Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~13~17
TITLE OF THE INVENTION
Tube AssemblY for Housing a Multistage Telescopic
Antenna for a Vehicle
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a tube assemblY for
housing a multistage telescopic antenna for a vehicle, and
more ParticularlY, to a tube assemblY for housing a vehicle
antenna having its waterproof property improved.
A vehicle antenna is usuallY constructed as having a
plurality of antenna rods fitted within one another in a
telescopic relation. The central rod of the antenna is
connected with a driving cord having a number of rack teeth
which are adaPted to engage with a driving gear. The
plurality of antenna rods together constitute an antenna
element which maY thus be operated to extend or retract in a
telescoPic manner through the movement of the driving cord.
Japanese UtilitY Model ApPlication Laid-open 1-100508 has
disclosed a vehicle antenna having a structure as shown in
Fig. 5. Referring to Fig. 5, a plurality of antenna rods
11, 12 and 13 are slidably connected with one another in a
telescopic relation and are housed in an outer tube 30 which
is vertically provided on a housing 20. The central rod 11
is connected with a driving cord 14 which is adapted to render
an antenna element 10 including the rods 11 - 13 to extend or
retract in a telescoPic manner.
The housing 20 contains a driving gear 21 engaging with
2 ;~ ~
rack teeth 15 formed on the driving cord 14. The antenna
.
element lO is caused to extend or retract through the movement
of the driving cord 14 into and out of the housing 20. At
this time, the driving cord 14 is pressed by a pressing roller
22 against the driving gear 21, thereby maintaining an
engagement of the rack teeth 15 with the driving gear 21.
The driving gear 21 itself is rotated by a driving Power
from an electric motor 40 contained with a motor bonnet 41.
Namely, an outPut Power of the motor 40 is transmitted to the
driving gear 21 through a worm 42,a worm wheel 43, and a
decelerating gear train 44. In Fig. 5, a reference numeral
45 represents a counter gear.
The driving cord 14, after being dragged into the housing
through the rotation of the driving gear 21, will be
disengaged from the driving gear 21 and be guided by a guide
member 23 to move towards and into a receiving drum 24.
The receiving drum 24 is a free drum provided coaxially with
the driving gear 21. Further, another guide member 25 is
provided in the receiving drum 24 to further guide the driving
cord 14 moved hereto.
However, a vehicle antenna as described above has a
severe Problem of rain water invasion. That is, rain water
is easy to flow along the driving cord 14 into the housing 20.
In order to solve such problem, there have been proposed manY
ideas trying to provide a kind of improved connecting means
and a kind of improved insertion condition for each antenna
lt~
rod, so as to obtain a higher waterproof property for a
vehicle antenna. Nevertheless, the present situation is
that it is still impossible to completely Prevent rain water
invasion.
Another suggestion to solve the rain water invasion is to
provide a drain hole at a lower portion of the housing 20,
trying to enable the rain water entered in the housing 20 to
flow away through the drain hole. However, whenever there is
a heavY rain shower which usuallY results in a severe water
invasion into the housing 20, it is difficult to drain off the
entered rain water as immediatelY as is required. As a
result, the rain water entered in the housing 20 is aPt to
flow up into the outer tube 30. Moreover, the rain water
flows from outside through gaPs between antenna rods 11 - 13
into a space formed between the outer tube 30 and an
insulating sleeve 31. In addition, rain water is easy to
flow down the antenna rods 11 - 13 into the same space between
the outer tube 30 and the insulating sleeve 31.
In the above-discussed conventional vehicle antenna, the
outer tube 30 is usuallY made of aluminium or an aluminium
alloy so as to render an antenna structure light in weight and
obtain a good corrosion resistance. However, after such an
outer tube 30 has been exPosed to rain water, a corroding
phenomena such as pitting corrosion is apt to occur on the
surface thereof. Consequently, many fine holes resulting
from the pitting corrosion are formed thereon, the outer tube
2 1 3 ~ ~ 1 7
can no longer be used for a vehicle antenna. The corrosion
problem is particularly severe when the outer tube is
exposed to an acid rain caused by increasingly deteriorating
environment.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
An object of the present invention is to provide a tube
assembly for housing a multistage telescopic antenna for a
vehicle, in which rain water invasion can be effectively
prevented and corrosion resistance has been improved.
According to the present invention, there is provided
a tube assembly for housing a multistage telescopic antenna
for a vehicle. The tube assembly of the present invention
comprises an outer tube for housing a multistage telescopic
antenna, an insulating sleeve inserted in the outer tube, an
electrically conductive sleeve inserted in the outer tube,
first sealing means for sealing an upper end portion and a
lower end portion of an annular space formed between the
insulating sleeve and the outer tube, second sealing means
for sealing an upper end portion of an annular space formed
between the electrically conductive sleeve and the outer
tube, and a stopper member provided at a lower end portion
of the annular space formed between the insulating sleeve
and the outer tube. The annular space formed between the
insulating sleeve and outer tube is sealed at the lower end
portion thereof further by the stopper member whose inner
surface is pressed by a rubber ring member provided adjacent
to the lower end of the insulating sleeve.
~ .
,~
~ .
~ 1 3 ~ ~ 1! 7
In an aspect of the present invention, the first
sealing means includes said rubber ring member provided on
the outer periphery surface of the insulating sleeve
adjacent to the lower end thereof and another rubber ring
member provided on the outer periphery surface of the
insulating sleeve adjacent to the upper end thereof. The
second sealing means includes a sealing ring member mounted
on the upper end of the electrically conductive sleeve.
The other objects and features of this invention will
become understood from the following descriptions with
reference to the accompanying drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
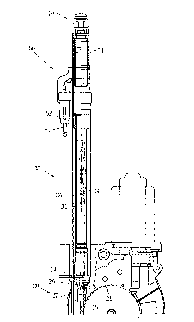
Fig. 1 is a schematic view showing a vehicle antenna in
which a tube assembly of the present invention is applied.
Fig. 2 is an exploded cross sectional view showing an
internal structure of the tube assembly of the present
invention.
Figs. 3a and 3b are front and bottom views respectively
showing a stopper member of the tube assembly of the present
invention.
Fig. 4 is a cross sectional view showing an assembled
condition of the tube assembly of the present invention.
Fig. 5 is a schematic view showing a conventional
vehicle antenna.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
In the drawings from Fig. 1 to Fig. 4 the same items
as those in Fig. 5 are represented by the same reference
numberals.
R~- Referring to Fig. 1, an outer tube 30 of a tub assembly
-5-
of the Present invention is verticallY Provided on a housing
20 as in a conventional vehicle antenna. A feeding section
50 is inserted in the outer tube 30 so as to become conductive
with an antenna element 10. The feeding section 50 has a
terminal 51 and a terminal 52 which are respectively connected
to a core conductor and an external conductor of a coaxial
cable.
The terminal 51 is electrically connected to an antenna
element 10 through a terminal 53 projectively formed on the
inner periphery surface of the outer tube 30 and through an
electrically conductive sleeve 54, as shown in Fig. 2.
Another terminal 52 is earthed through the outer tube 30.
Referring to Fig. 2, the electrically conductive sleeve 54 has
a lower end portion of a smaller diameter which is formed with
a notch (not shown). Such lower end portion of the
electrically conductive sleeve 54 serves to Position a
starting point for an antenna rod 13. In order to form a
complete feeding system for the vehicle antenna, a leaf spring
(not shown) connected to the coaxial cable ( serving as a
feeding cable ) is introduced into the electricallY
conductive sleeve 54 through said notch formed thereon, so as
to become contacted with the antenna rod 13.
Referring to Figs. 1 and 2, an insulating sleeve 31 is
inserted in the outer tube 30 to form an insulation between
the outer tube 30 and the antenna element 10. The
insulating sleeve 31 comprises a sleeve body 31a made of a
2131217
synthetic resin, a rubber ring member 31b Provided on the
outer periphery surface of the sleeve adjacent to the upper
end thereof and another rubber ring member 31c provided on the
outer periPherY surface of the sleeve adjacent to the lower
end thereof. The rubber ring members 31b and 31c together
constitute a first sealing means. Each of the rubber rings
members 31b and 31c has a plurality of small projections 31d
formed integrallY and circumferentiallY on the outer peripherY
surface thereof. Such small Proiections 31d Possess an
excellent waterProof ProPertY so that a rubber ring member as
a whole acts as a good packing.
The insulating sleeve 31 has an aPProPriate length such
that when it is inserted into the outer tube 30 the rubber
ring member 31b presses against an insulating layer 30a formed
on the inner surface of the outer tube 30. Accordingly, a
possible gap between the outer tube 30 and the insulating
sleeve 31 may be sealed bY the rubber ring member 31b so as to
prevent rain water invasion into the space formed between the
insulating sleeve 31 and the outer tube 30.
Further referring to Fig. 2, the insulating layer 30a has
a flange portion 30b formed at the upPer end thereof, which is
adapted to engage with the upper end face of the outer tube
30. Alternatively, an electricallY conductive resin may be
utilized to form a layer on the inner surface of the outer
tube 30, instead of using the insulating layer 30a and the
terminal 53 . In such a case, the electrically conductive
~ 1 3 ~
resin layer should be formed in a manner such that it is
insulated through proper means from the outer tube 30 and
conducted with the terminal 51.
The electricallY conductive sleeve 54, into which the
antenna element 10 is to be inserted, is Provided with a
sealing ring member 32 named herewith as a second sealing
means and mounted on the upper end portion thereof. The
sealing ring member 32 has a flange Portion 32a which is
adapted to engage with and Press against the flange Portion
30b of the insulating layer 30a when the electrically
conductive sleeve 54 is inserted in the outer tube 30, as
shown in Fig. 4.
Further, the outer tube 30 has a male screw Portion 30c
formed on the outer periphery surface of the outer tube
adiacent to the upper end thereof. The male screw portion
30c is formed so as to engage with a female screw portion 33a
formed on the inner peripherY surface of a cap member 33.
When the cap member 33 is screwed onto the outer tube 30 with
the electrically conductive sleeve 54 inserted in the outer
tube 30, an annular tightening portion 33b formed on the inner
periphery surface of the cap member 33 Presses on the flange
portion 32a of the sealing ring member 32, which in turn
presses against the flange portion 30b of the insulating layer
30a. Therefore, a possible gap is completely prevented which
otherwise is apt to occur between the outer tube 30 and the
electrically conductive sleeve 54, thereby preventing rain
water invasion.
The insulating sleeve 31 has a diameter smaller than that
of the outer tube 30. Thus, an annular space 34 as shown in
Figs. 1 and 4 is formed between the insulating sleeve 31 and
the outer tube 30 after the former is inserted in the later.
Such annular space 34 is sealed at the upper end portion
thereof bY the rubber ring member 31b Pressing against the
inner surface of the insulating layer 30a, and is sealed at
lower end Portion thereof by a stopper member 35 and the
rubber ring 31c Pressing against the inner surface of the
stopper member 35.
Referring to Figs. 3a and 3b, the stopper member 35 has a
cYlindrical bodY 35a, a flange portion 35b, an annular recess
35c and a plurality of guide elements 35d. The guide
elements 35d are arranged in directions toward the central
axis of the stoPPer member 35, as shown in Fig. 3b. A
space 35e is formed surrounded bY the guide elements 35d.
The space 35e serves as a guide hole to guide a driving cord
14 when it is raised up or lowered down along the tube
assemblY. Further, the stoPPer member 35 has an annular
inner tightening portion 35f formed on the inner surface
thereof.
In addition, the stopper member 35 has an 0-shaped ring
36 engaged in the annular recess 35c thereof. When the
outer tube 30 with the antenna element 10 contained therein is
inserted into the housing 20, the 0-shaPed ring 36 acts to
seal a possible gaP formed between the outer wall of the
stopper member 35 and the inner wall of an insertion recess 26
formed in the housing 20, as shown in Figs. 1 and 4.
Preferably, the insertion recess 26 is tapered on the inner
wall thereof. BY using the guide elements 35d which also
constitute a tapered face, such tapered inner wall of the
insertion recess 26 not only facilitates the positioning of
the outer tube 30 in it, but also improves the sealing effect
of 0-shaped ring 36.
Under the central bottom of the insertion recess 26,
there is formed an insertion hole 27, as shown in Fig. 1.
The driving cord 14 connected with the antenna rod 11 of the
antenna element 10 passes through the insertion hole 27 into
the housing 20, so that rack teeth 15 become engaged with a
driving gear 21. The movements of the driving cord 14 into
the housing 20 and out therefrom using the driving gear 21 are
similar to those in a conventional vehicle antenna as
described above with reference to Fig. 5.
After the insulating sleeve 31 and the electrically
conductive sleeve 54 are successively inserted in the outer
tube 30, the annular space 34 formed between the outer tube 30
and the insulating sleeve 31 may be sealed at upper and lower
portions thereof, as shown in Fig. 4.
Namely, the uPPer end Portion of the annular space 34
formed between the insulating sleeve 31 and the outer tube 30
is sealed bY the rubber ring member 31b with the small
--1 0--
projections 31d thereof Pressing against the insulating laYer
30a. Further, an annular sPace formed between the
electrically conductive sleeve 54 and the outer tube 30 is
sealed bY the sealing ring member 32 mounted on the upper end
of the electrically conductive sleeve 54 and pressing against
the uPPer end face of the outer tube 30 through the flange
portion 30b of the insulating layer 30a. AccordinglY, it
is impossible for rain water flowing along the antenna element
10 to reach the inner surface of the outer tube 30.
The lower portion of the annular space 34 is sealed by
the rubber ring member 31c Provided on the outer periphery
surface of the insulating sleeve 31 and pressing against the
inner surface of the stopPer member 35, further bY the stopper
member 35 with the flange portion 35b thereof Pressing against
the lower end face of the outer tube 30. Accordingly, it is
impossible for rain water to reach the inner surface of the
outer tube 30 even if the rain water flows up with the rising
of the driving cord 14 or the rain water flows up back from
the housing 20.
Since the inner surface of the outer tube 30 is protected
from being contacted with water, the tube itself can be used
for a comparatively longer period. The tube assembly of the
present invention, having a waterproof structure as described
above in this Preferred embodiment, is particularly suitable
for use in an area where an environment problem such as acid
rain is still existing.
2 1 ~
While the presently preferred embodiment of the present
invention has been shown and described above, it is to be
understood that this disclosure is onlY for the Purpose of
illustration and that various changes and modifications may be
made without departing from the scope of the invention as set
forth in the appended claims.
-12-