Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
, 2143989
' O
~UL~rl~UK~'OSK gICECRED
R~r~aRI OF T}ll;~ v~l~l
To make a patient feel more comfortable when he or she
i8 lying on a sickbed, the sickbed i8 usually 80 designed
that a head portion and/or a rear portion thereof can be
adjusted to incline at different angles. However, since not
all the patients have the same sick condition and therefore,
the in~-linsltion of the eickbed at its head portion and/or
rear portion is not necessarily suitable For or meeting the
requirement of all patients. Thus, it is still neces3ary for
a tender to help the patient to lie on side or in other
desirable position 80 that the patient may feel more
comfortable. And, for a bedrid patient, sometimes two tenders
are required to help the patient to the toilet room. It is
therefore desirable to develop a multipurpose sickbed of
which the head, middle, and rear portions as well as the left
and right sides can be raised or lowered, inclined or
leveled, or alternately raised for air vPntil~ti-n purpose
through different control mechanisms.
gur~R5r OF TEIE ~Vk~llU~.
A primary object o~ the present invention is to
provide a multipurpose sickbed, and more particularly to
provide a sickbed of which the bed boards can be partially
raised, lowered, inclined, and leveled through a number of
`' 21~398~
~ .
control means. The sickbed ~rr~r~inrj to the present invention
i8 eriuipped with a first control mechanism which controls the
axial inclination of a head section of the bed, a second
control i ~h~ni rm which controls the alternate raising of
movable boards of the head and a middle sections of the bed,
a third control mechanism which controls the axial
;nrl;n;~;on of a rear section of the bed 80 that a raised bed
rear board forms a footrest, a fourth control, ~h~n;r-- which
controls the leftward or rightward inclination of a le~t or a
right side of the head, middle, rear sections of the sickbed
80 that the patient on the bed may lie on side, and a fifth
control mechanism which controls the descent of the middle
section of the bed for the positioning of a bedpan or a
urinal thereat to facilitate the convenient and comfortable
excretion of the patient.
In brief, the multipurpose sickbed according to the
present invention is characterized in that:
1. The sickbed can be partially inclined at various angles
through a number of control mechanisms and therefore, it
is not necessary for a tender to directly turn the patient
lying on the sickbed;
2. The middle section of the sickbed can be lowered to
accommodate a bedpan or a urinal and therefore, the
patient may conveniently and comfortably excrete on the
sick})ed;
`"{ ~ 21~3989
3. The sickbed h as movable bed boards which can be adjustably
lowered for air v~nt;li~t;rn purpose when the patient,
especially a bedrid patient, feels uncomfortable due to
lying in the sickbed for a long time;
4. The sickbed has a rear section which can be raised with a
small utmost rear part thereof downward bent again to form
a footrest for the feet of patient to be comfortably
supported thereon;
5. The bed surface can ~e adjustably inclined through the
control mechanism~ and the sickbed is therefore very
practical in use; and
6. The change of lying po~ition and the excreting of the
patient can all be taken care through the use of control
mechanisms by the tender, and a lot of ef~orts and
manpower can be saved.
BKIEF IJ~h:K1~L1U-~ OF ~E DKAWING~
Pig.1 iB a perspective view of a sickbed according to the
present invention;
Fig.2 is still a per~pective view of the sickbed of the
present invention, in which the bed boards are
;nrl ;n~(9, lowered, or raiged to show the operation
thereof;
Fig.3 shows the operation of the first control, ~h~n;r- of
the present i ention;
`" 21~3989
Fig . 4 i8 an enlarged view showing the trapezoidal member of
the present invention;
Fig.5 shows the operation of the third control I ~h~n;r~ of
the present invention;
5 Fig . 6 is a disassembled perspective of the present
invention;
Fig . 7 illustrates the assembly of the present invention;
Figs . 8 and ~-1 illustrate the assembly of the movable frame
plates with the frame plate of the present invention;
Fig.9 is an enlarged view of the expansion rod of the
present invention, in which a part of it is cut away
for better ,o~l AnA~; nn;
Fig . lO illustrates the manner in which the movable bed boards
of the present invention i8 operated;
Pig.11 iB similar to Fig. 10 and shows a further operation of
the movable bed boards of the present invention;
Fig.12 is a ~ t;~mAl view of the middle section of the
sickbed according to the present invention;
Fig.13 is a disassembled perspective of the middle section of
the sickbed according to the present invention;
Fig. 14 illustrates the mechanism for inclining the left or
the right half of the head section of the sickbed;
Fig.15 illustrates the ;nrl;nA~;on of the left half of the
head section of the sickbed; and
Fig.16 illustrates the inclination of the right half of the
head section of the sickbed.
" `t ' ~ 3989
o
DETAILED JJ ~ Kll:' l OF THE I:'l~;l~ISKKI~
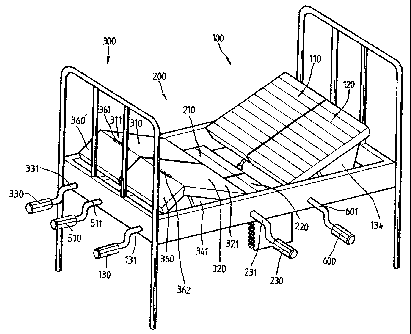
Please refer to ~igs. 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 12, 13. A
sickbed according to the preaent invention is divided into
three sections, namely, a head section 100, a middle section
200, and a rear section 300. All of these three sections
have the same bed board structure which includes a top layer,
a middle layer, and a bottom layer.
The top layer of each sec~ion 100, 200, 300 includes a
left half 110, 210, 310 and a right half 120, 220, 320. The
left half 110, 210 consists of a plurality of alternately
disposed fixed boards 111, 211 and movable boards 112, 212,
and the right half 120, 220 also consists of a plurality of
alternately disposed fixed boards 121, 221 and movable boards
122, 222.
The bottom layer of the head section 100 consists of a
frame plate 140 having two laterally opposite rectangular
openings 141, 141', a rotary shaft 142 fixed to a top middle
portion thereof between the two openings 141, 141' and
connecting a fourth and a fifth rotary wheels 144, 144'
thereon, and two threaded rods 160, 160' rotatably connected
near two side edges . of the frame plate 140 by means of two
pairs of fixing mounts 161, 161'.
The middle layer of the head section 100 consists of
two movable frame plates 150, 150' having an opening 151,
151' therein and laterally disposed on the frame plate 140
within the two rectangular openings 141, 141' and secured to
214~989
the latter by mean6 of hinges 159, 159' and screws 1591,
1592, as shown in Figs. 8 and 8-1, such that the movable
frame plates 150, 150' can be pivotly turned about the hingeG
159, 159'.
Pads 149, 149' are provided on a top surface of the
frame plate 140 at proper positione to ~acilitate the smooth
movement of the movable frame plates 150, 150'. When the
movable frame plates 150, 150' are lowered to a lowest
position in the frame plate 140, the movable boards 112, 122
and the fixed boards 111, 121 are also retained within the
openings 151, 151' of the movable frame plates 150, 150' with
their bottom surfaces in the plane of the frame plate 140.
The movable frame plates 150, 150'are formed with a plurality
of fixing holes 1111, I211 on an outer side edge thereof, and
connected on an upper inner side edge thereof two torsional
leaf springs 152 , 153 , 152 ', 153 ' by means of screws 154 ,
154 ' or by means of welding . Each pair of the torsional leaf
springs 152 , 152 ', 153 , 153 ' are connected to each other by
means of a pin 157, 157 ' passing through pin holes 158, 158 '
formed at another end of the torsional leaf springs 152,
152', 153, 153'. Moreover, half-crescent members 155, 155',
155", 155"', 156, 156', 156D, 156"' are provided between the
two movable frame plates 150, 150' at a lower inner edge
thereof .
Please refer to Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, and 7. The sickbed
of the present invention is elauipped with f ive control
` 21~3989
, -h:~n;, , namely, the ~irst, the second, the third, the
fourth, and the fifth control mechanisms 130, 510, 330, 600,
230 .
The first control mechanism 130 is used to control the
head section 100 and consists of a crank hand~e 130 near the
rear end of the sickbed, a main shaft 131 integrally
f~t~nAin~ from the crank handle 130 and having a threaded
section 132 formed at a predetermined position thereon, an
internally threaded block 133 engaged with the threaded
section 132 and haviny two stoppers 1331, 1332 formed at two
sides thereof, and a trapezoidal member 134 having two spaced
and downward tapered legs and an axially extended middle
groove 1341 formed betweeu the two legs 80 that the
tr~r~ l member 134 is received between the two stoppers
1331, 1332 with the threaded section 132 passing through the
middle groove 1341. By this arrangement, when the first
control ~h~n; ~ 130 is turned, the internally threaded
block 133 is prevented from turning along with the threaded
section 132 but moves forward or backward thereon in a linear
movement and thereby drives the trapezoidal member 134 to
move upward or downward, respectively. The two legs of the
trapezoidal member 134 have two outward projected flange:~
1342, 1342 ' by which the trapezoidal member 134 is stopped at
a certain height without disengaging from the ; n~rn~1 1 y
threaded block 133 when it is moved upward by the same. Since
an upper end of the trapezoidal member 134 is fixed to the
i~rame plate 140, when the trapezoidal member 134 is moved
~ 2143~8~
upward through the first control -. -h~lniç~n 130, the head
section 100 of the sickbed is lifted to form an in~l in_t;nn
as shown in Figs. 2 and 3.
Please refer to Figs. 1, 2, and 5. The rear section
300 of the present inveIltior. can be inclined through the
third control mechanism 330 in the same manner as that
adopted by the first control i ~h~n; ~rn 130 to incline the
head section 100. The third control mechanism 330 consists of
a crank handle 330, a main shaft 331, a threaded 8ection 332,
an ;ntP~n~lly threaded block 333, and a trapezoidal member
341, respectively having the same structure as that of the
crank handle 130, main shaft 131, threaded section 132, block
133, and member 134. When the crank handle 330 is turned in
a first direction to drive the main shaft 331 and the
threaded section 332 to turn, the internally threaded block
333 further drives the trapezoidal member 341 to move upward,
80 that the rear section 300 connected to the trapezoidal
member 341 is lifted to form an inclination as shown in Figs.
2 and 5. ~nd the descent of the rear section 300 is done with
the help of gravity and a turning of the third control
mechanism 330 in a second reverse direction. To avoid
repeated description, the structure shown in Fig. 5 has been
simplif ied .
The left and the right halves 310, 320 of the rear
section 300 each consists of a fixed board 311, 321 and a
~oot-~upport bo~rd 3~, 360' which i~ pivot~lly com~ected to
21~3~89
.
the ~ixed board 311, 321 by means of a hinge 361, 362, such
that when the rear section 300 i8 lifted by the trapezoidal
member 341, it is bent about the hinges 361, 362 and the
fixed boards 311, 321 are inclined forward and the foot-
support boards 360, 360' are inclined rearward, as shown in
Figs . 2 and 5, for the patient' 8 feet to put thereon.
Please refer to Figs. 1, 2, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, and 12
for the details of a elevation mechanism 500 for the head and
the middle sections 100, 200 of ~ the present invention . The
elevation mechanism 500 is actuated by the second control
j -h~n;~n~ 510 and mainly consists of a crank handle 510; a
main shaft 511 one end of which is integrally connected to
the crank handle 510 and the other end connects a f irst
rotary wheel 512; a second rotary wheel 521 being driven to
rotate by the first rotary wheel 512 through a chain 513
connecting them; a universal joint 522 which together with
the second rotary wheel 521 form a transmission Ul ~ ' 520
which is secured onto a fixed supporting member 410 by means
of a fixing mount 523 such that the second rotary wheel 521
and the universal joint 522 turn ~yllullLulluu81y; an expansion
rod 524 connected to an upper portion of the universal joint
522 and having a base 5241 inside which a long groove 5243 is
formed to fixedly receive an extended rod 5242 the~rein by
means of a pin 5244 threading through a pin hole 5245 on the
ba3e 5241, such that when the base 5241 is turned, the
extended rod 5242 turns simultaneously; and a fixing means
530 which linearly f xes the expansion rod 524 and the rotary
`~ 21~3989
'I~
shaf t 142 to two end6 thereof such that the rotary shaf t 142
and the expansion rod 524 turn synchronously.
When the second rotary wheel 521 is turned, the
universal joint 522 turns simultaneously, causing the
expansion rod 524 connected to the universal joint 522 and
the rotary ~haf t 142 to turn synchronously . The turning of
the rotary shaft 142 causes the fourth and the fifth rotary
wheels 144, 144' to synchronously turn, too. At this point, a
seventh and an eighth rotary wheels 147, 147 ' respectively
connected with the fourth and the fifth rotary wheels 144,
144' through chains 145, 145' and separately fixed to the
left and t~le right half 110, 120 of the head section 100 are
driven to rotate, too.
Please particularly refer to Figs. 6 and 7 for the
connection between the fixed boards 111, 121 and the movable
boards 112, 122. The fixed boardE: 111, 121 are parallelly
spaced and rrmn~ ti~-l one another by an axle with a gear 113,
123 provided on the axle at each space between every two of
the fixed boards. The movable boards 112, 122 are parallelly
spaced and each is disposed in a space between the fixed
boards 111, 121 and each of them is provided with a rack 114r
124 which engages with one of the gears 113, 123. Since the
seventh and the eighth rotary wheels 147, 147 ' are separately
fixed to the axle of the fixed boards 111, 121, the turning
of the seventh and the eighth rotary wheels 147, 147 ' causes
the axleEI and accordingly the gears 113, 123 to rotate and
` ` 21~3~89
. ~
the latter further bring the racks 114, 124 to move upward or
downward. To facilitate the ascent or descent of the movable
boards 112, 122, they are provided with guide bars 115, 115',
125, 125' which linearly slide up or down in the holes 1111,
1211 formed on the movable frame plates 150, 150' . The
descent of the movable boarcls 112, 122 to separate from the
fixed boards 111, 121 permits better: air ventilation of the
sickbed .
The elevation mechanism 500 further includes a third
rotary wheel 526, a sixth rotary wheel 525 connected to the
third rotary wheel 526 via a link 5261, and a ninth rotary
wheel 527 being coaxial with the sixth rotary wheel 525. The
ninth rotary wheel 527 iæ further connected to a tenth rotary
wheel 243 via a link (not shown) and drives the latter to
rotate by a chain 528. The tenth rotary wheel 243 locates at
a top middle portion of the middle section 200 between the
two second movable frame plates 250, 250 ' . Thus, when the
middle section 200 is lowered or elevated by a fifth control
r -h-n;r~ 230 as shall be described in details hereinafter,
the distance between the third rotary wheel 526 and the tenth
rotary wheel 243 changes, accordingly. However, since the
ninth rotary wheel 527 may cooperates with the sixth rotary
wheel 525 to adjust their position with the lowering or
elevation of the tenth rotary wheel 243, and since the sixth
rotary wheel 525 conrlect- with the third rotary wheel 526 via
the link 5261, the moved middle section 200 can still be
11
21~3989
driven by the third rotary wheel 526.
Please now refer to Figs. 1, 2, 3, 5, 12r and 13. The
middle section 200 has substantially the same structure as
that of the head section 100, that is, consists of a top
layer ;nrlllrl;nrJ the left and the right halves 210, 220 each
consists of fixed boards 211, 221 and movable boards 212,
222; a middle layer including movable frame plates 250, 250'
provided with pads 249, 249'; and a bottom layer;nrlurl;n~ a
frame plate 2~0 having rectangular openings 241, 241'. A
rota~y shaft 248 is fixed onto the frame plate 240 between
the two movable frame plates 250, 250' at a predetermined
position by means of fixing mounts 242, 242'. The above-
mentioned tenth rotary wheel 243 and an eleventh and a
twelfth rotary wheels 244, 245 are fixed to the rotary shaft
248. ~he tenth rotary wheel 243 is driven to rotate by the
ninth rotary wheel 527 via a chain 528, such that the
eleventh and the twelf th rotary wheels 244, 245 are rotated
to further drive thirteenth rotary wheels 246 fixed to one
end of the fixed boards 211, 221.
As shown in Fig. 13, a threaded rod 260 is provided
below the frame plate 240 of the middle section 200 and is
fixed thereto by means of fixing mounts 261. The threaded rod
26 is used to control the inclination of the left and/or t~le
right half 210, 220 and the structure thereof will be
described in details as below.
The fifth control mechanism 230 of the present
invention conslsts of a main shaft 231 extending between and
3989
.
f ixed onto two lateral sides of the f rame plate 240 . On each
end of the main shaft 231 inside the ~rame plate 240, a
driving gear 234, 234' are provided to drive a driven gear
235, 235' through a chain wheel 232 and a chain 233 such that
driven gears 235, 235 ' rotates with the driving gears 234,
234' synchronously.
The frame plate 240 ha3 two pairs of racks 247, 247~
formed at four bottom corners thereof engaging with the gears
234, 234', 235, 235', such that when the fifth control
1 -hAn;rm 230 is rotated, the gears 234, 234', 235, 235'
fixed thereto drive the racks 247, 247' to move upward or
downward and thereby, the middle section 200 iB elevated or
lowered .
When the middle section 200 is lowered, a recess 80 formed
between the head and the rear sections 100, 300 can be used
to accommodate a bedpan or a urinal to facilitate the
excretion of the patient without leaving the sickbed. The
tender can also save a lot of efforts.
Plea8e further refer to Figs. 1, 2, 3, 6, 10, 11, 12,
and 13 . The fourth control ~h;~ni 1 600 has a main shaft 601
on which a fourteenth, a fifteenth, a sixteenth, and a seven-
teenth rotary wheels 610, 620, 630, 640 are provided. The
fourteenth and the fifteenth rotary wheel3 610, 620 are used
to drive the threaded rods 160 , 160 ', the sixteenth rotary
wheel 630 is used to drive the lnrl ;n~ n of the middle
section 200, and the ~eventeenth rotary wheel 640 is used to
` ~ 214398!~
drive the inclination of the rear section 300. Since the
manner of transmission of these rotary wheels are similar to
those of other rotary wheels mentioned in previous
paragraphs, it is not repeated herein~
The fifteenth rotary wheel 620 connects an eighteenth
rotary wheel 622 by means of a link 6221 and drives the
latter to rotate via a chain 621. The eighteenth rotary wheel
622 is coaxial with a nineteenth rotary wheel 623 which is
connected tQ a twentieth rotary wheel 624 via a link (not
shown) and drives the latter to rotate through a chain (not
shown). Due to the link connecting the nineteenth and the
twentieth rotary wheels 623, 624, the distance between the
two rotary wheels can be adequately ad]usted when the movable
frame plate 150 displaces. With these dLL~LlLy. , when the
fifteenth rotary wheel 620 drives the eighteenth, and
accordingly, the nineteenth, and the twentieth rotary wheels
622, 623, 624 to rotate, a twenty-first rotary wheel 625
fixed onto the threaded rod 160 is driven to rotate the
threaded rod 160. Since the twentieth rotary wheel 624 has a
rotary shaft 6243 which is fixed to the frame plate 140 by
means of a fixing bracket 6244 and drives the twenty-first
rotary wheel 625 through a chain 627, the twentieth rotary
wheel 624 shall rotate when the frame plate 140 i8 ,~i ~pl :lr~
The turning of the twentieth and the twenty- f irst rotary
wheelE 624, 625 further causes the fourteenth rotary wheel
610 on the threaded rod 160 to drive via a chain 611 a
twenty-second rotary wheel 612 on the threaded rod 160' to
14
` ~ 21~389
rotate and thereby the threaded rod 160' rotates with the
threaded rod 160 synchronously.
The fourteenth, the sixteenth, and the seventeenth
rotary wheels 610, 630, 640 all have the same transmission
structure to effect 1l; ~pl ~ ~ and position adjustment of
the frame plate 140 and are therefore, not repeatedly
deacribed herein.
Referring to Figs. 3, 5, 6, 7, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
Since the threaded rods 160, 160', 260, 363 all have the same
transmission structure, only the threaded rod 160 is
described to explain the structure thereof.
The threaded rod 160 is provided near its middle point
a control member 162 and at each end a twenty-first rotary
wheel 625 . When the fourth control --h~n; Pm 600 is rotated,
due to the transmission by the rotary wheels mounted thereon
as mentioned in the above paragraphs, the threaded rod 160 is
turned in the same direction with the control member 162
moving leftward or rightward at the same time. The control
member 162 has two support rod 1621, 1622 on its top and
separately bearing against an inner side of the half-crescent
members 155, 155', 156, 156' such that, when the control
member 162 moves rightward, the movable frame plate 150 is
pivotally raised at its outer edge to form an inclination
while the other movable frame plate 150' is supported on the
plane of the frame plate 140 without being lowered down. The
fixed and the movable boards 121, 122 mounted on the movable
o 21~398~
frame plate 150 are thereby inclined, too That is, only one
lateral half of the sickbed is inwardly inclined 80 that the
patient may be turned to lie on his/her right side.
Similarly, when the fourth control ~ ^h~n; pm 600 is rotated
in a reverse direction 80 that the control member 162 on the
threaded rod 160 moves leftward, the inclined right half of
the sickbed shall be lowered down to recover its level
position. And, when the control member 162 keeps moving
leftward, the left half 110 o~ the sickbed shall be pivotally
raised at its outer edge to form an inward inclination 80
that the patient may be turned to lie on his/her left side.
Among the four rotary wheels 610, 620, 630, 640
mounted on the fourth control I ~hAn; ~m 600, the 14th and the
15th rotary wheels 610, 620 are used to control the pivotal
raising and inclination of the two halves of the head section
100, the 16th rotary wheel 630 is used to control the pivotal
raising and i nrl i n~; on of the two halves of the middle
section 200, and the 17th rotary wheel 640 is u~ed to control
the pivotal raising and ;nrl;n~;on of the two halves of the
rear section 300. That i~, the fourth control -h~nirm 600
may control the whole bed surface of the sickbed, causing the
left halves 110, 210, 310 or the right halves 120, 220, 320
thereof to pivotally raised at an outer edge to form an
inward inclination at the same time to help the patient to
lie on left or on right side.
Please refer to Figs. 1, 2, and 5. The rear section
300 has substantially the same structure as that of the head
16
398~
section 100, except that there i~ only one fixed board 311,
321 forming the Left and the right halves 310, 320 of the
rear ~ection 300. ~owever, movable board~ can also be
provided for the rear ~ection 300, ~lPr~nrl;n~ on actual need.
The fixed boards 311, 321 are ~upported on movable frame
plates 350, 350' which are hinged at inner edge to a frame
plate 340. The structure of thia portion i~: the same as that
of the head and the middle sections 100, 200 and is not
repeated herein.