Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2~589B
AUqoMOTTVE SEAT ADJU8TMENT MT~tT~M
The present invention relates to a mechanism for more
convenient seat adjustments on some automobiles. The present
invention enables more convenient seat adjustments by providing
memory functions at a low cost and with little weight increase.
Automotive seat adjustment mechanisms presently fall into two
categories: the manually operated type and the power-assisted type.
The manually operated type is operated by pulling a handle and
; adjusting to a comfortable position/angle. After a comfortable
position/angle is reached, the handle is released and the seat is
locked in the ~osition/angle. Usually, seats that use this mechanism
can be adjusted in two ways: the seat can be slid forward and
backward, and the angle of the back of the seat can be adjusted. The
- manually operated type is usually used on popular car models.
The power-assisted type uses electrical power in seat
adjustments. The user adjusts the seat by pressing buttons. For
~ example, if the user wants to move the seat forward, he/she presses
- the button that moves the seat forward and releases the button if a
comfortable position is reached. Usually, seats that use this
adjustment mechanism provide memory functions: a user can adjust the
seat to a comfortable configuration and store the configuration into
the memory of the mechanism. If the user later finds that the seat
is not in that configuration, he/she can select the number that
identifies his/her seat configuration, and the seat will be adjusted
to that particular configuration. The power-assisted type is usually
found on the more expensive car models.
Both the manually operated type and the power-assisted type
have drawbacks. The manually operated type, though inexpensive to
construct and relatively light, is not very convenient because of
- the lack of memory functions. This is especially true for cars such
as family sedans, where seat adjustments are needed often. The
power-assisted type, which usually provides memory functions, is
more convenient but is expensive to construct and leads to
215~896
significant vehicle weight increase.
The most useful function of the power-assisted type, the
inventor of the present invention was convinced, is the memory
function. The inventor of the present invention also believes that
the memory function can be added to the manually operated type at a
low cost and with little weight increase.
One embodiment of the present invention consists of five major
components: a control unit, two position detectors, and two locking
devices. In this embodiment of the present invention, the driver's
, .
seat is equipped with two position detectors and two locking
devices. A con'rol unit, with its control panel mounted on the car's
dashboard, is connected to an electrical power source and supplies
power to the two position detectors and the two locking devices.
The functions of the control unit are as follows: it memorizes
up to two pre-set seat configurations, and it turns on or off any of
the two position detectors and the two locking devices based on the
information from the user, the two position detectors, and the
control unit's memory. The two position detectors are for
-- determining the position of the seat and the angle of the back of
the seat. The two locking devices are for allowing or not allowing
seat adjustments: one device for position adjustment, and the other
- device for angle adjustment.
The operation of this embodiment of the present invention is
described as follows: if the user wants to input a seat
configuration into the memory of the control unit, he/she first
adjusts the seat to a comfortable configuration manual~y, and then
presses either one of the two buttons `SET 1' or `SET 2' on the
control unit's control panel, and the configuration will be stored
.,
in the selected memory position. After that, the user can press the
button again so that further seat adjustments will not affect the
memorized configuration.
If the same user later finds that the seat is not in his/her
215~89~
pre-set configuration, he/she can easily adjust the seat to his~her
pre-set configuration by pressing either one of the two buttons
`ADJUST 1' or `ADJUST 2' on the control unit's control panel,
depending on the particular memory position he/she chose. After
that, the user can adjust the seat in the same way he/she adjusts a
seat of the manually operated type. When the seat is in the pre-set
,, ~ ~ position/angle, the seat will be locked in that position/angle. When
the seat is adjusted to the pre-set configuration, the user presses
the button again and the adjustment procedure is finished at this.
For example, if a user wants to adjust the seat to the pre-set
configuration stored in memory position 1, he/she presses the button
`ADJUST 1' c~ then slides the seat forward and/or backward while
pulling the handle for seat position adjustment. When the seat is in
the pre-set position, the seat will be locked in that position and
the user can release the handle. The angle of the seat can be
adjusted in the same manner. After the seat is adjusted to the pre-
set configuration, the user presses the button `ADJUST 1' again to
turn off the mechanism, and the seat adjustment is finished.
The present invention provides seat adjustments more convenient
than seat adjustments provided by the manually operated type of seat
adjustment mechanisms, without significant increases in production
cost or vehicle weight. The present invention provides more
convenient seat adjustments by letting the user(s) input pre-set
seat configuration(s) into the memory of the mechanism, and locking
the position and angle of the seat in the chosen pre-set
configuration when the memory function is used ~uring seat
adjustments.
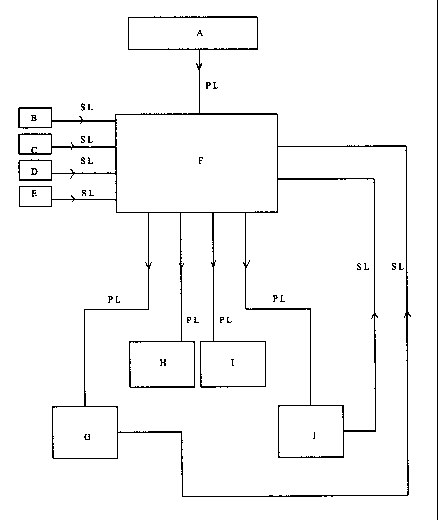
Figure 1 is a diagram that illustrates the relationship between
the various components of the embodiment of the present invention.
Referring to Figure 1, A represents a source of electrical
power. In the embodiment discussed, it is a constant voltage source
from the vehicle's electrical system. A supplies power to the
21~89~
embodiment of the present invention through supplying power to the
control unit.
B represents the button `SET 1' on the control unit's control
panel. It belongs to the type of buttons commonly used for functions
such as emergency flashers on vehicles. This type of buttons are
hereafter referred to as the go-in-and-come-out-alternately type of
buttons. The `SET 1' button is used when the user wants to input the
seat configuration into the memory of the control unit and identify
that configuration by the number 1.
C represents the button `SET 2' on the control unit's control
panel. It is of the go-in-and-come-out-alternatély type, and is used
~ for inputting a seat configuration and identifying that
-- ~ configuration by the number 2.
D represents the button `ADJUST 1' on the control unit's
control panel. It is of the go-in-and-come-out-alternately type, and
is used when the user is adjusting the seat to the configuration
identified by the number 1.
E represents the button `ADJUST 2' on the control unit's
control panel. It is also of the go-in-and-come-out-alternately
type. It is used when the user is adjusting the seat to the
configuration identified by the number 2.
F represents the control unit. It supplies electrical power to
the two position detectors and the two locking devices, based on
~r ~ information from the four buttons (represented by B, C, D, and E),
information from the control unit's memory, and information from the
two position detectors. The control unit's memory can ,store up to
, . ,
- ~ two pre-set seat configurations.
G represents the position detector responsible for detecting
the position of the seat. J represents the position detector that
detects the an~le of the back of the seat. The position detectors
receive electrical power from the control unit, and output
information regarding the position and angle of the seat to the
~- 4
2 1 5 ~ 8 9 8
control unit.
H represents the locking device that locks the seat into the
position if it is activated by the control unit. I represents the
locking device that locks the seat into the angle when activated by
the control unit.
PL denotes power line, each power line is for transferring
electrical power. SL denotes signal line, each signal line is
primarily for the transmission of electrical signals. Each power
line or signal line in Figure 1 represents a path for the
transferring of power or the transmission of electrical signals, and
may consist of more than one wire. Each arrow indicates the
direction of the transferring of power or the direction of the
transmission of signals.
In the intended method of operation, at most only one of the
four buttons (represented by B, C, D, and E) is pressed at any one
time. The two position detectors are turned on whenever one button
is pressed. If `SET 1' or `SET 2' is pressed, the corresponding site
of the control unit's memory is enabled and the seat configuration
will be stored there.
If `ADJUST 1' or `ADJUST 2' is pressed, the information from
the position detectors is compared to the information stored in the
corresponding memory site in the control unit. If the position or
the angle of the seat matches that of the memorized configuration,
the corresponding locking device, which may be the position-locking
device or the angle-locking device, will be activated. When both the
position and the angle of the seat are locked, the sea,t adjustment
process is finished and the button ~`ADJUST 1' or `ADJUST 2') can be
pressed again so that the button returns to the off state.
In the claims, the term `adjustability' refers to one aspect of
the seat that can be adjusted. For example, in the embodiment
explained, the seat has two adjustabilities, which are its position
and the angle of its back.
21~ 89~
Although only a single embodiment of the present invention has
been described and illustrated, the present invention is not limited
to the features of this embodiment, but includes all variations and
modifications within the scope of the claims.