Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~'A21 43391
The invention relates to an inflatable restraint for vehicle occupants.
There is, these days, an increasing use of air bags in motor vehicles. In the
United States of America, air bags are commonly fitted as standard equipment
5 in production vehicles and in the European market, the use of air bags is now
becoming more commonplace.
An air bag mounted on a steering column to protect the driver and an air bag
mounted in the dash board to protect the passenger is a typical arrangement
10 for providing occupant protection in the event of a front-end collision.
However, such an arrangement does little to protect the driver/passenger in the
event of a side impact and, in recent times, air bag arrangements have been
proposed in an attempt to provide a degree of side-impact protection.
In a typical air bag system, sensors are strategically placed on the vehicle andoperation of the sensors is arranged to fire a pyrotechnic generator to inflate
the air bag. In a 50 kph rigid barrier front impact test, it has been shown thatduring the 10 milliseconds after impact, the vehicle decelerates rapidly. Duringthat
IJA21 43391
period, the sensors will initiate air bag inflation although the occupants will not
have moved relative to the vehicle. At 20 milliseconds from impact, structural
deformation of the vehicle will have taken place, the air bag will have inflatedsubstantially and the occupants will have begun to move forward. After 40
milliseconds, the air bag will be fully inflated and the vehicle seat belts will have
begun to reduce forward movement of the occupants. By 80 milliseconds,
movement of the vehicle ceases and the air bag will be cushioning and
decelerating the driver, the bag deflating as gas is vented therefrom.
As there is usually a substantial distance between, say, the driver and the
steering wheel, there is sufficient time for an air bag to inflate fully to protect
the driver. However, where side-impact protection is required, the driver and
passenger sit very much closer to the sides of the vehicle than they do to the
steering wheel or dash board. Therefore, where an air bag is to be used for
side impact protection, the time taken for inflation to occur is more critical. If
a large air bag is used, ie to protect the torso, chest and head of the occupant,
it is extremely difficult to inflate the bag sufficiently to provide the protection
required in the short time available. On the other hand, if a smaller bag is used
and placed, say, at the height of the ribs of
('A 2 1 ~ 33 9 ~
the occupant, adequate inflation is not difficult to achieve but the chest and
head of the occupant are left unprotected.
An object of the present invention is to provide an inflatable restraint which can
be used to protect a driver/passenger in the event of a side impact and which
provides such protection over a larger area of the body than has hitherto been
possible .
According to the invention there is provided an inflatable restraint for a vehicle,
the restraint comprising a bag inflatable by means of a gas and having first andsecond sections, a source of gas for inflating the bag and means for controllingthe flow of gas from the first section to the second section such that, in use,
the first section is inflated prior to inflation of the second section and the
second section is inflated on receiving gas from the first section which passes
through the flow control means.
In the event of a side impact, the upper arm/chest area of an occupant is the
first area of the body to contact the vehicle door. In a side collision at 50 kph
the chest of an occupant will contact the door after about 15-25 milliseconds
after the initial impact. With the present invention, the first section of the bag
can be
-
21433~1
made of a size which can be inflated within less than that period using an
existing type of pyrotechnic generator. The head of an occupant can expect
to reach the cant rail, window or B-pillar of the vehicle after 45-55 milliseconds
from the initial impact. With the present invention, the second section can be
arranged to protect the head of the occupant. When the occupant contacts the
fully inflated lower section of the bag, the pressure in that section will rise and
the extra pressure will cause gas therein to vent to the second section through
the flow control means. The size of the second section of the bag is selected
such that before the 45-50 millisecond period has passed, it will become fully
inflated with gas transferred from the first section. Preferably, the second
section of the bag includes vent means to enable gas therein to vent to the
vehicle interior or back into first section.
The bag may comprise an envelope of material which defines the first and
second sections of the bag. The first and second sections may be separated
from each other by a web of material extending across the envelope. The flow
control means may be defined by or form part of the said web of material.
In another arrangement, the bag may comprise two envelopes of material which
define the respective first
~A 2 ~ 433 9 1
and second sections of the bag. In such a case, the envelopes may be suitably
interconnected to enable the flow control means to permit flow of gas from the
first section to the second section.
5 The flow control means may take the form of one or more valves.
The first section of the bag may have a smaller volume than the second
section.
10 The restraint may be fitted to the vehicle for use in combination with
cushioning means arranged to protect a lower part of the body. In such a case,
the cushioning means may be arranged, in use, on the vehicle door around the
height of the pelvis of the occupant with the inflatable restraint placed above
the cushioning means to provide protection for the chest and head regions of
1 5 the user.
The source of the gas may be a pyrotechnic generator which can be suitably
triggered by means of one or more sensors strategically placed on the vehicle.
20 An inflatable restraint in accordance with the invention will now be described
by way of example with reference to the accompanying drawings in which:
~`A2 1 433q 1
Fig 1 is a diagrammatic view of the front of an occupant and an adjacent door
of a vehicle having thereon an inflatable restraint in accordance with the
invention and, the restrain being non-inflated.
Figs 2 and 3 are views similar to Fig 1 showing the restraint partially and fully
inflated respectively and
Fig 4 is a side view of the arrangement shown in Fig 1 looking in the direction
of arrow Vl in Fig 1.
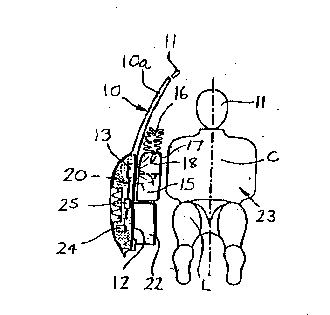
A vehicle has a door 10 defining a window 10a, a cant rail 11, and a B pillar
indicated at B in Fig 4. The door includes a panel 12 behind which is mounted
a pyrotechnic generator 13 of known kind. The pyrotechnic generator 13 has
a casing extending through the panel 12 and which normally contains a
deflated and folded air bag 14, the air bag comprising an envelope of material
such as a textile reinforced plastics. In Fig 1 the air bag 14 is in a non-inflated
condition .
As shown in Figs 2, 3 and 4, the air bag 14 has a lower first section 15, an
upper second section 16 and a flexible web or membrane 17 which separates
the first and second sections. The membrane has or incorporates two spaced
apart flow control devices 18 therein which may comprise, for example
pressure relief valves such that
~A2 1 43391
one way flow only is permitted above a certain pressure. Instead of using
valves 18, apertures may be defined in the membrane 17 which are closed by
thin patches of material capable of tearing when subject to a given pressure.
In another arrangement, the membrane itself may define weakened areas which
5 can tear at a given pressure to permit gas to enter the second bag section 16.The valves 18, tearable patches and tearable areas constitute the aforesaid
means for controlling the flow of gas from the first section to the second
section.
10 The upper second section 16 of the bag is formed with two vent apertures 19.
If desired, a plurality of tethers 20 may be attached between opposite surfaces
of the envelope for controlling the inflated shape of the air bag 14.
An impact sensor 24 and signal diagnostic unit 25 are mounted in the door 10
of the vehicle to provide a signal for the pyrotechnic generator 13 in the eventthat the air bag 14 is to be inflated.
In the event of an impact, the restraint operates as follows:
Following an impact against the side of the vehicle, and
~;A 2 1 4 33 9 ~
assuming that the sensor 24 and diagnostic unit 25 indicate that the
pyrotechnic generator should be fired, gas from the pyrotechnic generator
rushes into the lower section 15 of the bag (which may have a volume of
around 15 litres) and inflates the lower section fully within 10-12 milliseconds5 following impact as shown in Fig 2. The period taken for the lower section to
inflate fully is considerably less than the 15-25 milliseconds taken for the upper
arm/chest area C of the passenger to contact the door 10. Once the lower
section 15 has reached the point of full inflation and the occupant 23 contacts
the lower section 15 of the air bag, the pressure in the lower section 15 rises
10 considerably above that required to inflate the lower section. The valves 18,patches or tearable areas in the membrane 17 then permit gas from the lower
section to rush into and inflate the upper section 16 (which may have a volume
of 25 litres) such that the upper section is fully inflated as in Figs 3 and 4
within 35-60 milliseconds from initial impact immediately prior to the head 8
15 of the occupant striking the upper section 16 of the bag. It is anticipated that
the pyrotechnic generator 13 will still be producing gas for at least part of the
time that the upper section 16 is beginning to inflate. As the occupant 23
sinks into the bag 14 and decelerates, gas escapes from the upper section 16
from the vents 19 into the interior of the vehicle. If desired, the upper section
l,'~2 1 4339 1
16 can vent into the lower section 15 where the valves 18 or tearable
areas/patches permit. The lower body part L of the occupant is protected by
the cushioning 22 during the side impact. If desired a single suitable flow
control device 18 could be provided.
Although the air bag 14 in the embodiment described is a single envelope
divided by the membrane 17, it is envisaged that the air bag may be formed
from two separate envelopes defining the first and second sections and which
are suitably interconnected to enable gas in one bag section to pass into the
10 other following an impact.