c~mped
by its ~aws.
For the same reason, when the screw 4 rotates unticl~kwl~, by rneanY ofthe pawl de~ice, the up--and--down plate 3. 1 of the up--and--down .
sleeve 3 also rotates anticlockwise, retreats from the bottom of half nut 2
until it strlkes on the lefe slde plate 2. 1 oP the supporting seat 1. In ~he - ~:
meantime, due to the action of upper rise portion 2. 3 of cam profile of half
nut 2 itself, the half nut 2 is forced to make a downward movement until the p~
inner and ollter screw threads seperate from each other (as shown in ~ig. 3).
At that tlme, the screw 4 can be pushed Ot drawn at will in spite of the half
nut 2 to effect quick openlng or closing of the vice jaws.
ln order that the scrw threads of the half nut 2 and the screw 4 can be self--
locked after engagement, the outer surface of the up--and--down plate 3.1
of the up--and--down sleeve 3 can be made as an arcual face 3. 3 conccntric
with the screw 4 or a small flat face, which ~s in slid~ng fit with the bottom
surface 1. 5 of supporting seat 1. When the screw threads are in mesh, the
symlrKt.ric point of arcual face 3~ 3 or flat face is.hst at the poæition or a
slight over position to bear the bottom part cf the half n~t 2. In ~his rnanner,when the up--and--down plate 3.1 i stressed, it is not llke to slide out of
the bottom part of the half nut 2, therefore a bctter sta~ility exists.
The locking device 5 according to the invention, as shown in Fig. 7,
comprises an insert pin 5. 1, a spring 5. 2, a spring seat 5. 3 and an eccen~ic
handle 5. 5. In which, the insert pin 5.1 has a tip 5. 1. 1 on its front end
and a guiding column 5. 1. 2 at its iniddle part, the spring 5. 2 i9 mo~nted on
a spring seat 5. 3~ snd te eccentric handle 5. 5 is hinged on the ~ail end of
insert pin 5. 1 by a pin 5. 4. The locking device 5 is located on the lateral
surface of the supporting seat 1 at a position corresponding ~o the up--and--
8-- .
2~ 2~6
down sleeve 3, ~hich ha~ a locking hole 3. 4 correspondin8 to the inært pin
tip 6. 1. 1, when the up--and--down plate 3. 1 of the up--and--down
sleeve 3 is brought to the bottom of half nut 2, the locking hole 3. 4 is in
aL~gnment with the pIn tip 5. ~
The principle of said losking device 5 i~ as follows. When it is desired that
the screw ~ should have the function of slow advanse and ~low return, the
eccentric handle 5. 5 is turned to the horizoutal arrow position (as shown in
Fig. 7). At this time, the eccentric handle 5. 5 Is at a position of short a~as
~i. e. the bottom face 5. 5. Z of ecoentric hand~e 5 5 is in contact with the
front end face 5. 3. 1 of spring seat 5. 3) By inserting the insert pin 5.1
into the losking hole 3. 4, the up--and--down plate 3 of the up--and--
dow~ sleeve 3 is l~cked in the p~sition OI enga-glng in the bottom part of half
nut 2 and kee~ the scrcw threads of the scrcw 4 and the half nut 2 in mesh,
thercfore the screw drive mecha~srn remains to maintaln its function of 510w
advance and slow return. When it is desired that the screw 4 should have the
function of quick advance and quick return, the eccentric handle 5. 5 is
turned to the vertical arrow position. At this time, the eccentric handle 5. 5
is at a position of long axis (i. e. the lateral face 5. 5. 1 of eccentric handle
~. 5 is in contact with the front end face 5. 3. 1 of spring seat 5. 3), the pintip 5. 1. 1 is drawn from the locking hole 3. 4, the up--and--down sleeve 3
i9 allowed to rotate and bring the half nut 2 to move upward and downward g
therefore the screw drive mechanism can effect its function of quick advance
and quick return.
Accordin~ to the invcntion, as the rise portion of c~m profile controlling ~he
up--and--do~n movement of the half nu~ 2 Is located on the outer surface
of half nut9 so-the two main pa~ he half nut and the up--and--down
sleeve) are easy to process ~th lower cost. their accuracy is easy to be
con~olled.
r
- 2122096
., .. 1 .
c
..,
:3 ~rom the above, it is seen that the invention i~ compact and reasonable in
construction, with simple structure, easy to process, it tends to improve
. ~ 3 work efficlenc~r and rcduce rnanufacturing e~
Fig. 8 is the second embodiment of the invention when applied to scissor type ~ ~:
screw }ack for a vehicle.
As shown in Fig. 8--I, screw ,~ack is a common llfting apparatus used for
repl~cing a vehicle tire. As is known to all, when the hsnc~1e is turned and
chrough a gear reducer bringing the screw 4 to rotate clockwise or
anticlockwise, by means of a hinged shaft 1 ~cting as a conventional nut)
and four links, the di~tanoe between the two I~inged shafts. 01 and 2 can be
~. changeci, and the upper support 10. 3 can bring a heavy article such as
~ii vehicke W to riæ or drop. If the present invention is used to replace the nut
~ on the hinged shaft 0~ as shown in the block "K" ln Fig. 8, then this part of
hinged shaft 1 becomes the second emb~ment of the invention. The
structural drawings of the put in the block "K" are shown in l;ig. 8--II, 9
and l 0. By comparing thcse three f~gures with Fig. I, 2, 3 and 7 of the first
embodirnent of the invention, it can be se~n that their working principle ~re
substantially the same, especially the structural featuræ of the parts of up--
and--down sleeve, screw, locking device, ring spring and pawl represented
respectively by reference no. 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ~re all consistent, so it needs not
to be described further. The only distinction lies as follows. In Fig. 1, the
c~nter line of the supporting seat 1 and the screw 4 is not movable in vertical
. direction with respect to the vice body, and the half nut 2 can move up and
down freely with respect to the vice body for the screw enga~ement and
disengagement. While in Fig. 8, the half nut 2 ' is not movable in vertical
~: direction with respect to the the half nut 2 ', because on the two sides Of d~
are projected two concentric hinged shaft~ 2 . 7 and 2 . 8 on 0,--0
'~ . 10 -
~)'. '.
'.
- 2122096
(see Fig. 11 ) which are hinged in the link holes of the ~inkes 10. 1 and 10. Z
of the scissQr type screw jack 10, ~herefore they are not movable in vertieal
direction with respect to the jack body 10, and the screw 4 ar~d the supporting
seat 1 under the action of up--and--down sleeve can move upward and
downward with respect to the half nut 2 ' for engagement and disengagement.
The dimensional fit o~ the width B1 and the distance B10 between the inner ~
sides of llnks are movable fit. ~ ;
This novel kinematic combination can realize also automatic engagement and
disengagement between the inner and outcr screw threads. The procedures of
engagement and disengagement are as foUows. When it is desired to lift a
heavy article by the ærew jack 10, the handle 5. 5 is tutned to rotate the
screw 4 clockwise <see Fig. 8 and 9~, through the keyway 4. 1 and the pawl
7 bringing the inner acting face 3. 2 of the up--and--down plate 3.1 of the
up--and--down sleeve 3 to rotate also clockwise about the rise portion of
cam profile 2. 2 on the outer surfacc of the half nut 2' until said inner actlngface 3. 2 comes into contact with the upper flat face 2. 5 of the half nut 2',
as the half nut 2' is not movable in vertical direction, the up--and--down
sleeve 3 is forced to move upward and through the inner hole 3. 5 brings the
screw 4 to swing upward about tho hinged shaft 2 at right end of the screw
jack 10 (see Fig. R--1), thus realking the engagement between the outer
threads of the screw 4 and the inner threads less than half turn on the half
nut 2~.
By the same reason, when it is desired to drop the screw iack 10, it needs
only to turn the handle 5. 5, making the screw 4 to rotate anticlockwisc as
shown in Fig. 10. then the up--and--down sleeve 3 rotates anticlockwise
with ~he screw 4 under the action of the pawl device, moves downward under
the action of the lower cam profile ~. 3, and brings the screw 4 and the
supporting seat 1 to move together downward relative to the half nut 2'
21 22096 ~-~
(actually the screw 4 swin~s downward about the fulcrum of hinged shaft 2
of sc~ew jack 10), thus realizing the disengagement between thc inner and
outer screw threads. In the meantime, the screw 4 can quickly and freely
nx>ve in axial direction rel~tive to the half nut 2 . If there h a heavy articleon the upper support 10. 3 of the screw jack 10, then the heavy article can
drop quickly. If there is no such load, then the upper support 10. 3 will rise
automatically under the upward actlon of a plate spring 11, and makes the
distance between the two hinged shafts 0~ and 2 shorter. If the upper
support 10. 3 is pres9ed down by hand (or foot) to overcome the opening
forcc of the plate spring 11, then the distance between 0~ and 2 increases
again, thus realizing qslick rise and quick drop of the upper support 10. 3 of
screw jack ~0, attaining the object for quickly passing over idle stroke and
improving work efficiency.
According to the work requirement, in case the screw 3ack is only allowable
to bc operated with slow speed, it nees3s only to operate the arrow handle 5.
5 of the locking device 5 and allow the pin tip 5. 1. 1 inserted into the locking
hole 3. 4 of the up--and--down sleeve 3 as shown in Fig. 8--II. On the
revcrse, if the handle 5. 5 of the locking device 5 is operated so that the
arrow is in horizontal position, and the pin tip 5. 1. 1 is drawn out from the
locking hole 3. 4, the function of quick rise and quick drop can be restored.
ln some cases, the screw jack used necds not possessing the function of slow
drop, such as that used as convient tool for replacing the tire of a light car,
arter the car is llfted and replaced with new tire, the car i9 allowed to drop
instantly, since the car can be buffered by its leaf--spring suspension and its
tire. In that case, the locking device 5 shown in Fig. 8 can be eliminated.
Besides, the pawl 7 shown in Fig. 10 can be changed in shapc, its double
tapered faces which is in contact with the keyway 4. 1 of the sctew 4 can be
simplified to single tapered face, with one tapered face changed into vertical
face as the one--w8y pawl 7' shown in Fig. 12. In this rnanner, when the
2122~6 c ~ ~
screw 4 rotates anticlockwi~e, by means of the keyway 4. 1 and the vertical
face of one--way pawl 7', the up--and--doum sleeve 3 is forced to rotate
anticl~kwise about the upper and lower ci~n profiles in an iamount of about
18~ at maxim~m, the screw 4 i9 broughe into downward movement iand the
inner and outer screw thread9 9eperate quickly, the ~crew jack c21n be taken
away Instantly. This i9 that the car drivers desired, the con~entional screw
jack is that heavy load n the mechaT~ically driven screw j,ack can not drop
quickly . now this drawback is overcome.
If the screw jack shown in Fig. 8--I belongs to a light type, the screw 4 is
subjected to a smaller load, in this casc, another variant d the embodiment
can be used, i. c. the supporting seat 1 shown in Fi~. 8--Il is elLminated and
a shift preventing device of the up--and--d~wn sleeve 3 is added as shown in
Fig. 13. Said quick acting screw drive mect~nism is comp,osed of up--and--
down sleeve 3, pawl 7, ring spring 6, half nut 2' with hingcd shaft, and
shlft preventing device of up--and--down sleeve 3. 'Ille dimension of the
outside diameter d3 of the up--and--down sleeve 3 and the distance between
the inner sidesi of the, links B10 o~ screw jack sre in slidlng fit.
: .
There are many types of shift preventing device. That shown in Fig. 13 is
composed of a ~top pin 12 and a l~niting groove 2'. 9. The stop pin 12 i9
mounted on the up--and--down plate 3.1 of the up--and--down sleeve 3
(by means of screw joining, welding, or riveting etc. ),? corresponding to
this, a lin~iting groove 2'. 9 is machined on the half nut 2'. Said groove is inmovabile fit with the tail end guiding column 12. 1 of the stop pin 12. The
outside diarneter d3 of the up--and--down sleeve 3 and the corresponding
matching dimension of the carrier B10 are in movable fit. The working
principle is the same as Fig. 9 and IO, it is unneces~ary to go into details.
Fig. 14 shows anothcr type of shift prevent device which comprlses a frame
- 13
212209 6
with three holes, two of the holes 13. 1 and 13. Z on the left and right side
phtes are in movabb fit with the two hinged shaft 2. 7 and 2. 8 of the hdf
nut 2 respectively, and another hole 13. 3 in which the sc~ew 4 passes
througb. ~e two end facOEs 3. 6 and 3. 7 of the up--a}ld--down sleeve 3 are
fltted between th0 right end face 2 . 9 of the half nut 2' and the inner end
face 13. 4 of the frame with three holes so that the two end faces 3. 6 and 3.
7 can not make an axial shift with the screw 4. The dImension of outside
diameter d3 of ehe up--and--down sleeve 3 and the distance B13 between
two side plates of the frame with three holes are in movable fit to assure that
the screw 4 and the half nut 2 are on the same center line. The working
principle is the same as Fig. 9 and 10, it is unnecessary to repeat again.
There are many methoas to ~in the hinge type half nut 2' (as shown in Fig
8, 13, 14) with its employing carrier (such as scissor type screw jack,
bench vice, machine vice etc. ), besides the hinged shaft, other joining type
such as key, screw, pin, boss, recess, stop block etc. can be used according
to requirement.
The quick--and--slow speed screw drive rnechanisms shown in Fig. 15 to 18
are equipped with multi--segmental half nuts, which are derived from th~t
shown in Fig. 1 by the way that a single halt nut is changd into tWQ half nuts
opposite to each other and semrnetric to the screw axis ~or several half nuts
uniforrnly dlstributed). Its advantage lies in that after adopting thls type of
rnult--sygmental half nut, the radial force components acting on the screw
by the half nut can be balanced with the up--and--down sleeve, it needs not
through the screw transmitting to the supporting seat and getting balance
there, so the friction between the screw and the supporting holes can be
reduced.
Said screw drive mechanism with multi~segrnental haLf nuts i9 characterised
:'
'
~- 2122~96
in that, the screw is supported by the supporting seat, there are æveral (at
lea9t two~ half nuts surrounding ~he screw, the half nut~ are located between `~
;~! the supporting seat and the up--and--down sleeve, the half nuts are
provided with auto~tically up--and--do~n (open--and--dose~ device and
the up--and--down sleeve is provided with shift preventing devioe to prevent
¦ any shift along the axis of screw.
~1 .
,i Said screw dri~e mechanism comprises the following structure
' ~!. i
,'..ii
Supporting seat has supporting arm, supporting hole correspondingly, seat
body, and up--and--down guiding members to match with up and--down
guiding faces of multi--segmental half nuts, the screw passes through the
supporting holes in rnovable fit and rnatches with the half nuts and the up--
and--down de-~ice. In case thcre arc two supporting arms, then s~ift
~`I preventing device for thé up--and--down sleeve is a~so provided.
,~ .
Multi--segmental ha~f nuts (at least two) are arranged surrounding the screw
and symmetric to the screw axls. The half nuts have inner screw threads less
than half turn, guiding device for up--and--down movement, and up--and
--down acting member to transmit the force for that movenlent.
Up--and--down device which controls the automatic synchronous opening
and closing of the n~ulti--segmental half nut~ is equipped with up--and--
down acting device, overload ciutcl~ng device ~such as paw~, ring spTing~
and risë limitlng device.
'',
Locking device makes the screw to poss~s the function of advance and return
with quick and slow speeds.
~3 Fig. 15 and 16 show one embodiment A of the cluick--and--slow sp~d
~`;'1
"` '''1
$~,i
, ;:1
''1. ' , :
.,; ~
.
,:j .,
.,,; .
- 2122~96
;-- .
screw drive mechanism with multi--segmer~tal half nuts, which is composed
of a supporting seElt lA, the upper ~d lower two half ~uts 2A and 2A', ~n
expanding plate spring 14. an up--and--down sleeve 3A, a pawl device 7
and a screw 4, the scrcw 4 passes through the supporting holes lA. 5 and an
inner hole 3A. 1 of the up--and--down sleeve 3 ~s~e Fig. 16). The outer
lateral faces 2A. 2, 2A'. 2 and 2A. 3, 2A'. 3 at the left half por,tion of the
two h~lf nuts 2A and 2A ' are in movable fit with the Inrler guidlng faces 1A.
3 and lA. 4 of the supporting seat lA, while thc right half portion of the two
half nuts 2A and 2A ' are mounted within the large hole on the left end of the
up--and--down sleeve 3, said large hole is an inner curved cam whose
profile is composed of two symmctric segrncnts of inner arcs 3A. 2, 3A. 3 for
the rise portion of the cam, two SeglTlents of inner arcs 3A. 4 with the
minimum radius Rmtn and two segments of inner arcs 3A. 5 with the
maximurn radius R~ The expanding plate spring 14 mounted in the grooves
2A. 4 and 2A'. ~1 of ,the upper and lower two half nuts 2A and 2A ' forces the
upper and lower two halE nuts 2A and 2A ' to seperate rrom each other so that
the highest points of outer arc 2A. 5 and ZA'. 5 always firmly press on the
inner curved cam surface of the up--and--down sleeve 3A. W'hen the up--
and--down sleeve 3A rotates clockwise or anticlockwise with the screw 4
under the action of pawl 7 and ring spring 6, the inner curved cam profile
will simultaneously bring the upper and the lower two half nuts 2A, 2A' to
rnake up--and--down Copen and close) movement relative to the screw
axis, thus realizing thc cngagcmcnt (or disengagement) between the inner
threads 2A. 6 of the half nuts and the outer threads 4. 3~of the screw. Fig. 15
--II shows the work state when the inner and outer screw threads are in
mcsh. Fig. 15--III shows the work state when thc innor and outer screw
threads seperate from each other. In order that the engagement and
disengagement can be taken at an accurate position, the positionin~ pins 15,
1~- are provided. Furthermore. a locking device 5 is provided on the up-- -
and--down sleeve 3A which comprise~ a locking hole 3A. 4. The work~ng
--16--~ ~ :
'
: :
,,:,~j
f~ :
2l22a~
',~,,j principle is the same as Flg. 7 and the section D--D in Fig. 15--I which
illustrates the lock~ng device i~ the same as Fig. 7, so the sectional view taken
from D--D line i9 neglected, not to be repeat0d again.
,
Fig. 17 and 18 show the another embodiment B of said screw drive
mechaniYm with multi--se~nental half nuts, which i9 compa6ed oi~ a
3si supporting seat lB, the ~lpper and lower ~wo half nuts 2B, ?B', an up--and
--down sleeve 3B, two guiding pins 16, 16' for end face cam, a shift
prcventing stop ring 17 of the up--and--down sleeve 3B, and a positioning
pin 15B. The joinin~ method between the' supporting seat 1B and the
employing carrier (such a~ a screw jack) is a hlnged shaft such as IB. 1.
thcre is only o,ne supporting hole lB. Z in movable fit' with the screw 4, and
two guide sur~ces lB. 3 and lB. 4 aro provi~ed on the supporting seat 1 to be
,j'. in sliding fit with the two half nuts 2B and 2B'. Besides the pawl 7, the ring
spring 6, the, inner hole 3B. 1 in movable fit with the screw 4, the locking
hole 3A. 4 for quick--and--slow speed, the limitlng pin 15B arid the inner
curved carn profile (with maximum radius Rm~X and minimum radius R0~n ) in
engagement with the highest points 2Bl, 2B'1 of outer curve of the two half
nuts 2B. 1 and 2B~. 1, all those with the same structure ag that in the
embodiment A of Fig. 15 are provided on the up--and--down sleeve 3B,
there are further prQ~vided an axial shlft preventing stop ring 17 which is in
fit with the left end face lB. 5 of the supporting seat lB. 5 and two gwding
pins 16 and 16' for cams with end face formed grooves. Sa~d guiding plns
: are mounted on the inner side face 3B. 2 of thc up--and--do~,vn sleeve 3B
and are in engagement tespectively with the two end face formed cam grooves
2B. 2, 2B'. 2 on the two half nuts 2B and. 2B'. The function is the same as
the expanding plate spring 14 of the embodimcnt A shown in Fig. 15. When
the screw 4 rotate~ anticlockwise and brings the up--and--down sleeve 3B
,~ and guiding pins 16, 16'also to rotate anticlockw~se through the action of a
`~,'.j pawl device, then the guiding pins 16. 16' eneer into the end face ~ormed
- 17-
,;
!I,
. :
;' '11
2122~9~
~arn grooves 2B. 3 and 2B. 3, press on the outer circu}nferentia~ inner
curved cam profi~es 2B. 3, and force the two half nuts 2B and 2B to go out
frorn the center, thus realizing the diseng~gement betweerl the inner and
outer screw threads 2B. 6 and 4. 3. From the above, it is ~een that thc
embodirnent B is derived from the embodirnent A only by change of some
parts, this change basically belongs to an eqiuvalent transformat;on, so the
working procedures and work principles of the two embodimen~s are
substantically the same, it needs not to go in details.
There are many types of the eqiuvalent transforrnation of parts. For
example, when the load to be taken is smaller, the inner curved cam profiles
of the up--and--down sleeve 3B can be eliminated, instead, the guiding pins
16, 16 and the end face formed cam grooves on the half nuts 2B, 2B' can
be used. By prop~rly selecting the clearance of fit between the guiding pins
16. 16'and the inncr circumfcrential curved cam profiles 2B. 4 and 2B'. 4,
when the screw 4 and the up--and--down sleeve 3B rotate dockwise, the
guiding pins 16, 16 also rotate in that direction and enter into the end face
formed cam grooves, press on the inner circumferential curvcd cam profiles
2B. 4 and 2B'. 4, force the two half nuts 2B and 2B' to move inward toward
the screw center simultaneously, thus realizing the en8agernent between the
inner and outer screw threads. Other alike eqiuvalent dc~ices are numerous
such as if the width of the half nut is shortened, then three or four half nuts
can be uniformly distributed etc., lt needs not to~ enurnerate one by one, all
t~ese based on the same basic principle should be considered to be within the
protection scope of the present invention.
~ '
: '
--18--