Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
21AoOgg
,,
This invention relates to paving blocks for covering the
ground, ~loor, and like surfaces and, more specifically, to a
paving block, pentagonal in shape, which performs functions of
existing paving blocks, but which additionally allows a multitude
of modifiable pentagon and square paving block combinations with
the use of only two different paving blocks.
The concept of utilizing paving blocks-or pavers for covering
the ground or like surfaces is known. U.S. Patent No. 474,339,
issued to Graham, discloses a paving block or building block of
polygonal profile, relating to street and sidewalk pavements.
Paving blocks utilizing basic square or rectangular shapes have
long existed. A multitude of prior art exists directed to paving
blocks or ground covering elements of more complex dimensions.
U.S. Patent No. 3,494,2~6, issued to Baumberger, discloses a paving
stone having complementary concave and convex sides. U.S. Patent
No. 4,544,305, issued to Hair, discloses an interlocking slab
element comprising a main hexagonal section with one or more
attached tail sections which may be aligned in a variety of
configurations. U.S. Patent No. 5,173,003, also issued to Hair, is
likewise directed to a paving stone or slab element having a
hexagonal section and a square section. U.S. Patent No. 4,128,357,
issued to Barth, discloses a ground covering slab element comprised
of an octagonal head portion and a square or circular stem portion.
U.S. Patent No. 4,711,599, issued to Glickman, discloses a six-
sided paving block in a "chevron" shape. U.S. Patent No.
_ 2~40099
5,108,219, issued to Hair, discloses an interlocking paving block
having a twelve-sided main section and an eight-sided tail section.
U.S. Patent No. 5,054,957, issuëd to Johnson, II, discloses another
multi-sided paving block which provides paving in the way of
adjacent like blocks laid in various patterns. The above-
referenced prior art is generally directed to continual patterns of
the same paver or slab elements, albeit a variety of patterns may
be available with a single block.
The use of a general pentagonal shape in block construction
for ground covering, floor covering, or like surfaces is also
known. Great Britain Patent No. 209,316, issued to Wettern,
discloses a pentagonal block utilized to ~edge~ pavement comprised
of diagonally disposed rectangular homogeneous elements. European
Patent Office Patent No. 0415093Al, issued to Funfeck-Stein,
discloses a pentagonal paving element having 2 longer side
dimensions and three shorter side dimensions for use both in
patterns of homogeneous elements and in patterns with interspersed
squares and rectangles.
While all of the referenced prior art relates, in some
respect, to polygonal paving blocks, tiles or pavers, for the most
part, all of said inventions are directed primarily towards
arrangements of homogeneous elements of the respective invention.
To the extent that said referenced prior art discloses a pentagonal
block used in combination with other shapes, the pentagonal blocks
are utilized solely to create a linear edge to the paving pattern,
as in the Wettern patent, or require a minimum of three paver
214009g
dimensions to complete a paving pattern, as in the Funfeck-Stein
patent.
Paving blocks or elements such as those disclosed in the
referenced prior art are often used in the construction of
roadways, sidewalks, patios, decks, floors, embankments,and other
like uses. They are typically chosen over monolithic-type slabs
for durability, aesthetic, quality, pattern variety and ease of
installation replacement and pattern modification.
The referenced prior art and its progeny have each been able
to address these various qualities with varying degrees of success,
but none have been able to satisfactorily address all of the
qualities in an optimum manner.
Existing paving blocks or elements may be generally grouped
into two categories. These are, on the one hand, paving blocks
which allow a linear edge to the paving pattern and, on the other
hand, those that require cutting of elements or special pieces to
create a linear edge.
While paving blocks which are square or rectangular in shape
have long been known to supply a linear pattern edge, they lack
significantly in the areas of aesthetic quality and pattern
variety. The more complex paving blocks, such as those shown in
the referenced prior art, provide great advantage in the areas of
aesthetics and pattern variety, but, because of the variety of
sizes and shapes required to obtain a linear pattern edge, often
this advantage comes at the expense of installation economy.
-
2~4~099
Additionally, the referenced prior art paving blocks or
elements require selection of a pre-set pattern which may not be
significantly deviated from.
Additionally, in the field of ceramic tile, a configuration is
known which is often categorized as "pentagon and dot." In this
configuration, combinations of four pentagonal tiles having two
longer sides at right angles to each other and three shorter sides,
one of which opposes the right angle, surround a square tile whose
exterior side dimensions equal the length of the opposing shorter
sides of the pentagons. This design does not allow
interchangability of the square tile used as the "dot" and square
tiles which may be used to separate the groups of pentagons.
The interchangability of the ~Idot~l and square tiles is a critical
consideration in manufacturing. The manufacturer incurs
considerable expense in making the molds for each individual paving
block or tile. Any innovation in the field which allows a lesser
number of different size units to be utilized in any pattern will
result in significant cost savings and commercial advantage to the
manufacturer. Further, "pentagon and dot" has limited application
in paving block applications laid over a sand base, because the
difference in size of the pentagonal and square tiles does not
facilitate uniform compaction and resistance to loads.
Accordingly, a need exists for a paving block for covering the
ground, floor, or like surfaces, which provides for ease in
installation by providing a linear pattern edge, but which also
addresses aesthetic considerations and ease of installation,
CA 2 1 4 0099
replacement and modification. Specifically, what is needed is
a complex paving block, capable of being used in homogeneous
patterns, in the same manner as the referenced prior art, but
which may also be used in combination with no more than one
additional shape and size of block to create patterns which
have linear edges, without the need of cutting, and which
patterns may be irregular or regular and may be modified
during or after initial installation.
This invention is directed to provision of a paving block
for covering ground, floor and like surfaces which will permit
aesthetic designs and ease of installation, replacement and
modification.
More specifically, this invention is directed to
provision of a pentagonal paving block which may be used in
combination with a square paving block to provide patterns
which have linear edges without the need of cutting or
providing additional specially sized paving blocks. The
invention also provides a paving block which is adaptable to
homogeneous patterns as is currently known.
According to the invention, a paving block is pentagonal
in shape with three longer sides, two of which are at a right
angle to each other and the third of which opposes said right
angle. The pentagonal block has a flat upper surface and
lower surface with vertical side surfaces at each of the five
sides of the pentagon. In one embodiment of the invention,
CA2 1 4009q
the three longer sides are essentially equal and two shorter
sides are essentially equal. The two shorter sides are each
joined to one of the adjacent longer sides at a 90~ internal
angle and are each, in turn, joined to the third longer side
at a 135~ angle.
A combination of four pentagonal paving blocks
constructed according to the invention can surround a square
paving block so that the exterior perimeter of the four
pentagonal blocks is a square and the blocks are
interchangeable with four square paving blocks, each of which
is equal in dimension to the surrounded square paving block.
The paving block described herein may be used in
combination with only one additional size and shape of block
- to create patterns which have linear edges and which patterns
may be regular or irregular and may be modified during or
after initial installation. The pentagons and squares which
may be used are similar in size, sufficient to allow for
uniform compaction and load resistance when in place.
Spacer bars may be utilized on the vertical side
surface of the paving block to assure proper spacing
between stones. When spacer bars are utilized, the length
of the opposing longer side of the pentagonal
-- 6
2~40099
block may be increased slightly, but not more than 10%, sufficient
to allow four pentagonal blocks with spacers to form a square the
sides of which equal two times the length of one of the longer
sides plus the width of a spacer bar, so as to permit a square
block, each side of which equals one of the longer adjacent sides
of the pentagon! to be snugly placed in the middle of said four
pentagonal blocks.
According to a further feature of the-invention, the paving
block may be utilized in patterns for ground, floor or like
surfaces covering wherein a combination of the paving blocks and
other blocks are placed leaving a uniform space between the
adjacent vertical side surfaces of the paving blocks and the other
blocks utilized in the pattern. When a uniform space is used
between elements of a pattern, as stated, the length of the
opposing longer side of the pentagonal block may be increased
slightly, as with the use of spacer bars, but not more than lO
percent, sufficient to allow four pentagonal blocks with uniform
spaces between their adjacent shorter side surfaces to form a
square, the sides of which equal two times the length of one of the
longer sides of one of the pentagonal blocks plus the width of the
uniform space, so as to permit a square block, each side of which
equals one of the longer adjacent sides of the pentagon to be
placed in the middle of said four pentagonal blocks leaving the
same uniform space between each side of the square block and the
opposing adjacent sides of the four pentagonal blocks.
C A~ 1 40099
.~
The paving block described herein may be utilized in a
very large number of different patterns, the number of
different patterns being limited only by the size of the area
of ground, floor or like surface to be covered.
The upper edges of the paving block may be beveled to
prevent the upper edge of the paving block from catching on
shovel or plow blades or the like. Paving blocks of this
invention may be constructed of brick, concrete, ceramic tile,
or like material.
The above and additional features will become apparent in
conjunction with the accompanying drawings and the detailed
description which follows.
In the drawings,
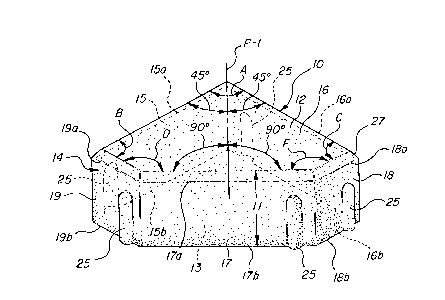
Figure 1 is a perspective view of a preferred embodiment
of the paving block embodying this invention with hidden lines
demonstrating dimensions hidden from view.
Figure 2 is a perspective view of a square paving block
used in conjunction with the paving block embodying this
invention with hidden lines demonstrating dimensions hidden
from view.
Figure 3 is a top view of one preferred embodiment of the
invention in which four paving blocks of this invention are
arranged in concert with one square paving block showing the
relative dimensions of the five-sided blocks.
Figure 4 is a top view of a block arrangement, which
includes spacer bars, in which four, five-sided paving blocks
are arranged in concert with one square paving block. This
-- 8
~, ~
..
CA2 1 40~q~
view shows the relative dimensions of the five-sided blocks
and the square block when spacer bars are utilized.
Figure 5 is a top view of a block pattern in which four,
five-sided paving blocks are arranged in concert with one
square paving block with a uniform space between the opposing
sides of said blocks, this view showing the relative
dimensions in said arrangement.
Figure 6 is a top view of a configuration of four equal
squares with an overlaying fifth square demonstrating the
relationship of the distance between paving blocks and the
lengths of the side surfaces.
Figure 7 is a top view of prior art utilizing pentagon
and square combinations including a top view of the relative
dimensions of three different sizes blocks necessary to
complete the pattern.
Figure 8 is a top view of paving configurations using
blocks constructed in accordance with the invention, including
a top view of the relative dimensions of the only two
different size blocks necessary to complete the pattern.
Figure 9 is a top view of representative circular
patterns with and without square paving blocks in combination
therewith.
Figure 10 is a top view of a homogeneous pattern of
blocks.
Figure 11 is a top view of a repeating third closed
pattern when only two different size blocks are necessary to
complete the pattern.
g
~\
Cd2 1 40099
Figure 12 is a top view of a repeating fourth closed
pattern when only two different size blocks are necessary to
complete the pattern.
Figure 13 is a top view of a repeating fifth closed
pattern when only two different size blocks are necessary to
complete the pattern.
Figure 14 is a top view of a repeating sixth closed
pattern when only two different size blocks are necessary to
complete the pattern.
Figure 15 is a top view of a repeating seventh closed
pattern when only two different size blocks are necessary to
complete the pattern.
Figure 16 is a top view of a repeating eighth closed
pattern when only two different size blocks are necessary to
complete the pattern.
The paving block of the invention for covering ground,
floor and like surfaces, broadly considered, includes a
generally pentagonal block 10 having a vertical dimension 11.
The pentagonal block 10 further comprises a five-sided planar
upper surface 12 and a corresponding five-sided planar lower
surface 13 parallel to the upper planar surface 12. The
pentagonal block 10 has vertical dimension 11 which is
comprised of a unitary side wall 14, which is further
comprised of five vertical side surfaces 15, 16, 17, 18 and
19. Side surfaces 15, 16 and 17 are longer side surfaces.
Side surfaces 18 and 19 are shorter side surfaces. Longer
side surfaces 15 and 16 are essentially equal in length. The
-- 10
- ~A21 400qq
third longer side surface 17 is at least as long as side
surfaces 15 and 16.
Side surfaces 15, 16, 17, 18 and 19 extend between upper
surface 12 and parallel lower surface 13 at each of the sides
15a, 16a, 17a, 18a and l9a of upper surface 12 and each of the
corresponding sides 15b, 16b, 17b, 18b and l9b of lower
surface 13.
Side surfaces 15 and 16 are joined at one end at a 90~
internal angle, designated as angle A in FIG. 1. Side
surfaces 15 and 16 are each further joined to an end of side
surfaces 19 and 18, respectfully, at 90~ internal angles
designated as angles B and C in FIG. 1. The opposite ends of
side surfaces 18 and 19 are each further joined to side
surface 17 at 135~ internal angles, designated as angles D and
F in FIG. 1.
Side surface 17 which opposes side surfaces 15 and 16 and
angle A between them, is at least as long as side surfaces 15
and 16 and is perpendicular to and bisected by a vertical
plane designated as P-l in FIG. 1. Vertical plane P-l further
bisects internal angle A between surfaces 15 and 16.
As shown in FIG. 3, vertical plane P-1 correspondingly
bisects side 17a of side surface 17 and bisects internal angle
A between sides 15a and 16a.
In the preferred embodiment of the invention the block 10
Z5 may be utilized in conjunction with a square block 20. Square
block 20 has a vertical dimension 2la identical to the
vertical dimension 11 of pentagonal block 10. Square block 20
has four identical side surfaces 21, 22, 23 and 24, each being
-- 11 --
~;
C~21 4009~
of equal dimension to side surfaces 15 and 16 of block 10.
Block 20 is used in conjunction with block 10 in a position
where, when side surface 17 of block 10 is juxtaposed against
any side surface 21, 22, 23 or 24, vertical plane P-l will
also bisect the adjacent side surface of square block 20.
This is shown in FIG. 3 as bisecting sides 23 and 21 of square
block 20.
In a further preferred embodiment of the invention each
side surface 15, 16, 17, 18 and 19 of block 10 has at lea'st
one outwardly disposed spacer bar 25. Said spacer bar 25 may
extend vertically as shown in FIGS. 1 and 2. Said spacer bar
may alternatively be a projection or nub of any vertical
height.
The outward projection of the spacer bar 25 from the
respective side surfaces 15, 16, 17, 18 and 19 would be
essentially uniform and normally within a range of zero to one
millimeter from the side surfaces.
In a further preferred embodiment, when utilized as
elements of ground, floor or like surfaces covering, the
paving blocks may be placed utilizing a uniform spacing
separation between adjacent side surfaces in the pattern.
This uniform space may be referred to in ceramic tile
applications as a grout joynt and may be referred to in other
applications as a space joynt. FIG. 5 demonstrates a
configuration of one square block 20 surrounded by four
pentagonal blocks 10 of the present invention utilizing a
uniform space 30, between all opposing side surfaces of the
respective elements.
- 12
f, ~ ~
~ !
~2~ 4Q;~
When spacer bars 25 or alternative projections or nubs
are not utilized, side surface 17 will be essentially equal in
length to side surfaces 15 and 16. When spacer bars 25 or
alternative projections or nubs are utilized in another
preferred embodiment of the invention, the length of side
surface 17 will exceed the length of side surfaces 15 and 16
by up to 10 percent of the equal length of said side surfaces
15 and 16. The appropriate length of side surface 17 within
said 10 percent range is dependent upon the distance of
uniform projection of the spacer bars 25 or alternative
projections or nubs from side surfaces 15, 16, 17, 18 and 19
in order to facilitate placement of a square block 20 snugly
within an arrangement of four pentagonal blocks 10 arranged in
contact with each other as shown in FIG. 4 so that the side
surfaces forming the 90~ internal angle A of each pentagonal
block 10 forms one internal 90~ angle of the perimeter of a
generally square area. In such a configuration, as shown in
FIG. 4, vertical plane P-1 will bisect square block 20.
In a further preferred embodiment, if the paving block is
to be utilized in patterns utilizing a uniform width between
the opposing side surfaces of all elements in the pattern, the
length of side surface 17 will exceed the length of
- 13
.'~,
21411099
side surfaces 15 and 16 by up to 10 percent of the equal length of
said side surfaces 15 and 16. The appropriate length of side
surface 17 within said 10 percent range is dependent upon the width
of the uniform distance between the opposing side surfaces 15, 16,
17, 18 and 19 in order to facilitate~placement of a square block 20
within an arrangement of four pentagonal blocks 10 arranged with a
uniform space 30 between the adjoining side surfaces of each, as
shown in FIG. 5, so that the side services forming the 90~ internal
angle A of each pentagonal block 10 forms one internal 90~ angle of
the perimeter of a generally square area, and the square block 20
is fitted within said arrangement providing an equal uniform space
30 between each side surface of the square block 20 and the
opposing side surface of each of the four pentagonal blocks 10. In
such a configuration, as shown in FIG. 5, vertical plane P-l will
bisect square block 20.
When spacer bar 25, or alternative projections or nubs are
utilized, or when blocks are manufactured to be installed with a
uniform space between adjoining blocks, the length of side surface
17 may be determined by placing four equal squares 40, 41, 42 and
43, said squares having sides equal in length to the equal longer
side surfaces 15 and 16 of pentagonal block 10, in such a manner
that said four squares 40, 41, 42 and 43 are separated from each
other on two sides of each square by the width of the desired
spacer bar 25, or other projection or nub, or by a uniform distance
30 between the opposing sides of each square 40 to form a larger
square 50. A fifth square 45 is then superimposed over the new
CA~ 1 40099
larger square 50, the center 51 of said fifth square 45, being
located directly over the center 51 of the new larger square
50 with the sides 45a, 45b, 45c and 45d of said fifth square
45 each being respectively bisected by a line bisecting one of
the 90~ internal angles of the larger square 50. Lines 46,
47, 4B and 49 are then drawn parallel with and outboard a
distance equal to uniform distance 30 of each of the sides
45a, 45b, 45c and 45d respectively, of the fifth square 45.
The distance between the points where lines 46, 47, 48 and 49
intersect two sides of squares 40, 41, 42 and 43,
respectively, for each square will define the length of side
surface 17.
FIG. 7 illustrates a top view illustration of prior art
utilizing a "pentagon and dot" design wherein the sides of the
square block or "dot" are shorter than the longer sides of the
pentagonal block requiring three shapes to complete all but a
continuous, non-modifiable pattern.
FIG. 8 illustrates a top view of a block configuration
constructed with blocks of the invention. While a continuous
uniform pattern is still possible using the configuration
illustrated in FIG. 3, or when spacer bars 25 are utilized, as
illustrated in FIG. 4, only two shapes are required to
construct or modify varying block configurations. As
illustrated, a preferred embodiment provides a ground, floor
or like surface covering comprising a combination of at least
two pentagonal blocks 10 and at least one square block 20.
P'
C~2 1 400q9
In a further preferred embodiment the side surface 17 of
each pentagonal block 10 corresponds with one side surface of
a square block 20. In such a configuration the dimensions of
side surfaces 21, 22, 23 and 24 of the square block 20 equal
the dimension of side surfaces 15, 16 and 17 of the pentagonal
block, as illustrated in FIG. 3. If spacer bars 25 or
alternative projections or nubs are utilized the length of the
side surface 17 of pentagonal block 10 may exceed the length
of side surfaces 15 and 16 and side surfaces 21, 22, 23 and 24
by not more than 10 percent.
As illustrated in FIG. 9, the pentagonal block 10 may be
arranged in circular series defining a center aperture. The
dimensions of said center aperture may be enlarged by
alternating each pentagonal block 10 with at least one square
block 20.
As illustrated in FIG. 10, the pentagonal block 10 may be
arranged in a continuous pattern using only pentagonal blocks
10 .
In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the edges
2015a, 16a, 17a, 18a and l9a of the planar upper surface 12 of
pentagonal block 10 are beveled as shown in FIGS. 1, 3 and 4.
The paving block of the present invention may be
constructed of concrete, brick or ceramic tile composition, or
other like suitable material.
25Preferred embodiments of the invention have been
illustrated and described herein in detail. It will be
apparent to those skilled in this art that various changes may
- 16
~A~ I 40099
-
be made in the disclosed embodiment without departing from the
spirit of the invention.
- 17
~,
;