Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~143~72
PROCESS FOR THE GUIDING OF AN ELONGATED T~'TT~'MT~'~T
The invention relates to a process for the guiding of
an elongated element for example a soot blower for the cleaning
S of firebox wall surfaces. More particularly, the invention
relates to a process for the guiding of an elongated element
along a preselected meander-shaped blow figure.
Such an elongated element can be the lancet pipe of a
soot blower used for the cleaning of the wall surfaces of pipes
through which a heat exchange medium flows and the outer wall of
which is exposed to soot laden flue gas as described in German
Patent No. DE-OS 41 42 448. The water jet exiting the soot
blower cleans the pipe surface of dust deposits. In order that
the blow jet come in contact with the whole pipe surface, the
lancet pipe is guided such that the output end thereof
successively follows horizontal and vertical path sections and
thereby follows a meandrical path. The lancet pipe has a
moveable and a fixed end and is mounted at the fixed end on first
and second spindles. Compliance with the meandrical blow figure
is achieved by rotating a first spindle for a preselected time
period with constant speed and subsequently operating the second
spindle. During operation and under rough operating conditions,
the spindles can become hard to rotate because of fouling or
wear. However, the operation of the spindles is time dependent.
Thus, when the spindles rotate too slowly the direction of
movement of the lancet pipe output end may change before reaching
21~72
-
the preselected turning point of the blow figure. This results
in incomplete cleaning of the pipe wall surface.
German Patent No. DD 281 452 discloses a controller for
S this type of soot blower which is used for the cleaning of a
soiled area of limited size and circumference. A blow figure is
stored in this controller which figure is optimized with respect
to the construction and the visually determined degree of soilage
of the wall surface. The blow figure is transposed onto the
spindles by way of a signal transducer and distance measuring
devices.
It is now an object of the present invention to provide
a process for the guiding of an elongated element of the above-
described general type and supported by two cardanic joints whichprocess allows strict compliance with a preselected blow figure
composed of a plurality of turning loops.
This is achieved by a process in accordance with the
invention wherein the control of the spindles is distance
dependent and no longer time dependent. This permits exact
determination of the distance traveled by the cardanic joint and
exact positioning of the moveable element. The travel distance
is thereby exclusively determined through the driving mechanism
of the element.
2143~72
Accordingly, the invention provides a process for
guiding an elongated element supported at its opposite ends in
first and second spaced apart cardanic joints in a predetermined,
meandrical figure, the first cardanic joint being fixed and the
second cardanic joint being supported on a first spindle and
axially moveable thereon by rotation of the first spindle,
opposite ends of the first spindle being supported on a pair of
parallel second spindles and axially moveable thereon by rotation
of the second spindles, whereby the first and one of the second
spindles are provided with non-mechanical, inductive end switches
that detect the rotations of the respectively associated spindle,
comprising providing a controller which has a memory and is
programmable, detecting a reference point in horizontal and
vertical direction by a pair of first end switches and detecting
with a pair of second end switches associated with the first and
second spindles the individual rotations of the first and second
spindles as a measure of the distance travelled by the second
cardanic joint, comparing the impulses detected by the second end
switches, which impulses are proportional to the distance
travelled by the second cardanic joint, in the controller with
impulse values corresponding to a preselected figure programmed
into the controller, and controlling the first and second
spindles so that the second cardanic joint follows the figure.
The process preferably includes the use of a frequency controller
for the control of the operating speed of the 3-phase breaking
motors driving the spindles. The residence time of the blow jet
- 2143~72
on any desired wall portion can be varied with such a motor speed
control according to the degree of soilage of the selected wall
portion. The inclusion of a speed control in the control process
in accordance with the invention is advantageous, because the
process is only distance and not time dependent, so that the
speed with which the blow jet is guided across the wall surface
has no influence on the exact execution of the blow figure.
A preferred embodiment of the invention will be further
10 described in the following with reference to the drawings,
wherein: -
Figure l a side elevational view of a soot blower
control arrangement;
Figure 2 shows a circuit diagram; and
Figure 3 shows a blow figure.
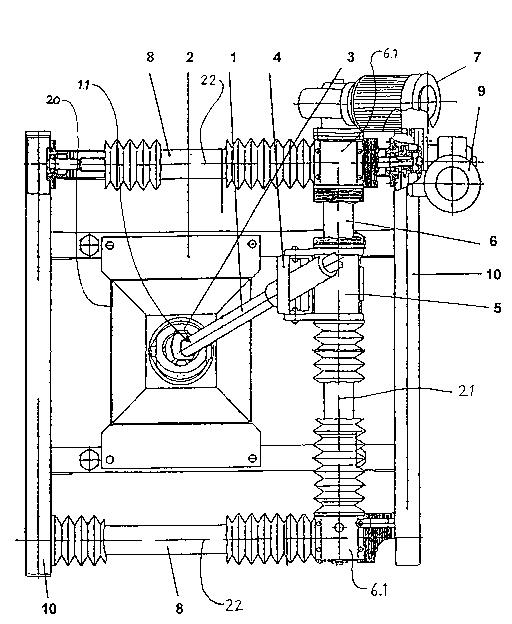
In a preferred embodiment the process in accordance
with the invention is used for the control of a water lance soot
blower arrangement as shown in Figure l, wherein the blow medium,
in this embodiment water, is pumped through a lance l. The
output end l.l of the lancet pipe l extends through an opening 20
closed by a cover 2 and into a steamboiler firebox which is
defined by pipe walls (not shown). The output end l.l of the
lance l is supported in the cover 2 by a first cardanic joint 3.
The other end of the lance l is supported in a second cardanic
21~3~72
-
joint 4. The second cardanic joint 4 is mounted on a first guide
sleeve 5 which is supported on a first spindle 6 and axially
moveable thereon by rotation of the spindle around a first axis
of rotation 21. The first spindle 6 is rotated by way of a 3-
S phase break motor 7. The ends 6.1 of the spindle 6 are mountedon second guide sleeves (not shown) supported on a pair of
parallel, second spindles 8. The second guide sleeves are
axially movable on the second spindles 8 by rotation of the
second spindles around parallel second axes of rotation 22
orthogonal to the first axis of rotation 21. One of the pair of
second spindles 8 is rotatable directly by way of a 3-phase break
motor 9 and the other spindle 8 is rotated by way of a pair of
chain drives 10 connecting the second spindles. Rotation of the
first spindle 6 translates into a vertcial movement of the guide
sleeve 5 and the second cardanic joint 4, mounted thereon whereby
the output end 1.1 of the lance 1 and, thus, the blow jet ejected
therefrom are also vertically displaced. Rotation of the second
spindles 8 translates into a horizontal movement of the guide
sleeve 5, the output end 1.1 and the blow jet (not illustrated).
The blow figure shown in figure 3 of the drawings which
has horizontal and vertical portions that merge at turning points
is achieved by alternatingly operating the first and second
spindles 6, 8. The blow figure includes a reference point PO,
which represents the origin of the coordinates used. The
distance between a starting point PS and the first turning point
21~3472
in the horizontal direction is X1, the distance between the left
and right turning points of the respectively horizontal sections
of the blow figure is X2. During the horizontal movement phase,
only the spindles 8 are operated. The vertical distance
travelled by the blow jet in the respective vertical sections of
the blow figure, when only the first spindle 6 is operated, is
Y1. The distance travelled at the turning points when all
spindles 6, 8 are operated is XY. The maximum vertical extent of
the blow figure is designated Y2. The frame Z defines the limit
defined by the construction of the operating mechanism and beyond
which the blow figure cannot be extended.
As schematically illustrated in figure 2, the first and
second spindles 6 and 8 are respectively provided with a pair of
non-mechanical, inductive end switches 11, 12, 13, and 14. The
end switches 11, 12 produce impulses corresponding to the
rotations of the spindles 6, 8. The distance travelled by the
second cardanic joint 4 can then be determined on the basis of
geometrical parameters of the arrangement, and from the number of
impulses produced. The location of the reference point PO is
determined by the end switches 13, 14. End switches 11 to 14 are
connected through control lines 15 with a controller 16 which has
a memory and is programmable. The desired blow figure (see
figure 3) to be followed by the blow jet is programmed into this
controller. The impulses detected by end switches 11, 12 are
counted and compared in the controller 16 with the impulse counts
21~3~72
corresponding to the stored blow figure. The 3-phase breaking
motors 7, 9 are each provided with a contactor 17 for the forward
and the backward rotation of the associated spindles 6, 8. The
contactors 17 are connected to the controller 16 through control
lines 15. Furthermore, a frequency converter 18 is provided
which is connected with the contactors 17 and the controller 16.
During operation, the soot blower arrangement is
controlled as follows. After release of the starting automatic,
the lance 1 is aimed at the reference point PO in order to set
the distance measuring system to zero. The arrival at the
reference point PO is relayed in the X and Y directions by the
end switches 13, 14 respectively. Thereafter, the spindles 6, 8
are operated until the lance 1 is aimed at the starting point PS.
Upon reaching the starting point PS, the supply of the blowing
medium to the soot blower is opened and the blow jet guided along
the blow figure by alternate operation of the first and second
spindles 6,8 as described above in detail. For each of the
horizontal or vertical distances travelled by the blow jet, the
impulses which are detected by the end switches 11, 12 and
represent a measure of the distance travelled by the guide sleeve
5 and, thus, the blow jet in horizontal and vertical direction,
are counted (actual value) and compared by the controller with
the stored values (desired value) of the programmed blow figure.
When the actual and desired values are equal, the required
distance has been travelled and the next movement step is
21~72
commenced. When the blow figure is completed, the supply of
blowing medium is shut-off and the soot blower arrangement moved
to the resting point PR.
If it is desired to change the residence time of the
blow jet, the speed of rotation of the 3-hase break motors 7, 9
is changed. This change in speed of the motors has no influence
on how well the blow path travelled by the blow jet complies with
the blow figure, since the end switches 11, 12 measure only the
distances travelled and therefore operate reliably independent of
how fast the blow figure is followed.
The disclosed control process is also suitable for
elements other than soot blowers, which elements are elongated
and supported in a pair of cardanic joints.
Changes and modifications in the specifically
described embodiments can be carried out without departing from
the scope of the invention which is intended to be limited only
by the scope of the appended claims.